tinyWebServer 学习笔记——四、日志系统
文章目录
- 一、基础知识
-
- 1. 概念
- 2. API
- 二、代码解析
-
- 1. 单例模式
- 2. 阻塞队列
- 3. 日志类定义
- 4. 生成日志文件并判断写入方式
- 5. 日志分级与分文件
- 参考文献
一、基础知识
1. 概念
- 日志:由服务器自动创建,用于记录运行状态和错误信息;
- 同步日志:日志写入函数与工作线程串行执行,由于涉及到 I/O 操作,当单条日志较大时,同步模式会阻塞整个处理流程,服务器所能处理的并发能力将有所下降,易称为性能的瓶颈;
- 异步日志:将所写的日志内容先存入缓存队列,写线程从阻塞队列中去除内容,写入日志;
- 生产者/消费者模型:生产者与消费者共享一个缓冲区,生产者往缓冲区添加消息,消费者从缓冲区中处理消息;
- 阻塞队列:将生产者/消费者模型进行封装,使用循环数组实现队列,作为两者共享的缓存区;
- 单例模式:保证一个类只创建一个实例,同时提供全局访问的方法,单例模式有懒汉模式与饿汉模式,前者在第一次使用时进行初始化,后者在程序运行时初始化;
- 日志分级:一般提供五种级别:
- Debug :调试代码时的输出,在系统实际运行时,一般不使用;
- Warn :调试代码时使用的终端警告;
- Info :报告系统当前的状态,当前执行的流程或接收的信息等;
- Error 和 Fatal :输出系统的错误信息;
- 日志分文件:根据日期、行数判断是否需要份文件;
2. API
-
pthread_cond_init函数:用于初始化条件变量; -
pthread_cond_destory函数:销毁条件变量; -
pthread_cond_broadcast函数:以广播的方式唤醒所有等待目标条件变量的线程; -
pthread_cond_wait函数:用于等待目标条件变量,调用时传入 mutex 参数(加锁的互斥锁),执行时先把调用线程放入条件变量的请求队列,然后将互斥锁解锁,成功时返回 0 ,表示重新抢到了互斥锁,将其再次锁上,因此函数内部会有一次解锁和加锁操作,使用方法如下:pthread _mutex_lock(&mutex) // 此处必须使用while,而不是if // 若使用if,假设此时有A、B两个线程竞争资源,当A的wait函数返回成功后,B已将资源使用,那么此时A将访问被消耗的资源或不访问资源 // 为避免这个问题,应当使用while循环判断资源是否真的可用 while(线程执行的条件是否成立){ pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex); } pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);-
由 API 介绍可知,在使用
pthread_cond_wait函数前需要加锁,这是为了避免资源竞争,使得每个线程互斥访问公有资源。 -
在函数内部将互斥锁解锁,是因为函数会阻塞自己,此时它仍持有互斥锁,若不解锁则其他线程无法访问公有资源。
-
在对互斥锁解锁前需要将调用线程放入请求队列,这是因为如果在把调用线程放入等待队列之前就释放互斥锁,会导致其他线程获得互斥锁从而访问公有资源,此时调用线程锁等待的条件改变了,但是它没有被放在等待队列上,导致调用线程忽略了等待条件被满足的信号,发生错误。
-
当调用线程放在条件变量之后,将互斥锁解锁,此时等待被唤醒,若成功竞争到互斥锁,再次加锁来访问公共资源。
-
-
int fputs(const char *str, FILE *stream);:str:一个包含了要写入的以空字符终止的字符序列;stream:指向 FILE 对象的指针,标识了被写入字符串的流;
-
__VA_ARGS__:可变参数的宏,可以在宏定义中使用省略号,若加##则更健壮,可以在可变参数为 0 时将逗号去掉://最简单的定义 #define my_print1(...) printf(__VA_ARGS__) //搭配va_list的format使用 #define my_print2(format, ...) printf(format, __VA_ARGS__) #define my_print3(format, ...) printf(format, ##__VA_ARGS__) -
int fflush(FILE *stream);:强迫缓存区内的数据协会参数stream指定的文件中,如果参数为 NULL ,则会将所有打开的文件数据更新。该函数主要用于防止新到的数据冲掉未输出完数据的缓冲区(即覆盖了原有数据),通常将其放在printf函数之后。
二、代码解析
1. 单例模式
经典的懒汉模式:
class single {
private:
//私有静态指针变量指向唯一实例
static single *p;
//静态锁,是由于静态函数只能访问静态成员
static pthread_mutex_t lock;
//私有化构造函数
single(){
pthread_mutex_init(&lock, NULL);
}
~single(){}
public:
//公有静态方法获取实例
static single* getinstance();
};
pthread_mutex_t single::lock;
single* single::p = NULL;
single* single::getinstance() {
// 懒汉模式,使用双锁检测
// 若只检测一次,则每次调用获取实例的方法时,都需要加锁,导致性能下降
if (NULL == p){
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
if (NULL == p){
p = new single;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
}
return p;
}
优雅的懒汉模式:
class single{
private:
single(){}
~single(){}
public:
static single* getinstance();
};
single* single::getinstance() {
// C++11能够保证静态变量的线程安全性,因此不用加锁
static single obj;
return &obj;
}
饿汉模式:
class single{
private:
static single* p;
single(){}
~single(){}
public:
static single* getinstance();
};
single* single::p = new single();
// 返回的是对象的指针,因此无需加锁
// 但是由于非静态对象在不同编译单元中的初始化顺序是未定义的,因此要防止在初始化之前调用
single* single::getinstance() {
return p;
}
//测试方法
int main(){
single *p1 = single::getinstance();
single *p2 = single::getinstance();
if (p1 == p2)
cout << "same" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2. 阻塞队列
template <class T>
class block_queue
{
public:
// 构造函数
block_queue(int max_size = 1000)
{
// 初始化私有成员
if (max_size <= 0)
{
exit(-1);
}
// 构造函数创建循环数组
m_max_size = max_size;
m_array = new T[max_size];
m_size = 0;
m_front = -1;
m_back = -1;
}
// 清空队列
void clear()
{
m_mutex.lock();
m_size = 0;
m_front = -1;
m_back = -1;
m_mutex.unlock();
}
// 析构函数
~block_queue()
{
m_mutex.lock();
if (m_array != NULL)
delete[] m_array;
m_mutex.unlock();
}
// 判断队列是否满了
bool full()
{
m_mutex.lock();
if (m_size >= m_max_size)
{
m_mutex.unlock();
return true;
}
m_mutex.unlock();
return false;
}
// 判断队列是否为空
bool empty()
{
m_mutex.lock();
if (0 == m_size)
{
m_mutex.unlock();
return true;
}
m_mutex.unlock();
return false;
}
// 返回队首元素
bool front(T &value)
{
m_mutex.lock();
if (0 == m_size)
{
m_mutex.unlock();
return false;
}
value = m_array[m_front];
m_mutex.unlock();
return true;
}
// 返回队尾元素
bool back(T &value)
{
m_mutex.lock();
if (0 == m_size)
{
m_mutex.unlock();
return false;
}
value = m_array[m_back];
m_mutex.unlock();
return true;
}
// 获取大小
int size()
{
int tmp = 0;
m_mutex.lock();
tmp = m_size;
m_mutex.unlock();
return tmp;
}
// 获取上限
int max_size()
{
int tmp = 0;
m_mutex.lock();
tmp = m_max_size;
m_mutex.unlock();
return tmp;
}
// 往队列添加元素,需要将所有使用队列的线程先唤醒
// 当有元素push进队列,相当于生产者生产了一个元素
// 若当前没有线程等待条件变量,则唤醒无意义
bool push(const T &item)
{
// 当前大小达到上限,唤醒所有线程工作,添加失败
m_mutex.lock();
if (m_size >= m_max_size)
{
m_cond.broadcast();
m_mutex.unlock();
return false;
}
// 插入队列
m_back = (m_back + 1) % m_max_size;
m_array[m_back] = item;
m_size++;
// 唤醒
m_cond.broadcast();
m_mutex.unlock();
return true;
}
// pop时,如果当前队列没有元素,将会等待条件变量
bool pop(T &item)
{
m_mutex.lock();
// 当前队列没有元素,等待
while (m_size <= 0)
{
// 等待mutex
if (!m_cond.wait(m_mutex.get()))
{
m_mutex.unlock();
return false;
}
}
// 更新头指针和大小
m_front = (m_front + 1) % m_max_size;
item = m_array[m_front];
m_size--;
m_mutex.unlock();
return true;
}
// 增加了超时处理
bool pop(T &item, int ms_timeout)
{
// timespec提供秒和纳秒,timeval提供秒和微妙
struct timespec t = {0, 0};
struct timeval now = {0, 0};
// 获取当前时间
gettimeofday(&now, NULL);
m_mutex.lock();
if (m_size <= 0)
{
// 更新到期时间
t.tv_sec = now.tv_sec + ms_timeout / 1000;
t.tv_nsec = (ms_timeout % 1000) * 1000;
// 超时等待
if (!m_cond.timewait(m_mutex.get(), t))
{
m_mutex.unlock();
return false;
}
}
if (m_size <= 0)
{
m_mutex.unlock();
return false;
}
m_front = (m_front + 1) % m_max_size;
item = m_array[m_front];
m_size--;
m_mutex.unlock();
return true;
}
private:
locker m_mutex; // 互斥锁
cond m_cond; // 条件变量
T *m_array; // 循环数组
int m_size; // 大小
int m_max_size; // 上限
int m_front; // 头元素
int m_back; // 尾元素
};
3. 日志类定义
class Log
{
public:
// C++11以后,使用局部变量懒汉不用加锁
static Log *get_instance()
{
static Log instance;
return &instance;
}
static void *flush_log_thread(void *args)
{
Log::get_instance()->async_write_log();
}
// 可选择的参数有日志文件、日志缓冲区大小、最大行数以及最长日志条队列
bool init(const char *file_name, int close_log, int log_buf_size = 8192, int split_lines = 5000000, int max_queue_size = 0);
// 将输出内容按照标准格式整理
void write_log(int level, const char *format, ...);
// 强制刷新缓冲区
void flush(void);
private:
Log();
virtual ~Log();
// //异步写日志方法
void *async_write_log()
{
string single_log;
// 从阻塞队列中取出一个日志string,写入文件
while (m_log_queue->pop(single_log))
{
m_mutex.lock();
fputs(single_log.c_str(), m_fp);
m_mutex.unlock();
}
}
private:
char dir_name[128]; // 路径名
char log_name[128]; // log文件名
int m_split_lines; // 日志最大行数
int m_log_buf_size; // 日志缓冲区大小
long long m_count; // 日志行数记录
int m_today; // 因为按天分类,记录当前时间是那一天
FILE *m_fp; // 打开log的文件指针
char *m_buf; // log缓冲区指针
block_queue<string> *m_log_queue; // 阻塞队列
bool m_is_async; // 是否异步标志位
locker m_mutex; // 互斥锁
int m_close_log; // 关闭日志
};
// 日志分级
// DEBUG,获取实例来写log,然后刷新,##__VA_ARGS__是可变参数宏
#define LOG_DEBUG(format, ...) \
if (0 == m_close_log) \
{ \
Log::get_instance()->write_log(0, format, ##__VA_ARGS__); \
Log::get_instance()->flush(); \
}
// log信息
#define LOG_INFO(format, ...) \
if (0 == m_close_log) \
{ \
Log::get_instance()->write_log(1, format, ##__VA_ARGS__); \
Log::get_instance()->flush(); \
}
// warning
#define LOG_WARN(format, ...) \
if (0 == m_close_log) \
{ \
Log::get_instance()->write_log(2, format, ##__VA_ARGS__); \
Log::get_instance()->flush(); \
}
// error
#define LOG_ERROR(format, ...) \
if (0 == m_close_log) \
{ \
Log::get_instance()->write_log(3, format, ##__VA_ARGS__); \
Log::get_instance()->flush(); \
}
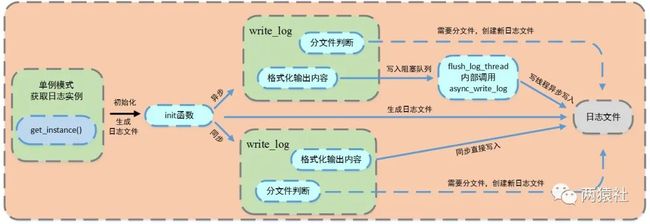
4. 生成日志文件并判断写入方式
// 初始化,异步需要设置阻塞队列的长度,同步不需要设置
bool Log::init(const char *file_name, int close_log, int log_buf_size, int split_lines, int max_queue_size)
{
// 如果设置了max_queue_size,则设置为异步
if (max_queue_size >= 1)
{
// 设置写入方式flag
m_is_async = true;
// 创建并设置阻塞队列长度
m_log_queue = new block_queue<string>(max_queue_size);
// 线程tid
pthread_t tid;
// flush_log_thread为回调函数,这里表示创建线程异步写日志
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, flush_log_thread, NULL);
}
// 关闭日志标志
m_close_log = close_log;
// 输出内容的长度
m_log_buf_size = log_buf_size;
m_buf = new char[m_log_buf_size];
memset(m_buf, '\0', m_log_buf_size);
// 设置日志最大行数
m_split_lines = split_lines;
// 获取当前时间
time_t t = time(NULL);
// 分解为tm结构,并用本地时区表示
struct tm *sys_tm = localtime(&t);
struct tm my_tm = *sys_tm;
// 搜索最后一次出现/的位置
const char *p = strrchr(file_name, '/');
char log_full_name[256] = {0};
// 相当于自定义日志名
// 若输入的文件名没有/,则直接将时间+文件名作为日志名
if (p == NULL)
{
// log_full_name存储处理后的字符串,复制大小为255,格式为第三个参数
// 组织内容:年 月 日 文件名
snprintf(log_full_name, 255, "%d_%02d_%02d_%s", my_tm.tm_year + 1900, my_tm.tm_mon + 1, my_tm.tm_mday, file_name);
}
else
{
// 设置log名
strcpy(log_name, p + 1);
// 设置路径名
strncpy(dir_name, file_name, p - file_name + 1);
snprintf(log_full_name, 255, "%s%d_%02d_%02d_%s", dir_name, my_tm.tm_year + 1900, my_tm.tm_mon + 1, my_tm.tm_mday, log_name);
}
// 设置日期
m_today = my_tm.tm_mday;
// 添加的方式打开log文件,存在m_fp中
m_fp = fopen(log_full_name, "a");
if (m_fp == NULL)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
5. 日志分级与分文件
// 写日志
void Log::write_log(int level, const char *format, ...)
{
// 获取时间
struct timeval now = {0, 0};
gettimeofday(&now, NULL);
// 将记录精确到秒
time_t t = now.tv_sec;
// 转为tm
struct tm *sys_tm = localtime(&t);
struct tm my_tm = *sys_tm;
// 日志分级
char s[16] = {0};
switch (level)
{
case 0:
strcpy(s, "[debug]:");
break;
case 1:
strcpy(s, "[info]:");
break;
case 2:
strcpy(s, "[warn]:");
break;
case 3:
strcpy(s, "[erro]:");
break;
default:
strcpy(s, "[info]:");
break;
}
// 写入一个log,对m_count++,m_split_lines最大行数
m_mutex.lock();
// 记录一行log
m_count++;
// 判断日期或行数是否合规
if (m_today != my_tm.tm_mday || m_count % m_split_lines == 0) // everyday log
{
char new_log[256] = {0};
// 将缓冲区内容写入m_fp
fflush(m_fp);
// 关闭m_fp
fclose(m_fp);
char tail[16] = {0};
// 在tail中记录日期
snprintf(tail, 16, "%d_%02d_%02d_", my_tm.tm_year + 1900, my_tm.tm_mon + 1, my_tm.tm_mday);
// 日期不匹配
if (m_today != my_tm.tm_mday)
{
// new_log中记录路径和时间
snprintf(new_log, 255, "%s%s%s", dir_name, tail, log_name);
// 更新日期
m_today = my_tm.tm_mday;
// 重设行数
m_count = 0;
}
// 行数达到最大
else
{
// 超过了最大行,在之前的日志名基础上加后缀, m_count/m_split_lines
snprintf(new_log, 255, "%s%s%s.%lld", dir_name, tail, log_name, m_count / m_split_lines);
}
// 创建文件
m_fp = fopen(new_log, "a");
}
// 解锁
m_mutex.unlock();
va_list valst;
// 获取可变参数列表的第一个参数的地址
va_start(valst, format);
string log_str;
m_mutex.lock();
// 写入的具体时间内容格式,时间、log级别,返回写入的字数
int n = snprintf(m_buf, 48, "%d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d.%06ld %s ",
my_tm.tm_year + 1900, my_tm.tm_mon + 1, my_tm.tm_mday,
my_tm.tm_hour, my_tm.tm_min, my_tm.tm_sec, now.tv_usec, s);
// 1存储位置,2大小,3格式,4内容,返回写入的字数,该函数用于va_list
int m = vsnprintf(m_buf + n, m_log_buf_size - n - 1, format, valst);
// 写完一行设置换行符
m_buf[n + m] = '\n';
// 换行符后面设置终止符
m_buf[n + m + 1] = '\0';
// 指向缓冲区当前位置
log_str = m_buf;
m_mutex.unlock();
// 如果是异步模式且阻塞队列未满,则往队列中添加元素(唤醒线程处理)
if (m_is_async && !m_log_queue->full())
{
m_log_queue->push(log_str);
}
// 否则把缓存区的字符串写入m_fp
else
{
m_mutex.lock();
fputs(log_str.c_str(), m_fp);
m_mutex.unlock();
}
va_end(valst);
}
参考文献
[1] 最新版Web服务器项目详解 - 09 日志系统(上)
[2] 最新版Web服务器项目详解 - 10 日志系统(下)