Spring 源码全面解析
前言
本文是对Spring容器初始化BeanFactory、初始化Bean过程的源码分析并注释。期望能帮助自己及准备看Spring源码的同学一些启发,起到抛砖引玉的作用。通过记流水账的方式一点一点对源码注释,所以文章篇幅略长,耐心看吧。本人能力有限,文中不足之处,还请不吝赐教,我会及时更新文章内容以免误导他人,谢谢。
基本环境:
版本:Spring Framework 5.0.x
Spring源码从GitHub上直接clone,Spring源码是使用Gradle构建的,怎么使用Gradle构建同学们自行百度/Google。

将Spring下载下来后如何运行,请自行百度,本文不赘述。
- MySpring Module 中的内容:
public interface UserService {
void queryUser();
}
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Override
public void queryUser() {
System.out.println("asdasd");
userDao.query();
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.jds")
public class AppConfig {
}
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、Context的初始化
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
// 2、向Context中注册
context.register(AppConfig.class);
// 3、Context启动
context.refresh();
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userServiceImpl");
userService.queryUser();
}
}
MySpring中的内容和下文无任何关系,仅是为了遇到不解时,方便Debug。所以,在看下文前,运行一遍自己的代码吧。
一、Context的初始化过程
1、站在背后的男人GenericApplicationContext
GenericApplicationContext和它的DefaultListableBeanFactory
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext extends GenericApplicationContext
因为AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 继承自GenericApplicationContext,所以在初始化AnnotationConfigApplicationContext时会先调用父类的构造方法:
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
/**
* 站在背后的男人
* step1 隐式调用super()
* 调用super(); 初始化beanFactory = DefalutListableBeanFactory()
*/
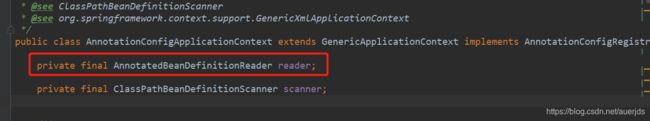
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
public GenericApplicationContext() {
// 实例化beanFactory
this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
}
在父类的构造器中实例化了一个DefaultLiatableBeanFactory。这个类就是充当“容器”的存在!!!
2、AnnotationBeanDefinitionReader
AnnotationBeanDefinitionReader
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
/**
*
* step2
* 实例化一个 支持读取器,将当前对象传递给reader!!!
* 用于读取被注解的类
*/
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
AnnotationConfigAppliactionContext 也是BeanDefinitionRegister的子类
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
/**
* 根据registry 判断使用哪种 Environment
* getOrCreateEnvironment(registry)
*
*/
this(registry, getOrCreateEnvironment(registry));
}
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
// conditionEvaluator 系统环境评估
this.conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator(registry, environment, null);
/**
*
* registerAnnotationConfigProcessors 这个方法很重要!
* 用于注册spring 自己的一些后置处理器
*
*/
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
public static void registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(registry, null);
}
/**
*
* 将Spring内部相关的后置处理器 注册 进BeanFactory中
* 一个有5个,这里重要关注 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor这个后置处理器
* BeanFactoryPostProcessor
* ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
* EventListenerMethodProcessor
*
* BeanPostProcessor
* AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
* CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
* PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
*
* DefaultEventListenerFactory
*
*
* Register all relevant annotation post processors in the given registry.
* @param registry the registry to operate on
* @param source the configuration source element (already extracted)
* that this registration was triggered from. May be {@code null}.
* @return a Set of BeanDefinitionHolders, containing all bean definitions
* that have actually been registered by this call
*/
public static Set registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
/**
* 判断获取BeanFactory是 什么类型并返回对应的beanFactory,但是AnnotatedConfigApplicationContext的父类默认使用的就是DefaultListableBeanFactory
* 所以返回的beanFactory是DefaultListableBeanFactory
*/
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
if (beanFactory != null) {
// 如果 beanFactory使用的依赖比较器 不是 AnnotationAwareOrderComparator 类型,就给这个beanFactory传入一个AnnotationAwareOrderComparator
if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
// 如果beanFactory使用的AutowireCandidateResolver 不是ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver,就这个beanFactory 传入一个ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver
if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());
}
}
/**
* 定义一个LinkedHashSet用于存放BeanDefinitionHolder,默认8个空间
* BeanDefinitionHolder 是BeanDefinition 的一层封装
* BeanDefinition
* java一切皆对象。
* 一个类 在jvm中是用Class对象来表示的。
* 在Spring中就是通过BeanDefionition来表示被Spring容器管理的类
*/
Set beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
/**
* 1
*
* 判断容器中是否已经存在org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
* 如果不存在,则 使用ConfigurationClassProcessor创建一个RootBeanDefinition。
* RootBeanDefintion 是 BeanDefinition的一个子类,
* ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 很重要!!!
* ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 这个类应该是使用了@Configuration注解的 类的后置处理器?
*
* org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
*
*/
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
/**
* 首先通过
* registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)
* 将 RootBeanDefinition注册到容器中
* beanDefs.add() 将返回的BeanDefinitionHolder 放进Set集合中
*/
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
/**
* 2
* 同上操作,这里判断的是 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
*
*/
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
/**
* 3
* 同上操作,这里判断的是 CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
*/
// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
/**
* 4
* 同上操作,这里判断的是 PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
*
*/
// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();
try {
def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME,
AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader()));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);
}
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
/**
* 5
* 同上操作,这里判断的是 EventListenerMethodProcessor
*/
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
/**
* 6
*
*/
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));
}
return beanDefs;
}
BeanDefinition主要是用来描述被Spring管理的类及其属性,如单例还是元型、依赖等
在上面的部分出现了一个超级超级重量级的嘉宾:ConfigurationClassPostProcessor。这个类是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的子类。而BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是BeanFactory的子类。在后面会介绍它为什么如此的重要。
此时,BeanFactory中已经将Spring内部的2个BeanFactoryPostProcessor和3个BeanPostProcessor和一个EventListenerFactory分别包装成BeanDefinition注册到BeanFactory中了!
3、ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
/**
* step3
* 实例化一个 扫描器,将当前对象传递给reader!!!
* 用于扫描指定路径包及包中的类
* 实际上在初始化是这个scanner并没有用?
* 先不看这个类的初始化
*/
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
这个scanner的作用主要在于程序员可以手动的指定包扫描路径。
例如:
annotationConfigApplicationContext.scan(“com.jds”);
实际上大部分时候,我们都是使用注解的方式指定包扫描路径:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.jds")
public class AppConfig {
}
二、向Context中注册
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、Context的初始化
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
annotationConfigApplicationContext.scan("com.jds");
// 2、向Context中注册
annotationConfigApplicationContext.register(AppConfig.class);
// 3、Context启动
annotationConfigApplicationContext.refresh();
UserService userService = (UserService) annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("userServiceImpl");
userService.queryUser();
}
@Override
public void register(Class... componentClasses) {
Assert.notEmpty(componentClasses, "At least one component class must be specified");
this.reader.register(componentClasses);
}
public class AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader {
public void register(Class... componentClasses) {
for (Class componentClass : componentClasses) {
registerBean(componentClass);
}
}
}
public class AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader {
private void doRegisterBean(Class beanClass, @Nullable String name,
@Nullable Class[] qualifiers, @Nullable Supplier supplier,
@Nullable BeanDefinitionCustomizer[] customizers) {
/**
* 将传入的Class对象封装成一个BeanDefinition类型的AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition对象
*
*/
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition abd = new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(beanClass);
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(abd.getMetadata())) {
return;
}
abd.setInstanceSupplier(supplier);
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(abd);
abd.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = (name != null ? name : this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(abd, this.registry));
/**
* 上面将传入的class 转换成AnnotedGenericBeanDefinition对象
* 使用AnnotationConfigUtils将这个beanDefinition 判断是否加了常用的注解并 设置beanDefinition的属性值以便后面可以正确的生成bean
*
*/
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd);
if (qualifiers != null) {
for (Class qualifier : qualifiers) {
if (Primary.class == qualifier) {
abd.setPrimary(true);
}
else if (Lazy.class == qualifier) {
abd.setLazyInit(true);
}
else {
abd.addQualifier(new AutowireCandidateQualifier(qualifier));
}
}
}
if (customizers != null) {
for (BeanDefinitionCustomizer customizer : customizers) {
customizer.customize(abd);
}
}
/**
* 将AnnotedGenericBeanDefinition转换成BeanDefinitionHolder
* AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode 这个是干嘛用的?
* 根据org.springframework.context.annotation.ScopedProxyMode 判断是否生成代理 替换到definitionHolder
*
*
*/
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName);
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
// 将 这个BeanDefinitionHolder 注册进容器中
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
通过BeanDefinitionReaderUtils将类注册到BeanFactory中,这个注册的过程还是很重要的。这里不详细叙述。
三、Context的启动
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、Context的初始化
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
annotationConfigApplicationContext.scan("com.jds");
// 2、向Context中注册
annotationConfigApplicationContext.register(AppConfig.class);
// 3、Context启动
annotationConfigApplicationContext.refresh();
UserService userService = (UserService) annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean("userServiceImpl");
userService.queryUser();
}
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext {
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
/**
* ConfigurableListableBeanFactory 实际是 DefaultListableBeanFactory
*/
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 什么也没做
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
/**
* 注册自定义的BeanFacotryPostProcessor和自定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor到BeanFactory中,部分已经由BeanDefinition实例化为bean
*
* 这里会解析@Connfiguration @Import @ComponetSacn @ImportSource 等注解
*
*
*
* 会完成包的扫描等工作,将扫描到的类转成BeanDefinition
*
*
*/
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
/**
* 注册Spring定义的BeanPostProcessor和自定义的BeanPostProcessor到BeanFactory中
*
* 部分自定义的BeanPostProcessor再这里已经由BeanDefinition实例化为bean
*
*/
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
/**
* 普通的非延迟加载的bean 在这里被beanFactory由BeanDefinition实例化为bean
*
* 这里进行Aspecjt织入、循环依赖处理等操作,最终实例化 bean
*
*/
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
}
对refresh每一步进行分析:
3.1、prepareRefresh();
这一步主要是容器初始化的一些配置,比如记录启动时间,启动监听器等…
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext {
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// Switch to active.
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.closed.set(false);
this.active.set(true);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
}
else {
logger.debug("Refreshing " + getDisplayName());
}
}
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment.
initPropertySources();
// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable:
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// Store pre-refresh ApplicationListeners...
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {
this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.applicationListeners);
}
else {
// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
}
3.2、获取beanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
3.3、容器启动的一些准备工作
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext {
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
if (!shouldIgnoreSpel) {
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
/**
* ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
*/
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (!IN_NATIVE_IMAGE && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
}
为beanFactory设置了 classLoader
添加了2个BeanPostProcessor new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this)、new ApplicationListenerDetector(this)
添加了几个Spring内部的单例bean : environment systemProperties systemEnvironment
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor从这个后置处理器可以发现Spring开放一些功能,让我们可以获取到Spring内置的变量。让程序员有能力使用Spring中的一些功能。比如大名鼎鼎的ApplicationContextAware
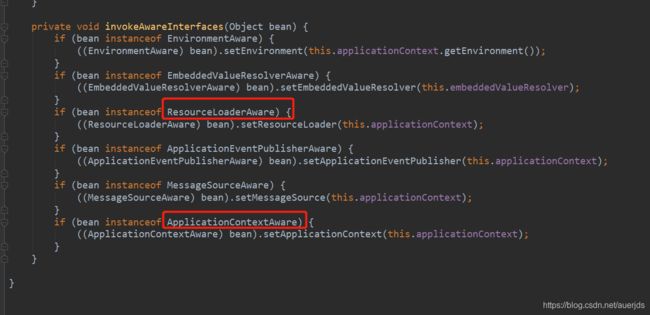
当前还有其他的BeanPostProcessor后主处理器。比如ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的内部类ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor。
3.4、postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
这里什么也没做!
3.5、invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
高能预警!
这个方法执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor及其子类。我们自定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor在交给Spring管理时也是在这里被执行的。
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext{
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
}
注意这里的getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法。
如果是程序员自定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor并且是通过context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor() 方式添加的,那么这里会获取到。
而如果是通过@Bean、@Component、@Import 方式这里是获取不到的,因为这几种方式并不会将BeanFactoryPostProcessor放入到AbstractApplicationContext中的beanFactoryPostProcessors 中,而是直接包装成BeanDefinition直接放入到BeanFactory中的beanDefinitionMap
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext{
private final List beanFactoryPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
}
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory {
private final Map beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
}
来仔细的看看是怎么执行这些BeanFactoryPostProcessor的。这里都做了一些什么工作呢?
咱们分为两个阶段去分析:
第一个阶段:执行所有的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
第二个阶段:执行所有的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
第一阶段
final class PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate {
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
//如果beanFactory是BeanDefinitionRegistry类型
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
//普通的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的后置处理器
List regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
//BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子类BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor型的后置处理器
List registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
//对context.register()方式测测的beanFactory进行分类
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
/**
* 执行 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 中扩展的方法postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry()
*
*/
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
List currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 从beanFacttory中拿出所有BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的子类
* 除了包含Spring内置的ConfigurationClassPostProcessor外,
*
* 但是如果仅仅是@Component方式,这里是不会被查询到的!
*/
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
/**
* 根据后置处理器的名字判断,这个后置处理器是否是PriorityOrdered的子类
* 而Spring内置的ConfigurationClassPostProcessor实现了PriorityOrdered接口
*/
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
/**
*
* beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)
* 因为要执行后置处理器中的方法,所以必须得到它的实例才能执行其中的方法。
* 所以在这里实例化了一个ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的单例,并放入到DefaultListableBeanFactory的earlySingletonObjects集合中
*
* currentRegistryProcessors.add()
* 将实例化的后置处理器实例放入 待执行的集合中
*/
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
/**
* 待执行的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的实例依次执行 扩展方法
*
*
* 因为ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 会 对DefaultListableBeanFactory中的beanDefinitionMap进行遍历,
* 并处理@Configuration @Component @ComponentScan @Import 注解
*
* 这个方法会扫描@ComponetScan 指定包下的类,这些类会封装成BeanDefinition放进beanFactory的Map中
* 也就是在这个时候自定义的@Bean @Component @Import方式的BeanFactiryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor 被放入beanFactory中
*
*
*/
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
//清空待执行的 currentRegistryProcessors集合
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
/**
* 自定义的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的实现类
* 如果自定义的类同时实现了org.springframework.core.Ordered接口则会立即执行自定义的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的实现类
*/
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
/**
* 执行没有实现org.springframework.core.Ordered接口的自定义BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
*
*/
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
/**
*
* 使用@Componet注解和register()方式进来的,都在这里被获取到
* 因为上面已经进行了扫描,将所有需要交给Spring管理的类 转换成了BeanDefinition对象
*
*/
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
//执行Spring内置的和自定义的并且直接继承BeanFactoryPostProceosser接口的后置处理器
/**
* priorityOrderedPostProcessors
*/
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
/**
* orderedPostProcessors
*/
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
/**
* other
*/
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
}
刨除用户通过context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor方式注册的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的实现类,看一看Spring都做了什么工作:
First
First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
final class PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate {
private static void invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(
Collection postProcessors, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
for (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
}
}
}
Spring内置的ConfigurationClassPostProcessor实现了PriorityOrdered接口。
咱们主要看看Spring内置的ConfigurationClassPostProcessor做了哪些工作。
public class ConfigurationClassPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,
PriorityOrdered, ResourceLoaderAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware {
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
int registryId = System.identityHashCode(registry);
if (this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
}
if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
}
this.registriesPostProcessed.add(registryId);
processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry);
}
}
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的processConfigBeanDefinitions()方法
processConfigBeanDefinitions从这个方法名,可以看出这个方法主要是来处理配置类的,也就是加了@Configuration注解的类
public class ConfigurationClassPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,
PriorityOrdered, ResourceLoaderAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware {
}
processConfigBeanDefinitions()
processConfigBeanDefinitions()方法拆分成几个Step进行查看:
Step1
先看该方法的前半部分,将BeanFactory中beanDefinitionNames进行遍历,判断是否是后续要解析的BeanDefinition.如果是需要解析的则标记是full类型还是lite类型,并放入configCandidates集合中。
List configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
//从beanFactory中获取所有的beanDefinition names
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanName : candidateNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (beanDef.getAttribute(ConfigurationClassUtils.CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef);
}
}
/**
* ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate()
* 判断 beanDef是否是被@Configuration注解的类,
* 并判断是full还是lite
*
* 包含@Configuration注解的类被标记为full
* 如果仅包含了一个或多个下面4种注解,则被标记为lite
* @Component.class
* @ComponentScan.class
* @Import.class
* @ImportResource.class
*
* 不管这个类是full 还是lite 程序会接着往下走。
* 否则就被返回
*/
else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));
}
}
通过ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate()方法判断BeanDefinition 是full还是lite类型:
abstract class ConfigurationClassUtils {
public static final String CONFIGURATION_CLASS_FULL = "full";
public static final String CONFIGURATION_CLASS_LITE = "lite";
public static final String CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE =
Conventions.getQualifiedAttributeName(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class, "configurationClass");
private static final String ORDER_ATTRIBUTE =
Conventions.getQualifiedAttributeName(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class, "order");
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ConfigurationClassUtils.class);
private static final Set candidateIndicators = new HashSet<>(8);
static {
candidateIndicators.add(Component.class.getName());
candidateIndicators.add(ComponentScan.class.getName());
candidateIndicators.add(Import.class.getName());
candidateIndicators.add(ImportResource.class.getName());
}
/**
* Check whether the given bean definition is a candidate for a configuration class
* (or a nested component class declared within a configuration/component class,
* to be auto-registered as well), and mark it accordingly.
* @param beanDef the bean definition to check
* @param metadataReaderFactory the current factory in use by the caller
* @return whether the candidate qualifies as (any kind of) configuration class
*/
public static boolean checkConfigurationClassCandidate(
BeanDefinition beanDef, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) {
String className = beanDef.getBeanClassName();
if (className == null || beanDef.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
// 如果 BeanDefinition对象中的类名为null 或者 BeanDefinition对象 定义了 工厂方法,那么返回false
return false;
}
AnnotationMetadata metadata;
if (beanDef instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition &&
className.equals(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef).getMetadata().getClassName())) {
// Can reuse the pre-parsed metadata from the given BeanDefinition...
metadata = ((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef).getMetadata();
}
else if (beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef).hasBeanClass()) {
// Check already loaded Class if present...
// since we possibly can't even load the class file for this Class.
Class beanClass = ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef).getBeanClass();
if (BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) ||
BeanPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) ||
AopInfrastructureBean.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) ||
EventListenerFactory.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass)) {
return false;
}
metadata = AnnotationMetadata.introspect(beanClass);
}
else {
try {
MetadataReader metadataReader = metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(className);
metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
}
catch (IOException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not find class file for introspecting configuration annotations: " +
className, ex);
}
return false;
}
}
/**
* 以上的if else 中 都是为了获取beanDefinition的metadata数据
*/
/**
* 根据metadata信息,判断BeanDefinition是否加了@Configuration注解
* 如果加了@Configuration注解,则将该BeanDefinition标记为full
*
* full 和 lite 的作用
*
*
*/
Map config = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(Configuration.class.getName());
if (config != null && !Boolean.FALSE.equals(config.get("proxyBeanMethods"))) {
beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_FULL);
}
/**
* 如果仅仅加了这4个注解标注的类 会被标记为 lite
* Component.class
* ComponentScan.class
* Import.class
* ImportResource.class
*
*/
else if (config != null || isConfigurationCandidate(metadata)) {
beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_LITE);
}
else {
// 如果没有加@Configuration @Component @ComponentScan @Import @ImportResource 任意一个注解,则返回false
return false;
}
// It's a full or lite configuration candidate... Let's determine the order value, if any.
Integer order = getOrder(metadata);
if (order != null) {
beanDef.setAttribute(ORDER_ATTRIBUTE, order);
}
return true;
}
}
已经被标记为full、lite类型的BeanDefinition已经被放入到了configCandidates集合中了。这个full、lite标记有什么作用呢?
Step2
该方法中间一部分,是进行一些排序、是否需要默认的beanName生成策略、是否要进行默认的系统环境信息等处理。
//如果configCandidates集合为空,则说明没有需要解析的类,则返回
// Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found
if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// BeanDefinition包装的类是否加了排序注解@Order,并根据@Order值进行排序
// Sort by previously determined @Order value, if applicable
configCandidates.sort((bd1, bd2) -> {
int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition());
int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition());
return Integer.compare(i1, i2);
});
// beanName 生成策略
// Detect any custom bean name generation strategy supplied through the enclosing application context
SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null;
if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) {
sbr = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry;
if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet) {
BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(
AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR);
if (generator != null) {
this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator;
this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator;
}
}
}
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();
}
Step3
该部分是高能核心部分了。对配置类进行解析并扫描类封装成BeanDefinition,以及@Import方式的类的处理等操作:
/**
* 解析@Configuration类的ConfigurationClassParser对象的实例化
*/
// Parse each @Configuration class
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
Set candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates);
Set alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size());
do {
/**
* 解析@Configuration注解类,判断是否包含@CompontScan注解,包含则进行包扫描,scanner是新实例化的
*
*/
parser.parse(candidates);
parser.validate();
Set configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);
// Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content
if (this.reader == null) {
this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(
registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,
this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);
candidates.clear();
if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {
String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
Set oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames));
Set alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>();
for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {
alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {
if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {
BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&
!alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) {
candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName));
}
}
}
candidateNames = newCandidateNames;
}
}
while (!candidates.isEmpty());
这里主要看其中的parser.parse(candidates);
class ConfigurationClassParser {
/**
* 开始解析
* @param configCandidates
*/
public void parse(Set configCandidates) {
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : configCandidates) {
BeanDefinition bd = holder.getBeanDefinition();
// 从bd获取一些信息 进封装,再进行解析
try {
if (bd instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName());
}
else if (bd instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).hasBeanClass()) {
parse(((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).getBeanClass(), holder.getBeanName());
}
else {
parse(bd.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to parse configuration class [" + bd.getBeanClassName() + "]", ex);
}
}
this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.process();
}
}
class ConfigurationClassParser {
protected final void parse(@Nullable String className, String beanName) throws IOException {
Assert.notNull(className, "No bean class name for configuration class bean definition");
MetadataReader reader = this.metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(className);
processConfigurationClass(new ConfigurationClass(reader, beanName), DEFAULT_EXCLUSION_FILTER);
}
protected final void parse(Class clazz, String beanName) throws IOException {
processConfigurationClass(new ConfigurationClass(clazz, beanName), DEFAULT_EXCLUSION_FILTER);
}
protected final void parse(AnnotationMetadata metadata, String beanName) throws IOException {
processConfigurationClass(new ConfigurationClass(metadata, beanName), DEFAULT_EXCLUSION_FILTER);
}
}
class ConfigurationClassParser {
protected void processConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, Predicate filter) throws IOException {
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION)) {
return;
}
ConfigurationClass existingClass = this.configurationClasses.get(configClass);
if (existingClass != null) {
if (configClass.isImported()) {
if (existingClass.isImported()) {
existingClass.mergeImportedBy(configClass);
}
// Otherwise ignore new imported config class; existing non-imported class overrides it.
return;
}
else {
// Explicit bean definition found, probably replacing an import.
// Let's remove the old one and go with the new one.
this.configurationClasses.remove(configClass);
this.knownSuperclasses.values().removeIf(configClass::equals);
}
}
/**
* 再进行一层封装
*/
// Recursively process the configuration class and its superclass hierarchy.
SourceClass sourceClass = asSourceClass(configClass, filter);
do {
sourceClass = doProcessConfigurationClass(configClass, sourceClass, filter);
}
while (sourceClass != null);
this.configurationClasses.put(configClass, configClass);
}
}
将configClass进行再一次的封装,执行doProcessConfigurationClass()方法:
class ConfigurationClassParser {
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass, Predicate filter)
throws IOException {
if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) {
// 处理内部类
// Recursively process any member (nested) classes first
processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass, filter);
}
// Process any @PropertySource annotations
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class,
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) {
if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
else {
logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() +
"]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment");
}
}
// 处理@ComponentScan注解
// Process any @ComponentScan annotations
Set componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
//TODO 扫描包
// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately
Set scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
}
// 处理@Import注解
// Process any @Import annotations
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), filter, true);
// c处理@ImportResource注解
// Process any @ImportResource annotations
AnnotationAttributes importResource =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class);
if (importResource != null) {
String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations");
Class readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader");
for (String resource : resources) {
String resolvedResource = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource);
configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass);
}
}
// 单独处理@Bean方法
// Process individual @Bean methods
Set beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass);
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {
configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
// Process default methods on interfaces
processInterfaces(configClass, sourceClass);
// Process superclass, if any
if (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) {
String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName();
if (superclass != null && !superclass.startsWith("java") &&
!this.knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) {
this.knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass);
// Superclass found, return its annotation metadata and recurse
return sourceClass.getSuperClass();
}
}
// No superclass -> processing is complete
return null;
}
}
doProcessConfigurationClass()针对@PropertySource、@ComponentScan、@Import、@ImportResource、@Bean以及父类方法依次进行处理。下面依次看一下它是如何处理这些注解的:
-
1、@PropertySource
-
2、@ComponentScan
这里的代码不一句一句分析了。底层使用了asm的技术读取指定包路径下的所有class文件,然后在将这些class包装成BeanDefinition对象,并判断是否是需要SpringContext管理的类,如果需要被管理那么就将这个BeanDefinition放入到BeanFactory(即DefaultListableBeanFactory)中。 -
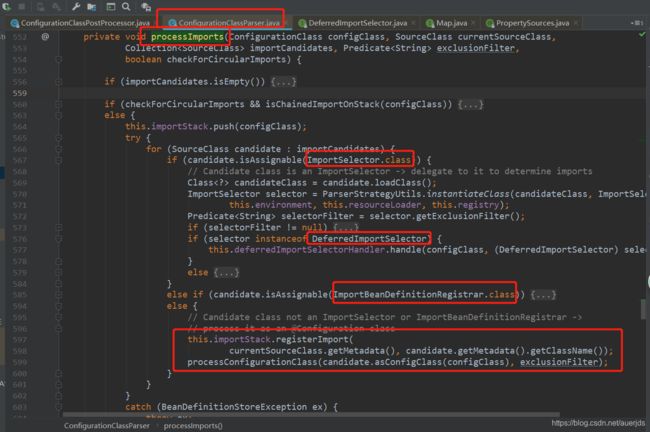
3、@Import
@Import 可以“导入”四种类型的类
- ImportSelector
- DeferredImportSelector
- ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
- 普通类(无@Component、@Import等注解的类)
这种方式提供了强大的整合功能。可以将其他框架整合到Spring环境中。
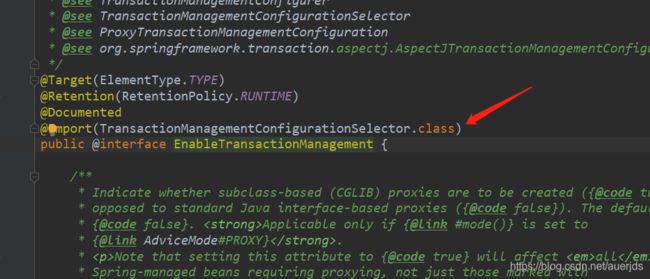
ImportSelector
开启Spring AOP 功能、开启声明式事务功能也是利用@Import“导入了”ImportSelector实现:

DeferredImportSelector
延迟“导入”,在SpringBoot中,这个接口的运用起到了很大的作用。
ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
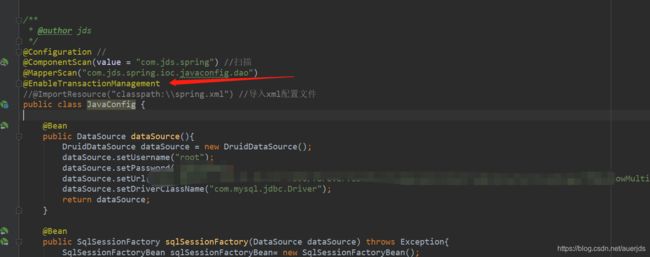
Mybaits在和Spring进行整合时,通过@MapperScan注解整合进Spring容器中。@MapperScan正是利用了@Import注解“导入”了一个ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar的子类MapperScannerRegistrar
-
4、@ImportResource
可以使用这个注解导入一个xml配置文件。实现了JavaConfig技术和xml技术混合使用的功能。 -
5、@Bean
可以在任意@Configuration、@Component、@Import 等注解的类中使用,向Spring容器注入一个bean。
比如:


注意
如果@Bean 的方法是static修饰的,那么该类在Spring将是元型的而不是单例的!
关于FactoryBean BeanFactory的区别、@Import的使用后面集合起来进行研究。
doProcessConfigurationClass()方法结束
Step4
// Register the ImportRegistry as a bean in order to support ImportAware @Configuration classes
if (sbr != null && !sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) {
sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) {
// Clear cache in externally provided MetadataReaderFactory; this is a no-op
// for a shared cache since it'll be cleared by the ApplicationContext.
((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this.metadataReaderFactory).clearCache();
}
将ImportRegistry实例化为一个bean,以支持ImportAware接口的子类。(Spring扩展点)
到这里ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的processConfigBeanDefinitions()就将所有需要Spring容器管理的类全部封装为BeanDefinition并放入到BeanFactory中。
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的processConfigBeanDefinitions() 方法 结束
通过ConfigurationClassPostProcessor这个BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的扩展方法postProcessorBeanDefinitionRegistry()将系统内置的和用户自定义的类封装成Spring可解析的BeanDefinition对象放入BeanFactory中了。
返回第一次执行的部分回顾一下后再接着往下看。
Next
Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
如果程序员自定义了@Component @Bean等注解的并且是Ordered实现的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors会在这里被执行扩展方法。
Finally
Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
剩下的所有已经添加到BeanFactory中并且未被执行的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors 实现类在这里会接着被执行扩展方法。
Now
Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
执行所有BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors实现类的实现方法postProcessorBeanFactory()。
这里咱们还是来看ConfigurationClassPostProcessor中实现方法做了什么事情:
public class ConfigurationClassPostProcessor{
....
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 判断当前这个对象有没有被同一个beanFactory调用过。(不能被同一个beanFactory多次调用)
int factoryId = System.identityHashCode(beanFactory);
if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(factoryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + beanFactory);
}
this.factoriesPostProcessed.add(factoryId);
// 是否执行了这个对象的扩展方法
if (!this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(factoryId)) {
// BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor hook apparently not supported...
// Simply call processConfigurationClasses lazily at this point then.
processConfigBeanDefinitions((BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory);
}
// full lite 的作用在这里体现出来了。被标记为full的类,使用cglib动态代理。为什么要这样呢?
enhanceConfigurationClasses(beanFactory);
// 向BeanFactroy中注册一个BeanPostProcessor.这个bean后置处理器就是为了使用户能够拥有ImportAware能力的处理器
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor(beanFactory));
}
...
}
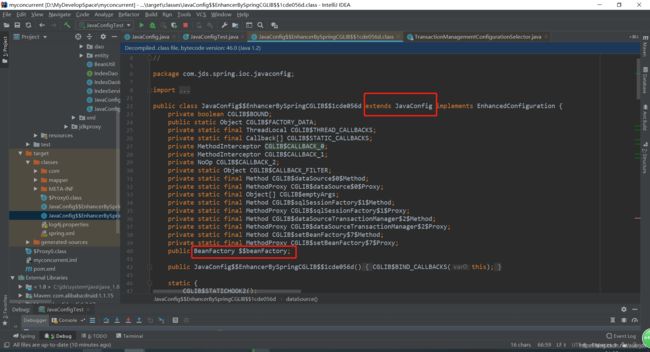
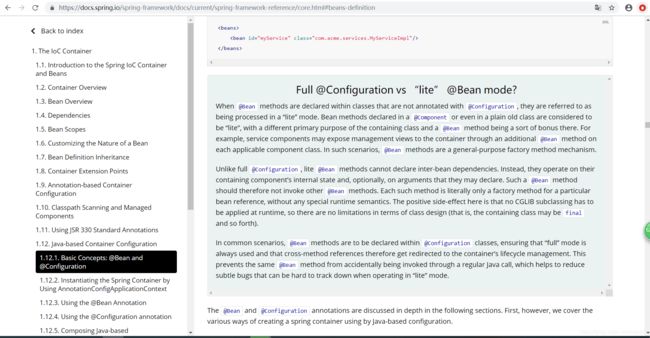
前面提到的full在这里就有了体现出来它的巨大作用了!对标记为full的类使用cglib动态代理。也就是对@Configuration注解的类进行动态代理。
那进行为什么要进行动态代理呢,目的是什么呢?
在前文提到@Bean可以在任何@Component类中使用,也可以在@Configuration类中使用。虽然都可以使用,但是它们是有不同的。
enhanceConfigurationClasses(beanFactory); 使用cglib代理将这些@Bean方法进行了方法代理。本篇不详细探讨该部分的源码了,以后有时间再详细看一看。
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor(beanFactory));
向beanFactory中注册了一个bean后置处理器,使得实现了ImportAware的类可以被拥有BeanFactory的引用。
到此,第一阶段完成,即所有的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor都已经执行完成(扩展的方法和父类的方法)。
第二阶段
第二阶段 开始执行所有BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子类。
Spring内置的两个:
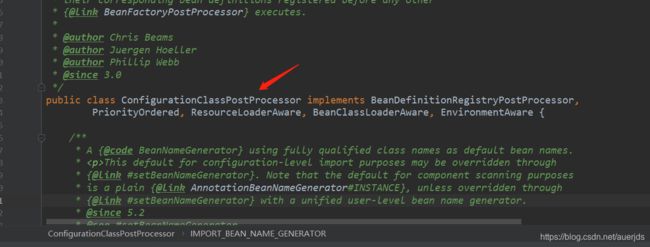

由于ConfigurationClassPostProcessor在第一阶段已经被执行完成了,所以在第二阶段会跳过。
而EventListenerMethodProcessor主要的作用对于加了@EventListener注解的方法转换成一个事件监听。具体怎么应用,目前还未研究过。
其它的由程序员定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor 。
第二阶段完成。
继续执行下面的代码:

在上文的分析中,我们可以发现所有的BeanFactoryPostProcessor在被执行前被实例化并注册到BeanFactory中了。
也就是从这个方法开始,Spring Bean的生命周期开始了!
3.6、registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
注册bean后置处理器
Spring内置了很多的bean后置处理器:
就当前这个环境,看看Spring容器使用了哪些Bean后置处理器呢?又做了什么事情呢?
还记得前文AnnotationBeanDefinitionReader的初始化吗?在那里就已经封装了3个BeanDefinition的BeanPostProcessor向BeanFactory中注册了。
- AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
- CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
- PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
其中 PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 是在使用jpa的时候才会注册到BeanFactory中。

那么registerBeanPostProcessors这个方法具体干嘛用呢?因为reader初始化的时候已经注册了啊。请看分析:
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
/**
* 从BeanFactory中取出已经注册的所有BeanPostProcessor的BD名字的数组
*/
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
/**
* BeanPostProcessorChecker对bean的初始化做检查,判断是否bean是否 适合被所有的BeanPostProcessor处理
*/
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
/**
* 以下代码是对所有的bean后置处理器进行bean的实例化,并注册到BeanFactory的beanPostProcessors集合中
*/
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
List nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// ApplicationListenerDetector bean的监听器
// Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
3.7、initMessageSource();
为此上下文初始化消息源。
3.8、initApplicationEventMulticaster();
为此上下文初始化事件多播器。
3.9、onRefresh();
空方法,什么也没做。
3.10、registerListeners();
检查侦听器bean并注册它们
3.11、 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
实例化所有的非延迟加载的类生成bean放入BeanFactory中。