python-csv文件数据处理
目录
- 概要
- 一、所需插件
- 二、使用步骤
-
- 1.引入库
- 2.读取数据
- 3.写入数据
- 4.应用示例
- 后记
概要
使用csv文件可以较容易地存储多行且列相同的数据,便于数据的读取与解析,也常用于自动化测试过程中的数据参数化。本文简单示例一种使用python处理csv文件的思路。
提示:以下为本篇文章正文内容,案例仅供参考。
一、所需插件
csv。python自带库,无需额外安装。
二、使用步骤
1.引入库
import csv
2.读取数据
# 读取完整csv文件内容,包括首行
def read_csv(self, filepath=None):
if filepath is None:
filepath = self.filepath
with open(filepath, 'r', encoding = 'utf-8') as file:
# 1、创建阅读器对象
reader = csv.reader(file)
# 2、读取文件数据
rows = [row for row in reader]
return rows
3.写入数据
# 读取完整csv文件内容,包括首行
# 按行写入数据到csv文件
# way写入方式,w-覆盖写入 at-追加写入
def write_csv(self, filepath, way, row):
if filepath is None:
filepath = self.filepath
with open(filepath, way, encoding = 'utf-8', newline = '') as file:
writer = csv.writer(file)
writer.writerow(row)
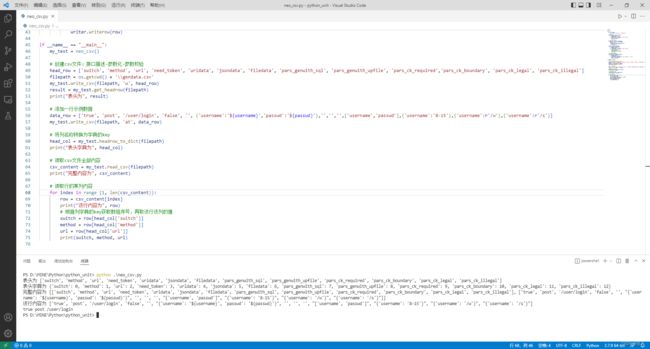
4.应用示例
import csv
import os
class neo_csv:
def __init__(self):
self.filepath = os.getcwd() + "\\neo_data.csv"
# 读取csv首行
def get_headrow(self, filepath=None):
if filepath is None:
filepath = self.filepath
with open(filepath, 'r', encoding = 'utf-8') as file:
reader = csv.reader(file)
row = next(reader)
return row
# 转换首行列名为字典key
def headrow_to_dict(self, filepath=None):
head_row = self.get_headrow(filepath)
head_col = {}
for index, col_name in enumerate(head_row):
head_col[col_name] = index
return head_col
# 读取完整csv文件内容,包括首行
def read_csv(self, filepath=None):
if filepath is None:
filepath = self.filepath
with open(filepath, 'r', encoding = 'utf-8') as file:
# 1、创建阅读器对象
reader = csv.reader(file)
# 2、读取文件数据
rows = [row for row in reader]
return rows
# 按行写入数据到csv文件
# way写入方式,w-覆盖写入 at-追加写入
def write_csv(self, filepath, way, row):
if filepath is None:
filepath = self.filepath
with open(filepath, way, encoding = 'utf-8', newline = '') as file:
writer = csv.writer(file)
writer.writerow(row)
if __name__ == "__main__":
my_test = neo_csv()
# 创建csv文件:接口描述-参数化-参数校验
head_row = ['switch', 'method', 'url', 'need_token', 'urldata', 'jsondata', 'filedata', 'pars_genwith_sql', 'pars_genwith_upfile', 'pars_ck_required','pars_ck_boundary', 'pars_ck_legal', 'pars_ck_illegal']
filepath = os.getcwd() + '\\gendata.csv'
my_test.write_csv(filepath, 'w', head_row)
result = my_test.get_headrow(filepath)
print("表头为", result)
# 添加一行示例数据
data_row = ['true', 'post', '/user/login', 'false', '', {'username':'${username}','passwd':'${passwd}'},'','','',['username','passwd'],{'username':'8-15'},{'username':r'/w'},{'username':r'/s'}]
my_test.write_csv(filepath, 'at', data_row)
# 将列名称转换为字典的key
head_col = my_test.headrow_to_dict(filepath)
print("表头字典为", head_col)
# 读取csv文件全部内容
csv_content = my_test.read_csv(filepath)
print("完整内容为", csv_content)
# 读取行的某列内容
for index in range (1, len(csv_content)):
row = csv_content[index]
print("该行内容为", row)
# 根据列字典的key获取数组序号,再取该行该列的值
switch = row[head_col['switch']]
method = row[head_col['method']]
url = row[head_col['url']]
print(switch, method, url)