负载均衡在线oj
1.项目源码load-balanced-online-oj · fortianyang/project - 码云 - 开源中国 (gitee.com)
2.相关技术⭐
⭕C++ STL 标准库⭕Boost 准标准库(字符串切割)⭕cpp-httplib 第三方开源网络库⭕ctemplate 第三方开源前端网页渲染库⭕jsoncpp 第三方开源序列化、反序列化库⭕负载均衡设计⭕多进程、多线程
3. 开发环境 ⚙
⭕quanCentos 7 云服务器⭕vscode
4.项目结构
5. compile服务设计
compile: 编译并且运行代码,得到格式化的相关结果
第一个功能compiler :编译功能❀ ❀❀
✍compile代码实现❤
//compile.hpp
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "../comm/util.hpp"
#include "../comm/log.hpp"
// 只负责进行代码的编译
namespace ns_compiler
{
// 引入路径拼接功能
using namespace ns_util;
using namespace ns_log;
class Compiler
{
public:
Compiler()
{}
~Compiler()
{}
//返回值:编译成功:true,否则:false
//输入参数:编译的文件名
//file_name: 1234
//1234 -> ./temp/1234.cpp
//1234 -> ./temp/1234.exe
//1234 -> ./temp/1234.stderr
static bool Compile(const std::string &file_name)
{
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid < 0)
{
LOG(ERROR) << "内部错误,创建子进程失败" << "\n";
return false;
}
else if (pid == 0)
{
umask(0);//⭐ 小细节 (*^_^*)
int _stderr = open(PathUtil::CompilerError(file_name).c_str(), O_CREAT | O_WRONLY, 0644);
if(_stderr < 0){
LOG(WARNING) << "没有成功形成stderr文件" << "\n";
exit(1);
}
//重定向标准错误到_stderr
dup2(_stderr, 2);
//程序替换,并不影响进程的文件描述符表
//子进程: 调用编译器,完成对代码的编译工作
//g++ -o target src -std=c++11
execlp("g++", "g++", "-o", PathUtil::Exe(file_name).c_str(),\
PathUtil::Src(file_name).c_str(),"-std=c++11", nullptr/*不要忘记*/);//♥
// PathUtil::Src(file_name).c_str(), "-D", "COMPILER_ONLINE","-std=c++11", nullptr/*不要忘记*/);//♥
LOG(ERROR) << "启动编译器g++失败,可能是参数错误" << "\n";
exit(2);//♥
}
else{
waitpid(pid, nullptr, 0);
//编译是否成功,就看有没有形成对应的可执行程序
if(FileUtil::IsFileExists(PathUtil::Exe(file_name))){
LOG(INFO) << PathUtil::Src(file_name) << " 编译成功!" << "\n";
return true;
}
}
LOG(DEBUG)< ✍Log功能♥
//log.hpp
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include "util.hpp"
namespace ns_log
{
using namespace ns_util;
// 日志等级
enum
{
INFO, //就是整数
DEBUG,
WARNING,
ERROR,
FATAL
};
inline std::ostream &Log(const std::string &level, const std::string &file_name, int line)
{
// 添加日志等级
std::string message = "[";
message += level;
message += "]";
// 添加报错文件名称
message += "[";
message += file_name;
message += "]";
// 添加报错行
message += "[";
message += std::to_string(line);
message += "]";
// 日志时间戳
message += "[";
message += TimeUtil::GetTimeStamp();
message += "]";
// cout 本质 内部是包含缓冲区的
std::cout << message; //不要endl进行刷新
return std::cout;
}
// LOG(INFo) << "message" << "\n";
// 开放式日志
#define LOG(level) Log(#level, __FILE__, __LINE__)
} ✍工具类♥
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
namespace ns_util
{
class TimeUtil
{
public:
static std::string GetTimeStamp()
{
struct timeval _time;
gettimeofday(&_time, nullptr);
return std::to_string(_time.tv_sec);
}
//获得毫秒时间戳
static std::string GetTimeMs()
{
struct timeval _time;
gettimeofday(&_time, nullptr);
return std::to_string(_time.tv_sec * 1000 + _time.tv_usec / 1000);
}
};
const std::string temp_path = "./temp/";
class PathUtil
{
public:
static std::string AddSuffix(const std::string &file_name, const std::string &suffix)
{
std::string path_name = temp_path;
path_name += file_name;
path_name += suffix;
return path_name;
}
// 编译时需要有的临时文件
// 构建源文件路径+后缀的完整文件名
// 1234 -> ./temp/1234.cpp
static std::string Src(const std::string &file_name)
{
return AddSuffix(file_name, ".cpp");
}
// 构建可执行程序的完整路径+后缀名
static std::string Exe(const std::string &file_name)
{
return AddSuffix(file_name, ".exe");
}
static std::string CompilerError(const std::string &file_name)
{
return AddSuffix(file_name, ".compile_error");
}
// 运行时需要的临时文件
static std::string Stdin(const std::string &file_name)
{
return AddSuffix(file_name, ".stdin");
}
static std::string Stdout(const std::string &file_name)
{
return AddSuffix(file_name, ".stdout");
}
// 构建该程序对应的标准错误完整的路径+后缀名
static std::string Stderr(const std::string &file_name)
{
return AddSuffix(file_name, ".stderr");
}
};
class FileUtil
{
public:
static bool IsFileExists(const std::string &path_name)
{
struct stat st;
if (stat(path_name.c_str(), &st) == 0)
{
//获取属性成功,文件已经存在
return true;
}
return false;
}
static std::string UniqFileName()
{
static std::atomic_uint id(0);
id++;
// 毫秒级时间戳+原子性递增唯一值: 来保证唯一性
std::string ms = TimeUtil::GetTimeMs();
std::string uniq_id = std::to_string(id);
return ms + "_" + uniq_id;
}
static bool WriteFile(const std::string &target, const std::string &content)
{
std::ofstream out(target);
if (!out.is_open())
{
return false;
}
out.write(content.c_str(), content.size());
out.close();
return true;
}
static bool ReadFile(const std::string &target, std::string *content, bool keep = false)
{
(*content).clear();
std::ifstream in(target);
if (!in.is_open())
{
return false;
}
std::string line;
// getline:不保存行分割符,有些时候需要保留\n,
// getline内部重载了强制类型转化
while (std::getline(in, line))
{
(*content) += line;
(*content) += (keep ? "\n" : "");
}
in.close();
return true;
}
};
class StringUtil
{
public:
/*************************************
* str: 输入型,目标要切分的字符串
* target: 输出型,保存切分完毕的结果
* sep: 指定的分割符
* **********************************/
static void SplitString(const std::string &str, std::vector *target, const std::string &sep)
{
//boost split
boost::split((*target), str, boost::is_any_of(sep), boost::algorithm::token_compress_on);
}
};
} ✍测试♥
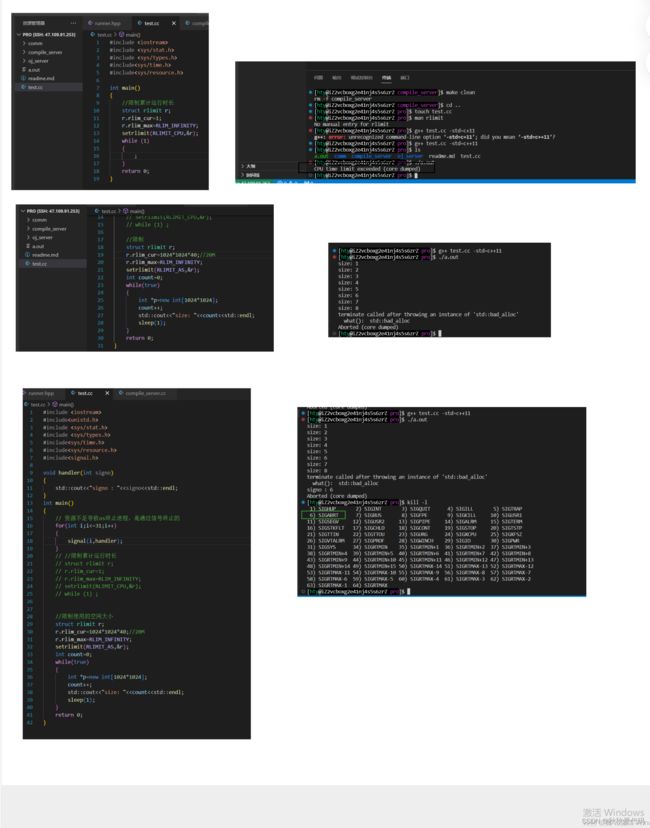
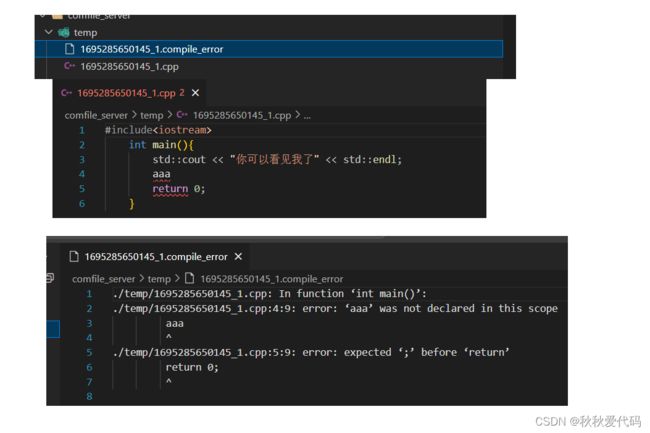
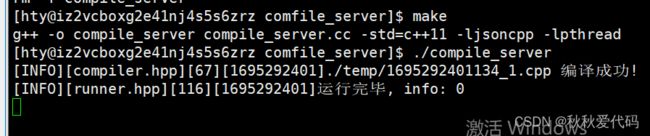
编译功能的基本代码已经完成,我们可以简单编写一个 temp目录,再在该目录下编写一个code.cpp才进行测试
//code.cc
#include
int main()
{
//aaa--也可以加一点错误的信息,更好观察stderr的内容⭐
std::cout<<"hello"< //compile_server.cc
#include"compiler.hpp"
using namespace ns_compiler;
#include "compile_run.hpp"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
std::string code="code";
Compiler::Compile(code);
return 0;
}
运行结果
运行结果 1.0
正常运行结束,stderr无输出。
运行结果 2.0
./temp/code.cpp: In function ‘int main()’:
./temp/code.cpp:6:5: error: ‘aaa’ was not declared in this scope
aaa
^
./temp/code.cpp:7:5: error: expected ‘;’ before ‘std’
std::cout<<"hello"<第二个功能 runner :运行功能
功能分析
⭕ 程序运行:
1. 代码跑完,结果正确
2. 代码跑完,结果不正确
3. 代码没跑完,异常了
Run需要考虑代码跑完,结果正确与否吗??不考虑!
▷ 结果正确与否:是由我们的测试用例决定的!
▷ 我们只考虑:是否正确运行完毕
*
我们必须知道可执行程序是谁?
▷ 一个程序在默认启动的时候
▷ 标准输入: 不处理
▷ 标准输出: 程序运行完成,输出结果是什么
▷ 标准错误: 运行时错误信息
❀基础版本
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "../comm/log.hpp"
#include "../comm/util.hpp"
namespace ns_runner
{
using namespace ns_util;
using namespace ns_log;
class Runner
{
public:
Runner() {}
~Runner() {}
public:
// 指明文件名即可,不需要代理路径,不需要带后缀
/*******************************************
* 返回值 > 0: 程序异常了,退出时收到了信号,返回值就是对应的信号编号
* 返回值 == 0: 正常运行完毕的,结果保存到了对应的临时文件中
* 返回值 < 0: 内部错误
*
* cpu_limit: 该程序运行的时候,可以使用的最大cpu资源上限
* mem_limit: 改程序运行的时候,可以使用的最大的内存大小(KB)
* *****************************************/
static int Run(const std::string &file_name)
{
/*********************************************
* 程序运行:
* 1. 代码跑完,结果正确
* 2. 代码跑完,结果不正确
* 3. 代码没跑完,异常了
* Run需要考虑代码跑完,结果正确与否吗??不考虑!
* 结果正确与否:是由我们的测试用例决定的!
* 我们只考虑:是否正确运行完毕
*
* 我们必须知道可执行程序是谁?
* 一个程序在默认启动的时候
* 标准输入: 不处理
* 标准输出: 程序运行完成,输出结果是什么
* 标准错误: 运行时错误信息
* *******************************************/
std::string _execute = PathUtil::Exe(file_name); // 可执行程序名
std::string _stdin = PathUtil::Stdin(file_name); // 标准输入
std::string _stdout = PathUtil::Stdout(file_name); // 标准输出
std::string _stderr = PathUtil::Stderr(file_name); // 标准错误
umask(0);
int _stdin_fd = open(_stdin.c_str(), O_CREAT | O_RDONLY, 0644);
int _stdout_fd = open(_stdout.c_str(), O_CREAT | O_WRONLY, 0644);
int _stderr_fd = open(_stderr.c_str(), O_CREAT | O_WRONLY, 0644);
if (_stdin_fd < 0 || _stdout_fd < 0 || _stderr_fd < 0)
{
LOG(ERROR) << "运行时打开标准文件失败"
<< "\n";
return -1; // 代表打开文件失败
}
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid < 0)
{
LOG(ERROR) << "运行时创建子进程失败"
<< "\n";
close(_stdin_fd);
close(_stdout_fd);
close(_stderr_fd);
return -2; // 代表创建子进程失败
}
else if (pid == 0)
{
dup2(_stdin_fd, 0);
dup2(_stdout_fd, 1);
dup2(_stderr_fd, 2);
execl(_execute.c_str() /*我要执行谁*/, _execute.c_str() /*我想在命令行上如何执行该程序*/, nullptr);
exit(1);
}
else
{
close(_stdin_fd);
close(_stdout_fd);
close(_stderr_fd);
int status = 0;
waitpid(pid, &status, 0);
// 程序运行异常,一定是因为因为收到了信号!
LOG(INFO) << "运行完毕, info: " << (status & 0x7F) << "\n";
return status & 0x7F;
}
}
};
} ✍ 测试
#include"compiler.hpp"
#include"runner.hpp"
using namespace ns_compiler;
using namespace ns_runner;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
std::string code="code";
Compiler::Compile(code);
Runner::Run(code);
return 0;
}
测试结果
程序正常运行结束,code.compile_error无输出
✍ 添加测试资源限制
小测试
我们通过下面这个简单的小实验来测试限制运行资源和时间资源,避免一些死循环或者资源消耗过大的测试恶意攻击
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
void handler(int signo)
{
std::cout<<"signo : "< 测试结果
添加资源限制功能到runner中
代码实现
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include //⭐
#include //⭐
#include "../comm/log.hpp"
#include "../comm/util.hpp"
namespace ns_runner
{
using namespace ns_util;
using namespace ns_log;
class Runner
{
public:
Runner() {}
~Runner() {}
public:
// 提供设置进程占用资源大小的接口
static void SetProcLimit(int _cpu_limit, int _mem_limit)
{
// 设置CPU时长
struct rlimit cpu_rlimit;
cpu_rlimit.rlim_max = RLIM_INFINITY;
cpu_rlimit.rlim_cur = _cpu_limit;
setrlimit(RLIMIT_CPU, &cpu_rlimit);
// 设置内存大小
struct rlimit mem_rlimit;
mem_rlimit.rlim_max = RLIM_INFINITY;
mem_rlimit.rlim_cur = _mem_limit * 1024; // 转化成为KB
setrlimit(RLIMIT_AS, &mem_rlimit);
}
// 指明文件名即可,不需要代理路径,不需要带后缀
/*******************************************
* 返回值 > 0: 程序异常了,退出时收到了信号,返回值就是对应的信号编号
* 返回值 == 0: 正常运行完毕的,结果保存到了对应的临时文件中
* 返回值 < 0: 内部错误
*
* cpu_limit: 该程序运行的时候,可以使用的最大cpu资源上限
* mem_limit: 改程序运行的时候,可以使用的最大的内存大小(KB)
* *****************************************/
static int Run(const std::string &file_name, int cpu_limit, int mem_limit)
{
/*********************************************
* 程序运行:
* 1. 代码跑完,结果正确
* 2. 代码跑完,结果不正确
* 3. 代码没跑完,异常了
* Run需要考虑代码跑完,结果正确与否吗??不考虑!
* 结果正确与否:是由我们的测试用例决定的!
* 我们只考虑:是否正确运行完毕
*
* 我们必须知道可执行程序是谁?
* 一个程序在默认启动的时候
* 标准输入: 不处理
* 标准输出: 程序运行完成,输出结果是什么
* 标准错误: 运行时错误信息
* *******************************************/
std::string _execute = PathUtil::Exe(file_name); // 可执行程序名
std::string _stdin = PathUtil::Stdin(file_name); // 标准输入
std::string _stdout = PathUtil::Stdout(file_name); // 标准输出
std::string _stderr = PathUtil::Stderr(file_name); // 标准错误
umask(0);
int _stdin_fd = open(_stdin.c_str(), O_CREAT | O_RDONLY, 0644);
int _stdout_fd = open(_stdout.c_str(), O_CREAT | O_WRONLY, 0644);
int _stderr_fd = open(_stderr.c_str(), O_CREAT | O_WRONLY, 0644);
if (_stdin_fd < 0 || _stdout_fd < 0 || _stderr_fd < 0)
{
LOG(ERROR) << "运行时打开标准文件失败"
<< "\n";
return -1; // 代表打开文件失败
}
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid < 0)
{
LOG(ERROR) << "运行时创建子进程失败"
<< "\n";
close(_stdin_fd);
close(_stdout_fd);
close(_stderr_fd);
return -2; // 代表创建子进程失败
}
else if (pid == 0)
{
dup2(_stdin_fd, 0);
dup2(_stdout_fd, 1);
dup2(_stderr_fd, 2);
SetProcLimit(cpu_limit, mem_limit);//⭐
execl(_execute.c_str() /*我要执行谁*/, _execute.c_str() /*我想在命令行上如何执行该程序*/, nullptr);
exit(1);
}
else
{
close(_stdin_fd);
close(_stdout_fd);
close(_stderr_fd);
int status = 0;
waitpid(pid, &status, 0);
// 程序运行异常,一定是因为因为收到了信号!
LOG(INFO) << "运行完毕, info: " << (status & 0x7F) << "\n";
return status & 0x7F;
}
}
};
} 编译并运行 compile_run 模块
通常我们的code.cpp并不是直接写在我们的某个文件夹中的,需要我们从网络中获取,这就需要我们了解一点json相关的知识了。
安装json
sudo yum install -y jsoncpp-devel使用json
✍ 代码示例
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
//序列化
//Value是Json的一个中间类,可以填充k,v对象
Json::Value root;
root["value"]="mycode";
root["user"]="hty";
root["age"]="22";
// Json::StyledWriter writer;
//反序列化
Json::FastWriter writer;
std::string str=writer.write(root);
std::cout< 运行结果
compile_run 模块
分析
⭕输入:
code: 用户提交的代码
input: 用户给自己提交的代码对应的输入,不做处理
cpu_limit: 时间要求
mem_limit: 空间要求
⭕输出:
必填
status: 状态码
reason: 请求结果
选填:
stdout: 我的程序运行完的结果
stderr: 我的程序运行完的错误结果
#pragma once
#include "compiler.hpp"
#include "runner.hpp"
#include "../comm/log.hpp"
#include "../comm/util.hpp"
#include
#include
#include
namespace ns_compile_and_run
{
using namespace ns_log;
using namespace ns_util;
using namespace ns_compiler;
using namespace ns_runner;
class CompileAndRun
{
public:
// code > 0 : 进程收到了信号导致异常奔溃
// code < 0 : 整个过程非运行报错(代码为空,编译报错等)
// code = 0 : 整个过程全部完成
//待完善
static std::string CodeToDesc(int code, const std::string &file_name)
{
std::string desc;
switch (code)
{
case 0:
desc = "编译运行成功";
break;
case -1:
desc = "提交的代码是空";
break;
case -2:
desc = "未知错误";
break;
case -3:
// desc = "代码编译的时候发生了错误";
FileUtil::ReadFile(PathUtil::CompilerError(file_name), &desc, true);
break;
case SIGABRT: // 6
desc = "内存超过范围";
break;
case SIGXCPU: // 24
desc = "CPU使用超时";
break;
case SIGFPE: // 8
desc = "浮点数溢出";
break;
default:
desc = "未知: " + std::to_string(code);
break;
}
return desc;
}
/***************************************
* 输入:
* code: 用户提交的代码
* input: 用户给自己提交的代码对应的输入,不做处理
* cpu_limit: 时间要求
* mem_limit: 空间要求
*
* 输出:
* 必填
* status: 状态码
* reason: 请求结果
* 选填:
* stdout: 我的程序运行完的结果
* stderr: 我的程序运行完的错误结果
*
* 参数:
* in_json: {"code": "#include...", "input": "","cpu_limit":1, "mem_limit":10240}
* out_json: {"status":"0", "reason":"","stdout":"","stderr":"",}
* ************************************/
static void Start(const std::string &in_json, std::string *out_json)
{
Json::Value in_value;
Json::Reader reader;
reader.parse(in_json, in_value); //最后在处理差错问题
std::string code = in_value["code"].asString();
std::string input = in_value["input"].asString();
int cpu_limit = in_value["cpu_limit"].asInt();
int mem_limit = in_value["mem_limit"].asInt();
int status_code = 0;
Json::Value out_value;//返回数据
int run_result = 0;
std::string file_name; //需要内部形成的唯一文件名
if (code.size() == 0)
{
status_code = -1; //代码为空
goto END;
}
// 形成的文件名只具有唯一性,没有目录没有后缀
// 毫秒级时间戳+原子性递增唯一值: 来保证唯一性
file_name = FileUtil::UniqFileName();
//形成临时src文件
if (!FileUtil::WriteFile(PathUtil::Src(file_name), code))
{
status_code = -2; //未知错误
goto END;
}
if (!Compiler::Compile(file_name))
{
//编译失败
status_code = -3; //代码编译的时候发生了错误
goto END;
}
run_result = Runner::Run(file_name, cpu_limit, mem_limit);
if (run_result < 0)
{
status_code = -2; //未知错误
}
else if (run_result > 0)
{
//程序运行崩溃了
status_code = run_result;
}
else
{
//运行成功
status_code = 0;
}
END:
out_value["status"] = status_code;
out_value["reason"] = CodeToDesc(status_code, file_name);
if (status_code == 0)
{
// 整个过程全部成功
std::string _stdout;
FileUtil::ReadFile(PathUtil::Stdout(file_name), &_stdout, true);
out_value["stdout"] = _stdout;
std::string _stderr;
FileUtil::ReadFile(PathUtil::Stderr(file_name), &_stderr, true);
out_value["stderr"] = _stderr;
}
Json::StyledWriter writer;
*out_json = writer.write(out_value);
}
};
}
测试
✍代码示例
#include "compile_run.hpp"
using namespace ns_compiler;
using namespace ns_runner;
using namespace ns_compile_and_run;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//通过Http 让client给我们上传一个json string
std::string in_json;
Json::Value in_value;
in_value["code"]=R"(#include
int main(){
std::cout << "你可以看见我了" << std::endl;
//aaaaaaaa
return 0;
})";
in_value["input"]="";
in_value["cpu_cimit"]=1;
in_value["mem_limit"]=10240*3;
Json::FastWriter writer;
in_json=writer.write(in_value);
std::cout< 输出结果1.0:
添加清理功能
static void RemoveTempFile(const std::string &file_name)
{
//清理文件的个数是不确定的,但是有哪些我们是知道的
std::string _src = PathUtil::Src(file_name);
if(FileUtil::IsFileExists(_src)) unlink(_src.c_str());
std::string _compiler_error = PathUtil::CompilerError(file_name);
if(FileUtil::IsFileExists(_compiler_error)) unlink(_compiler_error.c_str());
std::string _execute = PathUtil::Exe(file_name);
if(FileUtil::IsFileExists(_execute)) unlink(_execute.c_str());
std::string _stdin = PathUtil::Stdin(file_name);
if(FileUtil::IsFileExists(_stdin)) unlink(_stdin.c_str());
std::string _stdout = PathUtil::Stdout(file_name);
if(FileUtil::IsFileExists(_stdout)) unlink(_stdout.c_str());
std::string _stderr = PathUtil::Stderr(file_name);
if(FileUtil::IsFileExists(_stderr)) unlink(_stderr.c_str());
}将函数调用添加到END部分即可,为了观察现象比较明显,暂时屏蔽掉
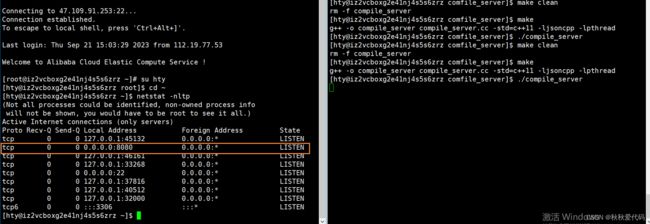
第三个功能: 把编译并运行功能,形成网络服务
引入httplib第三方库
另外,使用这个文件需要将gcc进行升级
升级 gcc
$ sudo yum install centos-release-scl scl-utils-build$ sudo yum install -y devtoolset-7-gcc devtoolset-7-gcc-c++
$ ls /opt/rh/启动: 细节,命令行启动只能在本会话有效
$ scl enable devtoolset-7 bash
$ gcc -v可选:如果想每次登陆的时候,都是较新的gcc,需要把上面的命令添加到你的~/.bash_profile中
$ cat ~/.bash_profile
# .bash_profile
# Get the aliases and functions
if [ -f ~/.bashrc ]; then
. ~/.bashrc
scl enable devtoolset-7 bash
or
scl enable devtoolset-8 bash
or
scl enable devtoolset-9 bash获得下面的结果gcc 就升级好啦
httplib文件测试
✍ 代码示例
#include "compile_run.hpp"
#include"../comm/httplib.h"
using namespace httplib;
using namespace ns_compiler;
using namespace ns_runner;
using namespace ns_compile_and_run;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//使用cpp-httplib
Server svr;
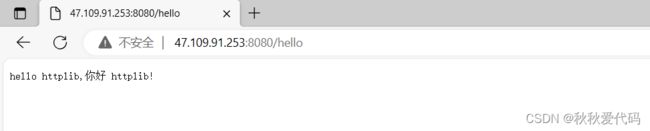
svr.Get("/hello",[](const Request &req, Response &resp){
// 用来进行基本测试
resp.set_content("hello httplib,你好 httplib!", "text/plain;charset=utf-8");
});
svr.listen("0.0.0.0",8080);
return 0;
}
输出结果
✍代码示例2
wwroot目录下的index.html文件(仅作测试使用)
测试
这是一个段落。
这是一个段落。
这是一个段落。
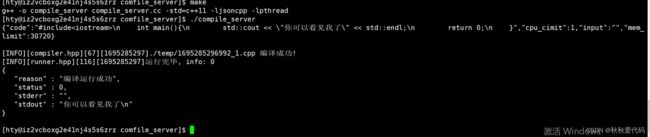
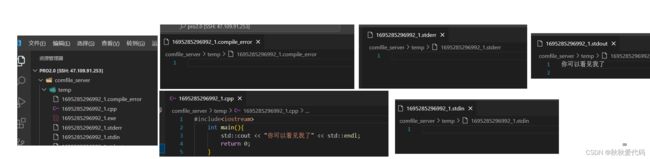
compile_server.cc
#include "compile_run.hpp"
#include"../comm/httplib.h"
using namespace httplib;
using namespace ns_compiler;
using namespace ns_runner;
using namespace ns_compile_and_run;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//使用cpp-httplib
Server svr;
svr.Get("/hello",[](const Request &req, Response &resp){
// 用来进行基本测试
resp.set_content("hello httplib,你好 httplib!", "text/plain;charset=utf-8");
});
svr.set_base_dir("./wwwroot");
svr.listen("0.0.0.0",8080);
return 0;
}
输出结果
用postman软件进行测试
5. 基于MVC 结构的oj 服务设计
⭕ 1. 获取首页,用题目列表充当⭕ 2. 编辑区域页面⭕ 3. 提交判题功能(编译并运行)M: Model,通常是和数据交互的模块,比如,对题库进行增删改查(文件版,MySQL)V: view, 通常是拿到数据之后,要进行构建网页,渲染网页内容,展示给用户的(浏览器)C: control, 控制器,就是我们的核心业务逻辑
✍第一个功能:用户请求的服务路由功能
#include
#include
#include "../comm/httplib.h"
#include "oj_control.hpp"
using namespace httplib;
using namespace ns_control;
static Control *ctrl_ptr = nullptr;
void Recovery(int signo)
{
ctrl_ptr->RecoveryMachine();
}
int main()
{
signal(SIGQUIT, Recovery);
//用户请求的服务路由功能
Server svr;
Control ctrl;
ctrl_ptr = &ctrl;
// 获取所有的题目列表
svr.Get("/all_questions", [&ctrl](const Request &req, Response &resp){
//返回一张包含有所有题目的html网页
std::string html;
ctrl.AllQuestions(&html);
//用户看到的是什么呢??网页数据 + 拼上了题目相关的数据
resp.set_content(html, "text/html; charset=utf-8");
});
// 用户要根据题目编号,获取题目的内容
// /question/100 -> 正则匹配
// R"()", 原始字符串raw string,保持字符串内容的原貌,不用做相关的转义
svr.Get(R"(/question/(\d+))", [&ctrl](const Request &req, Response &resp){
std::string number = req.matches[1];
std::string html;
ctrl.Question(number, &html);
resp.set_content(html, "text/html; charset=utf-8");
});
// 用户提交代码,使用我们的判题功能(1. 每道题的测试用例 2. compile_and_run)
svr.Post(R"(/judge/(\d+))", [&ctrl](const Request &req, Response &resp){
std::string number = req.matches[1];
std::string result_json;
ctrl.Judge(number, req.body, &result_json);
resp.set_content(result_json, "application/json;charset=utf-8");
// resp.set_content("指定题目的判题: " + number, "text/plain; charset=utf-8");
});
svr.set_base_dir("./wwwroot");
svr.listen("0.0.0.0", 8080);
return 0;
} ✍第二个功能:题目设计
分析
⭕ 题目的编号⭕ 题目的标题⭕ 题目的难度⭕ 题目的描述 , 题面⭕ 时间要求 ( 内部处理 )⭕ 空间要求 ( 内部处理 )两批文件构成第一个: questions . list : 题目列表(不需要题目的内容)第二个:题目的描述,题目的预设置代码 ( header . cpp ), 测试用例代码 ( tail . cpp )
测试用例的设计详细参见 测试用例设计
更多测试用例的编辑可以参考 题目以及测试用例
boost库引入(用于分割字符串)
安装boost库
sudo yum install -y boost-devel //是boost 开发库✍小实验
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
std::vector tokens;
const std::string str = "1 判断回文数 简单 30000";
const std::string sep = " ";
// boost::split(tokens,str,boost::is_any_of(sep),boost::algorithm::token_compress_off);
boost::split(tokens, str, boost::is_any_of(sep), boost::algorithm::token_compress_on);
for (auto &iter : tokens)
{
std::cout << iter << std::endl;
}
return 0;
} 运行结果
项目中的具体使用
✍第三个功能:control,逻辑控制模块
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "../comm/util.hpp"
#include "../comm/log.hpp"
#include "../comm/httplib.h"
#include "oj_model.hpp"
#include "oj_view.hpp"
namespace ns_control
{
using namespace std;
using namespace ns_log;
using namespace ns_util;
using namespace ns_model;
using namespace ns_view;
using namespace httplib;
// 提供服务的主机
class Machine
{
public:
std::string ip; // 编译服务的ip
int port; // 编译服务的port
uint64_t load; // 编译服务的负载
std::mutex *mtx; // mutex禁止拷贝的,使用指针
public:
Machine() : ip(""), port(0), load(0), mtx(nullptr)
{
}
~Machine()
{
}
public:
// 提升主机负载
void IncLoad()
{
if (mtx)
mtx->lock();
++load;
if (mtx)
mtx->unlock();
}
// 减少主机负载
void DecLoad()
{
if (mtx)
mtx->lock();
--load;
if (mtx)
mtx->unlock();
}
void ResetLoad()
{
if (mtx)
mtx->lock();
load = 0;
if (mtx)
mtx->unlock();
}
// 获取主机负载,没有太大的意义,只是为了统一接口
uint64_t Load()
{
uint64_t _load = 0;
if (mtx)
mtx->lock();
_load = load;
if (mtx)
mtx->unlock();
return _load;
}
};
const std::string service_machine = "./conf/service_machine.conf";
// 负载均衡模块
class LoadBlance
{
private:
// 可以给我们提供编译服务的所有的主机
// 每一台主机都有自己的下标,充当当前主机的id
std::vector machines;
// 所有在线的主机id
std::vector online;
// 所有离线的主机id
std::vector offline;
// 保证LoadBlance它的数据安全
std::mutex mtx;
public:
LoadBlance()
{
// assert(LoadConf(service_machine));
LOG(INFO) << "加载 " << service_machine << " 成功"
<< "\n";
}
~LoadBlance()
{
}
public:
bool LoadConf(const std::string &machine_conf)
{
std::ifstream in(machine_conf);
if (!in.is_open())
{
LOG(FATAL) << " 加载: " << machine_conf << " 失败"
<< "\n";
return false;
}
std::string line;
while (std::getline(in, line))
{
std::vector tokens;
StringUtil::SplitString(line, &tokens, ":");
if (tokens.size() != 2)
{
LOG(WARNING) << " 切分 " << line << " 失败"
<< "\n";
continue;
}
Machine m;
m.ip = tokens[0];
m.port = atoi(tokens[1].c_str());
m.load = 0;
m.mtx = new std::mutex();
online.push_back(machines.size());
machines.push_back(m);
}
in.close();
return true;
}
// id: 输出型参数
// m : 输出型参数
bool SmartChoice(int *id, Machine **m)
{
// 1. 使用选择好的主机(更新该主机的负载)
// 2. 我们需要可能离线该主机
mtx.lock();
// 负载均衡的算法
// 1. 随机数+hash
// 2. 轮询+hash
int online_num = online.size();
if (online_num == 0)
{
mtx.unlock();
LOG(FATAL) << " 所有的后端编译主机已经离线, 请运维的同事尽快查看"
<< "\n";
return false;
}
// 通过遍历的方式,找到所有负载最小的机器
*id = online[0];
*m = &machines[online[0]];
uint64_t min_load = machines[online[0]].Load();
for (int i = 1; i < online_num; i++)
{
uint64_t curr_load = machines[online[i]].Load();
if (min_load > curr_load)
{
min_load = curr_load;
*id = online[i];
*m = &machines[online[i]];
}
}
mtx.unlock();
return true;
}
void OfflineMachine(int which)
{
mtx.lock();
for (auto iter = online.begin(); iter != online.end(); iter++)
{
if (*iter == which)
{
machines[which].ResetLoad();
// 要离线的主机已经找到啦
online.erase(iter);
offline.push_back(which);
break; // 因为break的存在,所有我们暂时不考虑迭代器失效的问题
}
}
mtx.unlock();
}
void OnlineMachine()
{
// 我们统一上线,后面统一解决
mtx.lock();
online.insert(online.end(), offline.begin(), offline.end());
offline.erase(offline.begin(), offline.end());
mtx.unlock();
LOG(INFO) << "所有的主机有上线啦!"
<< "\n";
}
// for test
void ShowMachines()
{
mtx.lock();
std::cout << "当前在线主机列表: ";
for (auto &id : online)
{
std::cout << id << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "当前离线主机列表: ";
for (auto &id : offline)
{
std::cout << id << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
mtx.unlock();
}
};
// 这是我们的核心业务逻辑的控制器
class Control
{
private:
Model model_; // 提供后台数据
View view_; // 提供html渲染功能
LoadBlance load_blance_; // 核心负载均衡器
public:
Control()
{
}
~Control()
{
}
public:
void RecoveryMachine()
{
load_blance_.OnlineMachine();
}
// 根据题目数据构建网页
// html: 输出型参数
bool AllQuestions(string *html)
{
bool ret = true;
vector all;
if (model_.GetAllQuestions(&all))
{
sort(all.begin(), all.end(), [](const struct Question &q1, const struct Question &q2)
{ return atoi(q1.number.c_str()) < atoi(q2.number.c_str()); });
// 获取题目信息成功,将所有的题目数据构建成网页
view_.AllExpandHtml(all, html);
}
else
{
*html = "获取题目失败, 形成题目列表失败";
ret = false;
}
return ret;
}
bool Question(const string &number, string *html)
{
bool ret = true;
struct Question q;
if (model_.GetOneQuestion(number, &q))
{
// 获取指定题目信息成功,将所有的题目数据构建成网页
view_.OneExpandHtml(q, html);
}
else
{
*html = "指定题目: " + number + " 不存在!";
ret = false;
}
return ret;
}
// code: #include...
// input: ""
void Judge(const std::string &number, const std::string in_json, std::string *out_json)
{
// LOG(DEBUG) << in_json << " \nnumber:" << number << "\n";
// 0. 根据题目编号,直接拿到对应的题目细节
struct Question q;
model_.GetOneQuestion(number, &q);
// 1. in_json进行反序列化,得到题目的id,得到用户提交源代码,input
Json::Reader reader;
Json::Value in_value;
reader.parse(in_json, in_value);
std::string code = in_value["code"].asString();
// 2. 重新拼接用户代码+测试用例代码,形成新的代码
Json::Value compile_value;
compile_value["input"] = in_value["input"].asString();
compile_value["code"] = code + "\n" + q.tail;
compile_value["cpu_limit"] = q.cpu_limit;
compile_value["mem_limit"] = q.mem_limit;
Json::FastWriter writer;
std::string compile_string = writer.write(compile_value);
// 3. 选择负载最低的主机(差错处理)
// 规则: 一直选择,直到主机可用,否则,就是全部挂掉
while (true)
{
int id = 0;
Machine *m = nullptr;
if (!load_blance_.SmartChoice(&id, &m))
{
break;
}
// 4. 然后发起http请求,得到结果
Client cli(m->ip, m->port);
m->IncLoad();
LOG(INFO) << " 选择主机成功, 主机id: " << id << " 详情: " << m->ip << ":" << m->port << " 当前主机的负载是: " << m->Load() << "\n";
if (auto res = cli.Post("/compile_and_run", compile_string, "application/json;charset=utf-8"))
{
// 5. 将结果赋值给out_json
if (res->status == 200)
{
*out_json = res->body;
m->DecLoad();
LOG(INFO) << "请求编译和运行服务成功..."
<< "\n";
break;
}
m->DecLoad();
}
else
{
// 请求失败
LOG(ERROR) << " 当前请求的主机id: " << id << " 详情: " << m->ip << ":" << m->port << " 可能已经离线"
<< "\n";
load_blance_.OfflineMachine(id);
load_blance_.ShowMachines(); // 仅仅是为了用来调试
}
}
}
};
}
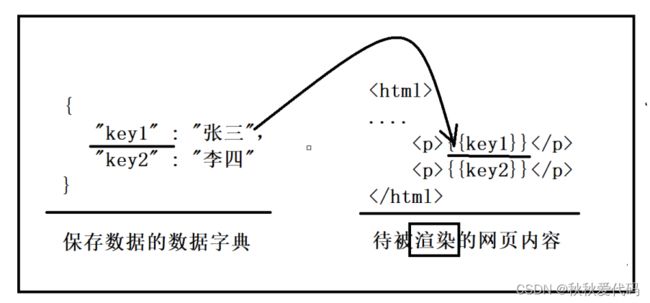
//git clone https://hub.fastgit.xyz/OlafvdSpek/ctemplate
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
std::string in_html="./test.html";
std::string value="学习";
//形成数据字典
ctemplate::TemplateDictionary root("test");
root.SetValue("key",value);
//获取被渲染网页对象
ctemplate::Template *tpl=ctemplate::Template::GetTemplate(in_html,ctemplate::DO_NOT_STRIP);
//添加字典数据到网页中
std::string out_html;
tpl->Expand(&out_html,&root);
std::cout< 运行结果
⭐ 如果后续引入了ctemplate ,一旦对网页结构进行修改,尽量的每次想看到结果,将 server 重启一下。 ctemplate 有 自己的优化加速策略,可能在内存中存在缓存网页数据(old)⭐ 当我们完成全部功能之后,需要注意:要给编译模块添加 —D 条件编译掉测试用例中的头文件 inclde
前端页面设计请移步 首页设计 和 后续网页设计