Pandas 模块-操纵数据(2)-重新索引-reindex()函数
2. 重新索引
请注意,DataFrame.rename() 函数是对行名和列名进行修改,并不修改数据,而DataFrame.reindex 可以引入新行/列,或者去掉旧行/列。
2.1 reindex() 函数
2.1.1 reindex() 语法
DataFrame.reindex(self, labels=None, index=None, columns=None, axis=None, method=None, copy=True, level=None, fill_value=nan, limit=None, tolerance=None)
使用可选的填充逻辑使DataFrame符合新索引。
- labels : 类似数组,可选,新 labels / index "axis"指定的轴与之一致。
- index, columns : 类似数组,可选;要使用的新labels/index 引要符合。最好是一个Index对象,以避免重复数据。
- axis: 默认是 index
- method : {默认 None,'backfill'/'bfill,'pad'/'ffill’, 'nearest'},
用于在重新索引的DataFrame中填充孔的方法。
请注意:这仅适用于具有单调递增/递减索引的DataFrames/Series。
1) None (default): 不填补空白
2) pad / ffill: 将上一个有效观察值向前传播到下一个有效值。
3) backfill / bfill: 使用下一个有效观察值填充空白。
4) nearest: 使用最近的有效观测值来填补空白。
- copy : boolean, 默认 True,即使传递的索引相同,也返回一个新对象。
- level : int 或 name,在一个级别上广播,在传递的MultiIndex级别上匹配索引值。
- fill_value : scalar, 默认为 np.NaN,用于缺失值的值。默认为NaN,但可以是任何“compatible”值。
- limit : int, 默认 None。向前或向后填充的连续元素的最大数量。
- tolerance: 可选。不精确匹配的原始标签和新标签之间的最大距离。
在匹配位置的索引值最符合公式
abs(index[indexer] - target) <= tolerance。
公差可以是一个标量值,它对所有值应用相同的tolerance;
也可以是类似列表的值,它对每个元素应用可变的tolerance。
list-like包括list、tuple、array、Series,
并且必须与索引相同大小,其 dtype 必须与索引的类型完全匹配。
Help on function reindex in module pandas.core.frame:
reindex(self, labels=None, index=None, columns=None, axis=None, method=None, copy=True, level=None, fill_value=nan, limit=None, tolerance=None)
Conform Series/DataFrame to new index with optional filling logic.
Places NA/NaN in locations having no value in the previous index. A new object
is produced unless the new index is equivalent to the current one and
``copy=False``.
Parameters
----------
keywords for axes : array-like, optional
New labels / index to conform to, should be specified using
keywords. Preferably an Index object to avoid duplicating data.
method : {None, 'backfill'/'bfill', 'pad'/'ffill', 'nearest'}
Method to use for filling holes in reindexed DataFrame.
Please note: this is only applicable to DataFrames/Series with a
monotonically increasing/decreasing index.
* None (default): don't fill gaps
* pad / ffill: Propagate last valid observation forward to next
valid.
* backfill / bfill: Use next valid observation to fill gap.
* nearest: Use nearest valid observations to fill gap.
copy : bool, default True
Return a new object, even if the passed indexes are the same.
level : int or name
Broadcast across a level, matching Index values on the
passed MultiIndex level.
fill_value : scalar, default np.NaN
Value to use for missing values. Defaults to NaN, but can be any
"compatible" value.
limit : int, default None
Maximum number of consecutive elements to forward or backward fill.
tolerance : optional
Maximum distance between original and new labels for inexact
matches. The values of the index at the matching locations most
satisfy the equation ``abs(index[indexer] - target) <= tolerance``.
Tolerance may be a scalar value, which applies the same tolerance
to all values, or list-like, which applies variable tolerance per
element. List-like includes list, tuple, array, Series, and must be
the same size as the index and its dtype must exactly match the
index's type.
Returns
-------
Series/DataFrame with changed index.
2.1.2 reindex() 函数范例-参数 labels 和 axis
先准备数据
首先 labels 是可以加也可以不加的,如果只有一个参数,默认是 labels
data.reindex(list(range(11))[:0:-1])从运行结果可以看到,
第一,新 index 里面没有提到的 index 0,已经被删除了;
第二,新 index 里面有,而旧 index 里面没有的 10,新加了一行,数据由 NaN 填充。
第三,整个数据按照新 index 的顺序重新排列了,伴随着部分数据值的变化。
其次 只有一个参数,加了 labels 效果是一样的
再次 axis 默认是0 即 index,如果设置为 1,则意味着 labels 作用于 columns,大家可以看到,因为 columns 上没有新 index 内容,所以原有的数据列全消失了,取而代之的是新 index 指定的列,都是用 NaN 填充
data.reindex(labels=list(range(11))[:0:-1],
axis=1)运行结果
2.1.3 reindex() 函数范例-参数 index 和 columns
index 和 columns 既可以组合用,也可以单独用;如果只用 index,作用相当于(labels,axis 为默认 0)的情况;如果只用 columns,作用相当于(labels,axis 为1 )的情况;
单独使用 index
data.reindex(index=list(range(11))[:0:-1])单独使用 columns
data.reindex(columns=["title","age","location","else"])运行结果
如果 index 和 columns 组合起来用,就比 labels 和 axis 的组合更有效果。
2.1.4 reindex() 函数范例-参数 copy
比较简单,略,要么是默认 True 即使传递的索引相同,也返回一个新对象。要么就是 False。
2.1.5 reindex() 函数范例-参数 fill_value
设置了 fill_value,那么原本默认填写 NaN 的数据,就会按照 fill_value 来填充
data.reindex(columns=["title","age","location","else"],
fill_value="Unknown")2.1.6 reindex() 函数范例-参数 method
method : {None, 'backfill'/'bfill', 'pad'/'ffill', 'nearest'} Method to use for filling holes in reindexed DataFrame.
Please note: this is only applicable to DataFrames/Series with a monotonically increasing/decreasing index.
* None (default): don't fill gaps
* pad / ffill: Propagate last valid observation forward to next valid. 向前填充值
* backfill / bfill: Use next valid observation to fill gap.向后填充值;
* nearest: Use nearest valid observations to fill gap.从距离最近的索引值开始填充。
请注意:这仅适用于具有单调递增/递减索引的 DataFrames/Series。
首先准备数据
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(6,3),columns=['col1','col2','col3'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(2,3),columns=['col1','col2','col3'])
print(df1)
print(df2)
1) 默认情况,即Method 为 None
2) method="ffill" 的情况
因为是向前填充,所以选择前一行的数据进行填充,填充2,3,4,5 行的即1行的数据
因为是向前填充,前一行没有数据,所以用 NaN 数据进行填充
3) method="backfill" 的情况
当method="backfill"时候,因为没有后一行,所以用 NaN 填充
当method="backfill"时候,要填充的 -2,-1 行 因为有后一行 1,所以用 0 行数据填充
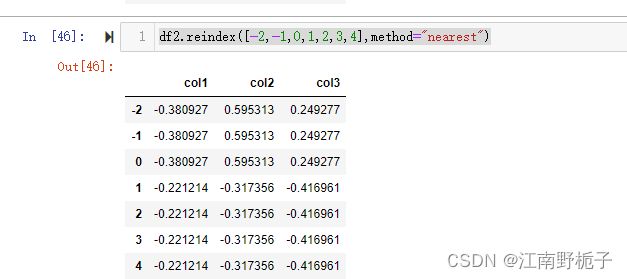
4) method="nearest" 的情况
method="nearest" 的情况,则分别选择最近的行进行填充
2.1.7 reindex() 函数范例-参数 limit
limit : int, 默认 None。向前或向后填充的连续元素的最大数量。
limit argument only valid if doing pad, backfill or nearest reindexing
使用2.1.6 的准备数据,limit 限制在1 时候,可以看到向前和向后填充的行数只能是1