uvm pack/unpack
- packing: 将一组数据(item中的某些域 da sa payload)打包到一个比特数组(bit流)中。
- unpacking:将一个比特数组拆解成一组数据(item中的某些域 da sa payload)。
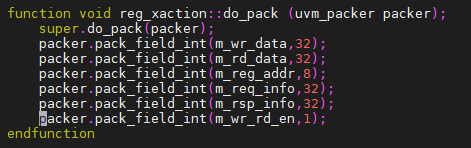
在item中定义do_pack函数
在driver中调用
下面的这些方法属于 uvm_object class 包含的function。
- pack
function int pack (ref bit bitstream[], input uvm_packer packer = null) - pack_bytes
function int pack_bytes (ref byte unsigned bytestream[], input uvm_packer packer = null) - pack_ints
function int pack_ints (ref int unsigned intstream[], input uvm_packer packer = null) - do_pack (回调函数)
virtual function void do_pack( ucm_packer packer)
使用field automation的pack; 1个bit的不会给对齐;

- m_reg_pack是一个存放pack_bytes的动态数组;
- item.pack_bytes(pack数组)
- pack数组可以定义在item里边;也可以定义在使用item的地方;
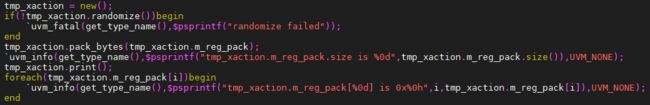
在用例中调用pack_bytes函数,返回的数据长度是0,即不会进行打包处理的.
自定义do_pack函数,其按照新的排列顺序打包.
参考
UVM糖果爱好者教程 - 15. “Do”钩子函数
do_pack
do_pack()方法由pack(),pack_bytes()和pack_ints()方法调用。 do_pack()用于使用uvm_packer策略对象打包jelly_bean_transaction对象的每个属性。请参阅寄存器抽象了解每个属性是如何打包的。打包器决定如何包装。我们必须调用super.do_pack()来打包超类的属性(第5行)。
virtual function void do_pack( uvm_packer packer );
bit R1; // reserved bit
bit [5:0] R6; // reserved bits
super.do_pack( packer );
packer.pack_field_int( .value( flavor ), .size( 3 ) );
packer.pack_field_int( .value( color ), .size( 2 ) );
packer.pack_field_int( .value( sugar_free ), .size( 1 ) );
packer.pack_field_int( .value( sour ), .size( 1 ) );
packer.pack_field_int( .value( R1 ), .size( 1 ) );
packer.pack_field_int( .value( taste ), .size( 2 ) );
packer.pack_field_int( .value( R6 ), .size( 6 ) );
endfunction: do_pack
do_unpack
do_unpack()方法由unpack(),unpack_bytes()和unpack_ints()方法调用。 do_unpack()用于使用uvm_packer策略对象解压jelly_bean_transaction对象的每个属性。分包器决定了拆包应该如何完成。我们必须调用super.do_unpack()来解压超级类的属性(第5行)。
virtual function void do_unpack( uvm_packer packer );
bit R1; // reserved bit
bit [5:0] R6; // reserved bits
super.do_unpack( packer );
flavor = flavor_e'( packer.unpack_field_int( .size( 3 ) ) );
color = color_e '( packer.unpack_field_int( .size( 2 ) ) );
sugar_free = packer.unpack_field_int( .size( 1 ) );
sour = packer.unpack_field_int( .size( 1 ) );
R1 = packer.unpack_field_int( .size( 1 ) );
taste = taste_e '( packer.unpack_field_int( .size( 2 ) ) );
R6 = packer.unpack_field_int( .size( 6 ) );
endfunction: do_unpack
//eth 类型 do_pack
rand fcs_kind_t fcs_kind;
rand bit [7:0] length;
rand bit [7:0] da;
rand bit [7:0] sa;
rand bit [7:0] data[];
rand byte fcs;
//9) Define do_pack() method which does the packing operation.
function void do_pack(uvm_packer packer);
super.do_pack(packer);
packer.pack_field_int(da,$bits(da));
packer.pack_field_int(sa,$bits(sa));
packer.pack_field_int(length,$bits(length));
foreach(data[i])
packer.pack_field_int(data[i],8);
packer.pack_field_int(fcs,$bits(fcs));
endfunction : do_pack
//10) Define do_unpack() method which does the unpacking operation.
function void do_unpack(uvm_packer packer);
int sz;
super.do_pack(packer);
da = packer.unpack_field_int($bits(da));
sa = packer.unpack_field_int($bits(sa));
length = packer.unpack_field_int($bits(length));
data.delete();
data = new[length];
foreach(data[i])
data[i] = packer.unpack_field_int(8);
fcs = packer.unpack_field_int($bits(fcs));
endfunction : do_unpack
参考:PHASE 4 PACKET
UVM:2.3 为验证平台加入各个组件->2.3.7 加入field_automation机制
参考
UVM Object
$bits $size
$size() gives the number of bits for a single dimension. $bits() gives the number of bits to completely represent the variable.
For example:
reg [9:0] a;
reg [9:0] b [5:0];
initial begin
$display("a Size ", $size(a));
$display("a Bits ", $bits(a));
$display("b Size ", $size(b));
$display("b Bits ", $bits(b)) ;
end
//output
//a Size 10
//a Bits 10
//b Size 6 // Depth of memory
//b Bits 60 // Width * Depth
- pack返回的是长度;
- m_pack调用do_pack
//uvm_object.sv
// m_pack
// ------
function void uvm_object::m_pack (inout uvm_packer packer);
if(packer!=null)
__m_uvm_status_container.packer = packer;
else
__m_uvm_status_container.packer = uvm_default_packer;
packer = __m_uvm_status_container.packer;
packer.reset();
packer.scope.down(get_name());
__m_uvm_field_automation(null, UVM_PACK, "");
do_pack(packer);
packer.set_packed_size();
packer.scope.up();
endfunction
// pack
// ----
function int uvm_object::pack (ref bit bitstream [],
input uvm_packer packer =null );
m_pack(packer);
packer.get_bits(bitstream);
return packer.get_packed_size();
endfunction
// pack_bytes
// ----------
function int uvm_object::pack_bytes (ref byte unsigned bytestream [],
input uvm_packer packer=null );
m_pack(packer);
packer.get_bytes(bytestream);
return packer.get_packed_size();
endfunction
// pack_ints
// ---------
function int uvm_object::pack_ints (ref int unsigned intstream [],
input uvm_packer packer=null );
m_pack(packer);
packer.get_ints(intstream);
return packer.get_packed_size();
endfunction