LeetCode 精选 TOP 面试题
写在前面
这里是LeetCode 精选TOP面试题,一共145道,但是一部分与LeetCode 热题 HOT 100中的题目重复。因此重复的题目我都会写在我另一篇博客LeetCode 热题 HOT 100中。
LeetCode 精选 TOP 面试题
https://leetcode.cn/problem-list/2ckc81c/?sorting=W3sic29ydE9yZGVyIjoiREVTQ0VORElORyIsIm9yZGVyQnkiOiJGUkVRVUVOQ1kifV0%3D
3. 无重复字符的最长子串(中等) ×!√
滑动窗口!
-
首先要判断slow需不需要更新,怎么判断?slow = max(umap[s[fast]], slow);什么意思,就是说:**umap[s[fast]]的意义是,为了在slow和fast之间不出现重复字符,slow能处于的最左位置。**如图,当j第一次到d,将umap[s[j]] = j + 1; 当再次遇到d时,slow就要判断一下,slow是不是比umap[s[j]]大,如果不是,就更新到它。
-
必须要先处理slow,也就是说,假定umap[s[fast]]已经设置好了。当fast走到重复子串的位置时,更新一下slow,怎么更新呢?就是更新到fast给slow提前安排好的位置。
-
fast到一个位置,就判断一下是否要更新slow,如何更新?用它给slow提前安排好的位置更新;
-
计算slow和fast的距离;
-
更新umap[s[fast]];
不可能先更新umap[s[fast]],再更新slow。本质上就是fast先往前走,走一步判断一下slow是否要前移。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-xq7RCAiZ-1675863835300)(https://pic.leetcode-cn.com/8b7cac826e572c65f8b77e0f380eaa93ab665857a8e916bc4ea36b7765eafc55-%E5%9B%BE%E7%89%87.png)]
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
int res = 0;
unordered_map umap;
for(int slow(0),fast(0); fast < s.size(); ++fast){
slow = max(umap[s[fast]], slow);
res = max(res, fast - slow + 1);
umap[s[fast]] = fast + 1;
}
return res;
}
};
18. 四数之和(中等)√
双指针。
关键在于去重,i要去一次重,j也要去一次重。
class Solution {
public:
vector> fourSum(vector& nums, int target) {
int n = nums.size();
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
vector> res;
for(int i = 0; i < n - 3; ++i){
if(i && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) continue; // !!!!!
for(int j = i + 1; j < n - 2; ++j){
int x = nums[i], y = nums[j];
if(j != i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) continue; // !!!
for(int slow(j + 1), fast(n - 1); slow < fast;){
long s = (long)x + y + nums[slow] + nums[fast];
if(s < target) ++slow;
if(s > target) --fast;
if(s == target){
res.push_back({x, y, nums[slow], nums[fast]});
for(++slow; slow < fast && nums[slow] == nums[slow - 1]; ++slow);
for(--fast; slow < fast && nums[fast] == nums[fast + 1]; --fast);
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
14. 最长公共前缀(简单)×
7. 整数反转 ××
summary:
- 不能判断正负号,因为INT_MAX 和INT_MIN的绝对值不一样;
- 最优办法是不需要判断正负号,因为对于x来说,它的最高位如果超过2的话,很可能就已经溢出了,所以说最高位不会超过2;那么翻转过后,他也是小于2的,所以不会溢出。
- 不要马虎!res == INT_MAX / 10 && p > INT_MAX % 10不可能同时成立,因为如果第一个条件成立,说明位数够了, 如果tmp大于2,那x本来就是溢出的,所以x的最高位一定小于2(位数不够的时候也能大于2,反正这两个条件不会同时成立)!INT_MIN也同理。
- while的时候记得更新x!
class Solution {
public:
int reverse(int x) {
int res = 0;
while(x){
int e = x % 10;
if((res > INT_MAX / 10 ) || (res < INT_MIN / 10))
return 0;
res = res * 10 + e;
x /= 10; // 不要忘了这里!!!!!!
}
return res;
}
};
217. 存在重复元素(简单) √
class Solution {
public:
bool containsDuplicate(vector& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 1; ++i){
if(nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) return true;
}
return false;
}
};
13. 罗马数字转整数(简单)×
summary:就是没想到处理4、9、40、90这些特殊情况。其实很简单,就是遍历s的时候,如果当前数字比下一个数字小,那么就减去当前数字,否则就加。
class Solution {
public:
int romanToInt(string s) {
unordered_map umap{{'I', 1}, {'V', 5},{'X', 10}, {'L', 50}, {'C', 100}, {'D', 500}, {'M', 1000}};
int res = 0;
int i = 0, n = s.size();
while(i < n - 1){
if(umap[s[i]] < umap[s[i + 1]])
res -= umap[s[i]];
else res += umap[s[i]];
++i;
}
res += umap[s[i]];
return res;
}
};
88. 合并两个有序数组(简单)√
class Solution {
public:
void merge(vector& nums1, int m, vector& nums2, int n) {
int s = m + n - 1;
int i = m - 1, j = n - 1;
while(i >= 0 && j >= 0){
if(nums1[i] > nums2[j]){
nums1[s] = nums1[i];
--i;
}else{
nums1[s] = nums2[j];
--j;
}
--s;
}
while(j >= 0){
nums1[s] = nums2[j];
--s;
--j;
}
}
};
8. 字符串转换整数 (atoi)(中等)×
summary:
判断正负号那里,只能用if-else,不能用if-if,因为只能取一个符号,读入的下一个如果还是正负号那么直接忽略所有后面的字符并返回0;
res == INT_MAX / 10 && num > INT_MAX % 10 这个判断,如果num是7,没溢出;
是8,正数溢出了,截断,INT_MIN个位数是8,没溢出,但是直接截断也正好。
class Solution {
public:
int myAtoi(string s) {
int res = 0, index = 0, n = s.size();
bool flag = true;
while(index < n && s[index] == ' ') ++index; // 消除前导空格
if(index < n && s[index] == '-'){ // 判断正负号
flag = false;
++index;
}else if(index < n && s[index] == '+') ++index; // 如果有正有负 那么就跳过一个 确保异常情况能输出0
while(index < n && s[index] >= '0' && s[index] <= '9'){
int num = s[index] - '0';
if(res > INT_MAX / 10 || res == INT_MAX / 10 && num > INT_MAX % 10) // 不能只判断res > INT_MAX,因为有可能再*10直接溢出,必须提前截断
return flag ? INT_MAX : INT_MIN;
res = res * 10 + num;
++index;
}
return flag ? res : -res;
}
};
26. 删除有序数组中的重复项(简单)√
class Solution {
public:
int removeDuplicates(vector& nums) {
int slow = 0, fast = 0, n = nums.size();
for( ; fast < n; ++fast){
if(nums[fast] != nums[slow]){
++slow;
nums[slow] = nums[fast];
}
}
return slow + 1;
}
};
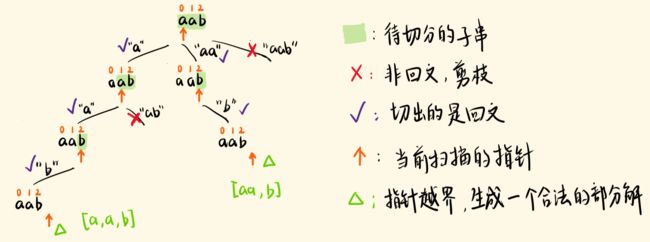
131. 分割回文串(中等)×!
回溯中中的i,就是数组的字符串的下标。
一开始是 a b b 开始回溯 变成 a bb
class Solution {
public:
vector path;
vector> res;
void backtracking(string &s, int startIndex){
if(startIndex >= s.size()){ // 一条分割的路径搜索完毕,分割的结果都是回文串
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
for(int i = startIndex; i < s.size(); ++i){
if(isPalindrome(s, startIndex, i)){
path.push_back(s.substr(startIndex, i - startIndex + 1));
backtracking(s, i + 1);
path.pop_back();
//比如['a', 'a', 'b'], 此时start=2,i=2; backtracking(s, 3), 说明当前path中的结果都是回文串,直接return;
// 回溯之前要把'b'弹出, 回到start=1,++i -> 2,判断‘ab’是不是回文串。
}
// 如果不是回文串,整个分支直接跳过,不搜索了,不会继续往下递归
}
}
// 记忆化搜索中,f[i][j] = 0 表示未搜索,1 表示是回文串,-1 表示不是回文串
bool isPalindrome(const string& s, int l, int r) {
while(l < r) if(s[l++] != s[r--]) return false;
return true;
}
vector> partition(string s) {
backtracking(s, 0); // 回溯
return res;
}
};
54. 螺旋矩阵(中等)×
summary:
- 转弯是由t来控制的, 当临时x和y越界或者遍历已经遍历过的位置时,t就更新,x和y也更新;
- 更新r,c时需要先用临时x,y判断一下越没越界。
class Solution {
public:
vector spiralOrder(vector>& matrix) {
vector res;
int row = matrix.size();
int col = matrix[0].size();
int s = row * col;
int dx[4]{0, 1, 0, -1};
int dy[4]{1, 0, -1, 0};
int r(0), c(0), x(0), y(0), t(0);
for(int i = 0; i < s; ++i){
res.push_back(matrix[r][c]);
matrix[r][c] = INT_MAX;
x = r + dx[t];
y = c + dy[t];
if(x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= row || y >= col || matrix[x][y] == INT_MAX){
t = (t + 1) % 4;
x = r + dx[t];
y = c + dy[t];
}
r = x;
c = y;
}
return res;
}
};
[202. 快乐数(简单)×
class Solution {
public:
int func(int n){
int res = 0;
while(n != 0){
res += (n % 10) * (n % 10);
n /= 10;
}
return res;
}
bool isHappy(int n) {
unordered_set umap;
int res = func(n);
while(umap.count(res) == 0){
if(res == 1) return true;
umap.insert(res);
res = func(res);
}
return false;
}
};
347. 前 K 个高频元素(中等)×
summary:注意comp的写法,pque底层是个vector,pque与sort的排序方式相反。
class Solution {
public:
using pii = pair;
struct comp{
bool operator()(pii& lhs, pii& rhs){
return lhs.second < rhs.second;
}
};
vector topKFrequent(vector& nums, int k) {
vector res;
unordered_map umap;
priority_queue, comp> pque;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i)
++umap[nums[i]];
for(auto &kv: umap){
pque.push(kv);
}
while(k-- > 0){
res.push_back(pque.top().first);
pque.pop();
}
return res;
}
};
41. 缺失的第一个正数(困难)×!
-
最关键的一点是,n = nums.size(),res只能是[1, n+1]中的一个,因为假设n为3,数组中的元素为1,2,3;那么res就是4;否则就是缺失的那一个。
-
所以说,只要把每个元素i,放在nums[i-1]的位置,然后再遍历一遍,找到nums[i] != i + 1;就找到缺失的正数了。
-
解释一下为什么是while:
nums[i] >= 1 && nums[i] <= n && nums[i] != nums[nums[i] - 1 比如用例是3,4,-1,1;如果是if: 首先判断3(nums[0]) 在不在 nums[2],不在的话就把3换到nums[2]的位置上; -1, 4, 3, 1; 然后判断4 -1,1,3,4;这个时候如果是if,那么1的判断就结束了,但是1应该是在nums[0]的位置上,所以必须是while保证当前元素在正确的位置上。 第一次-1换到了nums[0], 因为-1不在[1, n+1]的范围内,所以不用管,等着被换就行了!
class Solution {
public:
int firstMissingPositive(vector& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i){
while(nums[i] >= 1 && nums[i] <= n && nums[i] != nums[nums[i] - 1]){
swap(nums[i], nums[nums[i] - 1]);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if(nums[i] != i + 1) return i + 1;
return n + 1;
}
};
122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II(中等单调栈)×√
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector& prices) {
stack st;
int res = 0;
prices.emplace_back(0); // 末尾要加个0,因为要判断最后一天的股价能否盈利
for(int i = 0; i < prices.size(); ++i){
if(!st.empty() && prices[i] < st.top()){ // 如果新元素比栈顶小,说明栈内的元素是单调递增的,可盈利
int high = st.top(), slow = high; // 定义最高价与最低价,slow=high是处理栈内只有一个元素的情况
st.pop(); // 栈顶出栈
while(!st.empty()){ // 一直出到栈空,找到最低价,因为栈内是单调递增的,最后肯定是栈空
slow = st.top();
st.pop();
}
res += high - slow; // 记录一次利润
}
st.push(prices[i]); // 把新元素入栈
}
return res;
}
};
279. 完全平方数(中等)×
动态规划-背包问题
什么是背包问题?简单来说,就是dp[i]不能由dp[i-1]推出,而是和dp[0 - i-1]都有关系。
class Solution {
public:
int numSquares(int n) {
vector dp(n + 1, INT_MAX); // dp[i]表示和为i的完全平方数的最少数量
dp[0] = 0; // 0的最少数量为0
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
for(int j = 1; j * j <= i; ++j){
dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[i - j * j] + 1);
}
}
return dp[n];
}
};
300. 最长递增子序列(中等)×
背包问题。
时间复杂度是n方。
还能优化。
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLIS(vector& nums) {
int res = 1;
vector dp(nums.size(), 1);
for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); ++i){
for(int j = 0; j <= i; ++j){
if(nums[i] > nums[j]){
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
}
res = max(res, dp[i]);
}
}
return res;
}
};
179. 最大数(中等)×!
模拟题。
就是忘了应该怎么比了。直接看代码。
class Solution {
public:
string largestNumber(vector& nums) {
string res;
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end(), [](int& lhs, int& rhs){
string sl = to_string(lhs);
string sr = to_string(rhs);
return sl + sr > sr + sl;
});
// 如果排序后第一个数字是0,说明所有数字都是0
if(nums[0] == 0) return "0";
for(auto e: nums){
res += to_string(e);
}
return res;
}
};
118. 杨辉三角(简单)×
模拟、动态规划。
Vector的resize(n, e = T()); 第二个参数并不能改变容器中所有元素,只有当n大于当前size时,追加的元素才会赋值e。
class Solution{
public:
vector> generate(int numRows){
vector> res(numRows);
for(int i = 0; i < numRows; ++i){
res[i].resize(i + 1);
res[i][0] = res[i][i] = 1;
for(int j = 1; j < i; ++j){
res[i][j] = res[i-1][j] + res[i-1][j-1];
}
}
return res;
}
};
50. Pow(x, n)(中等)×!!
模拟——快速幂!有两种办法:https://leetcode.cn/problems/powx-n/solution/50-powx-n-kuai-su-mi-qing-xi-tu-jie-by-jyd/
第一种:二进制角度:主要是把幂转换成二进制,然后再将幂的二进制展开,具体看题解。
有个个问题:就算n < 0 ;每次用 n >> 1 为什么会超时呢? 应该可以算完啊
正数 负数 左移<< 右移>>
对于正数来说,左移右移都补0;
对于负数来说,左移添0,右移添1;
负数的右移:负数右移的话,由于要保持它是负数,所以负数的二进制的右边补1。如果一直右移的话,最后就就变成0xFFFFFFFF 即-1
如: -4>>1 为-2 ;-4>>2为-1(除二)
2)负数的左移:跟正整数左移一样,右边补0,一直左移的话,最后就是0啦。-2<<2 为-4 ; -2<<31为0(×2,负数越×越小)。
因此对于本题来说,如果使用n >> 1,那么n最终会变成-1且无限循环。
class Solution {
public:
double myPow(double x, int n) {
double res = 1.0;
if(x == 0.0) return 0.0;
if(n < 0) x = res / x; // 如果 n < 0; 令x = 1 / x
while(n){
if(n & 1) res *= x;
x *= x;
n /= 2;
}
return res;
}
};
第二种解法:分治法!!!!!
假设b = 13,1101
class Solution {
public double myPow(double x, int n) {
if(x == 0.0f) return 0.0d;
long b = n;
double res = 1.0;
if(b < 0) {
x = 1 / x;
b = -b;
}
while(b > 0) {
if((b & 1) == 1) res *= x;
x *= x;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
}
69. x 的平方根 (简单)×!
二分-寻找最右边的值。
为什么是寻找最右值?由于x平方根的整数部分res是**满足 k * k <= x的最大k值,最大即最右! **
注意,(long)mid * mid <= x这个是条件,小于或者等于,由于是找最右值,所以l = mid + 1;
而不是(long)mid * mid >= x;去找最左值,3*3 是大与8的最左值,这明显是错误的。
为什么lambda使用值捕获会出问题????
class Solution {
public:
int mySqrt(int x) {
if(x < 2) return x;
int l = 0, r = x / 2, mid = 0;
auto flag = [&](){return (long)mid * mid <= x; };
while (l <= r) {
mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
if (flag())
l = mid + 1;
else
r = mid - 1;
}
return r;
}
};
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先(中等)×
后续遍历!
- 如果left和right都空,说明当前root不是p、q的祖先;
- 如果left空 但right不空,说明right的子树中可能只有p或者只有q ;或者p、q都有;
- 如果right空 但left不空,说明left的子树中可能只有p或者只有q;或者p、q都有;
- 如果left和right都不空,说明root正好就是最近公共祖先。
class Solution{
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q){
if(root == nullptr || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if(left == nullptr && right == nullptr) return nullptr;
if(left == nullptr) return right;
if(right == nullptr) return left;
return root;
}
};
28. 找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标(中等)×!
KMP!!!!
454. 四数相加 II(中等)×
class Solution {
public:
int fourSumCount(vector& A, vector& B, vector& C, vector& D) {
unordered_map umap; //key:a+b的数值,value:a+b数值出现的次数
// 遍历大A和大B数组,统计两个数组元素之和,和出现的次数,放到map中
for (int a : A) {
for (int b : B) {
umap[a + b]++;
}
}
int count = 0; // 统计a+b+c+d = 0 出现的次数
// 在遍历大C和大D数组,找到如果 0-(c+d) 在map中出现过的话,就把map中key对应的value也就是出现次数统计出来。
for (int c : C) {
for (int d : D) {
if (umap.find(0 - (c + d)) != umap.end()) {
count += umap[0 - (c + d)];
}
}
}
return count;
}
};
134. 加油站(中等)×!!
贪心算法!
好好解释一下:
- 首先计算出rest[i] = gas[i] - cost[i]; 意思是从i出发到达i+1的加油站剩余的油量;如果rest[i]的总和 < 0 说明不管从哪个加油站出发,肯定无法走完一圈,大于0则肯定存在从某个加油站出发能走完一圈。
- curSum计算rest[i]的累加和,当小于0时,重新计算。为什么?当到i时累加和小于0了,说明从之前的出发点出发到不了i+1加油站,所以将start = i + 1,从i + 1重新出发。
- 如果restSum(rest[i]的和)大于0,那么start一定是有效的。小于0则start无效。
为什么是贪心算法:因为当curSum小于0时,说明从之前的出发点出发到不了i+1加油站,那就选择从i+1个加油站出发,即局部最优(你可能会问从出发点到i+1之间的加油站出发不行吗?我想了一下如果先减后增(<0),那start会直接更新;如果先增后减,那从i+1之前出发就没有意义)。
最终的答案是从局部最优中推出来的,因此,符合贪心算法。(因为只要restSum > 0,之前的局部最优start就一定是 有效的。)
如果频繁出现curSum小于0,那start就一直往后更新。为什么?因为如果restSum>0,也就是肯定能走完一圈的话,前面有多少小于的,后面就有多少大于0,所以从越后面的加油站出发剩余的油量越多,来抵消前面cost大的路段。
class Solution {
public:
int canCompleteCircuit(vector& gas, vector& cost) {
int n = gas.size();
int start(0), curSum(0), restSum(0);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
curSum += gas[i] - cost[i];
if(curSum < 0){
start = i + 1;
curSum = 0;
}
restSum += gas[i] - cost[i];
}
if(restSum < 0) return -1;
return start;
}
};
149. 直线上最多的点数(困难)×!!!
哈希表!!!这种本来是O(n3)的时间复杂度,通过哈希表降成O(n2)的操作一定好好好看好好学!!
https://leetcode.cn/problems/max-points-on-a-line/solution/xiang-xi-tong-su-de-si-lu-fen-xi-duo-jie-fa-by–35/ 好解法!!到时候用这个!!
为什么 * 1.0 就可以解决分母是0的问题???????????
/*
这种解法的思路是,对于每一个点,将它与其他所有点的斜率都放在哈希表中统计,同一斜率最大的value就是一条直线上最多的点数
形象点说就是遍历每一个点,向所有其他点发出射线,看哪一条射线上的点数最多!!
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxPoints(vector>& points) {
int ans = 0;
int n = points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
unordered_map ma;
int thisAns = 0;
for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) {
if (i == j)
continue;
long double k = 1.0 * (points[j][1] - points[i][1]) / (points[j][0] - points[i][0]);
ma[k]++;
thisAns = max(thisAns, ma[k]);
}
ans = max(ans, thisAns + 1);
}
return ans;
}
};
350. 两个数组的交集 II(简单)×
哈希、双指针!
进阶三问:
- 如果是排好序的数组,那么显然应该使用双指针,时间复杂度为O(n);
- 如果nums1的size较小,那么应该使用nums1进行哈希计数,然后在另一个数组中遍历,根据哈希来确定交集。
- 如果数组很大内存很小,显然不能使用哈希。应该先对数组进行外部排序,归并排序就是天然适合外部排序的算法。
可以将分割后的子数组写入单个文件进行排序,归并时将小文件合并为大文件。当两个数组均排序完成生成两个大文件后,即可使用双指针遍历两个文件,如此可以使空间复杂度降为最低。
哈希:注意选择size较小的nums存到哈希表中的技巧,很舒服!!!
class Solution{
public:
vector intersect(vector& nums1, vector& nums2){
// 好技巧!!!!!
if(nums1.size() > nums2.size()) return intersect(nums2, nums1);
vector res;
unordered_map umap;
for(auto e: nums1)
++umap[e];
for(auto e: nums2){
if(umap[e] > 0){
res.push_back(e);
--umap[e];
}
}
return res;
}
};
双指针:
class Solution{
public:
vector intersect(vector& nums1, vector& nums2){
sort(nums1.begin(), nums1.end());
sort(nums2.begin(), nums2.end());
vector res;
for(int p1(0), p2(0); p1 < nums1.size() && p2 < nums2.size();){
if(nums1[p1] < nums2[p2]) ++p1;
else if(nums1[p1] > nums2[p2]) ++p2;
else{
res.push_back(nums1[p1]);
++p1;
++p2;
}
}
return res;
}
};
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树(中等)×
看一眼图片一目了然。
1.后序数组的最后一个元素就是根节点。
2.然后用后续数组的最后一个元素去切割中序数组,左半部分就是左子树的中序数组,右半部分就是右子树的中序数组;
3.因为后序数组是先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树,最后遍历根节点,所以把后序数组的根节点删除。后序数组的左子树的后序数组 和 右子树的后序数组 数量是一样的, 只是顺序不一样。 因此可以直接用左 / 右 子树的中序数组的size来切割后序数组。
class Solution{
TreeNode* traversal(vector& inorder, vector& postorder){
if(postorder.size() == 0) return nullptr; // 递归出口
// 后序遍历数组的最后一个节点就是当前的根节点
int rootValue = postorder[postorder.size() - 1];
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootValue);
if(postorder.size() == 1) return root; // 叶子节点 递归出口
//找到中序遍历数组的切割点
int delimiterIndex;
for(delimiterIndex = 0; delimiterIndex < inorder.size(); ++delimiterIndex){
if(inorder[delimiterIndex] == rootValue) break;
}
// 切割中序数组
vector leftInorder(inorder.begin(), inorder.begin() + delimiterIndex);
vector rightInorder(inorder.begin() + delimiterIndex + 1, inorder.end());
// 舍弃后序数组的末尾元素,为了切割的左右后序数组size与左右中序数组size一样。
postorder.resize(postorder.size() - 1);
// 这里注意:postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size() 不是 + delimiterIndex
vector leftPostorder(postorder.begin(), postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size());
vector rightPostorder(postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size(), postorder.end());
root->left = traversal(leftInorder, leftPostorder);
root->right = traversal(rightInorder, rightPostorder);
return root;
}
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector& inorder, vector& postorder){
return traversal(inorder, postorder);
}
};
29. 两数相除(中等)×!?
二分 + 快速乘!(只有允许用long才行,因为在 0 和 被除数之间取 mid ,再去乘除数,很容易就溢出了,但long不会。)
更优:逐渐逼近法。
//假设:divedend - 10 divisor - 3; 先都映射成负数:divedend - (-10) divisor (-3);
while(dividend <= divisor){ // -10 <= -3
int s = divisor, d = -1;
while(s >= LIMIT && d >= LIMIT && s >= dividend - s){ // s = -6 d = -2时 -6 < -10 - (-6) = -4
s += s; d += d; // 更新dividend = -4 res = 0 + (-2) = -2
} // s = -3 < -4 - (-3) = -1
dividend -= s; // res += -1 = -3
res += d;
}
class Solution{
public:
int divide(int dividend, int divisor){
int res = 0;
// 由于操作数都是负数,因此自倍增过程中如果操作数小于INT_MIN / 2,则结果会发生溢出
int LIMIT = INT_MIN / 2;
// INT_MIN / -1 会溢出, 因此直接返回INT_MAX
if(dividend == INT_MIN && divisor == -1) return INT_MAX;
// 记录是否异号
bool flag = ((dividend > 0 && divisor < 0) || (dividend < 0 && divisor > 0)) ? true : false;
dividend = dividend > 0 ? -dividend : dividend;
divisor = divisor > 0 ? -divisor : divisor;
// 因为都变成了负号,因此除数比被除数大
while(dividend <= divisor){
int s = divisor, d = -1;
while(s >= LIMIT && d >= LIMIT && s >= dividend - s){
s += s; d += d;
}
dividend -= s;
res += d;
}
return flag ? res : -res;
}
};
class Solution {
int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int divide(int _a, int _b) {
long a = _a, b = _b;
boolean flag = false;
if ((a < 0 && b > 0) || (a > 0 && b < 0)) flag = true;
if (a < 0) a = -a;
if (b < 0) b = -b;
long l = 0, r = a;
while (l < r) {
long mid = l + r + 1 >> 1;
if (mul(mid, b) <= a) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
r = flag ? -r : r;
if (r > INF || r < -INF - 1) return INF;
return (int)r;
}
long mul(long a, long k) {
long ans = 0;
while (k > 0) {
if ((k & 1) == 1) ans += a;
k >>= 1;
a += a;
}
return ans;
}
}
44. 通配符匹配(困难)×!!???
表格动态规划!千万注意第一行第一列一般都是要初始化的!!太累了下次再看!
题目拓展
最长公共子串: 718. 最长重复子数组 (类似题目,只是由字符串变为数组)
- 编辑距离
- 最长公共子序列
- 正则表达式匹配
- 两个字符串的删除操作
- 最小窗口子序列
class Solution {
public boolean isMatch(String s, String p) {
int m = s.length(), n = p.length();
boolean[][] f = new boolean[m + 1][n + 1];
f[0][0] = true;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
f[0][i] = f[0][i - 1] && p.charAt(i - 1) == '*';
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
if(s.charAt(i - 1) == p.charAt(j - 1) || p.charAt(j - 1) == '?'){
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j - 1];
}
if(p.charAt(j - 1) == '*'){
f[i][j] = f[i][j - 1] || f[i - 1][j];
}
}
}
return f[m][n];
}
}
91. 解码方法(中等)×
动态规划!
注意:12 新加一个3:
对3来说,符合要求,但dp[“3”] = dp[“12”] 总数是没变的。
但 23 也符合要求,所以 dp[i] 要再 += dp[i - 2]; 因为23组合了 dp[“23”]也和dp[“1”]总数也一样。
对于i = 1时, b = " " - ‘0’ + 1 - ‘0’, ’ '对应32, ‘0’ 对应48 所以结果是 -161,不会成立。
class Solution {
public:
int numDecodings(string s) {
int n = s.size();
s = " " + s;
vector dp(n + 1); // dp[i]表示前i个字符解码方法的总数
dp[0] = 1; // 空字符解码出来空字符,次数为1 很好理解,其实主要是为了照顾转移方程里的dp[i-1]
for(int i = 1; i < n + 1; ++i){
int a = s[i] - '0';
int b = (s[i - 1] - '0') * 10 + s[i] - '0';
if(a > 0 && a <= 9) dp[i] = dp[i - 1];
if(b >= 10 && b <= 26) dp[i] += dp[i - 2];
}
return dp[n];
}
};
395. 至少有 K 个重复字符的最长子串(中等)×!!
学一下到底什么是分治?什么时候能用滑动窗口?
先说一个令我迷惑的点:就是用哈希统计了每个字符出现的次数之后,直接用个start和num遍历一下不就能得到最长子串了吗?其实不是,举个例子:
s = “xyaabbcabhhh”, k = 3
能说s[2:5] = "aabb"是个符合条件的子串吗?不能!因为虽然他们的计数都=3,但是a和b的第k次出现都被c隔开了。所以不能这么简单的梭哈。
故使用分治法:统计了每个字符出现的次数后,依次遍历字符串,当start = 2, num = 4时,他们的count都=3,我们就把这个子串递归处理,判断一下a和b的3次重复是不是都在这个子串里。如果不是,那G了。
再捋一遍思路:s = “xyaabbcabhhh”, k = 3:
1.先统计每个字符出现的次数;
2.判断是否所有字符都大于k,都大于返回s.size();
3.否则遍历s,截取大于k的连续子串,递归处理,判断子串中的所有字符的出现次数是否都大于k,还是说出现的k次被中间出现次数小于k的字符隔开了。
4.返回子串的数量。
class Solution{
public:
int longestSubstring(string s, int k){
unordered_map umap;
for(auto c: s) ++umap[c];
bool isAll = true;
for(auto& kv: umap){
if(kv.second < k){
isAll = false;
break;
}
}
if(isAll) return s.size();
int maxCount = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i){
int start = i, num = 0;
while(i < s.size() && umap[s[i]] >= k){ // 这里i不符合循环条件了说明出现次数 138. 复制带随机指针的链表(中等)
412. Fizz Buzz(简单)×
挺简单的,就是注意一下简洁的写法,在看一下string移动时发生了什么。
class Solution{
public:
vector fizzBuzz(int n){
vector res;
string tmp;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
if(i % 3 == 0) tmp += "Fizz";
if(i % 5 == 0) tmp += "Buzz";
if(tmp.size() == 0) tmp += to_string(i);
res.push_back(std::move(tmp));
}
return res;
}
};
315. 计算右侧小于当前元素的个数(困难)×??
归并排序及其应用!!!!?
class Solution {
public:
vector countSmaller(vector& nums) {
}
};
238. 除自身以外数组的乘积(中等)×!
双指针,解法很妙又很朴素!
eg [1,2,3,4]
先说一下大概思路,然后再说明过程:对于3,我们利用left从1一直累乘到2,res[2] *= left, 利用right从4累乘到4,res[2] *= right。 反正就是对于每个元素,分别从两边向它累乘。
但都没×自己!从左向右的或者从右向左的都只负责×自己前面元素的积!
初始化:res = [1,1,1,1], left = 1, right = 1;
class Solution {
public:
vector productExceptSelf(vector& nums) {
vector res(nums.size(), 1);
int left = 1, right = 1;
for(int i = 0, j = nums.size() - 1; i < nums.size(); ++i, --j){
res[i] *= left; res[j] *= right;
left *= nums[i]; right *= nums[j];
}
return res;
}
};
295. 数据流的中位数(困难-设计题(优先队列))×
整理一下排序和堆的仿函数!
设计题-优先队列!
为了能在O(1)的复杂度内取到中位数,需要两个优先队列,令lpque为大顶堆,rpque为小顶堆(即lpque中的元素都比rque中的元素小);
并且人为规定:
-
当数据流元素数量为偶数时,lpque和rpque大小相同,此时中位数为两者堆顶的平均值;
-
当数据流中元素数量为奇数时,lpque比rpque的size大1,此时中位数就是lque的堆顶元素。
-
为了满足上述人为规定,在进行addNum时,应当分情况处理:
- 1 当插入前两者大小相同,说明插入前数据流元素个数为偶数,我们期望达到插入后[lpque的size比rpque的size大1,且两个堆维持有序],进一步分情况讨论:
- 如果rpque为空,说明当前插入的是首个元素,直接添加到rpque;
- 如果r不空,继续分情况讨论:
- 如果num <= rpque.top(); 那么num直接添加到lpque就好(就算先添加到pque, 因为规定lpque的size比rpque大1,也会再放到lpque中)
- 如果num > rpque.top(); 那么num先添加到rpque中,再把rpque.top()放到lpque中。
- 2 当插入前两者大小不同,说明插入前lpque比rpque的size大1,我们期望插入后lpque和rpque大小相等,进一步分情况讨论:
- 如果num >= lpque.top(); 直接放进rpque;(就算先放进lpque,最后也要放到rpque里,所以要优先判断能否放了之后就不用动了)
- 如果num < lpque.top(); 先放进lpque,再把lpque.top()放到rpque中。
- 1 当插入前两者大小相同,说明插入前数据流元素个数为偶数,我们期望达到插入后[lpque的size比rpque的size大1,且两个堆维持有序],进一步分情况讨论:
class MedianFinder {
public:
priority_queue lpque;
priority_queue, std::greater> rpque; // 注意这里是小顶堆!!!!!!
MedianFinder() {}
void addNum(int num) {
int nl = lpque.size(), nr = rpque.size();
if(nl == nr){
if(rpque.empty() || num <= rpque.top()) lpque.push(num);
else{
lpque.push(rpque.top());
rpque.pop();
rpque.push(num);
}
}
else{
if(num >= lpque.top()) rpque.push(num);
else{
rpque.push(lpque.top());
lpque.pop();
lpque.push(num);
}
}
}
double findMedian() {
int nl = lpque.size(), nr = rpque.size();
if(nl == nr) return (lpque.top() + rpque.top()) / 2.0;
else return lpque.top();
}
};
162. 寻找峰值(中等-二分)×!
这道题如果暴力解的话很简单,但是要达到log(n)那肯定是要用2分。
为什么不是有序数组也能用二分?这个问题很关键。
首先,题中给了一个条件,nums[-1] = nums[n] = -∞。
所以 if(nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1]) r = mid; 此时r的右侧是一个上坡,令r = mid;继续从左寻找看能再找到一个从左往右的上坡。
5 4 3 6 5
l m r
6 5
l r
反正就是l更新了,nums[l]比nums[l-1]大;r更新了,nums[r]比nums[r+1]大.
更新了r, 是这样的‘\’,更了l,是这样的‘/’,lr了,说明是这样的:‘/\’说明找到山峰了。
就算整个序列是单调递减的,r一直向右更新,一直是这样‘\’,直到rl为0, 因为l[-1]是-∞,所以也是个山峰。 -∞ 3 2 1 -∞
你可能会想更新了r(r为5)之后 假设是这样 8 7 6 5 4,不怕呀,因为l[-1]=-∞,8就是个峰值。
补充一句二分的细节,如果确定数组中有我们要找的值,那么while中的条件是l < r,终止条件是l == r。
class Solution {
public:
int findPeakElement(vector& nums) {
int l = 0, r = nums.size() - 1, mid = 0;
while(l <= r){
mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
if(nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1]) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return l;
}
};
234. 回文链表(简单-链表)√
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* slow = head, *fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next){
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
ListNode* m = reverse(slow);
while(m != nullptr){
if(m->val != head->val) return false;
m = m->next;
head = head->next;
}
return true;
}
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* head){
ListNode* r = head;
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
while(r){
ListNode* next = r->next;
r->next = pre;
pre = r;
r = next;
}
return pre;
}
};
297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化(困难-二叉树)?
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Codec {
public:
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
}
};
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec ser, deser;
// TreeNode* ans = deser.deserialize(ser.serialize(root));
242. 有效的字母异位词(简单-哈希表)√
我这个脑子一开始只能想到用两个哈希表,去比
明明可以只用一个,然后一加一减就解决了。下次注意。
class Solution {
public:
bool isAnagram(string s, string t) {
unordered_map umap;
for(auto c: s) ++umap[c];
for(auto c: t) --umap[c];
for(auto& p: umap){
if(p.second != 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
};
189. 轮转数组(中等- 模拟)×
再做一遍,注意逻辑就好了,先翻转前半部分,再翻转后半部分,再翻转整个数组。
class Solution {
public:
void rotate(vector& nums, int k) {
if(k == 0) return;
k %= nums.size();
int n = nums.size() - 1;
reverse(nums, 0, n - k);
reverse(nums, n - k + 1, n);
reverse(nums, 0, n);
}
void reverse(vector& nums, int start, int end){
for(; start < end; ++start, --end)
swap(nums[start], nums[end]);
}
};
283. 移动零(简单-循环不变量)√
就是规定[0, notZero]为非0数。为了满足条件,notZero初始化为-1。
class Solution {
public:
void moveZeroes(vector& nums) {
int notZero = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i){
if(nums[i] != 0){
++notZero;
swap(nums[notZero], nums[i]);
}
}
}
};
125. 验证回文串(简单-字符串)×
- while(l < r && !isalnum(s[l])) ++l; 移动的时候用while,并且要注意不能越界;
- 判断是否是字母&数字:isalnum();判断字符是否是字母:isalpha; 大写转小写:tolower()。
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(string s) {
int l = 0, r = s.size() - 1;
while(l < r){
while(l < r && !isalnum(s[l])) ++l;
while(l < r && !isalnum(s[r])) --r;
if(tolower(s[l]) != tolower(s[r])) return false;
++l;
--r;
}
return true;
}
};
287. 寻找重复数(中等)?
我想到了用原地哈希,但是题目不是写着不能修改数组吗??
130. 被围绕的区域(中等)?
66. 加一(简单)√
直接像两数之和那样做,so easy。假设一开始需要进一位。
class Solution {
public:
vector plusOne(vector& digits) {
int flag = 1;
for(int i = digits.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i){
digits[i] += flag;
flag = digits[i] / 10;
digits[i] %= 10;
}
if(flag) digits.emplace(digits.begin(), 1);
return digits;
}
};
204. 计数质数(中等)?
237. 删除链表中的节点(中等-二叉树)×
删不了自己,那就先暂存一下儿子,把自己伪装成儿子照顾孙子,再把儿子弄死,自己就不存在了。
class Solution {
public:
void deleteNode(ListNode *node) {
ListNode* tmp = node->next;
node->val = node->next->val;
node->next = node->next->next; // 这里没有回收内存,有需要的同学可自行补充
delete tmp;
}
};
108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树(简单-二叉树构造)×
-
高度平衡的二叉树是指一棵树满足 [每个节点的两个左右子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1]的二叉树。
-
因为题目给的是升序数组,需要构建二叉搜索树,为了满足高度平衡的条件,可以让根节点是排序数组的中点,这样左右子树的高度差不会超过1。然后每次都递归处理。
-
因为先确定根节点,所以自然的是用谦虚遍历,先构造中间节点,然后递归左子树和右子树。
-
注意类似用数组构造二叉树的题目,每次分隔尽量不要定义新的数组,而是通过下标索引直接在原数组上操作,这样可以节约时间和空间上的开销。
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector& nums) {
int l = 0, r = nums.size();
return preorder(nums, 0, r);
}
// 使用左闭右开区间,[l, r),这样 int mid = l + (r - l) / 2 都正好可以作为根节点
TreeNode* preorder(vector& nums, int l, int r){
if(l >= r) return nullptr;
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root->left = preorder(nums, l, mid); // 注意是左闭右开区间!!! 不是0 是l!!!
root->right = preorder(nums, mid + 1, r);
return root;
}
};
654. 最大二叉树(中等-类似题)×
一开始想到排序那去了,但是排序就不知道根节点左右有哪些节点了。
所以只要每次遍历找到[l, r]范围内的最大值作为根节点,再递归处理左右子树就可以了。
class Solution {
private:
/* 在左闭右开区间[left, right),构造二叉树 */
TreeNode* traversal(vector& nums, int left, int right) {
/* 递归截止条件 */
if (left >= right) return NULL;
/* 求取分割点下标:maxValueIndex */
int maxValueIndex = left;// 赋值很巧妙可以更新 新数组的起点
for (int i = left + 1; i < right; i++)
if (nums[i] > nums[maxValueIndex]) maxValueIndex = i;
/* 更新节点最大值 */
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[maxValueIndex]);
/* 左闭右开:[left, maxValueIndex) */
root->left = traversal(nums, left, maxValueIndex);
/* 左闭右开:[maxValueIndex + 1, right)*/
root->right = traversal(nums, maxValueIndex + 1, right);
return root;
}
public:
TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector& nums) {
if(nums.size() == 0) return NULL;
return traversal(nums, 0, nums.size());
}
};
227. 基本计算器 II(中等-模拟题)×!
还需要多写几遍。
class Solution {
public:
int calculate(string s) {
stack operands; //存储表达式中的数值
stack operators; //存储表达式中的运算符
int index = 0;
/* 移除用户输入表达式中包含的无用的空格 */
s.erase(remove(s.begin(), s.end(), ' '), s.end());
while(index < s.size()){
if(isdigit(s[index])){
/* 将字符串转化为数字 */
int digit = 0;
for(;index < s.size() && isdigit(s[index]);index++)
digit = 10 * digit + (s[index] - '0');
operands.push(digit);
} else {
/* 取运算符 */ // 2 + 3 * 4 + 5 栈顶的优先级高,那就先算一下
// 2 + 12 + 5 栈顶优先级仍然高,还可以再算,所以要用while
while(operators.size() && priority(operators.top(), s[index]))
calc(operands,operators);
operators.push(s[index]);
index++;
}
}
/* 保存最后一次运算 */ // 3 + 2 * 2 这要用while
while(operators.size())
calc(operands,operators);
return operands.top();
}
/* a 的优先级是否高于等于 b */
bool priority(int a, int b){
if(b == '+' || b == '-')
return true;
else if(b=='*' || b=='/')
return (a == '*' || a == '/');
return true;
}
void calc(stack& operands,stack& operators){
int result;
int rhs = operands.top();operands.pop();//右操作数
int lhs = operands.top();operands.pop();//左操作数
switch(operators.top()){
case '+':result = lhs + rhs; break;
case '-':result = lhs - rhs; break;
case '*':result = lhs * rhs; break;
case '/':result = lhs / rhs; break;
default: break;
}
operators.pop(); //计算完成后,该运算符要弹栈
operands.push(result); //将新计算出来的结果入栈
return;
}
};
240. 搜索二维矩阵 II(中等-二分)×
先用一下抽象成BST的方法。第二次做再用一下二分(就是对每一行用一次二分)。
class Solution {
public:
bool searchMatrix(vector>& matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
int r = 0, c = n - 1;
while(r < m && c >= 0){
if(target == matrix[r][c]) return true;
else if(target > matrix[r][c]) ++r;
else --c;
}
return false;
}
};
二分:
每行用一次二分,找到了就返回true。
class Solution {
public:
bool searchMatrix(vector>& matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
bool flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int l = 0, r = n - 1;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
if (matrix[i][mid] == target){
flag = true;
break; // 这里要break!!!!!要不然会无限循环!!!
}
else if (matrix[i][mid] < target) l = mid + 1;
else r = mid - 1;
}
if (flag) return true;
}
return false;
}
};
341. 扁平化嵌套列表迭代器(中等)?
344. 反转字符串(简单-字符串)√
class Solution {
public:
void reverseString(vector& s) {
int l = 0, r = s.size() - 1;
while(l < r) swap(s[l++], s[r--]);
}
};
289. 生命游戏(中等)×
为了采用较低的时间复杂度的算法,采用原地修改矩阵的办法。
定义三种状态,对于一个节点:
如果原来是活细胞,当前仍是活细胞,那么仍为1;
如果原来是活细胞,当前变成了死细胞,那么设置为-1;
如果原来是死细胞,当前变成了活细胞,那么设置为2。
最终把-1还原会0,把2还原成1。
class Solution{
public:
void gameOfLife(vector>& board){
int m = board.size();
int n = board[0].size();
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i){
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j){
int num = alive(board, i, j);
if((board[i][j] == 1) && (num > 3 || num < 2)) board[i][j] = -1;
if(board[i][j] == 0 && num == 3) board[i][j] = 2;
}
}
// 还原
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i){
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j){
if(board[i][j] == 2) board[i][j] = 1;
if(board[i][j] == -1) board[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
// 计算某个细胞周围的细胞存货数量,对i,j的越界情况做特殊处理。
int alive(vector>& board, int row, int col){
int res = 0;
int m = board.size(), n = board[0].size();
int r_min = row > 0 ? row - 1 : row, c_min = col > 0 ? col - 1 : col;
int r_max = row == m - 1 ? row : row + 1, c_max = col == n - 1 ? col : col + 1;
for(int i = r_min; i <= r_max; ++i){
for(int j = c_min; j <= c_max; ++j){
if(i == row && j == col) continue;
if(abs(board[i][j]) == 1) res += 1;
}
}
return res;
}
};
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历(中等-二叉树) √
没什么问题,就是模拟的时候思路要清晰!
class Solution{
public:
vector> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root){
vector> res;
if(!root) return res;
bool flag = true;
deque dque;
dque.push_back(root);
vector tmp;
while(!dque.empty()){
int n = dque.size();
for(int i(0); i < n; ++i){
if(flag){
TreeNode* tmpNode = dque.front();
dque.pop_front();
tmp.push_back(tmpNode->val);
if(tmpNode->left) dque.push_back(tmpNode->left);
if(tmpNode->right) dque.push_back(tmpNode->right);
}else{
TreeNode* tmpNode = dque.back();
dque.pop_back();
tmp.push_back(tmpNode->val);
if(tmpNode->right) dque.push_front(tmpNode->right);
if(tmpNode->left) dque.push_front(tmpNode->left);
}
}
flag = !flag;
res.push_back(std::move(tmp));
}
return res;
}
};
73. 矩阵置零(中等)×
思路分析:
1.首先,不能遇到一个0就把行列刷0,因为刷了一个行列之后,再遇到其他的0,你不知道是原数组中本来就有0,还是被刷出来的0。
2.暴力思路:复制出一个原数组,然后遍历新数组,如果原数组当前位置为0,那么就把新数组的行列刷0。空间复杂度O(mn);
3.用一个数组+pair记录0出现的位置的话,因为最坏情况是所有位置都是0,所以空间复杂度还是O(mn);
4.用两个数组分别代表行和列记录0出现的行列坐标,空间复杂度为O(m + n);
5.最优方法:首先记录一下第一行和第一列有没有出现0,然后用第一行和第一列记录当前行或列有没有出现0,再刷。空间复杂度O(1)。补充一点:假设第一行没有0,那么本来的1和被刷出来的0不用变,如果第一行出现过0,那么整行全刷成0。
class Solution{
public:
void setZeroes(vector>& matrix){
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
bool r = false, c = false;
for(int i(0); i < n; ++i){
if(!matrix[0][i]) r = true;
}
for(int i(0); i < m; ++i){
if(!matrix[i][0]) c = true;
}
for(int i(1); i < m; ++i){
for(int j(1); j < n; ++j){
if(matrix[i][j] == 0){
matrix[i][0] = matrix[0][j] = 0;
}
}
}
for(int i(1); i < m; ++i){
for(int j(1); j < n; ++j){
if(!matrix[i][0] || !matrix[0][j])
matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
if(r){
for(int i(0); i < n; ++i) matrix[0][i] = 0;
}
if(c){
for(int i(0); i < m; ++i) matrix[i][0] = 0;
}
}
};
329. 矩阵中的最长递增路径(困难-DFS)×
其实已经算是做出来了,就是超时了。
关键这里要注意:
// 如果非要传pre: 假设[[1,1]]
int DFS(vector>& matrix, vector>& memo, int i, int j, int pre){
int cur = matrix[i][j];
if(cur <= pre) return 0; // 必须要写在这
if(memo[i][j] != 0) return memo[i][j]; // 否则以第二个1为起点时,那他可能获得memo[0][1]
int dx[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int dy[] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
// if(cur <= pre) return 0; 那么这一行一定不能写在这
int res = 1;
for(int t = 0; t < 4; ++t){
int r = i + dx[t];
int c = j + dy[t];
if(inArea(matrix, r, c)){ // && cur > matrix[r][c]
res = max(res, 1 + DFS(matrix, memo, r, c, cur));
}
}
memo[i][j] = res;
return res;
}
class Solution {
public:
int longestIncreasingPath(vector>& matrix) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
vector> memo(m, vector(n, 0));
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i){
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j){
if(memo[i][j] == 0){ // 不等于0,说明被以其他数为起点遍历过,以当前这个更大的数为起点遍历,长度只会更小。
int len = DFS(matrix, memo, i, j);
res = max(res, len);
}
}
}
return res;
}
int DFS(vector>& matrix, vector>& memo, int i, int j){
int cur = matrix[i][j];
if(memo[i][j] != 0) return memo[i][j];
int dx[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int dy[] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int res = 1; // 这不能是0,万一四周都比自己小,那自己也算长度1返回。
for(int t = 0; t < 4; ++t){
int r = i + dx[t];
int c = j + dy[t];
if(inArea(matrix, r, c) && cur > matrix[r][c]){
res = max(res, 1 + DFS(matrix, memo, r, c));
}
}
memo[i][j] = res;
return res;
}
bool inArea(vector>& matrix, int i, int j){
return i >= 0 && i < matrix.size() && j >= 0 && j < matrix[0].size();
}
};
387. 字符串中的第一个唯一字符(简单-字符串)√
class Solution {
public:
int firstUniqChar(string s) {
}
};
210. 课程表 II(中等-DFS/BFS)?
DFS/BFS太不熟练,脑子里框架一点都不清晰!
class Solution {
public:
vector tmp;
vector res;
vector isSelected;
bool flag = false;
vector findOrder(int numCourses, vector>& prerequisites) {
vector> adjacent(numCourses);
for(int i = 0; i < prerequisites.size(); ++i)
adjacent[prerequisites[i][1]].push_back(prerequisites[i][0]);
for(int i = 0; i < numCourses; ++i){
if(flag) break;
DFS(adjacent, isSelected, numCourses, i);
}
return res;
}
void DFS(vector>& adjacent, vector& isSelected,int numCourses, int i){
if(isSelected[i]) return;
isSelected[i] = 1;
tmp.push_back(i);
if(tmp.size() == numCourses){
res = tmp;
flag = true;
return;
}
for(auto e: adjacent[i]) DFS(adjacent, isSelected, numCourses, e);
tmp.pop_back();
isSelected[i] = 0;
return;
}
};
163. 缺失的区间(简单-模拟题)×!
简单题,我他妈就是没写对:
class Solution {
public:
vector findMissingRanges(vector& nums, int lower, int upper) {
vector res;
string s;
nums.insert(nums.begin(), lower);
nums.push_back(upper + 1);
for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); ++i){
if(nums[i] - nums[i - 1] == 2) res.push_back(to_string(nums[i] - 1));
if(nums[i] - nums[i - 1] > 2) res.push_back(to_string(nums[i - 1] + 1) + "->" + to_string(nums[i] - 1));
}
return res;
}
};
正解:
class Solution {
public:
vector findMissingRanges(vector& nums, int lower, int upper) {
// 关键就是这两行 如果是 1 1 放进vector是 0 2 可以返回1
nums.insert(nums.begin(),lower-1);
nums.push_back(upper+1);
vector ans;
for(int i = 1;i"+to_string(nums[i]-1));
return ans;
}
};
140. 单词拆分 II(困难-回溯)?
回溯/DFS/BFS都很不熟练!
class Solution {
public:
vector wordBreak(string s, vector& wordDict) {
}
};
150. 逆波兰表达式求值(中等-模拟题(栈))×
string转数字:atoi(s.c_str());
我一开始没做出来的原因:
class Solution {
public:
int evalRPN(vector& tokens) {
stack stk;
for(auto s: tokens){ // 我想单独判断每个字符串的第一个字符是不是运算符,但是tokens里会有负数,那么负号会被当成减号导致错误
if(isoptor(s[0])){
int rhs = stk.top(); stk.pop();
int lhs = stk.top(); stk.pop();
int res = cal(lhs, rhs, s[0]);
stk.push(res);
}
else stk.push(atoi(s.c_str()));
}
return stk.top();
}
bool isoptor(char c){
return c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '/' || c == '*';
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int evalRPN(vector& tokens) {
stack stk;
for(auto s: tokens){
if(isoptor(s)){
int rhs = stk.top(); stk.pop();
int lhs = stk.top(); stk.pop();
int res = cal(lhs, rhs, s[0]);
stk.push(res);
}
else stk.push(atoi(s.c_str()));
}
return stk.top();
}
bool isoptor(string& s){
return s == "+" || s == "-" || s == "*" || s == "/";
}
int cal(int lhs, int rhs, char optor){
switch(optor){
case '+': return lhs + rhs;
case '-': return lhs - rhs;
case '*': return lhs * rhs;
case '/': return lhs / rhs;
}
return 0;
}
};
253. 会议室 II(中等)×!
核心思路:所需的最少的会议室数量,可以转化为同一时间内举办的会议数量的最大值。用一个优先队列记录同时进行的会议数量。
为什么一定要先按start排序?举个例子[[2, 4], [7, 10]]:
如果排了序,那么能保证2会议一定比1会议开的晚,如果7再大于4,那么两个会议一定不冲突,也就是2会议后开,并且还是在1结束之后开的。
如果不排序呢?[[7, 10],[2, 4] ]因为我们是假定2会议比1晚开的,所以当2 < 10时;我们误以为2会议比1会议晚开,然后2又小于10,我们又误以为会议2跟会议1冲突了,实际上根本没冲突,导致错误。
//因为排了序,所以intervals[i][0]一定是晚开始的,如果当前会议开始的时间队列里的会议已经结束了,那么就出队。队列里只记录同时举行的会议的数量。
while(!pque.empty() && intervals[pque.top()][1] <= intervals[i][0])
pque.pop();//已经结束的会议出队
class Solution {
public:
int minMeetingRooms(vector>& intervals) {
sort(intervals.begin(),intervals.end());
// 使用小顶堆,默认是大顶堆噢
function cmp = [&](int a, int b){
return intervals[a][1] > intervals[b][1];
};
//结束时间早的优先级高先出队
priority_queue, function> pque(cmp);
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < intervals.size(); ++i)
{
while(!pque.empty() && intervals[pque.top()][1] <= intervals[i][0])
pque.pop();
pque.push(i);
res = max(res, (int)pque.size());//更新
}
return res;
}
};
268. 丢失的数字(简单-原地哈希)×
https://leetcode.cn/problems/missing-number/solution/gong-shui-san-xie-yi-ti-wu-jie-pai-xu-ji-te3s/
原地哈希的思路一定要掌握!!经常用!!
// 假设现在是 2 0 1
while(nums[i] != i && nums[i] < n) swap(nums[i], nums[nums[i]]);
// 好好解释下这一行
// 首先nums[0]<2> != 0 然后 swap(nums[0]<2>, nums[nums[i]<2>]<1>); 也就是把2换到它应该在的位置
// 为什么用while?因为1被换过来了,但是1也没在它应该在的位置,所以继续换,直到把0换过来
// 那如果0不存在呢? 假如是 2 3 1 最终3被换过来 然后结束当前次循环
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] != i) return i;
}
// 最后遍历一下,如果0 - n-1都在,那么缺失的数字是n。
class Solution {
public:
int missingNumber(vector& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
while(nums[i] != i && nums[i] < n) swap(nums[i], nums[nums[i]]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] != i) return i;
}
return n;
}
};
348. 设计井字棋(中等)?
230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素(中等-二叉树)√
该解法主要是用于二叉树经常被修改的情况,查找第k小的数的时间复杂度为O(logk)。
```c++
class Solution {
public:
priority_queue pque;
int kthSmallest(TreeNode* root, int k){
inorder(root, k);
return pque.top();
}
void inorder(TreeNode* root, int k){
if(!root) return;
inorder(root->left, k);
pque.push(root->val);
if(pque.size() > k) pque.pop();
inorder(root->right, k);
}
};
```
127. 单词接龙(困难-DFS/BFS)?
DFS/BFS 还得多做。
class Solution {
public:
int res = INT_MAX;
int tmp = 1;
int ladderLength(string& beginWord, string& endWord, vector& wordList) {
vector visited(wordList.size(), false);
DFS(beginWord, endWord, wordList, visited);
return res;
}
void DFS(string& beginWord, string & endWord, vector& wordList, vector& visited){
if(beginWord == endWord){
++tmp;
res = min(res, tmp);
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < wordList.size(); ++i){
string word = wordList[i];
if(replace(beginWord, word) && !visited[i]){
visited[i] = true;
DFS(word, endWord, wordList, visited);
visited[i] = false;
--tmp;
}
}
return;
}
bool replace(string& beginWord, string& word){
if(beginWord.size() != word.size()) return false;
int num = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < word.size(); ++i){
if(beginWord[i] != word[i]) ++num;
}
return num <= 1;
}
};
378. 有序矩阵中第 K 小的元素(中等-优先队列、二分、归并)√
这道题还可以用二分(最优)、归并排序来解,下次做再看看矩阵中应用二分的思路和代码,感觉会考。
优先队列:
class Solution {
public:
int kthSmallest(vector>& matrix, int k) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
priority_queue pque;
for(int i(0); i < m; ++i){
for(int j(0); j < n; ++j){
pque.push(matrix[i][j]);
if(pque.size() > k) pque.pop();
}
}
return pque.top();
}
};
171. Excel 表列序号(简单-模拟题)√
挺简单的,就是26进制加法。但是注意一点,res = res * 26 + c - ‘A’ + 1; 如果不给c - ‘A’ + 1加括号先计算,res * 26 + c 可能会溢出。解决办法有两个,要么res定义成unsigned,要么加括号。
class Solution {
public:
int titleToNumber(string columnTitle) {
int res = 0;
for(auto c: columnTitle)
res = res * 26 + (c - 'A' + 1);
return res;
}
};
166. 分数到小数(中等-模拟题-除法)?
class Solution {
public:
string fractionToDecimal(int numerator, int denominator) {
}
};
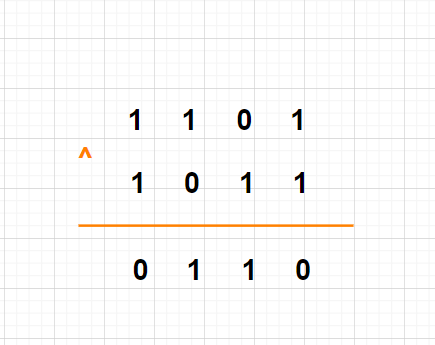
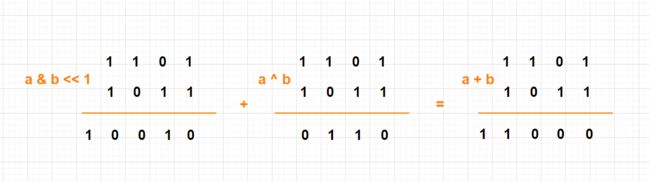
371. 两整数之和(中等 -位运算)?
a ^ b就是不进位的加法
a & b << 1正好可以算出进位
1 0 0 1 0
+ 0 1 1 0
1 1 0 0 0
https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-of-two-integers/solution/li-yong-wei-cao-zuo-shi-xian-liang-shu-qiu-he-by-p/
class Solution {
public:
int getSum(int a, int b) {
while(b != 0){
int temp = a ^ b;
b = (unsigned)(a & b) << 1;
a = temp;
}
return a;
}
};
38. 外观数列(中等-双指针)√
这道题我做的没啥问题。题解都是这么做的。
就是用双指针遍历,slow ~ fast - 1 之间的数字是一样的。
class Solution {
public:
string countAndSay(int n) {
string s = "1";
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i){
string tmp;
for(int slow(0), fast(0); fast <= s.size(); ++fast){
if(s[fast] != s[slow]){
tmp = tmp + to_string(fast - slow) + to_string(s[slow] - '0');
slow = fast;
}
}
s = std::move(tmp);
}
return s;
}
};
190. 颠倒二进制位(简单-位运算)×
位运算不太熟练!
简单做法,重新定义一个res,每次把n的末尾取出来给res,res再左移,就实现了翻转。时间复杂度是O(n)。
//错误写法:不能用while判n是否不是0为结束条件,假设n是5,那么右移3次就是0了,但是res明明应该左移32次
class Solution {
public:
uint32_t reverseBits(uint32_t n) {
uint32_t res = 0;
while(n){
res = res << 1 | (n & 1);
n >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
};
// 正确写法
class Solution {
public:
uint32_t reverseBits(uint32_t n) {
uint32_t res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 32; ++i){
res = res << 1 | (n & 1);
n >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
};
更优解法:分治!O(1)的办法,没看懂。
class Solution {
public:
uint32_t reverseBits(uint32_t n) {
n = (n >> 16) | (n << 16);
n = ((n & 0xff00ff00) >> 8) | ((n & 0x00ff00ff) << 8);
n = ((n & 0xf0f0f0f0) >> 4) | ((n & 0x0f0f0f0f) << 4);
n = ((n & 0xcccccccc) >> 2) | ((n & 0x33333333) << 2);
n = ((n & 0xaaaaaaaa) >> 1) | ((n & 0x55555555) << 1);
return n;
}
};
191. 位1的个数(简单-位运算)√
class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(uint32_t n) {
int res = 0;
while(n != 0){ // 这里可以用while,因为如果n是0说明所有比特位都是0
if(n & 1) ++res;
n = n >> 1;
}
return res;
}
};
328. 奇偶链表(中等-链表)×
有必要多练习!
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-w1hcYyYD-1675863835304)(https://pic.leetcode.cn/1672974277-auUVVZ-LeetCode328.%20%E5%A5%87%E5%81%B6%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8.png)]
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* oddEvenList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head) return nullptr;
// 只需要一个preHead处理偶数节点
ListNode* preHead = new ListNode(-1), *slow= preHead;
ListNode* fast = head;
while(fast){
// 先处理偶数节点
slow->next = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
// 1 2 3
// f s
// 只有3存在(slow->next != nullptr),才有必要更改fast->next,否则倒数第二行就会报错(fast->next = preHead->next;)
// fast必须指向最后一个不空的奇数节点,因为它还要指向第一个偶数节点
if(slow && slow->next){
fast->next = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}else
break;
}
fast->next = preHead->next;
return head;
}
};
116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针(中等-二叉树)√
注意!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
// dque.size(); 千万不能写在for循环里!!!!因为队列的size会变化!
int n = dque.size();
Node* pre = nullptr;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
class Solution {
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
if(!root) return nullptr;
deque dque;
dque.push_front(root);
while(!dque.empty()){
int n = dque.size();
Node* pre = nullptr;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
Node* node = dque.back(); dque.pop_back();
node->next = pre;
if(node->right) dque.push_front(node->right);
if(node->left) dque.push_front(node->left);
pre = node;
}
}
return root;
}
};
218. 天际线问题(困难)?
class Solution {
public:
vector> getSkyline(vector>& buildings) {
}
};
340. 至多包含 K 个不同字符的最长子串(中等-滑动窗口)√
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstringKDistinct(string s, int k) {
int res = 0;
unordered_map umap;
for(int slow(0), fast(0); fast < s.size(); ++fast){
++umap[s[fast]];
while(umap.size() > k){
--umap[s[slow]];
if(!umap[s[slow]]) umap.erase(s[slow]);
++slow;
}
res = max(res, fast - slow + 1);
}
return res;
}
};
172. 阶乘后的零(中等-数学)?
class Solution {
public:
int trailingZeroes(int n) {
}
};
380. O(1) 时间插入、删除和获取随机元素(中等)?
我不理解为什么不能用集合?
插入,删除都是O(1)。
对于随机取元素,用一个随机数加上起始迭代器不能实现吗?
为什么非要用map存储元素在数组中的下标,然后用随机数去数组中随机存取呢?
class RandomizedSet {
public:
RandomizedSet() {
}
bool insert(int val) {
}
bool remove(int val) {
}
int getRandom() {
}
};
/**
* Your RandomizedSet object will be instantiated and called as such:
* RandomizedSet* obj = new RandomizedSet();
* bool param_1 = obj->insert(val);
* bool param_2 = obj->remove(val);
* int param_3 = obj->getRandom();
*/
326. 3 的幂(简单-数学)×
朴素做法:
class Solution {
public:
bool isPowerOfThree(int n) {
if(!n) return 0;
while(n % 3 == 0) n /= 3;
return n == 1;
}
};
O(1)做法:先分析出int内最大的3次幂。
为什么能这样做?举例,3是质数,因此27的因子只有27,9,3,1。
所以只要n能整除INT_MAX内最大的3次幂,说明n就是3的幂。
但是不是质数不能用这个办法,比如4,16 % 8 = 0;但是8不是4的幂。
class Solution {
public:
bool isPowerOfThree(int n) {
return n > 0 && 1162261467 % n == 0;
}
};
324. 摆动排序 II(中等-双指针、桶排序)× ?桶排序
https://leetcode.cn/problems/wiggle-sort-ii/solution/by-jiang-hui-4-5qdr/
O(n)的桶排序我可以不会,但是排序+双指针我总得会吧?
class Solution {
public:
void wiggleSort(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> arr(nums);
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());
// 偶数:2233 奇数:112
int left = (arr.size() - 1) / 2;
int right = arr.size() - 1;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i){
if(i % 2 == 0){
nums[i] = arr[left];
--left;
}else{
nums[i] = arr[right];
--right;
}
}
}
};