Micropython实现 基于模块 urequests 的 HTTP GET请求 (附示例代码:MicroPython ESP8266 网络时钟)
注:以下代码和说明是在ESP8266 开发板上实现。参考资料下载:
1.ESP8266 连接到网络
2.ESP8266实现WEB端控制 LED
简介
本MicroPython教程旨在阐释如何借助urequests模块用MicroPython执行HTTP GET请求。本教程在ESP8266的MicroPython上均进行了测试。下文所示数据出自ESP8266 上的测试,你可以在这里(https://github.com/micropython/micropython-lib/blob/master/urequests/urequests.py)访问库的源代码。
重要提示:本文撰写之际,所用的MicroPython版本内含urequests模块。请注意,此情况或有变化,之后版本的默认配置可能不会包含该模块,你需要先进行手动安装。
当然,为适用本教程,我们首先需要连接到WiFi网络,以便访问互联网。本教程将不再赘述如何连接WiFi网络。如果你想手动连接,请参阅这篇(http://mc.dfrobot.com.cn/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=272122)详细指南。
我们将通过连接MicroPython提示符并一次发送一个命令来运行代码。如果你愿意的话,可以在脚本中编写命令并从你的计算机运行该脚本,如此处(翻译中)所述。另一个选择是将脚本上传到MicroPython的文件系统并从提示符运行该脚本,如此处(https://www.dfrobot.com/index.php?route=DFblog/blogs)所述。
1. GET请求命令的实现:
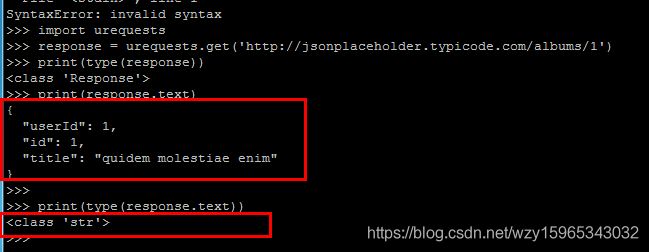
import urequests
response = urequests.get('http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/albums/1')#注: 我们要通过HTTP GET请求访问的网站URL是http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/albums/1,你可以通过在web浏览器上
# 访问该网站来查看预期结果。访问该网站时,你应该会得到如下所示的内容,这是虚拟相册对象的JSON结构。
print(type(response))
#返回的对象是Response类
print(response.text)
#访问HTTP请求响应得到实际内容,只要访问其text属性
print(type(response.text))JSON格式
parsed = response.json()
#请求响应是 json 格式
print(type(parsed))
#因此可知json 是字典类数据
print(parsed["userId"])
print(parsed["id"])
print(parsed["title"])
#可以通过字典对象上值的键来获取每个单独的JSON值
##可借助ujson库来解析内容
另一个检索请求响应内容的有趣方法是使用以字节为单位返回响应的content属性
print(response.content)
#b'{\n "userId": 1,\n "id": 1,\n "title": "quidem molestiae enim"\n}'
print(type(response.content))
#HTTP状态代码和原因
print(response.status_code)
#200
print(response.reason)
#b'OK'
# ESP8266 MicroPython Web Clock
# by Alan Wang
import network
import urequests
import ujson
import utime
import ssd1306
import machine
from machine import RTC, I2C, Pin
# user data
ssid = "ssid" # wifi router name
pw = "pw" # wifi router password
url = 'http://worldtimeapi.org/api/timezone/Asia/Hong_Kong'
# see http://worldtimeapi.org/timezones
#url = http://worldtimeapi.org/timezone/Asia/Hong_Kong
web_query_delay = 60000 # interval time of web JSON query
retry_delay = 5000 # interval time of retry after a failed Web query
# initialization
# SSD1306 OLED display
print("Connecting to wifi...")
oled = ssd1306.SSD1306_I2C(128, 64, I2C(scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4)))
oled.fill(0)
oled.text("Connecting", 0, 5)
oled.text(" to wifi...", 0, 15)
oled.show()
# internal real time clock
rtc = RTC()
# wifi connection
wifi = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF) # station mode
wifi.active(True)
wifi.connect(ssid, pw)
# wait for connection
while not wifi.isconnected():
pass
# wifi connected
print("IP: " + str(wifi.ifconfig()[0]) + "\n")
oled.text("Connected. IP: ", 0, 35)
oled.text(" " + str(wifi.ifconfig()[0]), 0, 45)
oled.show()
# set timer
update_time = utime.ticks_ms() - web_query_delay
# main loop
while True:
# if lose wifi connection reboot ESP8266
if not wifi.isconnected():
machine.reset()
# query and get web JSON every web_query_delay ms
if utime.ticks_ms() - update_time >= web_query_delay:
# HTTP GET data
response = urequests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200: # query success
print("JSON response:\n" + response.text)
# parse JSON
parsed = ujson.loads(response.text)
# you can also use parsed = response.json()
datetime_str = str(parsed["datetime"])
year = int(datetime_str[0:4])
month = int(datetime_str[5:7])
day = int(datetime_str[8:10])
hour = int(datetime_str[11:13])
minute = int(datetime_str[14:16])
second = int(datetime_str[17:19])
subsecond = int(round(int(datetime_str[20:26]) / 10000))
# update internal RTC
rtc.datetime((year, month, day, 0, hour, minute, second, subsecond))
update_time = utime.ticks_ms()
print("RTC updated\n")
else: # query failed, retry retry_delay ms later
update_time = utime.ticks_ms() - web_query_delay + retry_delay
# generate formated date/time strings from internal RTC
date_str = "{:02}/{:02}/{:4}".format(rtc.datetime()[1], rtc.datetime()[2], rtc.datetime()[0])
time_str = "{:02}:{:02}:{:02}".format(rtc.datetime()[4], rtc.datetime()[5], rtc.datetime()[6])
# update SSD1306 OLED display
oled.fill(0)
oled.text("ESP8266 Clock", 0, 5)
oled.text("Date: " + date_str, 0, 25)
oled.text("Time: " + time_str, 0, 45)
oled.show()
utime.sleep(0.1)