C for Graphic:Ugui Line
最近个人项目中写了一个ugui的画线组件,水一篇博客算鸟。
现在正在做一个项目是纯二维的,我就直接用的ugui去写的,因为本身我已经四年没怎么做ui了,虽然市面上的gui插件都比ugui好用,组件丰富,功能齐全,但是我都没用过也不太会用。所以我就需要什么实现什么算了,下面就来说一下ugui中line的实现方式之一。
我们知道三维引擎中一切渲染皆是几何数据:点线面纹理材质等,ui也一样,都是世界空间中的几何数据。本身unity提供的linerenderer和tailrenderer可以在世界空间画线,那么我们仿写一个ugui版本的就行了,如下:
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.UI;
public class UguiTestMeshGraphic : Graphic
{
public float width = 100;
public float height = 10;
[Range(-50, 50)]
public float diff = 50;
protected override void OnPopulateMesh(VertexHelper vh)
{
base.OnPopulateMesh(vh);
vh.Clear();
UIVertex vertex = new UIVertex();
vertex.position = new Vector3(0, 0, 0);
vh.AddVert(vertex);
vertex = new UIVertex();
vertex.position = new Vector3(0, height, 0);
vh.AddVert(vertex);
vertex = new UIVertex();
vertex.position = new Vector3(width, height + diff, 0);
vh.AddVert(vertex);
vertex = new UIVertex();
vertex.position = new Vector3(width, diff, 0);
vh.AddVert(vertex);
vh.AddTriangle(0, 1, 2);
vh.AddTriangle(0, 2, 3);
}
}
直接通过UI.Graphic的OnPopulateMesh函数即可完成对UIMesh的绘制,比我们自己去实现顶点栅格化等图形流水线操作方便多了(我们之前聊过栅格化绘制线段和多边形的做法)。和创建Mesh一样,只需要将顶点坐标、三角拓扑、uvs等参数赋值,再写一个着色器渲染,就ok了,如下:
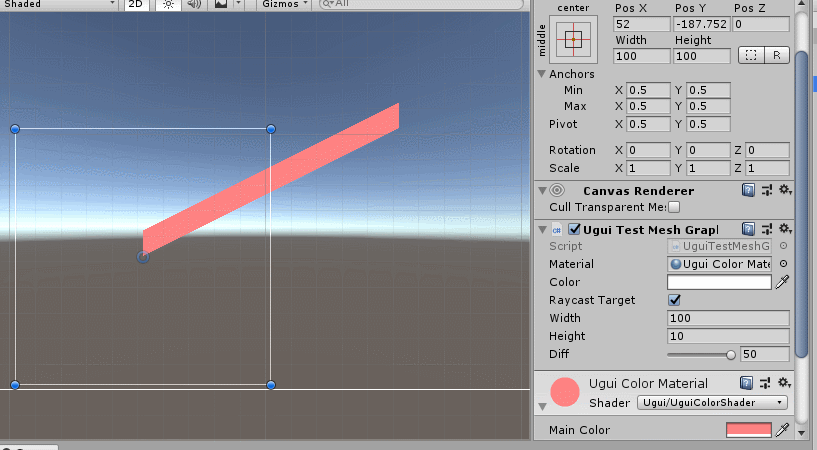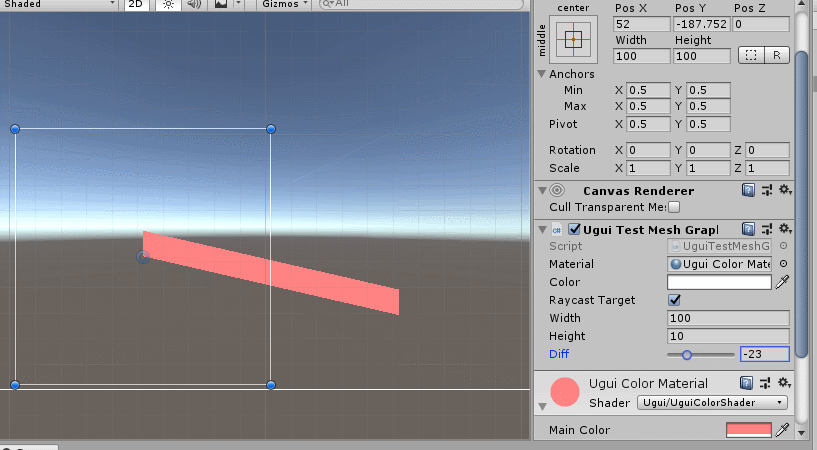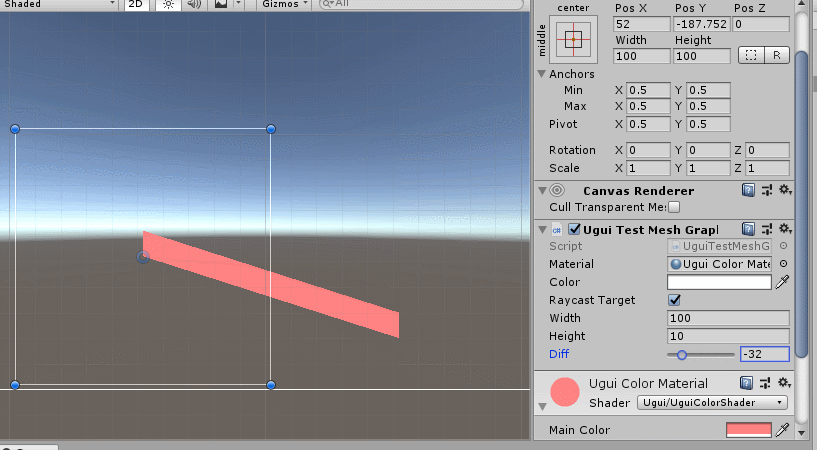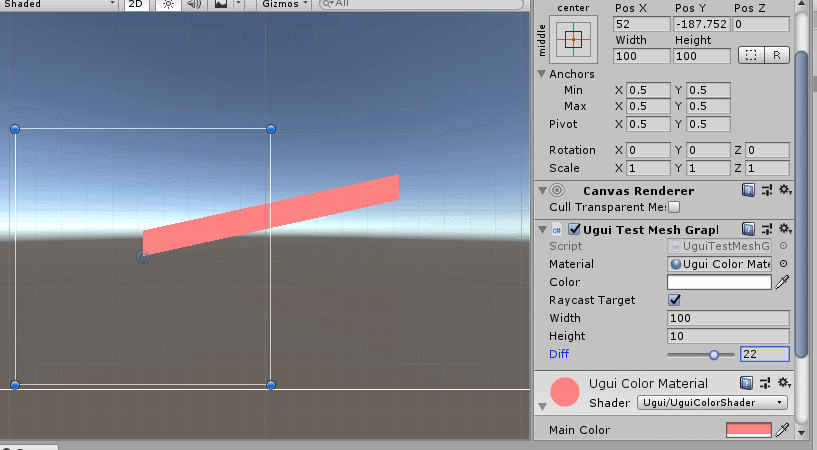
虽然线段在数学上就是一个公式,没有宽度,但是在图形学里它是有宽度的,也就是一个矩形,我们上面绘制的就可以认为是一个线段(虽然两个端的坐标是错误的)。那么继续扩展线段绘制功能,最好支持多坐标的连线,跟linerenderer一样,如下:
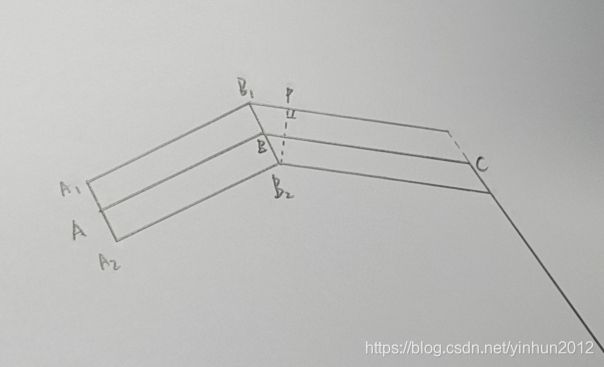
可以看出来一个问题,那就是我们用等高垂点计算法,则B2P模长小于B2B1,则中间BC线段会比起始AB线段“窄”。那么我们还得思考等宽线段绘制的解决方法,其实也不难解决,首先我们假定线段AB和BC的宽度相同,那么它们就存在两个交点B1B2,如下:

可以看得出来正确的B1和B2应该是线段(矩形)AB和BC的两条平行边的交点,那么问题就转化为求直线和直线相交的问题,首先让我们求出线段(矩形)AB的两条平行边,如下:

在二维平面上计算平行线A1B1和A2B2就相对简单。例如求A1和A2坐标,只需要根据A3点顺/逆时针旋转90度就得到了(B1和B2同理),那么实现以下:
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.UI;
public class UguiTestLineGraphic : Graphic
{
[Range(0, 20)]
public float width = 10f;
public Vector2 from;
public Vector2 to;
public RectTransform rectA;
public RectTransform rectB;
protected override void OnPopulateMesh(VertexHelper vh)
{
base.OnPopulateMesh(vh);
Vector2 a = from;
Vector2 b = to;
rectA.anchoredPosition = a;
rectB.anchoredPosition = b;
Vector2[] a1a2 = CalculateVerticalPoints(a, a, b, width);
Vector2[] b1b2 = CalculateVerticalPoints(b, a, b, width);
Vector2 a1 = a1a2[0];
Vector2 a2 = a1a2[1];
Vector2 b1 = b1b2[0];
Vector2 b2 = b1b2[1];
vh.Clear();
UIVertex vertex = new UIVertex();
vertex.position = a2;
vh.AddVert(vertex);
vertex = new UIVertex();
vertex.position = a1;
vh.AddVert(vertex);
vertex = new UIVertex();
vertex.position = b1;
vh.AddVert(vertex);
vertex = new UIVertex();
vertex.position = b2;
vh.AddVert(vertex);
vh.AddTriangle(0, 1, 2);
vh.AddTriangle(0, 2, 3);
}
/// 代码涉及的矩阵运算和向量运算以前已经讲过很多了,不再补充原理说明,如不清楚的同学可以回到我之前博客阅读理解。只需计算出A1A2和B1B2构建UIMesh即可,效果如下:

这样我们就绘制出了UILine,当然我们需要的功能支持顶点列表线段绘制,类似linerenderer的positions参数,我们继续改造,如下:

上图标注了两条线段(矩形)“上下边”的“交点”,同时我们需要处理直线相交的问题:
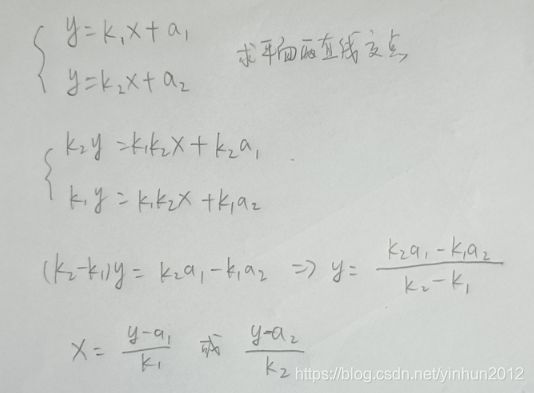
而且还要处理多个线段矩形(或多边形)组成的拓扑结构:
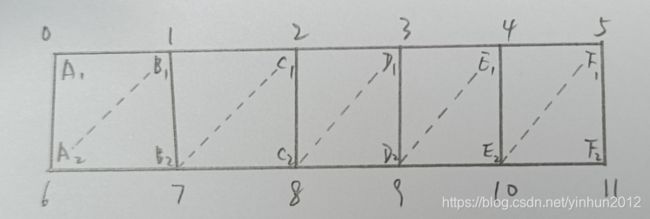
接下来才能开始写代码:
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.UI;
public class UguiLineGraphic : Graphic
{
[Range(0, 20)]
public float width = 10f;
public Vector2[] positions;
protected override void OnPopulateMesh(VertexHelper vh)
{
base.OnPopulateMesh(vh);
if (positions == null || positions.Length < 2)
{
return;
}
vh.Clear();
//如果只有两个顶点
//直接生成直线即可
if (positions.Length == 2)
{
Vector2 a = positions[0];
Vector2 b = positions[1];
Vector2[] a1a2 = CalculateVerticalPoints(a, a, b, width);
Vector2[] b1b2 = CalculateVerticalPoints(b, a, b, width);
Vector2 a1 = a1a2[0];
Vector2 a2 = a1a2[1];
Vector2 b1 = b1b2[0];
Vector2 b2 = b1b2[1];
UIVertex vertex = new UIVertex();
vertex.position = a2;
vh.AddVert(vertex);
vertex = new UIVertex();
vertex.position = a1;
vh.AddVert(vertex);
vertex = new UIVertex();
vertex.position = b1;
vh.AddVert(vertex);
vertex = new UIVertex();
vertex.position = b2;
vh.AddVert(vertex);
vh.AddTriangle(0, 1, 2);
vh.AddTriangle(0, 2, 3);
}
else
{
//如果是多顶点组成的矩形数组
//储存A1A2/B1B2...Z1Z2
List<Vector2[]> ptslist = new List<Vector2[]>();
//先储存A1A2
{
Vector2[] a1a2 = CalculateVerticalPoints(positions[0], positions[0], positions[1], width);
ptslist.Add(a1a2);
}
//再储存B1B2...Y1Y2
{
for (int i = 1; i < positions.Length - 1; i++)
{
Vector2 a = positions[i - 1];
Vector2 b = positions[i];
Vector2 c = positions[i + 1];
Vector2 d = positions[i]; //d=c
Vector2[] a1a2 = CalculateVerticalPoints(a, a, b, width);
Vector2[] b1b2 = CalculateVerticalPoints(b, a, b, width);
Vector2[] c1c2 = CalculateVerticalPoints(c, d, c, width);
Vector2[] d1d2 = CalculateVerticalPoints(d, d, c, width);
Vector2 a1 = a1a2[0];
Vector2 a2 = a1a2[1];
Vector2 b1 = b1b2[0];
Vector2 b2 = b1b2[1];
Vector2 c1 = c1c2[0];
Vector2 c2 = c1c2[1];
Vector2 d1 = d1d2[0];
Vector2 d2 = d1d2[1];
//如果线段AB和DC平行
if (IsVector2Approximiate(b1, d1) && IsVector2Approximiate(b2, d2))
{
//任意储存b1b2或d1d2
ptslist.Add(b1b2);
}
//如果线段AB和DC相交
else
{
Vector2 crossb1 = CalculateLineCross(a1, b1, c1, d1);
Vector2 crossb2 = CalculateLineCross(a2, b2, c2, d2);
//储存交点b1b2
ptslist.Add(new Vector2[] { crossb1, crossb2 });
}
}
}
//最后储存Z1Z2
{
Vector2[] z1z2 = CalculateVerticalPoints(positions[positions.Length - 1], positions[positions.Length - 2], positions[positions.Length - 1], width);
ptslist.Add(z1z2);
}
//再来构建网格
int ptcount = ptslist.Count * 2;
for (int i = 0; i < ptcount; i++)
{
int firstindex = i % ptslist.Count;
int secondindex = i / ptslist.Count;
UIVertex vertex = new UIVertex();
vertex.position = ptslist[firstindex][secondindex];
vh.AddVert(vertex);
}
int quadcount = ptslist.Count - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < quadcount; i++)
{
//quad左上角顺时针
int topleftindex = i;
int bottomleftindex = i + ptslist.Count;
vh.AddTriangle(topleftindex, topleftindex + 1, bottomleftindex);
vh.AddTriangle(topleftindex + 1, bottomleftindex + 1, bottomleftindex);
}
}
}
/// 效果如下:
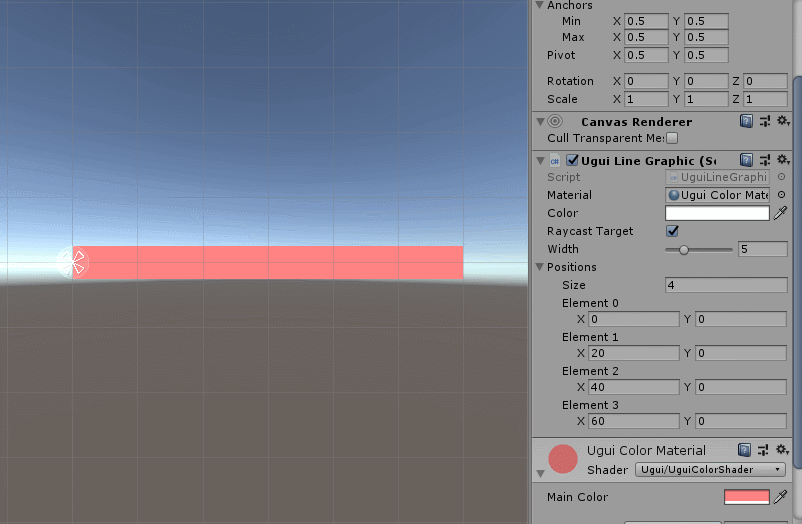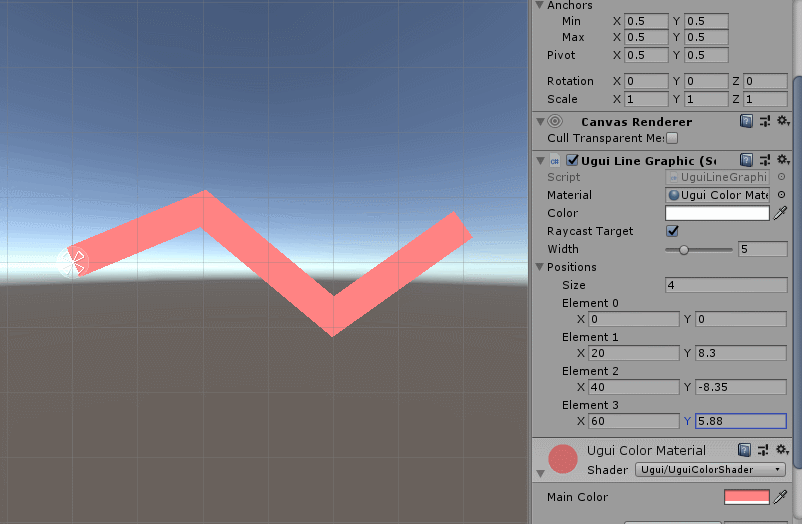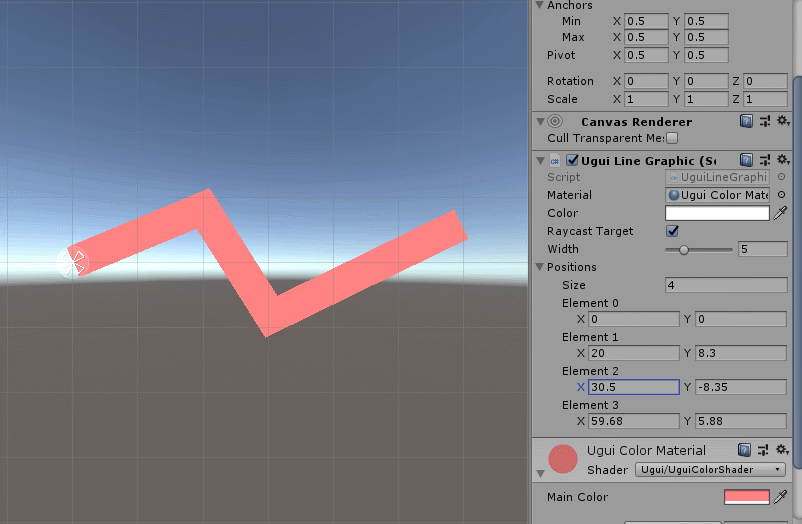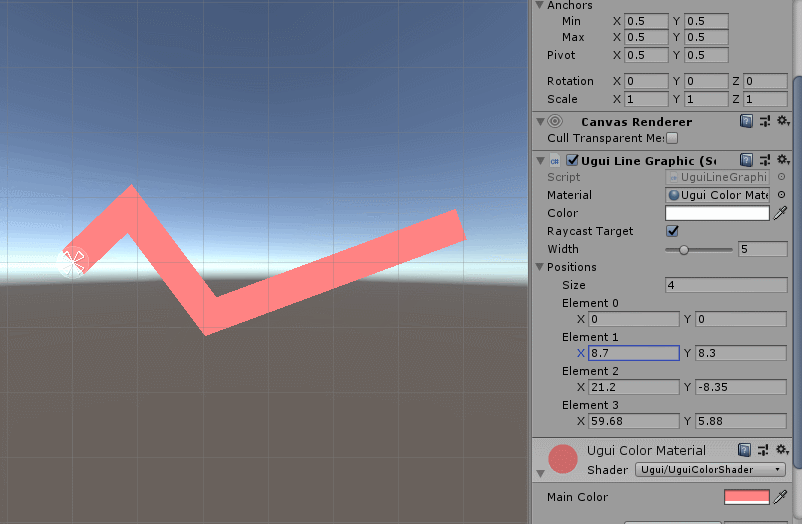
这样我们就将多节点线段绘制出来了,下面我们测试一下,比如写个“波浪线”:
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class UguiTestWaveLine : MonoBehaviour
{
[Range(0, 20)]
public float width = 5;
[Range(0, 20)]
public float height = 5;
[Range(10, 200)]
public int count = 100;
[Range(1, 20)]
public int wave = 10;
private UguiLineGraphic lineGraph;
public bool isRebuild = true;
void Start()
{
lineGraph = GetComponent<UguiLineGraphic>();
}
private void Update()
{
if (isRebuild)
{
Vector2[] poses = new Vector2[count];
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
Vector2 pos = new Vector2(width * i, Mathf.Sin((float)i / (float)wave * 360f * Mathf.Deg2Rad) * height);
poses[i] = pos;
}
lineGraph.positions = poses;
lineGraph.OnRebuildRequested();
isRebuild = false;
}
}
}
效果如下:

这样我们就完成了ui line的绘制,当然这里只是讲解绘制的原理,并不做特殊的图形渲染效果,如果有需要后面我再凑一篇讲解。