Spring源码解析-构造函数
1、构造函数概述
构造函数中,主要创建两个对象分别用来读取注解参数和classpath下的文件
-
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 专门读取注解参数的Reader
-
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 专门读取classpath下的文件,例如yml、properties等。
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 可以通过扫描指定的包或类来自动检测和注册带有特定注解的组件,例如@Service、@Repository和@Controller等。使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,我们可以使用注解来配置和管理Spring应用程序的各种组件,而不需要显式地在XML配置文件中进行配置。这样可以简化配置过程并提高开发效率。
1.1 构造器源码
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
StartupStep createAnnotatedBeanDefReader = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.context.annotated-bean-reader.create");
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
createAnnotatedBeanDefReader.end();
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
主要的代码在this.reader和this.sanner。
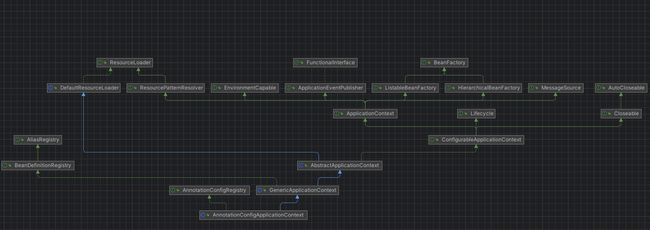
1.2 继承关系
总览继承关系:
从继承关系来看,AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 继承 GenericApplicationContext 类,GenericApplicationContext 又实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry 接口,所以AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 本身就具备了BeanDefinitionRegistry 的功能。其他的关系也可以从上图中看出.
总结一些主要的特性:
-
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext是一个BeanDefinitionRegistry注册器。 -
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext是一个ConfigurableApplicationContext上下文配置的容器 -
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext继承GenericApplicationContext,DefaultListableBeanFactory是GenericApplicationContext的一个final属性。
2、AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader注解读取器
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 构造函数:
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this(registry, getOrCreateEnvironment(registry));
}
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
this.conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator(registry, environment, null);
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
从构造函数可以看出是在需要传递一个Bean定义对象的注解器BeanDefinitionRegistry,这个register就是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。
构造函数中主要做了两件事情,创建条件解析器以及注解注解配置处理器
-
this.conditionEvaluator条件解析器,主要针对Conditional.class -
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors注册注解配置处理器
2.1 条件解析器this.conditionEvaluator
ConditionEvaluator用于在运行时评估条件表达式。它的主要作用是根据条件表达式的结果来决定是否应该创建或注册某个Bean。
在Spring中,我们可以使用条件注解(如@Conditional)来根据条件来决定是否应该创建或注册某个Bean。ConditionEvaluator就是用于解析和评估这些条件表达式的。
ConditionEvaluator 的构造器仅仅是new了一个ConditionContextImpl, 且ConditionContextImpl是ConditionEvaluator的内部类。
这个不是本章节的重点,有兴趣的笔友可以深入研究。
2.2 注册注解配置处理器
再了解`AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors`方法之前,我们先看`AnnotationConfigUtils`都给我们提供了那些方法。
AnnotationConfigUtils提供了公用定义的注解的处理、注册注解后置处理器、注解后置处理器以及一些常量。这些常量也是公用内置的公用类。常量如下:
-
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
-
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationBeanNameGenerator
-
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
-
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalRequiredAnnotationProcessor(已过时)
-
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
-
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalPersistenceAnnotationProcessor
-
org.springframework.orm.jpa.support.PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
-
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
-
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
从命名可以看出,大部分的类都是以internal 开头的。这个都是解析注解所必要的内部使用的类,不对外暴露的类。
2.3 来研究具体的注册注解处理器的方法
源码
public static void registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(registry, null);
}
public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
// ......
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
// ......
return beanDefs;
}
从源码来看,注册注解处理器调用重载方法registerAnnotationConfigProcessors( BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source)
2.3.1 源码(1)
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
if (beanFactory != null) {
if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());
}
}
拆解
registry是不是DefaultListableBeanFactoryBean工厂,如果是就会设置属性,如果不是,则会忽略。 由于上面1.2继承关系的分析,我们知道当前的registry继承自GenericApplicationContext。
private static DefaultListableBeanFactory unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (registry instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
return (DefaultListableBeanFactory) registry;
}
else if (registry instanceof GenericApplicationContext) {
return ((GenericApplicationContext) registry).getDefaultListableBeanFactory();
}
else {
return null;
}
}
所以我们必然可以得到一个DefaultListableBeanFactory对象。
接下来,就是给beanFactory 设置属性,根据是否满足条件设置对应的属性。
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator() 给BeanFactory设置依赖的比较器,主要用来排序。设置的是AnnotationAwareOrderComparator的单例。
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver() 给BeanFactory设置候选的解析器,也就new了一个ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver对象,设置了进去。
ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver对象的父类QualifierAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver的构造器中添加了对Qualifier.class的支持,私有方法中又包含Value.class,所以注解注入的解析器可以处理两个注解:
-
@Qualifier与@Autowired配合使用,按照名称注入 -
@Value源码中通过 findValue() 解析总结一下,beanFactory设置以上两个属性,让beanFactory具备了使用比较器、以及解析
@Qualifier、@Value的能力。
2.3.2 源码(2)
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// ......
因为我们之前调用的方法是`registerAnnotationConfigProcessors`,没有返回值。所以我们没有必要关心`beanDefs.add()`的结果。只需要关注`registerPostProcessor()` 这个方法即可。
接下来的源码大致的含义就是判断`register` 中是否包含某些`BeanDefinition`,如果不存在就会注册到`register`中。也就是`register`中一定会有这些`BeanDefinition`。
-
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
- 对应ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class,主要用来处理@Configuration类
-
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
- 对应AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class 主要用来处理@Autowired和@Value,还支持JSR-330de @Inject注解,可以替代@Autowired。
-
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
- 对应CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class,主要用来处理JSR-250的@Resource,以及@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy初始化和销毁注解
-
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalPersistenceAnnotationProcessor
- 其实加载的是org.springframework.orm.jpa.support.PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类,注解检查对JPA的支持。
-
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
- 对应EventListenerMethodProcessor.class类,主要处理
ApplicationListener的实例,也就是Spring的事件驱动的模型。
- 对应EventListenerMethodProcessor.class类,主要处理
-
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
- 对应DefaultEventListenerFactory.class类,支持@EventListener纾解的一个默认实现
总结一下,通过一系列的设置可以处理的注解包括:
-
@Configuration
-
@Resource
-
@Autowired
-
@Inject
-
@PostConstruct
-
@PreDestroy
-
@Value
-
@EventListener
3、ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 扫描器
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 构造函数
public ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this(registry, true);
}
public ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean useDefaultFilters) {
this(registry, useDefaultFilters, getOrCreateEnvironment(registry));
}
public ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean useDefaultFilters,
Environment environment) {
this(registry, useDefaultFilters, environment,
(registry instanceof ResourceLoader ? (ResourceLoader) registry : null));
}
public ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean useDefaultFilters,
Environment environment, @Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
if (useDefaultFilters) {
registerDefaultFilters();
}
setEnvironment(environment);
setResourceLoader(resourceLoader);
}
该构造函数有不同参数的重载。最终主要的是三个方法:
-
registerDefaultFilters()注册默认的过滤器 -
setEnvironment(environment)设置运行环境 -
setResourceLoader(resourceLoader)设置resource资源的加载器
3.1 注册默认的过滤器
从上面的构造函数看,默认传递的`useDefaultFilters` 参数为true,也就是`registerDefaultFilters()` 一定会执行。
注册默认的注解过滤器,处理`@Component`,以及具有`@Component`元注解的扩展注解,如`@Service`、`@Controller`、`@respository`.
如果支持Java EE 6的`@ManagedBean`以及JSR-330的`@Named` 注解。
源码如下:
protected void registerDefaultFilters() {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(Component.class));
ClassLoader cl = ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.class.getClassLoader();
try {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(
((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.annotation.ManagedBean", cl)), false));
logger.trace("JSR-250 'javax.annotation.ManagedBean' found and supported for component scanning");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-250 1.1 API (as included in Java EE 6) not available - simply skip.
}
try {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(
((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Named", cl)), false));
logger.trace("JSR-330 'javax.inject.Named' annotation found and supported for component scanning");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-330 API not available - simply skip.
}
}
3.2 设置运行的环境
从ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 构造函数可知,获取环境的方法是:getOrCreateEnvironment(registry)
源码如下:
private static Environment getOrCreateEnvironment(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
if (registry instanceof EnvironmentCapable) {
return ((EnvironmentCapable) registry).getEnvironment();
}
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
如果registry 具备环境的能力,也就是实现EnvironmentCapable,就直接返回环境,如果没有,就直接创建标椎的环境。
设置环境很简单,就是简单的赋值。
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");
this.environment = environment;
this.conditionEvaluator = null;
}
3.3 设置资源加载器
public void setResourceLoader(@Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.resourcePatternResolver = ResourcePatternUtils.getResourcePatternResolver(resourceLoader);
this.metadataReaderFactory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory(resourceLoader);
this.componentsIndex = CandidateComponentsIndexLoader.loadIndex(this.resourcePatternResolver.getClassLoader());
}
从传递参数来看,resourceLoader是通过register强制转化过来的。
this(registry, useDefaultFilters, environment,
(registry instanceof ResourceLoader ? (ResourceLoader) registry : null));
我们的registry是间接实现ResourceLoader接口的,所以resourceLoader 也是registry本身。
主要设置是三个属性:
-
this.resourcePatternResolver
-
this.metadataReaderFactory
-
this.componentsIndex
3.3.1 设置资源正则解析器
this.resourcePatternResolver = ResourcePatternUtils.getResourcePatternResolver(resourceLoader);
源码:
public static ResourcePatternResolver getResourcePatternResolver(@Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
return (ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader;
}
else if (resourceLoader != null) {
return new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(resourceLoader);
}
else {
return new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
}
}
根据逻辑,返回的是new的PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver对象。解析项目中的资源文件,如xml等
3.3.2 设置原数据读取的工厂
this.metadataReaderFactory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory(resourceLoader);
源码:
public CachingMetadataReaderFactory(@Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
super(resourceLoader);
if (resourceLoader instanceof DefaultResourceLoader) {
this.metadataReaderCache =
((DefaultResourceLoader) resourceLoader).getResourceCache(MetadataReader.class);
}
else {
setCacheLimit(DEFAULT_CACHE_LIMIT);
}
}
CachingMetadataReaderFactory的父类是SimpleMetadataReaderFactory,为元数据的读取设置缓存。
3.3.3 设置候选的Component的索引
this.componentsIndex = CandidateComponentsIndexLoader.loadIndex(this.resourcePatternResolver.getClassLoader());
源码:
public static CandidateComponentsIndex loadIndex(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
classLoaderToUse = CandidateComponentsIndexLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
return cache.computeIfAbsent(classLoaderToUse, CandidateComponentsIndexLoader::doLoadIndex);
}
其中CandidateComponentsIndexLoader::doLoadIndex 会加载META-INF/spring.components 下的URL。
4、小结
构造函数中主要设置了两个东西,一个是处理注解的解析器以及扫描Bean定义的解析器。
注解解析处理的注解包括:
-
@Configuration
-
@Resource
-
@Autowired
-
@Inject
-
@PostConstruct
-
@PreDestroy
-
@Value
-
@EventListener
-
@Qualifier
Classpath的扫描器可以处理的注解
-
@Service
-
@Controller
-
@Respository
-
@ManagedBean
-
@Named
-
@Component