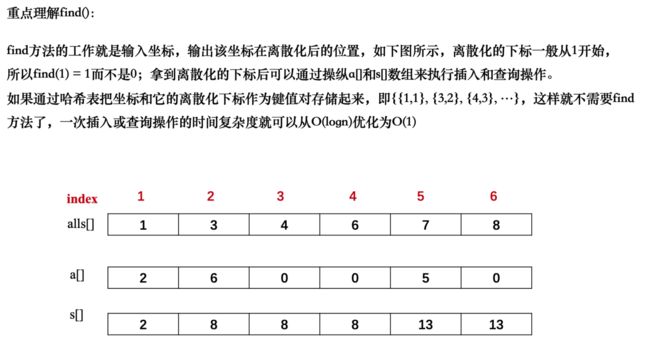
基础算法--离散化
基本介绍
离散化:把无限空间中有限的个体映射到有限的空间中去,以此提高算法的时空效率。通俗的说,离散化是在不改变数据相对大小的条件下,对数据进行相应的缩小。
适用范围:数组中元素值域很大,但个数不是很多。
比如将a[]=[1,3,100,2000,500000]映射到[0,1,2,3,4]这个过程就叫离散化。
离散化常与差分、前缀和、数组数组、线段树结合考查。
离散化实现方式:
手写离散化
例如:对于序列 [105,35,35,79,-7],排序并去重后变为 [-7,35,79,105],由此就得到了对应关系 -7->1, 35->2, 79->3, 105->4。
基本的步骤可以分为:
- 用一个辅助的数组把你要离散的所有数据存下来。
- 排序,排序是为了后面的二分。
- 去重,因为我们要保证相同的元素离散化后数字相同。
- 索引,再用二分把离散化后的数字放回原数组。
vector<int> alls; // 存储所有待离散化的值
sort(alls.begin(), alls.end()); // 将所有值排序
alls.erase(unique(alls.begin(), alls.end()), alls.end()); // 去掉重复元素
// 二分求出x对应的离散化的值
int find(int x) // 找到第一个大于等于x的位置
{
int l = 0, r = alls.size() - 1;
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (alls[mid] >= x) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return r + 1; // +1:映射到1, 2, ...n(不加的话就是0~n-1)
}
【知识点】
对于随机给定的一个数组,去除其中所包含的重复元素可以通过调用C++的库函数unique来实现。
但有一点需要注意的是,unique仅是对相邻的重复元素进行去重,若要对随机给定的数组进行去重则需要先对数组进行排序,使得重复元素相邻.
#include数组新的长度 4
新数组 2 4 6 7
注意事项:
1、去重并不是把数组中的元素删去,而是重复的部分元素在数组末尾,去重之后数组的大小要减一。
2、二分的时候,注意二分的区间范围,一定是离散化后的区间。
3、如果需要多个数组同时离散化,那就把这些数组中的数都用数组存下来。
map映射
(由于不需要排序和去重等操作,会比第一种好写,且代码量会少很多):可以用 map(每次在map中查询一下这个值是否存在,如果存在则返回对应的值,否则对应另一个值)或 hash表(即unordered_map或手写hash表,运用方式和map相同)。
map与unordered_map的区别
- 对于map的底层原理,是通过红黑树(一种非严格意义上的平衡二叉树)来实现的,因此map内部所有的数据都是有序的(默认按key进行升序排序),map的查询、插入、删除操作的时间复杂度都是O(logn)。
- unordered_map和map类似,都是存储的key-value的值,可以通过key快速索引到value。不同的是unordered_map不会根据key的大小进行排序,存储时是根据key的hash值判断元素是否相同,即unordered_map内部元素是无序的。unordered_map的底层是一个防冗余的哈希表(开链法避免地址冲突)。
巩固练习
电影
【题目链接】
步骤:
1、用 alls数组收集所有语言。
2、对 alls数组排序、去重。
3、find 函数用于把原始的稀疏编号转变为稠密编号。
4、ans 数组记录每种语言的科学家数。即这门语言有多少科学家会。
5、遍历所有电影,以每部电影的语音语言为条件,在ans数组中找最大值,若有多个相同的最大值,就找字幕语言最多的。
【代码实现】
#include 区间和
#include