AUTOSAR 面试知识回顾
如果答不上来,就讲当时做了什么
1. Ethernet基础:
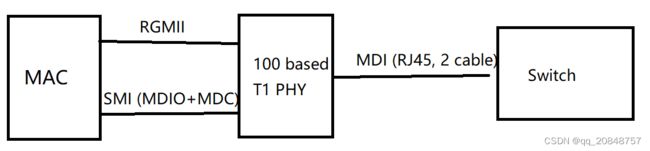
硬件接口:
- ECU到PHY: data 是MII总线, 寄存器控制是SMI总线【MDC+MDIO两根线, half duplex】
- PHY输出(100BASE-T1): MDI总线,2 wire 【T1: twisted 1 pair cable, full duplex】
MII接口:
MII RMII RGMII
MII to GMII: 4pin to 8pin, fast speed
GMMM to RGMII: 8pin to 4pin, same speed 【by samples data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock】
MDIO/MDC接口:
【SMI接口】用于MCU控制PHY芯片的register, 分为MDC和MDIO两根线,MDC 为clock,MDIO为data【半双工,双向传输】
MDI接口:
MDI的输出就是我们常说的 Automotive Ethernet Frame
我们用的是Ethernet II frame
6+6+2+46+4 = 64 bytes 6+6+2+1500+4 = 1518 bytes
VLAN:
Ethernet Stack 架构:
Ethernet frame:
VLAN: 0x 8100 0003 8100代表是VLAN,003代表VLAN ID(12-bit)
Ethernet Type:
0x0800: IPv4
TCP/IP on Ethernet:
6 byes -> 4bytes -> 2bytes 很好记
IP:
注意total length是在IP header里面,而不是在Ethernet 或者TCP的header里面
TCP/UDP:
ip地址: 192.0.0.1 4bytes
tcp 端口号: 0x8100 2 byts + sequence number 4 bytes 【就像CANTP的PCI一样】
TCP的三次握手:
-
client sequence number 【SYN】
-
client sequence number + server sequence number 【SYN-ACK】
-
client Confirm/Acknowledge to server 【confirm the ACK】
UDP:
不需要建立连接
client直接发 ip +port + data, server会去监听该port
【udp有length,而TCP用sequence number】
SomeIP:
SO : Service-Oriented Middleware over IP
a sender only sends data when at least one receiver in the network needs the data
可以看到SomeIP和DoIP是同级的,也就是说SomeIP和UDS是同级 的,都是根据service ID来决定数据格式
AUTOSAR实际例子:
There are two EthIf mainfunction under OS task:
· EthIf_MainFunctionRx
· EthIf_MainFunctionTx
There is only one mainfunction for switch under OS Task:
· EthSwt_11_MVQ622x_MainFunction
【Polling mode,所以EthIf_MainFunctionRx会在收到frame以后,调用 EthIf_Rxindication函数,EthIf_Rxindication 根据EthIf module里面的EthType与callback_function的配置,决定调用 CDD_RxIndication还是RMU_RxIndication】
【所有的配置信息都存在一个全局变量的struct里面,被OS周期性call的RMU_Mainfunction 调用Eth MCAL function 把它发出去。struct可以通过各个driver API函数修改,为方便测试我们创建了test_mainfunction SWC 来调用这些API】
Rx函数流程:
RX: 核心是EthIf_Mainfunction
EthIf_Mainfunction在收到frame后, 会去调用MCAL driver Eth_43_GMAC 处理一下,然后通知到EthIF_Rx Indication ,然后是 Jasper的 RxIndication
Tx函数流程:
TX: 核心是EthSwitch_Mainfunction
本质上 Ethernet switch driver 就是发送和接受RMU的信息(只干这一件事情),全是通过全局变量 EthSwt_6_88Q515x_Info_ast【】 这个结构体来实现的
RTE scheduler 里面两个函数:
-
Test component main function
-
EthSwitch main function
函数2本身会每个cycle将 指定的RMU发出去(将EthSwt_6_88Q515x_Info_ast【】这个结构体内容copy到TX buffer里面),于是我们通过函数1对RMU这个全局变量的内容进行更改。
所以说其实EthSwitch_Mainfunction,它主要参与的是TX。RX的核心是EthIf_Mainfunction
EthSwt_11_MVQ622x_MainFunction is mainly taking charge of sending out the Tx buffer, it also maintain the state machine 【状态机表示Switch硬件是active或者是别的什么状态】 [not directly analysis the Rx data, but switch driver will set flag for EthSwt_11_MVQ622x_MainFunction to use]
Debug实例:
【Worked Independent, within a team, talked with customer】
2. CAN基础:
硬件接口:
2.5V 3.5V 1.5V differetial twisted pair
CAN frame:
CAN:
11/29 bit ID + 8 byte data up to 1Mbit/s
CANFD:
11/29 bit ID + up to 64 byte data
ID field bit rate up to 1Mbps; Data field bit rate up to 8Mbps
Difference between CAN and CANFD
- CANFD Data field length could be up to 64 bytes
- CANFD data field bit rate could be 8Mbps 【BRS: bit rate switching】
- Data frame: most common frame type
- Remote frame: used to request specific CAN ID data from other nodes on the CAN network
Partial networking
CanTrcv very low power consumption in standby and sleep modes
every CAN frame can trigger it from sleep to standby mode, but only the selectied CAN frame【SPI config the Cantrcv register for CAN ID and data mask】 can wake it up from standy to wakeup mode(otherwise back to sleep mode after timeout)
why ID mask: only NM frame can wake it up?
UDS frame:
CAN ID 没什么好说的
PCI: CAN-TP负责的,如果想发多帧,就靠这个记录Sequence number
PCI之后的蓝色就是 ISO14229-2 里面规定的,各个UDS的service的格式
用CAN-TP协议,就可以发现PCI 0x03的含义
-
0: single frame
-
3: 3byte data length after PCI
UDS on CAN stack架构
ISO-14229 ISO-15765
CAN MCAL:
BRS: bit rate switch for CAN-FD data filed (both in Tresos MCAL and Canalyzer)
Sampling point:
分四块segment的原因是,第一块用来同步,第二块用来仲裁,第三块用来采样
Mailbox(HOH):
- Each mailbox is a buffer (rx and/or tx), but it can be configured to only work with one specific CAN identifier
- One more advanced, but fairly common setup, is to combine a Rx FIFO with mailboxes, so that high priority messages will end up in their dedicated mailbox, while everything else ends up in the FIFO
Difference between FULL CAN and basic CAN mailbox
FULL CAN 是硬件filter,只能过滤一个ID
Basic CAN是CPU filter,可以过滤多个ID
CanDriver:
- Offer transmit API to CanIf_Tx
- Invoke Callback function of CanIf for notify the data received
- One controller for one CAN Tx/Rx channel on MCU
一个MCU芯片内部可以有多个CAN controller,每个CAN controller对应一个TX/RX pin 【在MCAL里面新建2个CAN controller就可以控制两路CAN了】
CANIF:
after import dbc file
CanIf maps the upper layer PDU into CAN HOH of each corresponding CAN controller in transmit side
CanIf extract the PDU from the CAN frame based on the CAN ID
The CAN ID is only visible in the Can driver and in CanIf. When a frame is received, CanIf converts the CAN ID to a PduId and passes that value to the target module in the Rx indication callback, in this case to CanNm.
CANTP: (Network layer)
- Segment data in transmit direction
- reassemble data in receving direction
- Control data flow
【STMin 在 0x19 06 extende data服务中被用到,ECU和Canlyzer设置不匹配的话,Canlyzer就收不到consecutive frame】
通过multi-frame,最多可以发送4095个byte (2^12)
所以CANTP主要做了两个事情
-
把长数据切分成多个frame发送出去 (有Index来计数到底是第多少个byte)
-
通过Flow control frame的ST参数,控制frame之间的separation time
FF: 告知data size,即数据的总长度 in bytes
CF: 用4个bit来表示sequence number
FC: receiver可以用FC让server 暂停发送数据,恢复发送数据,ST时间,以及接下来发多少CF,然后receiver会重新再发一个FC
注意是tester告诉发送方接下来的frame ST间隔是多少
STmin, N_As, Ar, Br
上面这些参数主要都是针对PCI 30: flow control 而言的, receiver是指发送flow control,等待server发消息的测试方而言。
N_Ar: 收到从server来的第一帧之后,flow control 没有在timeout之前被发送出去
N_As: 一帧FF 从开始发到time out后还没有被发出去(没收到CanIf_TxConfimation)
结合consecutive frame的发送流程,就能轻易看懂下图了【server是sender,发FF和CF】
physical /functional addressing: 【在CANIf模块里面设置,不同的ID进入CanTp,PduR还是CANNM】
- Physcial addressing (send to a specific CAN node)and functional addressing(broadcast to the whole CAN bus network)
- 如果是一条CAN bus,不知道是哪个ECU出了故障,就可以用functional ID直接发0x19 服务来读取DTC,这样就知道是哪个ECU出问题了
- 每个ECU有自己独立的一个CAN ID作为Physcial addressing, 所有的ECU公用一个CAN ID作为functional addressing
PduR:
PDUR routing the PDU between different modules as user pre-configuration:
PduR will send out the i-PDU from COM to CanIf or LinIf, or routing the PDU from DCM to CanTp 【I checked the code, most of the function is Macro】
IpduM:
multiplexing of a pdu,说白了就是在8 byte的data里面又定义了一个select field,根据它的值,决定data field该怎么解读(interpret)。 也就是说在CAN ID之后又加了个ID,目的是节约CAN ID
Com:
COM is between RTE and PDUR
Provide Signal data to RTE
Pakage the Signal data from RTE to PDU for transmission
Byte order convertion (big / little endian for the multi-byte signal)
DCM: (Session Layer)
- Receive the diagnostic information from PDUR
- implement / trigger the UDS service define in ISO-14229 while retrieve the request message
- independent from network
- DSL: Receive data from PduR, and transfer to DSD, DSL provide access to security and session state(change these state)
- DSD: SID table is in there, valid if the request is valid( verified the security/session level), return Negative response if validate fail
- DSP: check the SID format, execute required function call on DEM and/or SWC
0x19 ReadDTCInfomation 最重要的UDS service
- 对我们常用的非OBD的DTC,长度是3个Bytes
- 每个DTC代表一个特定的故障,当故障发生时,SWC通过函数 “Rte_Call_DiagnosticMonitor_DTC0A2F00_SetEventStatus” 去set这个DTC。【Rte_Call 说明是C/S port】
- 同时,每个DTC都有一个DTC Status 变量与之对应,它的长度是一个Byte, 记录这个DTC的状态:
因为有下图status byte的存在,可以通过DTC number来读指定的DTC是什么状态,也可以按照status mask来批量读取对应状态的DTC是哪些 【pending, confirmed】
-
SWC 通过C/S interface 调用DEM的Dem_SetEventStatus( EventID, Event Status) 来indicate DTC set 【SWC在 set DTC 是client, routine control 就是server】【在DCM,DEM里面配置好了这些服务,BSW gen以后会生成DCM_SWCD.arxml,里面会自动生成这些函数的interface,和operation】
-
DEM 的每个DTC都要设置debouncing threshold, 【计次】当达到次数的时候status byte里面的test failed bit才会被置1
-
同时DEM模块里面可以创建与DTC绑定的结构体,比如存放电压 Ud,Uq什么的。当SWC去setDTC的时候,也可以通过S/R interface去给结构体赋值。这个就叫做extended data,用来存储DTC发生时的车辆各种信息
-
当debouncing通过的时候,DEM会调用NvM接口函数,把DTC还有extended data存储到Flash里面
-
S3Client:client要在该时间内发送0x3E服务,从而保持ECU server维持在非default session,否则ECU就有可能会超时回退到default session(在DCM-DSL里面 diagnostic session layer)
-
S3Server:server在该时间内未收到任意诊断报文,就会回退到default session
-
P2: (在DCM-DSL模块里面配置的)
找几个UDS的服务聊一下,根据之前的邮件
DEM:
- process diagnostic event reported from BSW and APPL
- Communicate with NvM to store the fault data into Flash 【DEM里面 DTC attribute 下面会去选择Memory destination,这个就是在选NvM里面配置好的分区】【在做routine control的时候callback函数里面也用到了 NvM 的API去存储data】
- provide the access of fault data to DCM
Debouncing: pre-pass / pre-fail, still in pending status counter based deboucing(每次调用Dem_SetEvent, counter 就会加1) or time based debouncing, we use counter based deboucing in current project
Aging:基本都是 counter based, 当前项目没启用,因为客户好像没要求
Status byte: Operation cycle【power on cycle, ignition cycle】, confirmed DTC
Extended data / FreezeFrame
RTE:
邮件里面有一个专门的RTE文件夹
Routine_Control 就是client server interface, DCM 里面是client 去set event, SWC里面是server 被这个event trigger,于是相当于DCM call 了SWC 的函数 【在composition里面去把interface下面的Operation给mapping起来】
- SWC1 internal behavior : client -> set Event_A
- SWC2 internal behavior: Event_B -> trigger server start
- composition editor: link Event_A and Event_B
看SWC的arxml文件也能看得很清楚
security access也是client server interface,SWC里面的runnable属于server/Pport,被event 触发开始执行
这个interface是在DCM模块里面定义好的,配置了DCM的security access服务,生成BSW,就会生成这个swcd.arxml,然后在创建SWC的时候就可以在创建port的时候选择这个interface
ComM and CanSM:
- ComM通过CanSM模块实现功能
杂项补充:
【I worked alone at the begining, assigned task which was easy to him when new team member joined in.】
with bootloader:
- bootloader之前需要用到的UDS服务 【通过programming session触发ecu reset进入BootLoader,但在这之前需要调用UDS服务做一些准备工作】
- 0x10 03 to extended session
- 0x85 02 turn off DTC storage 因为在关掉communication以后,会出现很多DTC,所以直接关掉
- 0x28 01 turn off communication control (用来留出带宽给BootLoader上传/下载程序) 关掉01 Normal Communication,保留02 NM message
LD-com:
CAN gateway:
AUTOSAR实际例子:
Rx 流程:
Tx流程:
Debug实例:
union的妙用
3. CAN trcv CDD配置
MCAL SPI + OS:
sampling at rising edge
BSW CanTrcv source code:
Partial networking:
CanTrcv very low power consumption in standby and sleep modes
every CAN frame can trigger it from sleep to standby mode, but only the selectied CAN frame【SPI config the Cantrcv register for CAN ID and data mask】 can wake it up from standy to wakeup mode(otherwise back to sleep mode after timeout)
讲讲CanTrcv partial networking 和 NM 的联动:
- 下电流程: ECU -> CanTrcv -> TLE35584 -> powerdown
- 上电流程:CanTrcv -> TLE35584 -> ECU
4. AUTOSAR OS
S/R and C/S interface:
S/R: 数据传输, interface下面的元素是 data element
C/S: 函数调用,interface下面的元素是 operation
IDT and ADT:
Implementation Data Type:tool自己创建的的,跟base type 绑定,SWC生成的c代码里面变量用的就是IDT
Application Data Type: 用户自己起的名字,interface下面的 data element绑定的是ADT,用户在创建SWC的时候要自己去SWC component editor里面声明 ADT 跟哪个 IDT 对应
Compute Method:
Task:
- Basic task: 3种状态, suspend,ready,run
- Extended task: 4种状态, suspend,ready,run, wait (wait for event)
Baisc 和 Extend task 最大的区别是: extend task 多一个 wait 的状态,可以wait for event
ISR:
- Category 1: could not use OS service, will continue the instruction before the interrupt
- Category 2: could use some of OS service, OS scheduler will reschedule the task just after the interrrupt. (如果我们在Category 2里面去active了一个更高优先级的task2,那么在ISR结束时 task2会开始运行,而不是回到 task1)
Application:
(functional safety)
memory partiton 的对象是 OS-Application, 核心目的是 Application与Application之前内存是相互独立的。 这样就可以让不同ASIL级别的代码放在不同的Applicantion下面
OS-Application: Application 下面可以有多个task,每个task下面可以有多个runnable
“一个 SWC只能分配给一个OS-Applications”
Share resource:
一个核内部,不同task之间对share memory的保护 【mutex/semaphore】
IOC:
用于多核ECU,核间通讯 【Spinlock】
Exclusive area:
OS里面的概念,对每个模块的各个exclusive area【mutex】,可以声明是block all interrupt 还是 block 某一部分 或者NONE。 因为在实际的情况下,我们发现COM模块的exclusive area会经常block APPL 10kHZ主算法的 ISR,导致最终频率只有不到10KHZ。 因此,根据mentor自带的COM模块的getting start.pdf,update COM模块exclusive area为NONE后,该问题解决【讲道理APPL的主算法的ISR一定是优先级最高,所以exclusive area的调整很重要】
Timing protection:
-
deadline monitor: 只是检查每个task 从开始到结束的时间有没有超过deadline,问题在于如果被另一个高优先级任务抢占了导致超时,deadline monitor是不知道的
-
timing protection: 检查的不是task 从开始到结束的时间,而是execution time。同时会去检测task 占用shared resource或者disable 中断的时间(进入critical area)
Memory protection:
原理: MPU硬件模块监控内存的访问权限
OS任务切换的原理:
Tick 的ISR 里面做了三件事情
-
寻找任务就绪表里面优先级最高的Task 【1】
-
与当前任务对比
-
如果比当前任务优先级高,则调用scheduler发生切换【2】
-
最后一行set pc 【这样就可以跳转到另一个task,或者是返回到之前的task继续运行】
【1】有可能在之前别的ISR里面,让其他的任务进入了就绪状态。(scheduler table里面的expiry point只会让task进入就绪状态,Task上下文切换,开始运行还是在这个Tcik ISR的scheduler里面发生)
【2】如果不需要任务切换,这次ISR里面其实就执行了不到10行代码,损耗很少
5. SWC的配置
0. Prerequesit:
- AUTOSAR tool 会自己生成"PlatformTypes.arxml"
- Implementation Data Type
- BaseType
- DataConstr 【通过BaseType和DataConstr,把IDT定义了】
- 用户自己创建一个"TypesAndInterface.arxml"
- Application Data Type
- Interface
- S/R: Data Element 【ADT type】
- C/S: Operation 【如果有arguement,也是ADT type】
1. SWC的创建:
用户在ISOLAR中新建一个空白的arxml文件,就可以右键arxml创建SWC了【一个arxml下面可以创建任意多个SWC】。通过component editor,可以对SWC添加 port 和 internal behavior
- arxml
- SWC
- port 【Pport就是Write,Rport就是Read】
- C/S interface 【函数/Operation】
- S/R interface 【变量/Data Element】
- internal behavior
- runnable
- DataAccessPoint 【读/写 Data Element】
- ServerCallPoint 【调用Operation来实现函数调用】
- Event 【触发runnable的运行,周期/Operation trigger】
- DataType Mapping 【IDT 到 ADT】
- runnable
- port 【Pport就是Write,Rport就是Read】
- SWC
【C/S interface最好还是看tool 自带的例子,这样比较好理解】
2. Composition的创建:
用户在ISOLAR中新建一个空白的arxml文件,就可以右键arxml创建composition了
composition的主要用途是,把需要的SWC全部添加进来,然后再assembly connector里面把port下面的data element 或者是 operation连接上,从而实现 数据传输 和 函数调用
3. Import CAN DBC file
通过import dbc文件,tool会自动生成一个或多个arxml,自动将dbc文件里面的Signal,PDU,ECU等信息转换到这些arxml文件内, 用来以AUTOSAR的格式存放dbc的信息,相当于一个DLL库 【Signal 用于之后的SystemSignalMapping】
4. System Description的创建:
右键新建system,会自动生成一个arxml,此为system description 【此操作因软件而异,不要纠结操作步骤】
![]()
system description是 system level配置的核心文件,有两大功能
- SWC to ECU mapping: 将 composition的那些SWC分配到各个ecu【这个界面下会选择使用哪个composition】
- System Data mapping: 将SWC的port里面的需要和外界通讯的data element与刚才import dbc产生的CAN signal连起来【相当于库文件,里面的system signal等信息会被自动识别出来等待被调用】
5. ECU Extract的创建:
右键System Description arxml,可生成EcuExtract.arxml
通过RTE editor打开EcuExtract,里面包含RunnableToTaskMapping的界面
- 将之前创建的SWC下面的unmapping runnable拖拽分配到Task下面
实例:
1. 在现有AUTOSAR project中,新建一个test SWC 用来监测/处理其他ECU传输过来的某些CAN/Ethernet信息的流程是什么? 【sender/receiver interface】
- 新建一个arxml,并创建SWC 【port + internal behavior/runnable】
- 将SWC添加到现有的composition下面,以供之后能在system Description中能被识别到
- system Description里面做两件事, 将SWC分配给这个ECU,然后将system signal 和 SWC的port里面的data element连起来
- ECU Extract 的RTE editor界面里面将 runnable Mapping到对应的Task
【如果有SWC之间通讯的需求,第二步在composition的assembly connector里面把两个SWC的port里面的data element连起来】
2. 在UDS的服务,需要创建针对routine control server 的callback函数的DiagnosticSWC实现【client server interface】
- 新建一个arxml,并创建SWC 【port + internal behavior/runnable】,因为该SWC是server,所以设置为OperationInvokeEvent触发runnable的运行
- 将SWC添加到现有的composition下面,以供之后能在system Description中能被识别到,然后在composition的assembly connector里面把SWC的port下的Operation和DCM下的routine control下的Operation连起来
- system Description里面做两件事, 将SWC分配给这个ECU
- ECU Extract 的RTE editor界面里面将 runnable Mapping到对应的Task
扩展
6. Composition Sample
可以看到SWC分为2大类:
- RTE以上,传统的SWC
- RTE一下,BSW模块,在配置了相应的服务/功能以后,也会产生SWC,提供C/S 或者S/R interface 【比如在DCM模块里面配置routine control以后,生成BSW阶段会生成DCM_SWCD.arxml,这就是下图所见的CPT_Dcm】
6. AUTOSAR startup phase
Standard AUTOSAR启动流程:
[before entering mainfunction] copy .bss/ init stack -> main() -> EcuM_init() [start_PreOS]-> BswM_init() [active OS counter]-> OS scheduler table start [task running]
EcuM_Init:
- item list: MCAL_init()
- Start_PreOS()
BswM_Init:
- action list: NvM init, ComM(FULL com)
- Start OS counter[scheduler run]
reset vector -> init stack and memory -> main() -> EcuM_Init() -> MCAL_Init() -> StartOS() -> BswM_StartupOne() -> MemStack_Init()/NvM_ReadALL - > BswM_StartupTwo() -> Rte_start() - >
进入main函数之前会初始化 stack 和 memory .bss .data 这些?
main函数里面第一行就是EcuM_Init() 函数
EcuM_Init() 里面干了两件事,调用MCAL的各个init 函数,然后 startPreOS()
startOS() 只是一个while(1)的无限循环, TimerISR去触发Task运行,Task切换这些OS内核服务还没开始
之后就到了BswM模块,最重要的就是通过Rte_start()函数激活OS counter,开启scheduler table的运行,至此task的调度开始运行
multi-core OS 启动流程
- 硬件启动master core0, core0去唤醒slave core1,2,3
- init .bss, stack, and Start_PreOs, then first synchronize
- init OS-Application/user application, the second synchronize
- start scheduler table at the same time
![]()
7. 杂项
Network Management:
网络管理的目的:
通过监听CAN网络中是否存在指定的NM message,来决定该网络节点是否进入sleep/wakeup 模式,从而达到省电的目的 【NM state machine负责这件事情】
- 当连续5秒未能监测/接收到NM message,该网络节点进入sleep模式
- 当CAN transceiver接收到NM message,该网络节点应从sleep模式转换到wakeup模式
名词解释:
- NM message: network management message,用户事先指定好的某一个/某几个 CAN ID frame,称为该网络的NM
- sleep状态的定义: 该ECU,以及为ECU供电的电源芯片TLE 35584均处于掉电状态,仅有CAN transceiver TJA 1145处于上电状态【但处于sleep模式】持续监听是否收到NM message,从而达到省电的目的,
- 如何进入sleep状态: ECU通过SPI发送CMD,使CAN transceiver进入sleep模式,CAN transceiver在sleep模式下,其引脚INH会被拉低,switch off,从而导致35584掉电,ECU也随之掉电【CAN transceiver并不是由35584供电,所以仍然处于上电状态】
- 如何wakeup: sleep状态下的CAN transceiver仍然在持续监听CAN 网络,当收到任意一条事先指定的NM message后,CAN transceiver会从sleep模式转换到wakeup模式,引脚INH被拉高,switch on,35584和ECU重新上电【通过SPI来修改CAN transceiver的寄存器 CAN ID和CAN mask,可以实现由某一条/某几条 CAN ID来唤醒】
- 【任意CAN frame都可以让CAN transceiver保持工作,但只有selected CAN frame才能wakeup它,这就是为什么要让ECU 通过SPI 来让它 sleep】
NvM:
- Create NvM blocks, link to FEE, setup in Tresos for flash driver
- Communicate with NvM to store the fault data into Flash 【DEM里面 DTC attribute 下面会去选择Memory destination,这个就是在选NvM里面配置好的分区】
Fix/Flex EcuM
BswM:
ACTION list like if else condition, then excuted the action or user callout function
like: PowerUp的时候ComM_RequestComMode(CANchannel2 ,COMM_FULL_COMMUNICATION), NvM_READALL, DEMShutDown
ShutDown 也是通过BswM来检测各个condition/ModeRequest,最终触发DEMShutDown, Rte_ShutDown
【这么说,上下电的时候,都会触发(if condition triggered)BswM的action list】
h/w and s/w break point
- Hardware breakpoints use dedicated hardware features, have a limited number, and are generally faster and less intrusive.
- Software breakpoints are implemented by modifying the program's code, are practically unlimited in number, and are highly versatile but may be slower and more intrusive due to software handling.
How does debugger work?
Debuggers add special code or instructions to the program being debugged. This added code is often called "debug symbols" or "breakpoints" and serves as markers to pause or interrupt the program's execution at specific points
8. 针对性准备
根据linkdin技术背景,给每个面试官都准备一个故事
AUTOSAR那个人:
- Ethernet:Tx/Rx 流程 NXP S32k ARM cortex-M
- 【Polling mode,所以EthIf_MainFunctionRx会在收到frame以后,调用 EthIf_Rxindication函数,EthIf_Rxindication 根据EthIf module里面的EthType与callback_function的配置,决定调用 CDD_RxIndication还是RMU_RxIndication】
- 【所有的配置信息都存在一个全局变量的struct里面,被OS周期性call的RMU_Mainfunction 通过调用Eth_transmit 函数API,实现了用Eth MCAL function 把它发出去。struct可以通过各个driver API函数修改,为方便测试我们创建了test_mainfunction SWC 来调用这些API】
- CANTrcv CDD: sampling on SPI rising edge + partial networking
- UDS on CAN:从CAN driver 到RTE都可以讲,太多了, timing parameter, PCI, DTC, RTE CS port
苹果那个人:
C语言:
OS:
Embedded system:
Manager:
讲讲商业角度上project的意义(而不是技术角度) + 跟客户沟通
- ETAS:work independent, in a team, support customer【batch file for automation】
- Jingjin: work alone at beginning, assign task to new member which is easy to him
【communication stack[ethernet/CAN] + diagnostic + automation/script】
Most difficult thing:
understand both software and hardware,可以讲NM的例子。 ECU monitor Nm message, SPI cmd to CanTrcv to sleep mode, CanTrcv INH pin low which leads to TLE35584 power down. ECU power down
HR:
why you want to move:
- JD job duty is:
- I am enjoying the xx part
- I can see I will be xx expert in xx area in the future
纯CS那个:
看看glassdoor,随缘了