Spring编程常见错误50例-Spring Bean依赖注入常见错误(下)
@Value没有注入预期的值
问题
对于@Value可以装配多种类型的数据:
- 装配对象:
@Value("#{student}")
private Student student;
@Bean
public Student student(){
Student student = createStudent(1, "xie");
return student;
}
- 装配字符串:
@Value("我是字符串")
private String text;
- 注入系统参数、环境变量或者配置文件中的值:
@Value("${ip}")
private String ip
- 注入其他Bean属性:
@Value("#{student.name}") // student是bean的ID
private String name;
但是使用该注解时遇到以下场景会出现问题:在控制器类中引用配置类中的属性时部分值返回错误
username=admin
password=pass
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class ValueTestController {
@Value("${username}")
private String username;
@Value("${password}")
private String password;
@RequestMapping(path = "user", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getUser(){
return username + "," + ", " + password; // username返回的是运行这段程序的计算机用户名,password能正确返回
};
}
原因
从下面代码中可以看到@Value的工作分为三个核心步骤:
// DefaultListableBeanFactory#doResolveDependency
@Nullable
public Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames,
@Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
// ...
// ①寻找@Value
Object value = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getSuggestedValue(descriptor);
if (value != null) {
// ②解析value值
if (value instanceof String) {
String strVal = resolveEmbeddedValue((String) value);
BeanDefinition bd = (beanName != null && containsBean(beanName) ? getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName) : null);
value = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(strVal, bd);
}
// ③转化Value解析的结果到装配的类型
TypeConverter converter = (typeConverter != null ? typeConverter : getTypeConverter());
try {
return converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getTypeDescriptor());
}
catch (UnsupportedOperationException ex) {
...
}
}
// ...
}
- 寻找
@Value:判断属性字段是否标记为@Value
// QualifierAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver#findValue
@Nullable
protected Object findValue(Annotation[] annotationsToSearch) {
if (annotationsToSearch.length > 0) { // qualifier annotations have to be local
AnnotationAttributes attr = AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotationAttributes(
// valueAnnotationType即为@Value
AnnotatedElementUtils.forAnnotations(annotationsToSearch), this.valueAnnotationType);
if (attr != null) {
return extractValue(attr);
}
}
return null;
}
-
解析
@Value的字符串值:如果字段标记了@Value,则可拿到对应的字符串值,然后就可以根据字符串值去做解析,解析结果可能是字符串,也可能是对象 -
将解析结果转化为要装配的对象的类型:
分析完对应的步骤后,可以定位到问题原因在解析@Value指定字符串过程中,对${xxx}的查找不局限在application.properties,而是针对多个源,这些源在启动时被有序固定,所以在查找时也是按序查找的。当查找到systemEnvironment时发有个username和配置文件中的重合:
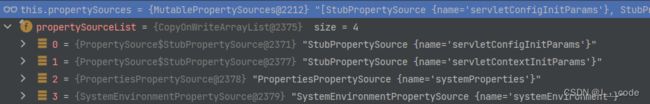
// PropertySourcesPropertyResolver#getProperty
@Nullable
protected <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetValueType, boolean resolveNestedPlaceholders) {
if (this.propertySources != null) {
for (PropertySource<?> propertySource : this.propertySources) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Searching for key '" + key + "' in PropertySource '" +
propertySource.getName() + "'");
}
Object value = propertySource.getProperty(key);
if (value != null) {
if (resolveNestedPlaceholders && value instanceof String) {
value = resolveNestedPlaceholders((String) value);
}
logKeyFound(key, propertySource, value);
return convertValueIfNecessary(value, targetValueType);
}
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not find key '" + key + "' in any property source");
}
return null;
}
解决方式
避免存在与系统或环境变量有同名的配置
myname=admin
password=pass
错乱的注入集合
问题
假设存在多个学生Bean,需找出来并存储到List里并在控制器类中输出:
// 可以理解为收集方式
@Bean
public Student student1(){
return createStudent(1, "psj1");
}
@Bean
public Student student2(){
return createStudent(2, "psj2");
}
private Student createStudent(int id, String name) {
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(id);
student.setName(name);
return student;
}
private List<Student> students;
public StudentController(List<Student> students){
this.students = students;
}
@RequestMapping(path = "students", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String listStudents(){
return students.toString();
};
此时需要再增加学生Bean,换了一种方式注入集合类型:
// 可以理解为直接装配方式
@Bean
public List<Student> students(){
Student student3 = createStudent(3, "psj3");
Student student4 = createStudent(4, "psj4");
return Arrays.asList(student3, student4);
}
但上述两种方式都存在,只会输出前面两个学生
原因
- 进行第一种装配方式时(即收集方式),主要分为以下过程:
// DefaultListableBeanFactory#resolveMultipleBeans
@Nullable
private Object resolveMultipleBeans(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) {
final Class<?> type = descriptor.getDependencyType();
if (descriptor instanceof StreamDependencyDescriptor) {
...
// 装配stream
return stream;
}
else if (type.isArray()) {
...
// 装配数组
return result;
}
else if (Collection.class.isAssignableFrom(type) && type.isInterface()) {
// 装配集合
// 获取集合的元素类型
Class<?> elementType = descriptor.getResolvableType().asCollection().resolveGeneric();
if (elementType == null) {
return null;
}
// 根据元素类型查找所有的bean
Map<String, Object> matchingBeans = findAutowireCandidates(beanName, elementType,
new MultiElementDescriptor(descriptor));
if (matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
if (autowiredBeanNames != null) {
autowiredBeanNames.addAll(matchingBeans.keySet());
}
// 转化查到的所有bean放置到集合并返回
TypeConverter converter = (typeConverter != null ? typeConverter : getTypeConverter());
Object result = converter.convertIfNecessary(matchingBeans.values(), type);
...
return result;
}
else if (Map.class == type) {
...
// 解析map
return matchingBeans;
}
else {
return null;
}
}
- 进行第二种装配方式时(即直接装配方式),具体过程在
DefaultListableBeanFactory#findAutowireCandidates中 - 当同时满足这两种装配方式时,从下面代码中可以看出它们是不能共存的:
// DefaultListableBeanFactory#doResolveDependency
// 采用收集方式
Object multipleBeans = resolveMultipleBeans(descriptor, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
if (multipleBeans != null) {
return multipleBeans;
}
// 上述方式不执行才会执行直接装配方式
Map<String, Object> matchingBeans = findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor);
解决方式
对于同一个集合对象的注入不要混合多种注入方式
参考
极客时间-Spring 编程常见错误 50 例
https://github.com/jiafu1115/springissue/tree/master/src/main/java/com/spring/puzzle/class3