程序员面试金典3.1-3.6
程序员面试金典3.1-3.6
文章目录
- 3.1 三合一
- 3.2栈的最小值
- 3.3 堆盘子(×)
- 3.4化栈为队
- 3.5栈排序
- 3.6动物收容所
3.1 三合一
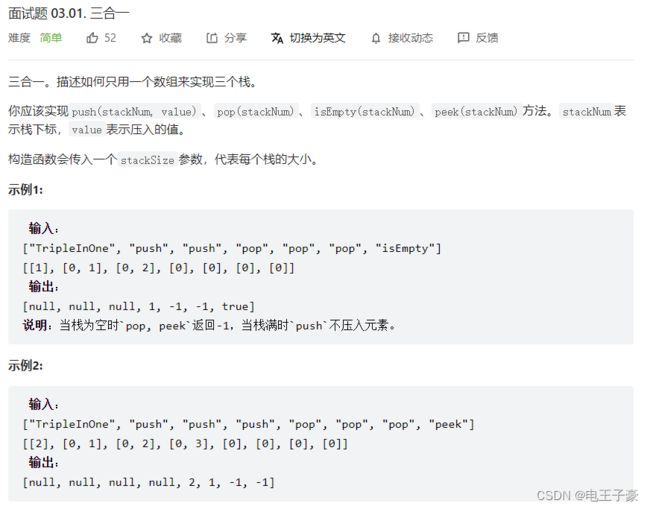
题读不懂,直接上链接吧。就是让用一个数组实现三个栈。
链接
稍微写了一下代码:
class TripleInOne {
int[] stack;
int []pointer;
//pointer永远指向最前面的没有被放数据的
public TripleInOne(int stackSize) {
stack=new int[stackSize*3];
pointer=new int[3];
pointer[0]=0;
pointer[1]=1;
pointer[2]=2;
}
public void push(int stackNum, int value) {
if(pointer[stackNum]<stack.length){
stack[pointer[stackNum]]=value;
pointer[stackNum]+=3;
}
}
public int pop(int stackNum) {
if(isEmpty(stackNum)) return -1;
pointer[stackNum]-=3;
return stack[pointer[stackNum]];
}
public int peek(int stackNum) {
if(isEmpty(stackNum)) return -1;
int val=pointer[stackNum]-3;
return stack[val];
}
public boolean isEmpty(int stackNum) {
if(pointer[stackNum]-3<0)
return true;
else return false;
}
}
3.2栈的最小值
用两个栈,一个栈每次+数据,一个栈+当前的最小值。弹出的时候一起弹出。
class MinStack {
/** initialize your data structure here. */
Stack<Integer> stk1;
Stack<Integer> stk2;
public MinStack() {
stk1=new Stack<>();
stk2=new Stack<>();
stk2.push(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public void push(int x) {
stk1.push(x);
stk2.push(Math.min(x,stk2.peek()));
}
public void pop() {
stk1.pop();
stk2.pop();
}
public int top() {
return stk1.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return stk2.peek();
}
}
Java中看一个数是peek()而不是top();
用Integer.MAX_VALUE是为了第一个数方便。
3.3 堆盘子(×)
二维数组的感觉。不过有一个严重的问题是,没有说前面拿出去的盘子要不要补上。反正很奇怪
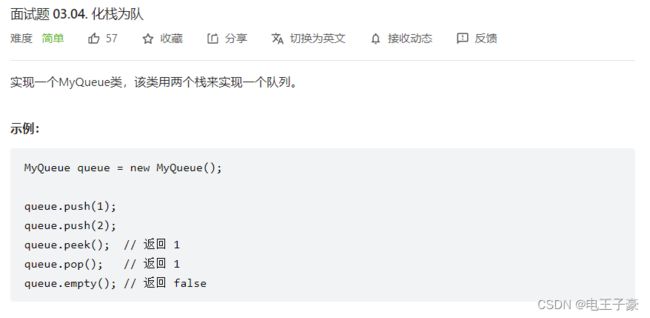
3.4化栈为队
class MyQueue {
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
Stack<Integer> stackWrite;
Stack<Integer> stackRead;
public MyQueue() {
stackWrite = new Stack<>();
stackRead = new Stack<>();
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
stackWrite.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
peek();
return stackRead.pop();
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
if(!stackRead.isEmpty()) return stackRead.peek();
while(!stackWrite.isEmpty()) stackRead.push(stackWrite.pop());
return stackRead.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return stackWrite.isEmpty() && stackRead.isEmpty();
}
}
我们知道:同一段序列,分别存进一个栈和一个队列,那么出栈序列T和出队序列S顺序刚好是相反的。
那么,假如我们有两个栈的话,一段序列list通过第一个栈后,再压入第二个栈,这时第二个栈的出栈序列应该和list直接压入队列后的出队序列是一样的。
既然如此,我们用两个栈就可以模拟队列,一个栈专门用来存入数据,记为StackWrite;一个栈专门用来读取数据,记为StackRead。基于上面的结论,我们每次入队时,就把数据压入StackWrite,每次读数据时,就把StackWrite中的数据再压入StackRead,这时StackRead中的栈顶元素就是我们所期望的队首元素。
在出队的时候,要注意一点:
如果StackRead中有数据,那么就直接弹出StackRead的栈顶元素;
如果StackRead为空,先考虑把StackWrite中的元素压入StackRead,再弹出StackRead的栈顶元素。
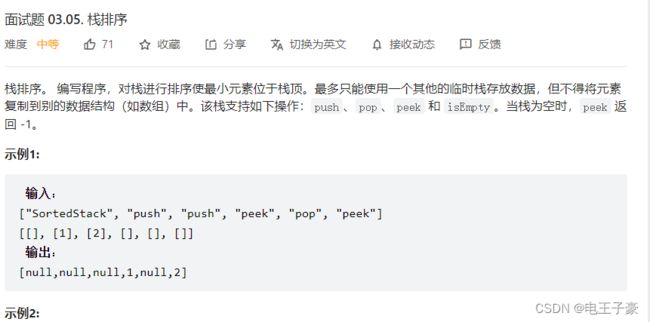
3.5栈排序
class SortedStack {
Stack<Integer>stack2;
Stack<Integer>stack1;
public SortedStack() {
stack2=new Stack<>();// 2 辅助栈
stack1=new Stack<>();// 8 7 3 原栈
//辅助栈 2 3 6 原栈 8 7
}
public void push(int val) { //5
while(!stack2.isEmpty() && stack2.peek()>val){
stack1.push(stack2.peek());
stack2.pop();
}
while(!stack1.isEmpty() && stack1.peek()<val){
stack2.push(stack1.peek());
stack1.pop();
}
stack1.push(val);
}
public void pop() {
while(!stack2.isEmpty()){
stack1.push(stack2.peek());
stack2.pop();
}
if(!stack1.isEmpty()) stack1.pop();
}
public int peek() {
while(!stack2.isEmpty()){
stack1.push(stack2.peek());
stack2.pop();
}
if(!stack1.isEmpty()) return stack1.peek();
else return -1;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return stack2.isEmpty() && stack1.isEmpty();
}
}
这个改了好久的bug,主要是忘记判断为isEmpty();
push那边的思想也要注意
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-of-stacks-lcci/solution/cliang-chong-fu-zhu-zhan-jie-fa-by-yizhe-shi/
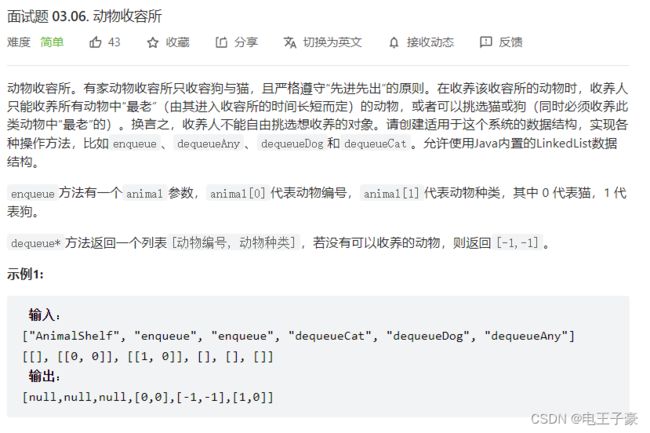
3.6动物收容所
用一个猫队列和一个狗队列
或者用一个大队列也行
而且大队列也可以用数组代替。emm还是用队列吧
class AnimalShelf {
Queue<int[]>cat;
Queue<int[]>dog;
public AnimalShelf() {
dog=new LinkedList<>();
cat=new LinkedList<>();
}
public void enqueue(int[] animal) {
if(animal[1]==0) cat.offer(animal);
else dog.offer(animal);
}
public int[] dequeueAny() {
if(cat.isEmpty() && dog.isEmpty()) return new int[]{-1,-1};
if(cat.isEmpty()) return dog.poll();
if(dog.isEmpty()) return cat.poll();
if(dog.peek()[0]>cat.peek()[0]) return cat.poll();
else return dog.poll();
}
public int[] dequeueDog() {
if(dog.isEmpty()) return new int[]{-1,-1};
return dog.poll();
}
public int[] dequeueCat() {
if(cat.isEmpty()) return new int[]{-1,-1};
return cat.poll();
}
}
Queue继承了Collection接口
Queue使用时要尽量避免Collection的add()和remove()方法,add()和remove()方法在失败的时候会抛出异常。
要使用offer()来加入元素,使用poll()来获取并移出元素。取出元素可以用peek();
值得注意的是LinkedList类实现了Queue接口,因此我们可以把LinkedList当成Queue来用。