使用shader绘制矩形、矩形框、圆形、圆形框(WebGL-Shader开发基础02)
绘制矩形、矩形框、圆形、圆形框
- 1.绘制矩形
-
- 1.1 使用if语句绘制
- 1.2 使用step函数绘制
- 1.3 使用step函数简化方法绘制
- 1.4 使用abs对称思想绘制
- 1.5 绘制矩形边框
- 2. 绘制圆
-
- 2.1 绘制圆形
- 2.2 绘制圆形框
- 3. demo代码
1.绘制矩形
上一篇文章学习如何绘制线,现在学习如何绘制面,先从绘制矩形开始,其实绘制矩形的思想与绘制线的思想一样,只不过绘制线时限制的区域窄一些,绘制矩形限制的区域宽一些,先来看看绘制第一种绘制矩形的代码
1.1 使用if语句绘制
思想上面已经说过了,这里只是实践一下,我们封装一个绘制矩形的函数box0,过程是定义四个边界的值,如果满足矩形区域的坐标返回1.0,否则返回0.0
float box0(vec2 st){
float left = 0.0;
float right = 0.4;
float top = 0.6;
float bottom = 0.2;
if(st.x > left && st.x < right && st.y > bottom && st.y < top){
return 1.0;
}else{
return 0.0;
}
}
调用过程
pct = box0(st);
color = mix(color,line_color,pct);
1.2 使用step函数绘制
使用step函数绘制,其实就是第一种方式的使用step函数转换,顺便说一句,在写shader的过程中尽量避免使用if判断,因为在逐片元处理的过程中做if判断很耗费性能,这次封装为函数box1
float box1(vec2 st){
float left = 0.0;
float right = 0.4;
float top = 0.6;
float bottom = 0.2;
//左右边界
float x1 = step(left,st.x);
float x2 = step(right,1.0-st.x); //检测值要小于右边界才应该返回1.0,所以使用1.0-st.x
//上下边界
float y1 = step(bottom,st.y);
float y2 = step(top,1.0-st.y);//检测值要小于上边界才应该返回1.0,所以使用1.0-st.y
float pct = x1 * x2 *y1 *y2;
return pct;
}
1.3 使用step函数简化方法绘制
上面的函数中分别使用屏幕坐标st.x 和 st.y 分别进行处理,能否合并呢,答案是可以的,不过处理时先处理左下边界,在处理右上边界,然后通过乘法将它们合并,具体如下
float box2(vec2 st){
float left = 0.0;
float right = 0.4;
float top = 0.6;
float bottom = 0.2;
//左下边界
vec2 bl = step(vec2(left,bottom),st);
float pct = bl.x * bl.y;
//右上边界
vec2 tr = step(vec2(right,top),1.0-st);//检测值要小于右上边界才应该返回1.0,所以使用1.0-st
pct *= tr.x * tr.y;
return pct;
}
1.4 使用abs对称思想绘制
其实绘制矩形的方法可以进一步简化,利用abs函数通过原点对称的思想只需要限制上边界和右边界,就可以绘制出矩形,具体如下
float box3(vec2 st){
float right = 0.9;
float top = 0.3;
//通过右上角绘制原点对称的四边形
vec2 bl = 1.0-step(vec2(right,top),abs(st));
float pct = bl.x * bl.y;
return pct;
}
1.5 绘制矩形边框
第四种方法代码量最少,又高大上,我们就在它的基础上从里面扣掉小一点的矩形,就可以得到一个矩形边框,实现如下
float box4(vec2 st){
float right = 0.9;
float top = 0.3;
float line_width = 0.03;
//通过右上角绘制原点对称的四边形
vec2 b1 = 1.0-step(vec2(right,top),abs(st));
float boxouter = b1.x * b1.y;
vec2 b2 = 1.0-step(vec2(right-line_width,top-line_width),abs(st));
float boxinner = b2.x * b2.y;
float pct = boxouter -boxinner;
return pct;
}
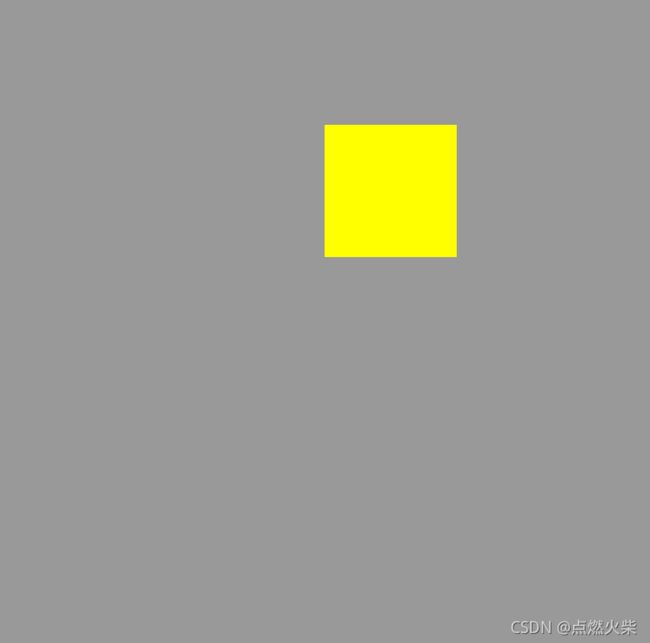
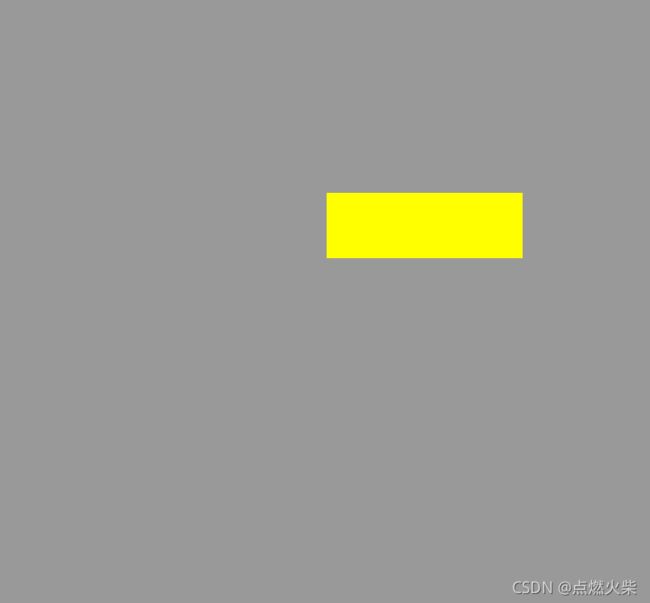
执行结果如下

如果你对绘制的结果不满意,可以调整边界和线框宽度,有小伙伴可能要问,我不想让它经过原点,又希望使用这种方式绘制,怎么办,可以先绘制好然后将它平移一下,平移这里就不讲了,后面写一遍文章专门讲述图形的平移、旋转、缩放
2. 绘制圆
2.1 绘制圆形
绘制圆思想也是一样,给满足条件的圆内涂上定义的颜色,圆的定义是到某一点的距离等于定长的点的集合,我们分别使用 distance(), length() 或 sqrt() 方式绘制圆,这一次使用smoothstep函数绘制,目的是为了消除锯齿,具体如下
float circle(vec2 st,vec2 center,float radius) {
float blur = 0.002;
//float pct = distance(st,center);//计算任意点到圆心的距离
vec2 tC = st-center; //计算圆心到任意点的向量
//float pct = length(tC);//使用length函数求出长度
float pct = sqrt(tC.x*tC.x+tC.y*tC.y);//使用开平方的方法求出长度
return 1.0-smoothstep(radius,radius+blur,pct);
}
2.2 绘制圆形框
绘制了圆,绘制圆形框就是在圆上扣掉一个较小的圆即可,具体如下
float circleLine(vec2 st,vec2 center,float radius) {
float pct = distance(st,center);//计算任意点到圆心的距离
float line_width = 0.02;
float radius2 = radius-line_width;
float blur = 0.002;
return (1.0-smoothstep(radius-blur,radius+blur,pct))-(1.0-smoothstep(radius2-blur,radius2+blur,pct));
}
3. demo代码
老规矩,附上demo所有代码
<body>
<div id="container"></div>
<script src="http://www.yanhuangxueyuan.com/versions/threejsR92/build/three.js"></script>
<script>
var container;
var camera, scene, renderer;
var uniforms;
var vertexShader = `
void main() {
gl_Position = vec4( position, 1.0 );
}
`
var fragmentShader = `
#ifdef GL_ES
precision mediump float;
#endif
uniform float u_time;
uniform vec2 u_mouse;
uniform vec2 u_resolution;
float box0(vec2 st){
float left = 0.0;
float right = 0.4;
float top = 0.6;
float bottom = 0.2;
if(st.x > left && st.x < right && st.y > bottom && st.y < top){
return 1.0;
}else{
return 0.0;
}
}
float box1(vec2 st){
float left = 0.0;
float right = 0.4;
float top = 0.6;
float bottom = 0.2;
//左右边界
float x1 = step(left,st.x);
float x2 = step(right,1.0-st.x); //检测值要小于右边界才应该返回1.0,所以使用1.0-st.x
//上下边界
float y1 = step(bottom,st.y);
float y2 = step(top,1.0-st.y);//检测值要小于上边界才应该返回1.0,所以使用1.0-st.y
float pct = x1 * x2 *y1 *y2;
return pct;
}
float box2(vec2 st){
float left = 0.0;
float right = 0.4;
float top = 0.6;
float bottom = 0.2;
//左下边界
vec2 bl = step(vec2(left,bottom),st);
float pct = bl.x * bl.y;
//右上边界
vec2 tr = step(vec2(right,top),1.0-st);//检测值要小于右上边界才应该返回1.0,所以使用1.0-st
pct *= tr.x * tr.y;
return pct;
}
float box3(vec2 st){
float right = 0.9;
float top = 0.3;
//通过右上角绘制原点对称的四边形
vec2 bl = 1.0-step(vec2(right,top),abs(st));
float pct = bl.x * bl.y;
return pct;
}
float box4(vec2 st){
float right = 0.9;
float top = 0.3;
float line_width = 0.03;
//通过右上角绘制原点对称的四边形
vec2 b1 = 1.0-step(vec2(right,top),abs(st));
float boxouter = b1.x * b1.y;
vec2 b2 = 1.0-step(vec2(right-line_width,top-line_width),abs(st));
float boxinner = b2.x * b2.y;
float pct = boxouter -boxinner;
return pct;
}
float circle(vec2 st,vec2 center,float radius) {
float blur = 0.002;
//float pct = distance(st,center);//计算任意点到圆心的距离
vec2 tC = st-center; //计算圆心到任意点的向量
//float pct = length(tC);//使用length函数求出长度
float pct = sqrt(tC.x*tC.x+tC.y*tC.y);//使用开平方的方法求出长度
return 1.0-smoothstep(radius,radius+blur,pct);
}
float circleLine(vec2 st,vec2 center,float radius) {
float pct = distance(st,center);//计算任意点到圆心的距离
float line_width = 0.02;
float radius2 = radius-line_width;
float blur = 0.002;
return (1.0-smoothstep(radius-blur,radius+blur,pct))-(1.0-smoothstep(radius2-blur,radius2+blur,pct));
}
void main( void ) {
//窗口坐标调整为[-1,1],坐标原点在屏幕中心
vec2 st = (gl_FragCoord.xy * 2. - u_resolution) / u_resolution.y;
//窗口坐标调整为[0,1],坐标原点在屏幕左下角
//vec2 st = gl_FragCoord.xy/u_resolution;
vec3 line_color = vec3(1.0,1.0,0.0);
vec3 color = vec3(0.6);//背景色
float pct = 0.0;
pct = box0(st);
pct = box1(st);
pct = box2(st);
pct = box3(st);
pct = box4(st);
//color = mix(color,line_color,pct);
pct = circle(st,vec2(-0.3),0.4);
//color = mix(color,line_color,pct);
pct = circleLine(st,vec2(0.3),0.4);
color = mix(color,line_color,pct);
gl_FragColor = vec4(color, 1);
}
`
init();
animate();
function init() {
container = document.getElementById('container');
camera = new THREE.Camera();
camera.position.z = 1;
scene = new THREE.Scene();
var geometry = new THREE.PlaneBufferGeometry(2, 2);
uniforms = {
u_time: {
type: "f",
value: 1.0
},
u_resolution: {
type: "v2",
value: new THREE.Vector2()
},
u_mouse: {
type: "v2",
value: new THREE.Vector2()
}
};
var material = new THREE.ShaderMaterial({
uniforms: uniforms,
vertexShader: vertexShader,
fragmentShader: fragmentShader
});
var mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
scene.add(mesh);
renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
//renderer.setPixelRatio(window.devicePixelRatio);
container.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
onWindowResize();
window.addEventListener('resize', onWindowResize, false);
document.onmousemove = function (e) {
uniforms.u_mouse.value.x = e.pageX
uniforms.u_mouse.value.y = e.pageY
}
}
function onWindowResize(event) {
renderer.setSize(800, 800);
uniforms.u_resolution.value.x = renderer.domElement.width;
uniforms.u_resolution.value.y = renderer.domElement.height;
}
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
render();
}
function render() {
uniforms.u_time.value += 0.02;
renderer.render(scene, camera);
}
</script>
</body>