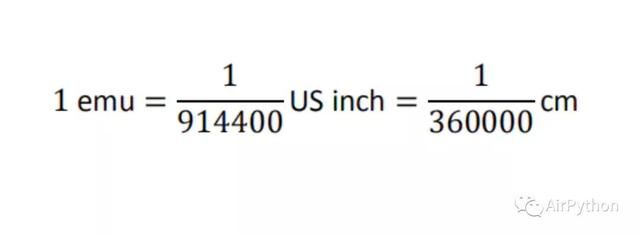python办公自动化图片,聊聊python 办公自动化之 Word(中)
作者:星安果
来源:AirPython(公众号)
上一篇文章,对 Word 写入数据的一些常见操作进行了总结,详情请看聊聊python 办公自动化之 Word(上)。相比写入数据,读取数据同样很实用!本篇文章,将谈谈如何全面读取一个 Word 文档中的数据,并会指出一些要注意的点。
基本信息
我们同样使用 python-docx 这个依赖库来对 Word 文档进行读取。首先我们来读取文档的基本信息,它们分别是:章节、页边距、页眉页脚边距、页面宽高、页面方向等。
在获取文档基础信息之前,我们通过文档路径构建一个文档对象 Document。
from docx import Document# 源文件目录self.word_path = './output.docx'# 打开文档,构建一个文档对象self.doc = Document(self.word_path)
1 - 章节( Section )
# 1、获取章节信息# 注意:章节可以设置本页的大小、页眉、页脚msg_sections = self.doc.sectionsprint("章节列表:", msg_sections)# 章节数目print('章节数目:', len(msg_sections))
2 - 页边距( Page Margin )
通过章节对象的 left_margin、top_margin、right_margin、bottom_margin 属性值可以获取当前章节的左边距、上边距、右边距、下边距
def get_page_margin(section):""" 获取某个页面的页边距(EMU) :param section: :return: """ # 分别对应:左边距、上边距、右边距、下边距 left, top, right, bottom = section.left_margin, section.top_margin, section.right_margin, section.bottom_margin return left, top, right, bottom# 2、页边距信息first_section = msg_sections[0]left, top, right, bottom = get_page_margin(first_section)print('左边距:', left, ",上边距:", top, ",右边距:", right, ",下边距:", bottom)
返回值的单位是 EMU,和厘米、英尺的转换关系如下:
3 - 页眉页脚边距
页眉边距:header_distance
页脚边距:footer_distance
def get_header_footer_distance(section):""" 获取页眉、页脚边距 :param section: :return: """ # 分别对应页眉边距、页脚边距 header_distance, footer_distance = section.header_distance, section.footer_distance return header_distance, footer_distance# 3、页眉页脚边距header_distance, footer_distance = get_header_footer_distance(first_section)print('页眉边距:', header_distance, ",页脚边距:", footer_distance)
4 - 页面宽度和高度
页面宽度:page_width
页面高度:page_height
def get_page_size(section):""" 获取页面宽度、高度 :param section: :return: """ # 分别对应页面宽度、高度 page_width, page_height = section.page_width, section.page_height return page_width, page_height# 4、页面宽度、高度page_width, page_height = get_page_size(first_section)print('页面宽度:', page_width, ",页面高度:", page_height)
5 - 页面方向( Page Orientation )
页面方向分为:横向和纵向
使用章节对象的 orientation 属性去获取一个章节的页面方向
def get_page_orientation(section):""" 获取页面方向 :param section: :return: """ return section.orientation# 5、页面方向# 类型:class 'docx.enum.base.EnumValue# 包含:PORTRAIT (0)、LANDSCAPE (1)page_orientation = get_page_orientation(first_section)print("页面方向:", page_orientation)
同样,可以直接使用这个属性设置一个章节的方向
from docx.enum.section import WD_ORIENT# 设置页面方向(横向、竖向)# 设置为横向first_section.orientation = WD_ORIENT.LANDSCAPE# 设置为竖向# first_section.orientation = WD_ORIENT.PORTRAITself.doc.save(self.word_path)
段落
使用文档对象的 paragraphs 属性可以获取文档中所有的段落
注意:这里获取的段落不包含页眉、页脚、表格中的段落
# 获取文档对象中所有的段落,默认不包含:页眉、页脚、表格中的段落paragraphs = self.doc.paragraphs# 1、段落数目paragraphs_length = len(paragraphs)print('文档中一共包含:{}个段落'.format(paragraphs_length))
1 - 段落内容
我们可以遍历文档中所有的段落列表,通过段落对象的 text 属性,获取全部的段落内容
# 0、读取所有段落数据contents = [paragraph.text for paragraph in self.doc.paragraphs]print(contents)
2 - 段落格式
通过上一篇文章,我们知道段落也存在格式的
使用 paragraph_format 属性获取段落的基本格式信息
包含:对齐方式、左右缩进、行间距、段落前后间距等
# 2、获取某一个段落的格式信息paragraph_someone = paragraphs[0]# 2.1 段落内容content = paragraph_someone.textprint('段落内容:', content)# 2.2 段落格式paragraph_format = paragraph_someone.paragraph_format# 2.2.1 对齐方式# alignment = paragraph_format.alignmentprint('段落对齐方式:', alignment)# 2.2.2 左、右缩进left_indent, right_indent = paragraph_format.left_indent, paragraph_format.right_indentprint('段落左缩进:', left_indent, ",右缩进:", right_indent)# 2.2.3 首行缩进first_line_indent = paragraph_format.first_line_indentprint('段落首行缩进:', first_line_indent)# 2.2.4 行间距line_spacing = paragraph_format.line_spacingprint('段落行间距:', line_spacing)# 2.2.5 段落前后间距space_before, space_after = paragraph_format.space_before, paragraph_format.space_afterprint('段落前、后间距分别为:', space_before, ',', space_after)
文字块 - Run
文字块 Run 属于段落的一部分,所以,要获取文字块信息,必须先拿到一个段落实例对象
以文字块基本信息、字体格式信息为例
1 - 文字块基本信息
我们使用段落对象的 runs 属性获取段落内所有的文字块对象
def get_runs(paragraph):""" 获取段落下所有的文字块信息,包含:数目、内容列表 :param paragraph: :return: """ # 段落对象包含的文字块Run runs = paragraph.runs # 数量 runs_length = len(runs) # 文字块内容 runs_contents = [run.text for run in runs] return runs, runs_length, runs_contents
2 - 文字块格式信息
文字块是文档中最小的文字单元,使用文字块对象的 font 属性可以拿到它的字体属性
和设置文字块格式属性一一对应,字体名称、大小、颜色、是否加粗、是否斜体等都可以获取到
# 2、文字块格式信息# 包含:字体名称、大小、颜色、是否加粗等# 某一个文字块的字体属性run_someone_font = runs[0].font# 字体名称font_name = run_someone_font.nameprint('字体名称:', font_name)# 字体颜色(RGB)# font_color = run_someone_font.color.rgbprint('字体颜色:', font_color)print(type(font_color))# 字体大小font_size = run_someone_font.sizeprint('字体大小:', font_size)# 是否加粗# True:加粗;None/False:没有加粗font_bold = run_someone_font.boldprint('是否加粗:', font_bold)# 是否斜体# True:协议;None/False:不是斜体font_italic = run_someone_font.italicprint('是否斜体:', font_italic)# 带下划线# True:带有下滑线;None/False:字体没有带下滑线font_underline = run_someone_font.underlineprint('带有下滑线:', font_underline)# 删除线/双删除线# True:带有删除线;None/False:字体没有带删除线font_strike = run_someone_font.strikefont_double_strike = run_someone_font.double_strikeprint('带有删除线:', font_strike, "\n带有双删除线:", font_double_strike)
表格
文档对象的 tables 属性可以获取当前文档中所有的表格对象
# 文档中所有的表格对象tables = self.doc.tables# 1、表格数量table_num = len(tables)print('文档中包含的表格数量:', table_num)
1 - 表格所有数据
获取表格中所有数据有 2 种方式
第一种方式:通过遍历文档中所有表格,然后按行和单元格进行遍历,最后通过单元格的 text 属性获取所有单元格的文本内容
# 2、读取所有表格数据# 所有表格对象# tables = [table for table in self.doc.tables]print('内容分别是:')for table in tables:for row in table.rows: for cell in row.cells: print(cell.text, end=' ') print() print('\n')
另外一种方式是使用表格对象的 _cells 属性获取表格中所有的单元格,然后遍历获取单元格的值
def get_table_cell_content(table):""" 读取表格中所有单元格是内容 :param table: :return: """ # 所有单元格 cells = table._cells cell_size = len(cells) # 所有单元格的内容 content = [cell.text for cell in cells] return content
2 - 表格样式
# 3、表格样式名称# Table Gridtable_someone = tables[0]style = table_someone.style.nameprint("表格样式:", style)
3 - 表格行数量、列数量
table.rows:表格中的行数据迭代对象
table.columns:表格中的列数据迭代对象
def get_table_size(table):""" 获取表格的行数量、列数量 :param table: :return: """ # 几行、几列 row_length, column_length = len(table.rows), len(table.columns) return row_length, column_length
4 - 行数据、列数据
有时候,我们需要单独按照行或者列,获取全部数据
def get_table_row_datas(table):""" 获取表格中行数据 :param table: :return: """ rows = table.rows datas = [] # 每一行获取单元格的数据组成列表,加入到结果列表中 for row in rows: datas.append([cell.text for cell in row.cells]) return datasdef get_table_column_datas(table): """ 获取表格中列数据 :param table: :return: """ columns = table.columns datas = [] # 每一列获取单元格的数据组成列表,加入到结果列表中 for column in columns: datas.append([cell.text for cell in column.cells]) return datas
图片
有时候,我们需要将 Word 文档中的图片下载到本地,Word 文档实际上也是一个压缩文件,我们使用解压工具后发现,文档包含的图片都放置在/word/media/ 目录下
提取文档图片有 2 种方法,分别是:
解压文档文件,将对应目录下的图片拷贝出来使用 python-docx 内置的方法提取图片( 推荐 )def get_word_pics(doc, word_path, output_path): """ 提取word文档内的图片 :param word_path:源文件名称 :param output_path: 结果目录 :return: """ dict_rel = doc.part._rels for rel in dict_rel: rel = dict_rel[rel] if "image" in rel.target_ref: # 图片保存目录 if not os.path.exists(output_path): os.makedirs(output_path) img_name = re.findall("/(.*)", rel.target_ref)[0] word_name = os.path.splitext(word_path)[0] # 新的名称 newname = word_name.split('\\')[-1] if os.sep in word_name else word_name.split('/')[-1] img_name = f'{newname}_{img_name}' # 写入到文件中 with open(f'{output_path}/{img_name}', "wb") as f: f.write(rel.target_part.blob)
页眉页脚
页眉和页脚都是基于章节,我们以某一个章节对象为例进行说明。
# 获取某一个章节first_section = self.doc.sections[0]
使用章节对象的 header、footer 属性可以获取页眉、页脚对象。由于页眉、页脚可能包含多个段落 Paragraph,因此,我们可以先使用页眉页脚对象的 paragraphs 属性获取所有段落,然后遍历出所有段落的值,最后拼接起来就是页眉页脚的全部内容。
# 注意:页眉、页脚都有可能包含多个段落# 页眉所有的段落header_content = " ".join([paragraph.text for paragraph in first_section.header.paragraphs])print("页眉内容:", header_content)# 页脚footer_content = " ".join([paragraph.text for paragraph in first_section.footer.paragraphs])print("页脚内容:", footer_content)
举报/反馈