MyBatis 插件机制
文章目录
- 前言
- 自定义插件
-
- 创建拦截器
- 配置拦截器
- 效果验证
- 插件实现原理
-
- 初始化操作
- 如何创建代理对象
-
- Executor
- StatementHandler
- ParameterHandler
- ResultSetHandler
- 执行流程
前言
插件是一种常见的扩展方式,大多数开源框架也都支持用户通过添加自定义插件的方式来扩展或者改变原有的功能,MyBatis中也提供的有插件,虽然叫插件,但是实际上是通过拦截器(Interceptor)实现的。
自定义插件
实现自定义插件必须要实现Interceptor接口,Interceptor接口的定义为
public interface Interceptor {
// 执行拦截逻辑的方法
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
// 决定是否触发 intercept()方法
default Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
// 根据配置 初始化 Intercept 对象
default void setProperties(Properties properties) {
// NOP
}
}
在MyBatis中Interceptor允许拦截的内容是
- Executor (update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback, getTransaction, close, isClosed)
- ParameterHandler (getParameterObject, setParameters)
- ResultSetHandler (handleResultSets, handleOutputParameters)
- StatementHandler (prepare, parameterize, batch, update, query)
创建拦截器
创建一个拦截Executor中的query和close的方法
/**
* 自定义的拦截器
* @Signature 注解就可以表示一个方法签名, 唯一确定一个方法
*/
@Intercepts({
@Signature(
type = Executor.class // 需要拦截的类型
,method = "query" // 需要拦截的方法
// args 中指定 被拦截方法的 参数列表
,args={MappedStatement.class,Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}
),
@Signature(
type = Executor.class
,method = "close"
,args = {boolean.class}
)
})
public class FirstInterceptor implements Interceptor {
private int testProp;
/**
* 执行拦截逻辑的方法
* @param invocation
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("FirtInterceptor 拦截之前 ....");
Object obj = invocation.proceed();
System.out.println("FirtInterceptor 拦截之后 ....");
return obj;
}
/**
* 决定是否触发 intercept方法
* @param target
* @return
*/
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target,this);
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
System.out.println("---->"+properties.get("testProp"));
}
public int getTestProp() {
return testProp;
}
public void setTestProp(int testProp) {
this.testProp = testProp;
}
}
配置拦截器
创建好自定义的拦截器后,需要在全局配置文件中添加自定义插件的注册
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.interceptor.FirstInterceptor">
<property name="testProp" value="1000"/>
plugin>
plugins>
效果验证
执行对应的查询操作验证是否生效。
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception{
// 1.获取配置文件
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
// 2.加载解析配置文件并获取SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
// 3.根据SqlSessionFactory对象获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
// 4.通过SqlSession中提供的 API方法来操作数据库
List<User> list = sqlSession.selectList("com.mapper.UserMapper.selectUserList");
for (User user : list) {
System.out.println(user);
}
// 5.关闭会话
sqlSession.close();
}
插件实现原理
自定义插件的步骤还是比较简单的,分析下插件的实现原理。
初始化操作
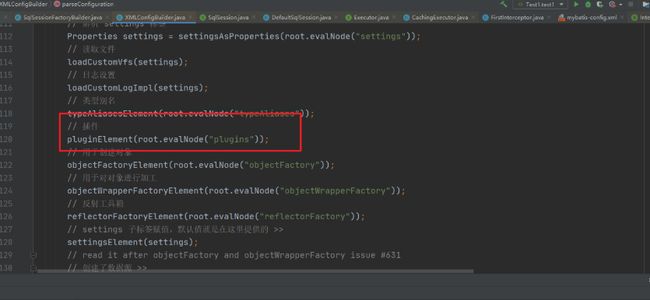
在全局配置文件加载解析的时候做了什么操作。
该方法用来解析全局配置文件中的plugins标签,然后对应的创建Interceptor对象,并且封装对应的属性信息。最后调用了Configuration对象中的方法。 configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance)
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptorChain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
通过这个代码发现自定义的拦截器最终是保存在了InterceptorChain这个对象中。而InterceptorChain的定义为
public class InterceptorChain {
// 保存所有的 Interceptor 也就我所有的插件是保存在 Interceptors 这个List集合中的
private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
//
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) { // 获取拦截器链中的所有拦截器
target = interceptor.plugin(target); // 创建对应的拦截器的代理对象
}
return target;
}
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptors.add(interceptor);
}
public List<Interceptor> getInterceptors() {
return Collections.unmodifiableList(interceptors);
}
}
如何创建代理对象
在解析的时候创建了对应的Interceptor对象,并保存在了InterceptorChain中,那么这个拦截器是如何和Executor、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler、StatementHandler关联的。
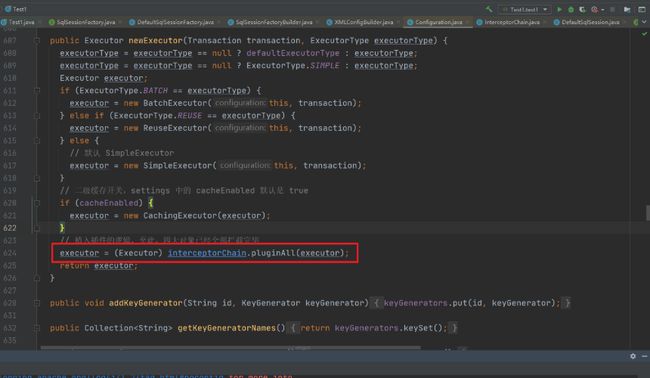
Executor
可以看到Executor在装饰完二级缓存后会通过pluginAll来创建Executor的代理对象。
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) { // 获取拦截器链中的所有拦截器
target = interceptor.plugin(target); // 创建对应的拦截器的代理对象
}
return target;
}
StatementHandler
在获取StatementHandler的方法中的newStatementHandler方法可以看到statementHandler的代理对象
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 植入插件逻辑(返回代理对象)
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
ParameterHandler
在上面步骤的RoutingStatementHandler方法中,来看看
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
// StatementType 是怎么来的? 增删改查标签中的 statementType="PREPARED",默认值 PREPARED
switch (ms.getStatementType()) {
case STATEMENT:
delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case PREPARED:
// 创建 StatementHandler 的时候做了什么? >>
delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case CALLABLE:
delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
default:
throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType());
}
}
在newParameterHandler的步骤我们可以发现代理对象的创建
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
// 植入插件逻辑(返回代理对象)
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
ResultSetHandler
在上面的newResultSetHandler()方法中,也可以看到ResultSetHander的代理对象
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql, rowBounds);
// 植入插件逻辑(返回代理对象)
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
执行流程
以Executor的query方法为例,当查询请求到来的时候,Executor的代理对象是如何处理拦截请求的呢?当请求到了executor.query方法的时候
然后会执行Plugin的invoke方法,最终会进入我们自定义的 FirstInterceptor对象中