【MySQL】 MySQL的增删改查(进阶)--贰
文章目录
- 新增
- 查询
-
- 聚合查询
-
- 聚合函数
- GROUP BY子句
- HAVING
- 联合查询
-
- ⚾内连接
- ⚽外连接
- 自连接
- 子查询
- 合并查询
- MySQL的增删改查(进阶)总结
- ⭕总结
本节目标:
新增
查询
新增
插入查询结果
在一张表中插入另一张表的查询结果
语法为:
INSERT INTO table_name [(column [, column ...])] SELECT ...
举个例子,我们有这样一个student表如下:
接下来我们创建一张用户表,设计有name姓名、email邮箱、sex性别、mobile手机号字段。
需要把已有的学生数据复制进来,可以复制的字段为name、qq_mail
操作代码如下:
-- 创建用户表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test_user;
CREATE TABLE test_user (
id INT primary key auto_increment,
name VARCHAR(20) comment '姓名',
age INT comment '年龄',
email VARCHAR(20) comment '邮箱',
sex varchar(1) comment '性别',
mobile varchar(20) comment '手机号'
);
-- 将学生表中的所有数据复制到用户表
insert into test_user(name, email) select name, qq_mail from student;
我们来看一下经历这些操作后的test_user表吧
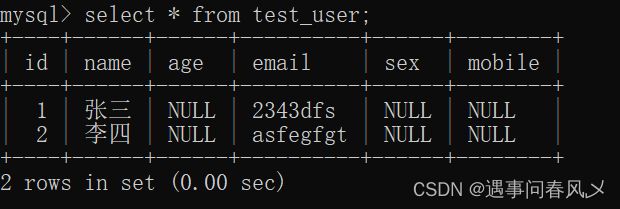
上面已经有了student上面的元素
查询
聚合查询
聚合函数
常见的统计总数、计算平局值等操作,可以使用聚合函数来实现,常见的聚合函数有:
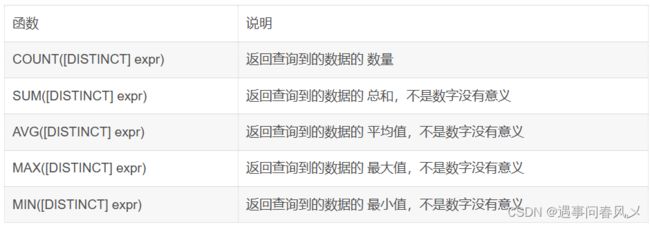
案例举例:
- COUNT
统计班级共有多少同学
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM student;
-- 统计班级收集的 qq_mail 有多少个,qq_mail 为 NULL 的数据不会计入结果
SELECT COUNT(qq_mail) FROM student;
- SUM
-- 统计数学成绩总分
SELECT SUM(math) FROM exam_result;
-- 不及格 < 60 的总分,没有结果,返回 NULL
SELECT SUM(math) FROM exam_result WHERE math < 60;
- AVG
-- 统计平均总分
SELECT AVG(chinese + math + english) as 平均总分 FROM exam_result;
- MAX
-- 返回英语最高分
SELECT MAX(english) FROM exam_result;
- MIN
-- 返回 > 70 分以上的数学最低分
SELECT MIN(math) FROM exam_result WHERE math > 70;
GROUP BY子句
SELECT 中使用 GROUP BY 子句可以对指定列进行分组查询。需要满足:使用 GROUP BY 进行分组查询时,SELECT 指定的字段必须是“分组依据字段”,其他字段若想出现在SELECT 中则必须包含在聚合函数中
语法如下:
select column1, sum(column2), .. from table group by column1,column3;
接下来我们用一个案例进行说明
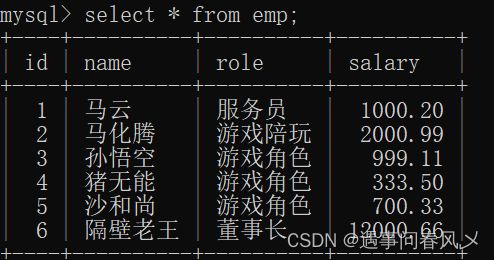
- 准备测试表及数据:职员表,有id(主键)、name(姓名)、role(角色)、salary(薪水
create table emp(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) not null,
role varchar(20) not null,
salary numeric(11,2)
);
insert into emp(name, role, salary) values
('马云','服务员', 1000.20),
('马化腾','游戏陪玩', 2000.99),
('孙悟空','游戏角色', 999.11),
('猪无能','游戏角色', 333.5),
('沙和尚','游戏角色', 700.33),
('隔壁老王','董事长', 12000.66);
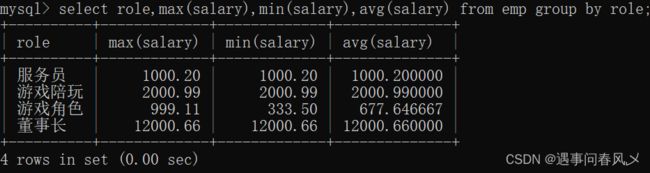
- 查询每个角色的最高工资、最低工资和平均工资
select role,max(salary),min(salary),avg(salary) from emp group by role;
HAVING
GROUP BY 子句进行分组以后,需要对分组结果再进行条件过滤时,不能使用 WHERE 语句,而需要用HAVING
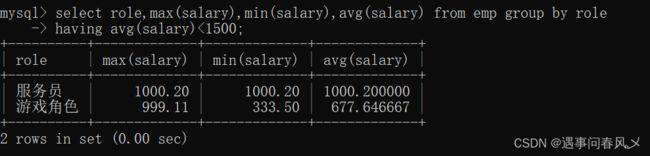
案例如下:对上述emp表显示平均工资低于1500的角色和它的平均工资
select role,max(salary),min(salary),avg(salary) from emp group by role
having avg(salary)<1500;
联合查询
实际开发中往往数据来自不同的表,所以需要多表联合查询。多表查询是对多张表的数据取笛卡尔积
什么时笛卡尔积呢?请看下图
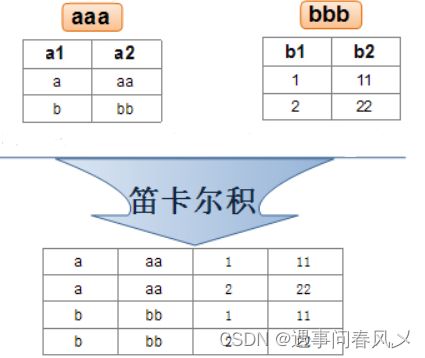
接下来我们来一起看看怎么实现联合查询吧
我们需要注意的是:关联查询可以对关联表使用别名
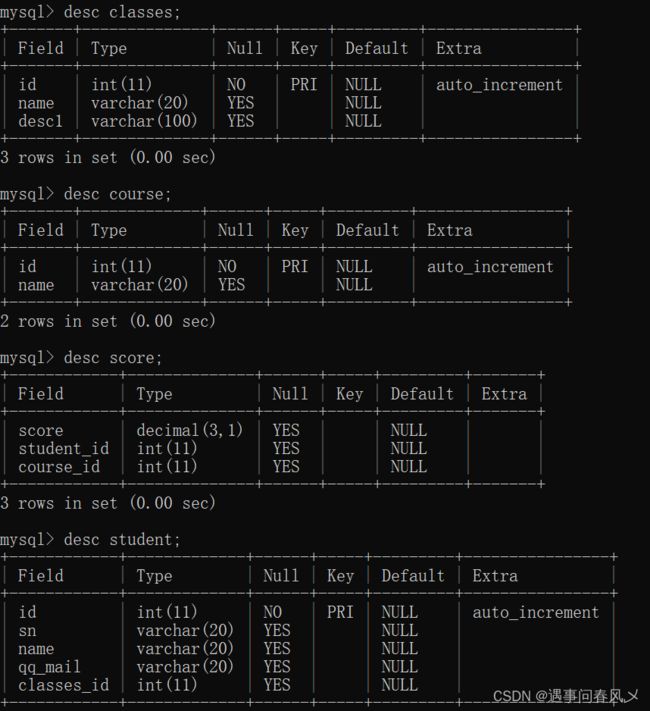
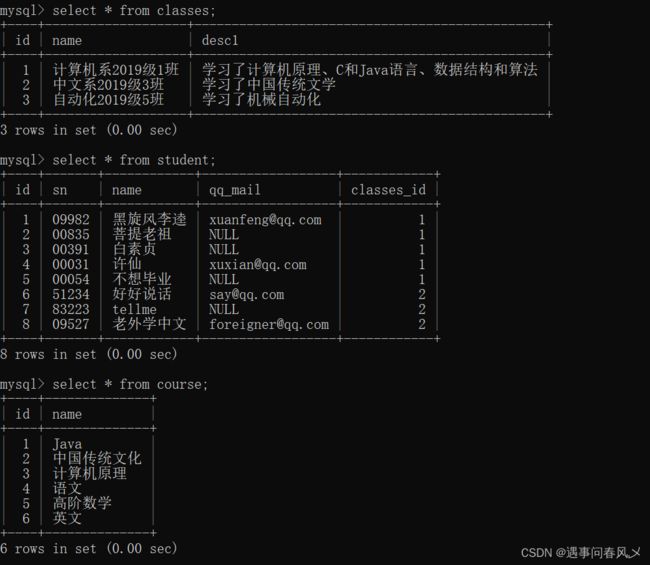
首先我们先初始化一些数据,方便后续查询
create table classes (
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
desc1 varchar(100)
);
create table student (
id int primary key auto_increment,
sn varchar(20),
name varchar(20),
qq_mail varchar(20),
classes_id int
);
create table course(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20)
);
create table score(
score decimal(3,1),
student_id int,
course_id int
);
insert into classes(name, desc1) values
('计算机系2019级1班', '学习了计算机原理、C和Java语言、数据结构和算法'),
('中文系2019级3班','学习了中国传统文学'),
('自动化2019级5班','学习了机械自动化');
insert into student(sn, name, qq_mail, classes_id) values
('09982','黑旋风李逵','xuanfeng@qq.com',1),
('00835','菩提老祖',null,1),
('00391','白素贞',null,1),
('00031','许仙','xuxian@qq.com',1),
('00054','不想毕业',null,1),
('51234','好好说话','say@qq.com',2),
('83223','tellme',null,2),
('09527','老外学中文','foreigner@qq.com',2);
insert into course(name) values
('Java'),('中国传统文化'),('计算机原理'),('语文'),('高阶数学'),('英文');
insert into score(score, student_id, course_id) values
-- 黑旋风李逵
(70.5, 1, 1),(98.5, 1, 3),(33, 1, 5),(98, 1, 6),
-- 菩提老祖
(60, 2, 1),(59.5, 2, 5),
-- 白素贞
(33, 3, 1),(68, 3, 3),(99, 3, 5),
-- 许仙
(67, 4, 1),(23, 4, 3),(56, 4, 5),(72, 4, 6),
-- 不想毕业
(81, 5, 1),(37, 5, 5),
-- 好好说话
(56, 6, 2),(43, 6, 4),(79, 6, 6),
-- tellme
(80, 7, 2),(92, 7, 6);
⚾内连接
内连接也称为等同连接,返回的结果集是两个表中所有相匹配的数据,而舍弃不匹配的数据。也就是说,在这种查询中,DBMS只返回来自源表中的相关的行,即查询的结果表包含的两源表行,必须满足ON子句中的搜索条件。作为对照,如果在源表中的行在另一表中没有对应(相关)的行,则该行就被过滤掉,不会包括在结果表中。内连接使用比较运算符来完成。
语法:
select 字段 from 表1 别名1 [inner] join 表2 别名2 on 连接条件 and 其他条件;
select 字段 from 表1 别名1,表2 别名2 where 连接条件 and 其他条件;
依旧采用案例来讲解:
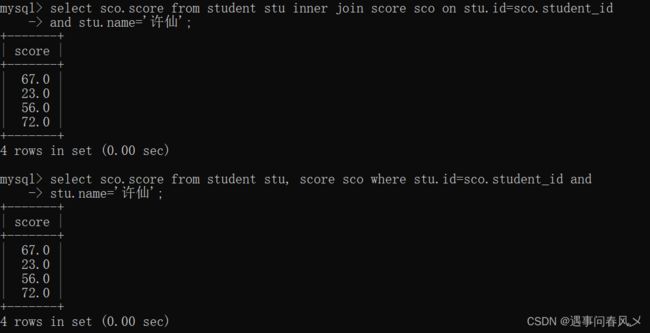
- 查询“许仙”同学的 成绩`
select sco.score from student stu inner join score sco on stu.id=sco.student_id
and stu.name='许仙';
-- 或者
select sco.score from student stu, score sco where stu.id=sco.student_id and
stu.name='许仙';
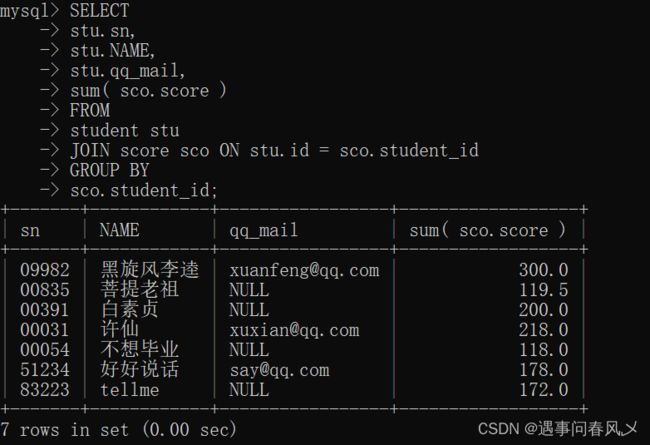
- 查询所有同学的总成绩,及同学的个人信息
-- 成绩表对学生表是多对1关系,查询总成绩是根据成绩表的同学id来进行分组的
SELECT
stu.sn,
stu.NAME,
stu.qq_mail,
sum(sco.score)
FROM
student stu
JOIN score sco ON stu.id = sco.student_id
GROUP BY
sco.student_id;
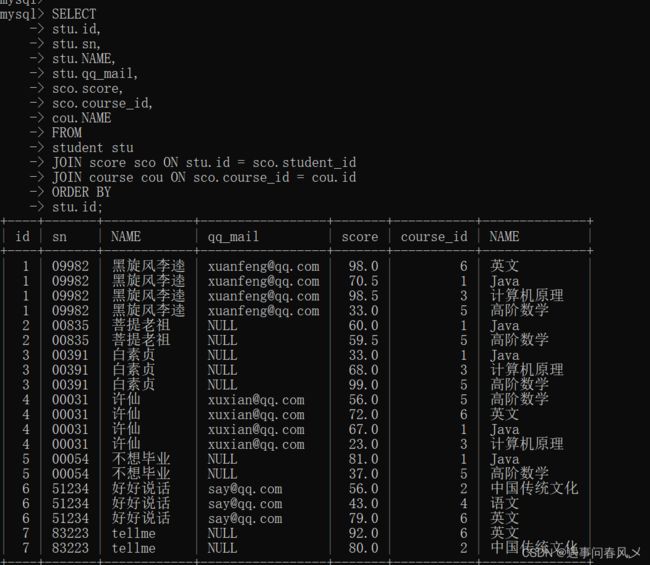
- 查询所有同学的成绩,及同学的个人信息
-- 学生表、成绩表、课程表3张表关联查询
SELECT
stu.id,
stu.sn,
stu.NAME,
stu.qq_mail,
sco.score,
sco.course_id,
cou.NAME
FROM
student stu
JOIN score sco ON stu.id = sco.student_id
JOIN course cou ON sco.course_id = cou.id
ORDER BY
stu.id;
⚽外连接
外连接分为左外连接和右外连接。如果联合查询,左侧的表完全显示我们就说是左外连接;右侧的表完
全显示我们就说是右外连接。
-- 左外连接,表1完全显示
select 字段名 from 表名1 left join 表名2 on 连接条件;
-- 右外连接,表2完全显示
select 字段 from 表名1 right join 表名2 on 连接条件;
接下来我们进行以下查询
查询所有同学的成绩,及同学的个人信息,如果该同学没有成绩,也需要显示
- 我们首先进行左连接
select * from student stu left join score sco on stu.id=sco.student_id;
查询结果如下:
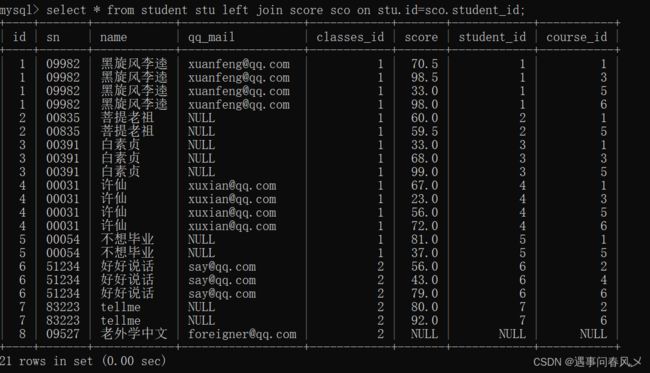
“老外学中文”同学 没有考试成绩,也显示出来了
- 接下里右连接查询
select * from score sco right join student stu on stu.id=sco.student_id;
我们最后再对三张表进行关联查询(内连接),有兴趣的同学可以结合着看一下
SELECT
stu.id,
stu.sn,
stu.NAME,
stu.qq_mail,
sco.score,
sco.course_id,
cou.NAME
FROM
student stu
LEFT JOIN score sco ON stu.id = sco.student_id
LEFT JOIN course cou ON sco.course_id = cou.id
ORDER BY
stu.id;
自连接
自连接是指在同一张表连接自身进行查询
举个例子吧
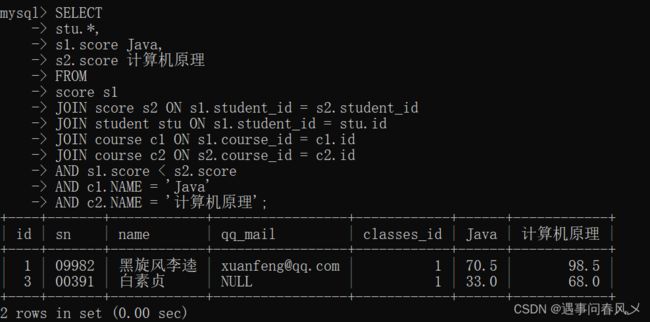
查询显示所有“计算机原理”成绩比“Java”成绩高的成绩信息
-- 先查询“计算机原理”和“Java”课程的id
select id,name from course where name='Java' or name='计算机原理';
SELECT
s1.*
FROM
score s1
JOIN score s2 ON s1.student_id = s2.student_id
AND s1.score < s2.score
AND s1.course_id = 1
AND s2.course_id = 3;
查询结果如下:
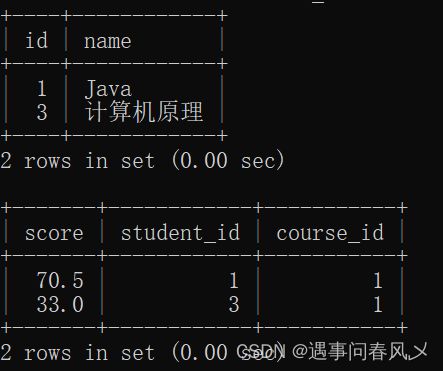
以上查询只显示了成绩信息,并且是分布执行的。要显示学生及成绩信息,并在一条语句显示:
就可以使用以下内连接来进行查询:
SELECT
stu.*,
s1.score Java,
s2.score 计算机原理
FROM
score s1
JOIN score s2 ON s1.student_id = s2.student_id
JOIN student stu ON s1.student_id = stu.id
JOIN course c1 ON s1.course_id = c1.id
JOIN course c2 ON s2.course_id = c2.id
AND s1.score < s2.score
AND c1.NAME = 'Java'
AND c2.NAME = '计算机原理';
子查询
子查询是指嵌入在其他sql语句中的select语句,也叫嵌套查询
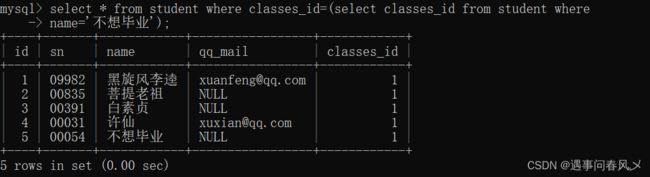
- 单行子查询:返回一行记录的子查询
查询与“不想毕业” 同学的同班同学
select * from student where classes_id=(select classes_id from student where
name='不想毕业');
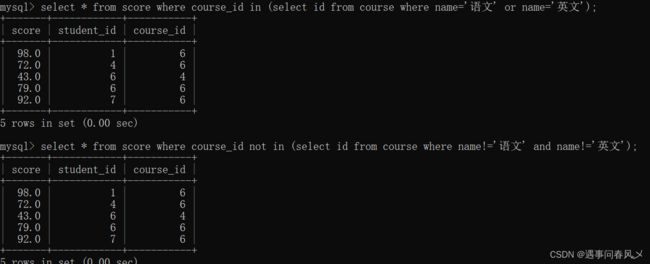
- 多行子查询:返回多行记录的子查询
案例为:查询“语文”或“英文”课程的成绩信息
- 使用[NOT] IN关键字:
-- 使用IN
select * from score where course_id in (select id from course where
name='语文' or name='英文');
-- 使用 NOT IN
select * from score where course_id not in (select id from course where
name!='语文' and name!='英文');
- 使用[NOT] EXISTS关键字:
-- 使用 EXISTS
select * from score sco where exists (select sco.id from course cou
where (name='语文' or name='英文') and cou.id = sco.course_id);
-- 使用 NOT EXISTS
select * from score sco where not exists (select sco.id from course cou
where (name!='语文' and name!='英文') and cou.id = sco.course_id);
查询结果与上面一样,这里就不展示了
- 在from子句中使用子查询:子查询语句出现在from子句中。这里要用到数据查询的技巧,把一个
子查询当做一个临时表使用
查询所有比“中文系2019级3班”平均分高的成绩信息
-- 获取“中文系2019级3班”的平均分,将其看作临时表
SELECT
avg( sco.score ) score
FROM
score sco
JOIN student stu ON sco.student_id = stu.id
JOIN classes cls ON stu.classes_id = cls.id
WHERE
cls.NAME = '中文系2019级3班';
SELECT
*
FROM
score sco,
(
SELECT
avg( sco.score ) score
FROM
score sco
JOIN student stu ON sco.student_id = stu.id
JOIN classes cls ON stu.classes_id = cls.id
WHERE
cls.NAME = '中文系2019级3班'
) tmp
WHERE
sco.score > tmp.score;
合并查询
在实际应用中,为了合并多个select的执行结果,可以使用集合操作符 union,union all。使用UNION
和UNION ALL时,前后查询的结果集中,字段需要一致。
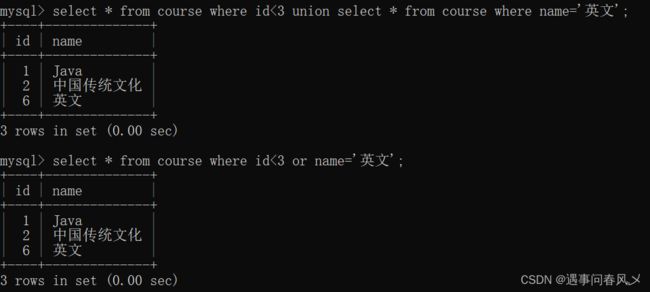
- union
该操作符用于取得两个结果集的并集。当使用该操作符时,会自动去掉结果集中的重复行。
案例如下:
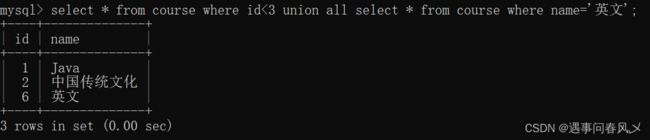
查询id小于3,或者名字为“英文”的课程
select * from course where id<3
union
select * from course where name='英文';
-- 或者使用or来实现
select * from course where id<3 or name='英文';
- union al
该操作符用于取得两个结果集的并集。当使用该操作符时,不会去掉结果集中的重复行。
案例如下:
查询id小于3,或者名字为“Java”的课程
-- 可以看到结果集中出现重复数据Java
select * from course where id<3
union all
select * from course where name='英文';
MySQL的增删改查(进阶)总结
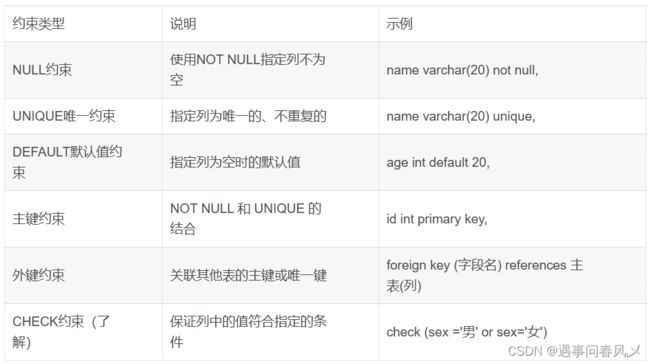
- 数据库约束
- 表的关系
- 一对一:
- 一对多:
- 多对多:需要创建中间表来映射两张表的关系
- 新增
INSERT INTO table_name [(column [, column ...])] SELECT ...
- 查询
- 聚合函数:MAX、MIN、AVG、COUNT、SUM
select ... from 表1,表2 where 条件
-- inner可以缺省
select ... from 表1 join 表2 on 条件 where 其他条件
- 分组查询:GROUP BY… HAVING …
select ... from 表1 left/right join 表2 on 条件 where 其他条件
- 内连接
select ... from 表1,表2 where 条件
-- inner可以缺省
select ... from 表1 join 表2 on 条件 where 其他条件
- 外连接:
select ... from 表1 left/right join 表2 on 条件 where 其他条件
- 自连接
select ... from 表1,表1 where 条件
select ... from 表1 join 表1 on 条件
- 子查询:
-- 单行子查询
select ... from 表1 where 字段1 = (select ... from ...);
-- [NOT] IN
select ... from 表1 where 字段1 in (select ... from ...);
-- [NOT] EXISTS
select ... from 表1 where exists (select ... from ... where 条件);
-- 临时表:form子句中的子查询
select ... from 表1, (select ... from ...) as tmp where 条件
- 合并查询
-- UNION:去除重复数据
select ... from ... where 条件
union
select ... from ... where 条件
-- UNION ALL:不去重
select ... from ... where 条件
union all
select ... from ... where 条件
-- 使用UNION和UNION ALL时,前后查询的结果集中,字段需要一致
SQL查询中各个关键字的执行先后顺序: from > on> join > where > group by > with > having >
select > distinct > order by > limit
⭕总结
关于《【MySQL】 MySQL的增删改查(进阶)–贰》就讲解到这儿,感谢大家的支持,欢迎各位留言交流以及批评指正,如果文章对您有帮助或者觉得作者写的还不错可以点一下关注,点赞,收藏支持一下!