SpringCloud之restTemplate与Feign调用RPC
文章目录
- HttpClient
-
- get请求
- RestTemplate
-
- RestTemplate请求方式
- get请求
- exchange方法
-
- POST请求
- PUT请求
- DELETE请求
- GET请求
- 常用方法
- 微服务之间通信(RPC)
-
- restTemplate
-
- restTemplate实现
- Feign
-
- Feign实现
- Feign的优势
HttpClient
Java请求网络资源的类。
get请求
private static final CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault();
HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet(url);
CloseableHttpResponse response = httpclient.execute(httpget);
String result = null;
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
if (entity != null) {
result = EntityUtils.toString(entity);
}
System.out.println(result);
RestTemplate
Spring封装了库,提供更为简洁的资源请求方式RestTemplate。
RestTemplate是Spring提供的用于访问Rest服务的客户端,提供了多种便捷访问远程Http服务的方法。
RestTemplate请求方式
restTemplate使用simpleClientHttpRequestFactory工厂,
默认以HttpURLConnection方式发起请求。
get请求
RestTemplate restTemplate=new RestTemplate();
String result = restTemplate.getForObject(url, String.class);
System.out.println(result);
其中get代表get请求,Object代表结果封装类型。restTemplate会自动发起请求,接收响应并帮我们对响应结果进行反序列化。
exchange方法
exchange方法提供统一的方法模板进行四种请求:POST,PUT,DELETE,GET
POST请求
String reqJsonStr = "{\"code\":\"testCode\", \"group\":\"testGroup\",\"content\":\"testContent\", \"order\":1}";
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
HttpEntity<String> entity = new HttpEntity<String>(reqJsonStr,headers);
ResponseEntity<Map> resp = restTemplate.exchange(DIC_DATA_URL, HttpMethod.POST, entity, Map.class);
PUT请求
ResponseEntity<Map> resp = restTemplate.exchange(DIC_DATA_URL, HttpMethod.PUT, entity, Map.class);
DELETE请求
Response`Entity<Map> resp = restTemplate.exchange(DIC_DATA_URL + "?id={id}", HttpMethod.DELETE, null, Ma`p.class, 227);
GET请求
ResponseEntity<String> results = restTemplate.exchange(url,HttpMethod.GET, null, String.class, params);
- 说明
1)url: 请求地址;
2)method: 请求类型(如:POST,PUT,DELETE,GET);
3)requestEntity: 请求实体,封装请求头,请求内容
4)responseType: 响应类型,根据服务接口的返回类型决定
5)uriVariables: url中参数变量值
常用方法
restTemplate大多是基于Http的方法。
getForObject: 发送get请求,结果封装为指定对象。 提供class指定
getForEntity: 发送get请求,结果为Entity类型。
postForObject: 发送post请求,结果封装为指定对象
put:
delete:
exchange:通用执行方法
微服务之间通信(RPC)
RPC即remote procedure call,远程程序调用。你像调本地接口一样调用远程接口的方式,就是RPC。
SpringCloud开发的多个微服务之间是相对独立的,但有时候也是需要相互访问的。这就是微服务之间的RPC。

一般使用RestTemplate与Feign两种方式实现。
restTemplate
RestTemplate是Spring提供的用于访问Rest服务的客户端。
restTemplate实现
注册RestTemplate
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
服务提供方,服务名称:service1,端口:8082;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/service1")
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping(value = "test", method = {RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET})
public String test(@RequestParam(value = "testParam") String testParam) {
System.println.out(testParam);
return "success";
}
}
消费方根据URL调用
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/serviceFront")
public class ServiceFrontController {
private final static String SERVICE1_URL = "http://SERVICE1:8082";
private final static String SERVICE1 = "SERVICE1";
@Autowired
LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient;
@Autowired
RestTemplate restTemplate;
@RequestMapping(value = "testFront", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public HashMap<String,Object> testFront(@RequestParam String testParam) {
this.loadBalancerClient.choose(SERVICE1);// 随机访问策略
String result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE1_URL + "/service1/test?testParam={1}", String.class, testParam);
HashMap<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("result", "测试结果!"+result);
return map;
}
}
Feign
Feign是一种声明式的伪Http客户端。
用来优雅地调用Http API。
Feign封装了Ribbon和Hystrix也就是客户端负载均衡以及服务容错保护。
Ribbon里面有个啥?RestTemplate
RestTemplate是个啥?封装了Http请求,实现了客户端负载均衡。
咋实现的负载均衡,在注册RestTemplate的时候添加l@LoadBalanced注解
最后Feign做了啥?简化了我们自行封装RestTemplate服务调用客户端的开发量
Feign实现
消费方创建一个接口继承服务提供方的接口,使用注解的方式配置该接口,这样就完成了对服务提供方的接口绑定。
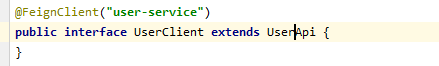
- 服务提供方,服务名称:service2,端口:8083;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/service2")
public class TestController2 {
@RequestMapping(value = "test2", method = {RequestMethod.POST,RequestMethod.GET})
public String test2(@RequestParam(value = "testParam2") String testParam2) {
System.println.out(testParam2);
return "success";
}
}
- 服务调用接口
/**
* 封装调用服务接口
*/
@FeignClient(name = "SERVICE2")
public interface TestFeignClient {
//@RequestLine("GET /service2/test2")
@RequestMapping(value="/service2/test2",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String test2(@RequestParam("testParam2") String testParam2);
}
- 服务调用控制器
@RestController
@RefreshScope
@RequestMapping("/serviceFront2")
public class TestFeignController {
@Autowired
private TestFeignClient testFeignClient;
@RequestMapping(value = "test2", method = { RequestMethod.POST })
public HashMap<String,Object> test2(@RequestParam String testParam2) {
String result = testFeignClient.test2(testParam2);
HashMap<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("result", "测试结果!"+result);
return map;
}
}
Feign的优势
- 微服务通信更加方便,只需要声明调用服务的ID。如果使用restTemplate则需要自己拼接URL。
- Feign内置了ribbon。如果使用restTemplate则需要自己开启@LoadBalanced。
- Feign内置了hystrix,但默认关闭,如果开启对性能消耗比较大。