力扣-第242题--有效的字母异位词(python)
给定两个字符串 s 和 t ,编写一个函数来判断 t 是否是 s 的字母异位词。
注意:若 s 和 t 中每个字符出现的次数都相同,则称 s 和 t 互为字母异位词。
示例 1:
输入: s = “anagram”, t = “nagaram”
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: s = “rat”, t = “car”
输出: false
题解:哈希表
碰到这种类似什么字符出现次数啥的,如果没有思路了,都可以往哈希的思路上便一下。
再来看关键点,这道题字符串 s 和 t 仅包含小写字母,小写字母就固定的 26个。
这种定长的范围且和字符次数相关,用哈希妥妥的没问题。
下面就是找出哈希函数,就是把每一个 key 对应到 0 ~ N-1 的范围内,并且放在合适的位置。
----这里用的哈希函数 f(key) = key - ‘a’。这里其实是对字符 ASCII 的操作,字母 a ~ z 的 ASCII 是连续的 26 个数值。
----比如 f(a) = ‘a’ - ‘a’ = 0,f(b) = ‘b’ - ‘a’ = 1,即字母 a 对应的是哈希表下标为 0 的位置,字母 b 对应的是哈希表下标为 1 的位置,剩下的依此类推。
- 哈希函数找好,下面的就很简单:
----遍历字符串 s,哈希表对应的字符值加。
----遍历字符串 t,哈希表对应的字符值减。
----如果哈希表中的值都为 0,则 s 和 t 互为字母异位词。
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-anagram/solution/acm-xuan-shou-tu-jie-leetcode-you-xiao-d-npjv/
- 代码逐步调试:
class Solution:
def isAnagram(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
# 如果两个字符串长度不等,肯定不是字母异位词
if len(s) != len(t):
return False
# 如果两个字符串的长度相等
# 初始化哈希函数,字符串只包含小写字母,故初始化 26 个
hash = [0] * 26
# 循环两个字符串
# 对于字符串 s,在对应位置加(比如出现 a,就在 a 的位置 +1)
for i in range(len(s)):
print('i',i)
print('s[i]:', s[i])
print('ord(s[i]:',ord(s[i]))
print('ord(a):', ord('a'))
print('前hash[ord(s[i]) - ord(a)]', hash[ord(s[i]) - ord('a')])
hash[ord(s[i]) - ord('a')] += 1
print('hash-i:', hash)
print('后hash[ord(s[i]) - ord(a)]', hash[ord(s[i]) - ord('a')])
# 对于字符串 t,在对应位置减(比如出现 a,就在 a 的位置 -1)
for j in range(len(t)):
print('j', j)
print('s[j]:', s[j])
print('ord(s[j]:', ord(s[j]))
print('ord(a):', ord('a'))
print('前hash[ord(s[j]) - ord(a)]', hash[ord(s[j]) - ord('a')])
hash[ord(t[j]) - ord('a')] -= 1
print('hash-j:', hash)
print('后hash[ord(s[j]) - ord(a)]', hash[ord(s[j]) - ord('a')])
print('hash:',hash)
# 遍历哈希表,如果值都为 0,则为字母异位词
# 如果存在任一值不为 0 的哈希值,则不为字母异位词
for i in range(26):
if hash[i] != 0:
return False
return True
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = Solution()
s1 = "agram"
t1 = "garam"
result_list = s.isAnagram(s1,t1)
print('result_list:', result_list)
- 输出为:
i 0 | j 0
s[i]: a | s[j]: a
ord(s[i]: 97 | ord(s[j]: 97
ord(a): 97 | ord(a): 97
前hash[ord(s[i]) - ord(a)] 0 | 前hash[ord(s[j]) - ord(a)] 2
后hash[ord(s[i]) - ord(a)] 1 | 后hash[ord(s[j]) - ord(a)] 2
hash-i: [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
hash-j: [2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
i 1 | j 1
s[i]: g | s[j]: g
ord(s[i]: 103 | ord(s[j]: 103
ord(a): 97 | ord(a): 97
前hash[ord(s[i]) - ord(a)] 0 | 前hash[ord(s[j]) - ord(a)] 0
后hash[ord(s[i]) - ord(a)] 1 | 后hash[ord(s[j]) - ord(a)] 0
hash-i: [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
hash-j: [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
i 2 | j 2
s[i]: r | s[j]: r
ord(s[i]: 114 | ord(s[j]: 114
ord(a): 97 | ord(a): 97
前hash[ord(s[i]) - ord(a)] 0 | 前hash[ord(s[j]) - ord(a)] 1
后hash[ord(s[i]) - ord(a)] 1 | 后hash[ord(s[j]) - ord(a)] 0
hash-i: [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
hash-j: [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
i 3 | j 3
s[i]: a | s[j]: a
ord(s[i]: 97 | ord(s[j]: 97
ord(a): 97 | ord(a): 97
前hash[ord(s[i]) - ord(a)] 1 | 前hash[ord(s[j]) - ord(a)] 1
后hash[ord(s[i]) - ord(a)] 2 | 后hash[ord(s[j]) - ord(a)] 0
hash-i: [2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
hash-j: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
i 4 | j 4
s[i]: m | s[j]: m
ord(s[i]: 109 | ord(s[j]: 109
ord(a): 97 | ord(a): 97
前hash[ord(s[i]) - ord(a)] 0 | 前hash[ord(s[j]) - ord(a)] 1
后hash[ord(s[i]) - ord(a)] 1 | 后hash[ord(s[j]) - ord(a)] 0
hash-i: [2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
hash-j: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
hash: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
result_list: True
第一步,
遍历字符串 s,碰到相应的字符,对应下标的哈希值 + 1。
对于 s = “anagram”,第 1 个字符为 a,a 对应哈希表下标为 0,则下标 0 对应值 +1:

# 对于字符串 s,在对应位置加(比如出现 a,就在 a 的位置 +1)
for i in range(len(s)):
hash[ord(s[i]) - ord('a')] += 1
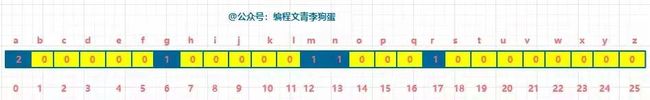
依次遍历完字符串 s,哈希表如下图:

第二步,
遍历字符串 t,碰到对应的字符,相应下标的哈希值 -1。
对于 t = “nagaram”,第 1 个字符为 n,n 对应的下标为 13,则下标 13 对应的哈希值 -1:
# 对于字符串 t,在对应位置减(比如出现 a,就在 a 的位置 -1)
for i in range(len(t)):
hash[ord(t[i]) - ord('a')] -= 1
同样,依次遍历完字符串 t,哈希表如下图:
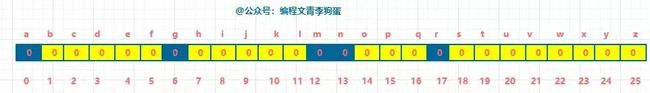
第三步,
遍历哈希表,所有的值均为 0,则 s 和 t 互为字母异位词,反之为否。
# 遍历哈希表,如果值都为 0,则为字母异位词
# 如果存在任一值不为 0 的哈希值,则不为字母异位词
for i in range(26):
if hash[i] != 0:
return False
return True
在此例中,字符串 s 和 t 互为字母异位词。
此题解法,时间复杂度为 O(n),n 为 s 和 t 中较长的那个字符串的长度。
因为额外开了一个长为 26 的数组,所以空间复杂度为 O(m),m = 26。
