skynet学习笔记之require xxx.core
发现不少公司都在用skynet框架,趁着周末就fork了风哥的仓库来学习学习。
单单这一句代码就收获良多:
--lualib/sproto.lua
local core = require "sproto.core"一个小插曲:
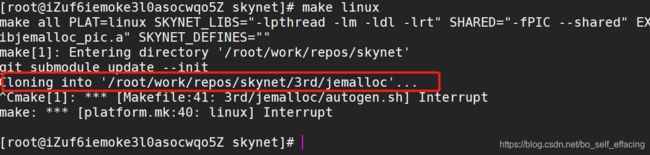
clone完仓库后, 执行 make linux 卡在了Makefile执行 clone jemalloc 仓库的地方,如下图所示:
 试了几次都卡住,我也不想去研究 git submodule update --init 这命令相关的配置还是什么导致的问题,简单粗暴的解决了:
试了几次都卡住,我也不想去研究 git submodule update --init 这命令相关的配置还是什么导致的问题,简单粗暴的解决了:
- 将 3rd/jemalloc 文件夹删除,没有clone成功 其中本来也是空的。
- cd 3rd
- git clone https://github.com/jemalloc/jemalloc.git
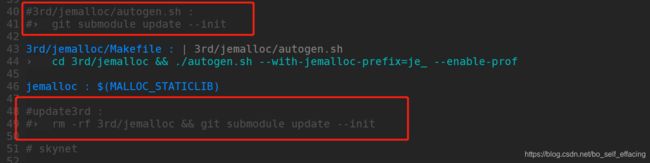
- 修改Makefile 将之前自动从github上clone的代码注释掉,如下图所示,不过如此一来就不会自动更新该库了,当你提交修改的时候记得删除一下jemalloc。
- 如此造成一些不便,有时间研究下为何git submodule update --init 会卡住吧,当前只是想学习skynet,怎么能跑起来就怎么弄吧。
接着重新make linux 编译通过,生成可执行文件 skynet,就可以按照风哥readme上的测试指令来跑一下程序了:
./skynet examples/config # Launch first skynet node (Gate server) and a skynet-master (see config for standalone option)
./3rd/lua/lua examples/client.lua # Launch a client, and try to input hello.正常运行测试程序后,我就view了下 examples/client.lua 文件,大概展示的功能就是循环读取屏幕输入,发送给服务器;接收服务器的消息,打印到屏幕。
进入正题:
"sproto.core" 这个参数给我搞懵了,我在目录下grep,find 都找不到带.core的文件,经过一番折腾,总算搞清了这里require "xxx.core" 的语义啦。以下为探索步骤:
1.从 core.newproto 可以知道该库有newproto这个方法,所以全局搜索 newproto() 这个方法
2.在lsproto.c文件中找到了以下函数定义:
LUAMOD_API int
luaopen_sproto_core(lua_State *L) {
#ifdef luaL_checkversion
luaL_checkversion(L);
#endif
luaL_Reg l[] = {
{ "newproto", lnewproto }, //搜索的函数
{ "deleteproto", ldeleteproto },
{ "dumpproto", ldumpproto },
{ "querytype", lquerytype },
{ "decode", ldecode },
{ "protocol", lprotocol },
{ "loadproto", lloadproto },
{ "saveproto", lsaveproto },
{ "default", ldefault },
{ NULL, NULL },
};
luaL_newlib(L,l);
pushfunction_withbuffer(L, "encode", lencode);
pushfunction_withbuffer(L, "pack", lpack);
pushfunction_withbuffer(L, "unpack", lunpack);
return 1;
}3.在luaconf.h 中找到了LUAMOD_API的定义和一句注释:
/* more often than not the libs go together with the core */
#define LUALIB_API LUA_API
#define LUAMOD_API LUALIB_API4.很明显了,sproto.core 一定就是对应的lsproto.c文件包含的函数的库,不过require是怎么联系到 lsproto.c 的呢,继续探索。
5.我想确认一下是否调用到了 luaopen_sproto_core 函数,就要在该函数里加断点,但是从Makefile里看到 lsproto.c 是和 sproto.c一起编译到 sproto.so 文件里了,通过 nm sproto.so 也能看到luaopen_sproto_core:
$(LUA_CLIB_PATH)/sproto.so : lualib-src/sproto/sproto.c lualib-src/sproto/lsproto.c | $(LUA_CLIB_PATH)
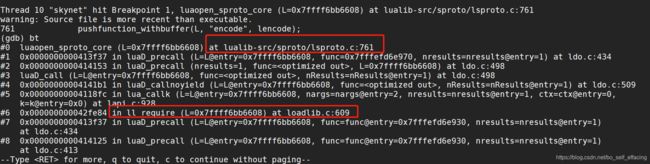
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(SHARED) -Ilualib-src/sproto $^ -o $@6. 给.so文件加断点方法参考:如何在so共享库中打断点,果然调用到了 luaopen_sproto_core 函数:
7.再来研究 int ll_require 方法,即是在lua层注册的 require函数,这里不赘述了,只看其中调用的一个关键函数:
static int ll_require (lua_State *L) {
const char *name = luaL_checkstring(L, 1);
lua_settop(L, 1); /* LOADED table will be at index 2 */
lua_getfield(L, LUA_REGISTRYINDEX, LUA_LOADED_TABLE);
lua_getfield(L, 2, name); /* LOADED[name] */
if (lua_toboolean(L, -1)) /* is it there? */
return 1; /* package is already loaded */
/* else must load package */
lua_pop(L, 1); /* remove 'getfield' result */
findloader(L, name); /************这里通过require传入的参数找到对应的c函数***********/
lua_pushstring(L, name); /* pass name as argument to module loader */
lua_insert(L, -2); /* name is 1st argument (before search data) */
lua_call(L, 2, 1); /* run loader to load module */
if (!lua_isnil(L, -1)) /* non-nil return? */
lua_setfield(L, 2, name); /* LOADED[name] = returned value */
if (lua_getfield(L, 2, name) == LUA_TNIL) { /* module set no value? */
lua_pushboolean(L, 1); /* use true as result */
lua_pushvalue(L, -1); /* extra copy to be returned */
lua_setfield(L, 2, name); /* LOADED[name] = true */
}
return 1;
}8.再看findloader 函数:
static void findloader (lua_State *L, const char *name) {
int i;
...
/* push 'package.searchers' to index 3 in the stack */
if (lua_getfield(L, lua_upvalueindex(1), "searchers") != LUA_TTABLE)
luaL_error(L, "'package.searchers' must be a table");
/* iterate over available searchers to find a loader */
for (i = 1; ; i++) { //遍历serchers表
...
lua_pushstring(L, name);
lua_call(L, 1, 2); /* call it */ //调用 serchers表的对应方法
...
}
}
static const lua_CFunction searchers[] =
{searcher_preload, searcher_Lua, searcher_C, searcher_Croot, NULL};
static int searcher_Croot (lua_State *L) {
const char *filename;
const char *name = luaL_checkstring(L, 1);
const char *p = strchr(name, '.');
int stat;
if (p == NULL) return 0; /* is root */
lua_pushlstring(L, name, p - name);
filename = findfile(L, lua_tostring(L, -1), "cpath", LUA_CSUBSEP);
if (filename == NULL) return 1; /* root not found */
if ((stat = loadfunc(L, filename, name)) != 0) {
if (stat != ERRFUNC)
return checkload(L, 0, filename); /* real error */
else { /* open function not found */
lua_pushfstring(L, "\n\tno module '%s' in file '%s'", name, filename);
return 1;
}
}
lua_pushstring(L, filename); /* will be 2nd argument to module */
return 2;
}
/*
** Try to find a load function for module 'modname' at file 'filename'.
** First, change '.' to '_' in 'modname'; then, if 'modname' has
** the form X-Y (that is, it has an "ignore mark"), build a function
** name "luaopen_X" and look for it. (For compatibility, if that
** fails, it also tries "luaopen_Y".) If there is no ignore mark,
** look for a function named "luaopen_modname".
*/
static int loadfunc (lua_State *L, const char *filename, const char *modname) {
const char *openfunc;
const char *mark;
modname = luaL_gsub(L, modname, ".", LUA_OFSEP);
mark = strchr(modname, *LUA_IGMARK);
if (mark) {
int stat;
openfunc = lua_pushlstring(L, modname, mark - modname);
openfunc = lua_pushfstring(L, LUA_POF"%s", openfunc);
stat = lookforfunc(L, filename, openfunc);
if (stat != ERRFUNC) return stat;
modname = mark + 1; /* else go ahead and try old-style name */
}
openfunc = lua_pushfstring(L, LUA_POF"%s", modname);
return lookforfunc(L, filename, openfunc);
}
9.就不细说几个函数的每一行代码了,简单总结下 local score = require "sproto.core" 这句代码的执行步骤:
- findloader 函数遍历 serchers 表,这个表里装的是不同加载方式的库的查找方法,前三个方法查找无果,轮到执行searcher_Croot 函数了。
- searcher_Croot 函数先以"."字符来分割 "sproto.core", 以sproto为名字到指定的 package.cpath 目录查找对应库文件,找到了 sproto.so,然后调用loadfunc。
- loadfunc就会将 "sproto.core" 先拆分,再和 LUA_POF拼接起来,就是 luaopen_sproto_core 了 :
/* prefix for open functions in C libraries */
#define LUA_POF "luaopen_"- 调用 lookforfunc(L, filename, openfunc) 查找 luaopen_sproto_core 函数地址
- 首先内存中查找对应的动态库 sproto.so
- 如果没有加载该动态库,则会调用 lsys_load 加载该动态库
- dlopen 系统调用加载动态库
- 然后调用 lsys_sym 函数从加载好的动态库中获取到 luaopen_sproto_core 函数地址
10.最后找到的函数放在栈顶,在require中调用,就将 lsproto.c 中的函数注册到了 "sproto.core" 这个模块名下了。
最后推荐几篇有助于自顶向下学习skynet框架的好文章:
- skynet设计综述
- 浅析skynet底层框架
- Actor模型