Spring结合自定义注解实现 AOP 切面功能【详解】
Spring结合自定义注解实现 AOP 切面功能
- Spring AOP 注解概述
- @Aspect 快速入门
- execution 切点表达式 拦截指定类的方法
- @Pointcut("@annotation(xx)") 拦截拥有指定注解的方法
- 常用注解
-
- 1.@Before:在切点方法前执行
- 2.@After:在切点方法后执行
- 3.@Around:在切点方法外环绕执行
- 4.@AfterRetruning: 在方法返回之前,获取返回值并进行记录操作
- 5.@AfterThrowing: 在异常抛出前进行处理,比如记录错误日志
- JoinPoint和ProceedingJoinPoint的概念与方法说明
-
- JoinPoint的概念与方法说明
- ProceedingJoinPoint的概念与方法说明
- 编入(执行顺序)的优先级
- 访问目标方法的形参
- 切入点的使用
-
- 定义切入点
- 切入点指示符
- 切点表达式组合
- 案例
-
- 1:环绕通知 实现开关目标方法
- 2:自定义注解+切面实现统一日志处理
-
- 2.1 自定义日志注解
- 2.2 声明日志切面组件
- 2.3 控制层运行结果
- 2.4 运行结果
- 3:自定义注解与切面类
-
- 3.1 创建自定义注解
- 3.2 创建一个类,定义方法后使用自定义注解
- 3.3 定义切面类进行,扫描自定义注解,并对切入点进行处理
- 4. After应用实例
-
- 4.1 使用After增强处理
- 4.2 使用Around增强处理
Spring AOP 注解概述
1、Spring 的 AOP 功能除了在配置文件中配置一大堆的配置,比如切入点、表达式、通知等等以外,使用注解的方式更为方便快捷,特别是 Spring boot 出现以后,基本不再使用原先的 beans.xml 等配置文件了,而都推荐注解编程。
| 注解 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| @Aspect | 切面声明,标注在类、接口(包括注解类型)或枚举上。 |
| @Pointcut | 切入点声明,即切入到哪些目标类的目标方法。既可以用 execution 切点表达式, 也可以是 annotation 指定拦截拥有指定注解的方法.value 属性指定切入点表达式,默认为 “”,用于被通知注解引用,这样通知注解只需要关联此切入点声明即可,无需再重复写切入点表达式 |
| @Before | 前置通知, 在目标方法(切入点)执行之前执行。value 属性绑定通知的切入点表达式,可以关联切入点声明,也可以直接设置切入点表达式注意:如果在此回调方法中抛出异常,则目标方法不会再执行,会继续执行后置通知 -> 异常通知。 |
| @After | 后置通知, 在目标方法(切入点)执行之后执行 |
| @AfterReturning | 返回通知, 在目标方法(切入点)返回结果之后执行.pointcut 属性绑定通知的切入点表达式,优先级高于 value,默认为 “” |
| @AfterThrowing | 异常通知, 在方法抛出异常之后执行, 意味着跳过返回通知pointcut 属性绑定通知的切入点表达式,优先级高于 value,默认为 ""注意:如果目标方法自己 try-catch 了异常,而没有继续往外抛,则不会进入此回调函数 |
| @Around | 环绕通知:目标方法执行前后分别执行一些代码,类似拦截器,可以控制目标方法是否继续执行。通常用于统计方法耗时,参数校验等等操作。 |
正常流程:【环绕通知-前】-> 【前置通知】-> 【返回通知】-> 【后置通知】->【环绕通知-后】。
2、上面这些 AOP 注解都是位于如下所示的 aspectjweaver 依赖中:
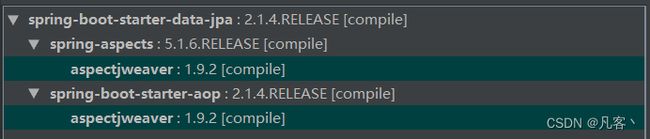
3、对于习惯了 Spring 全家桶编程的人来说,并不是需要直接引入 aspectjweaver 依赖,因为 spring-boot-starter-aop 组件默认已经引用了 aspectjweaver 来实现 AOP 功能。换句话说 Spring 的 AOP 功能就是依赖的 aspectjweaver !
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aopartifactId>
<version>2.1.4.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
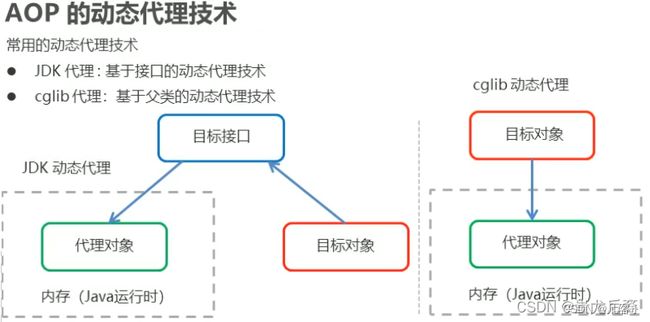
4、AOP 底层是通过 Spring 提供的的动态代理技术实现的,在运行期间动态生成代理对象,代理对象方法执行时进行增强功能的介入,再去调用目标对象的方法,从而完成功能的增强。主要使用 JDK 动态代理与 Cglib 动态代理。
5、所以如果目标类不是 Spring 组件,则无法拦截,如果是 类名.方法名 方式调用,也无法拦截。
@Aspect 快速入门
1、@Aspect 常见用于记录日志、异常集中处理、权限验证、Web 参数校验、事务处理等等
2、要想把一个类变成切面类,只需3步:
- 在类上使用 @Aspect 注解使之成为切面类
- 切面类需要交由 Sprign 容器管理,所以类上还需要有
@Service、@Repository、@Controller、@Component等注解 - 在切面类中自定义方法接收通知
3、AOP 的含义就不再累述了,下面直接上示例:
/**
* 切面注解 Aspect 使用入门
* 1、@Aspect:声明本类为切面类
* 2、@Component:将本类交由 Spring 容器管理
* 3、@Order:指定切入执行顺序,数值越小,切面执行顺序越靠前,默认为 Integer.MAX_VALUE
*
* @author wangMaoXiong
* @version 1.0
* @date 2020/8/20 19:22
*/
@Aspect
@Order(value = 999)
@Component
public class AspectHelloWorld {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AspectHelloWorld.class);
/**
* @Pointcut :切入点声明,即切入到哪些目标方法。value 属性指定切入点表达式,默认为 ""。
* 用于被下面的通知注解引用,这样通知注解只需要关联此切入点声明即可,无需再重复写切入点表达式
*
* 切入点表达式常用格式举例如下:
* - * com.wmx.aspect.EmpService.*(..)):表示 com.wmx.aspect.EmpService 类中的任意方法
* - * com.wmx.aspect.*.*(..)):表示 com.wmx.aspect 包(不含子包)下任意类中的任意方法
* - * com.wmx.aspect..*.*(..)):表示 com.wmx.aspect 包及其子包下任意类中的任意方法
*
* value 的 execution 可以有多个,使用 || 隔开.
*/
@Pointcut(value =
"execution(* com.wmx.hb.controller.DeptController.*(..)) " +
"|| execution(* com.wmx.hb.controller.EmpController.*(..))")
private void aspectPointcut() {
}
/**
* 前置通知:目标方法执行之前执行以下方法体的内容。
* value:绑定通知的切入点表达式。可以关联切入点声明,也可以直接设置切入点表达式
*
* * @param joinPoint:提供对连接点处可用状态和有关它的静态信息的反射访问
* * * Object[] getArgs():返回此连接点处(目标方法)的参数,目标方法无参数时,返回空数组
* * * Signature getSignature():返回连接点处的签名。
* * * Object getTarget():返回目标对象
* * * Object getThis():返回当前正在执行的对象
* * * StaticPart getStaticPart():返回一个封装此连接点的静态部分的对象。
* * * SourceLocation getSourceLocation():返回与连接点对应的源位置
* * * String toLongString():返回连接点的扩展字符串表示形式。
* * * String toShortString():返回连接点的缩写字符串表示形式。
* * * String getKind():返回表示连接点类型的字符串
* * *
*/
@Before(value = "aspectPointcut()")
public void aspectBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
Object target = joinPoint.getTarget();
Object aThis = joinPoint.getThis();
JoinPoint.StaticPart staticPart = joinPoint.getStaticPart();
SourceLocation sourceLocation = joinPoint.getSourceLocation();
String longString = joinPoint.toLongString();
String shortString = joinPoint.toShortString();
LOG.debug("【前置通知】" +
"args={},signature={},target={},aThis={},staticPart={}," +
"sourceLocation={},longString={},shortString={}"
, Arrays.asList(args), signature, target, aThis, staticPart, sourceLocation, longString, shortString);
}
/**
* 后置通知:目标方法执行之后执行以下方法体的内容,不管目标方法是否发生异常。
* value:绑定通知的切入点表达式。可以关联切入点声明,也可以直接设置切入点表达式
*/
@After(value = "aspectPointcut()")
public void aspectAfter(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
LOG.debug("【后置通知】kind={}", joinPoint.getKind());
}
/**
* 返回通知:目标方法返回后执行以下代码
* value 属性:绑定通知的切入点表达式。可以关联切入点声明,也可以直接设置切入点表达式
* pointcut 属性:绑定通知的切入点表达式,优先级高于 value,默认为 ""
* returning 属性:通知签名中要将返回值绑定到的参数的名称,默认为 ""
*
* @param joinPoint :提供对连接点处可用状态和有关它的静态信息的反射访问
* @param result :目标方法返回的值,参数名称与 returning 属性值一致。无返回值时,这里 result 会为 null.
*/
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "aspectPointcut()", returning = "result")
public void aspectAfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
LOG.debug("【返回通知】,shortString={},result=", joinPoint.toShortString(), result);
}
/**
* 异常通知:目标方法发生异常的时候执行以下代码,此时返回通知不会再触发
* value 属性:绑定通知的切入点表达式。可以关联切入点声明,也可以直接设置切入点表达式
* pointcut 属性:绑定通知的切入点表达式,优先级高于 value,默认为 ""
* throwing 属性:与方法中的异常参数名称一致,
*
* @param ex:捕获的异常对象,名称与 throwing 属性值一致
*/
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "aspectPointcut()", throwing = "ex")
public void aspectAfterThrowing(JoinPoint jp, Exception ex) {
String methodName = jp.getSignature().getName();
if (ex instanceof ArithmeticException) {
LOG.error("【异常通知】" + methodName + "方法算术异常(ArithmeticException):" + ex.getMessage());
} else {
LOG.error("【异常通知】" + methodName + "方法异常:" + ex.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 环绕通知
* 1、@Around 的 value 属性:绑定通知的切入点表达式。可以关联切入点声明,也可以直接设置切入点表达式
* 2、Object ProceedingJoinPoint.proceed(Object[] args) 方法:继续下一个通知或目标方法调用,返回处理结果,如果目标方法发生异常,则 proceed 会抛异常.
* 3、假如目标方法是控制层接口,则本方法的异常捕获与否都不会影响目标方法的事务回滚
* 4、假如目标方法是控制层接口,本方法 try-catch 了异常后没有继续往外抛,则全局异常处理 @RestControllerAdvice 中不会再触发
*
* @param joinPoint
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Around(value = "aspectPointcut()")
public Object handleControllerMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
this.checkRequestParam(joinPoint);
StopWatch stopWatch = StopWatch.createStarted();
LOG.debug("【环绕通知】执行接口开始,方法={},参数={} ", joinPoint.getSignature(), Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs()).toString());
//继续下一个通知或目标方法调用,返回处理结果,如果目标方法发生异常,则 proceed 会抛异常.
//如果在调用目标方法或者下一个切面通知前抛出异常,则不会再继续往后走.
Object proceed = joinPoint.proceed(joinPoint.getArgs());
stopWatch.stop();
long watchTime = stopWatch.getTime();
LOG.debug("【环绕通知】执行接口结束,方法={}, 返回值={},耗时={} (毫秒)", joinPoint.getSignature(), proceed, watchTime);
return proceed;
}
/**
* 参数校验,防止 SQL 注入
*
* @param joinPoint
*/
private void checkRequestParam(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
if (args == null || args.length <= 0) {
return;
}
String params = Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()).toUpperCase();
String[] keywords = {"DELETE ", "UPDATE ", "SELECT ", "INSERT ", "SET ", "SUBSTR(", "COUNT(", "DROP ",
"TRUNCATE ", "INTO ", "DECLARE ", "EXEC ", "EXECUTE ", " AND ", " OR ", "--"};
for (String keyword : keywords) {
if (params.contains(keyword)) {
LOG.warn("参数存在SQL注入风险,其中包含非法字符 {}.", keyword);
throw new RuntimeException("参数存在SQL注入风险:params=" + params);
}
}
}
}
如上所示在不修改原来业务层代码的基础上,就可以使用 AOP 功能,在目标方法执行前后或者异常时都能捕获然后执行。
execution 切点表达式 拦截指定类的方法
1、@Pointcut 切入点声明注解,以及所有的通知注解都可以通过 value 属性或者 pointcut 属性指定切入点表达式。
2、切入点表达式通过 execution 函数匹配连接点,语法:execution([方法修饰符] 返回类型 包名.类名.方法名(参数类型) [异常类型])
- 访问修饰符可以省略;
- 返回值类型、包名、类名、方法名可以使用星号*代表任意;
- 包名与类名之间一个点.代表当前包下的类,两个点…表示当前包及其子包下的类;
- 参数列表可以使用两个点…表示任意个数,任意类型的参数列表;
3、切入点表达式的写法比较灵活,比如:* 号表示任意一个,… 表示任意多个,还可以使用 &&、||、! 进行逻辑运算,不过实际开发中通常用不到那么多花里胡哨的,掌握以下几种就基本够用了。
4、特别注意:当明确指定了切入的类时,类必须存在,否则启动报错,此时可以在类名前后加上*号表示模糊包含。
切入点表达式常用举例
| 标题 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| execution(* com.wmx.aspect.EmpServiceImpl.findEmpById(Integer)) | 匹配 com.wmx.aspect.EmpService 类中的 findEmpById 方法,且带有一个 Integer 类型参数。 |
| execution(* com.wmx.aspect.EmpServiceImpl.findEmpById(*)) | 匹配 com.wmx.aspect.EmpService 类中的 findEmpById 方法,且带有一个任意类型参数。 |
| execution(* com.wmx.aspect.EmpServiceImpl.findEmpById(…)) | 匹配 com.wmx.aspect.EmpService 类中的 findEmpById 方法,参数不限。 |
| execution(* grp.basic3.se.service.SEBasAgencyService3.editAgencyInfo(…)) || execution(*grp.basic3.se.service.SEBasAgencyService3.adjustAgencyInfo(…)) | 匹配 editAgencyInfo 方法或者 adjustAgencyInfo 方法 |
| @Pointcut(“(execution(* grp.basic3…Controller.(…)) && !execution( grp.basic3.BaseExceptionController*.*(…)))”) | 匹配 grp.basic3包及其子包下面名称包含 ‘Controller’ 类中的全部方法,但是排除掉其中的以 BaseExceptionController 开头的类。 |
| execution(* com.wmx.aspect.EmpService.*(…)) | 匹配 com.wmx.aspect.EmpService 类中的任意方法 |
| execution(* com.wmx.aspect..(…)) | 匹配 com.wmx.aspect 包(不含子包)下任意类中的任意方法 |
| execution(* com.wmx.aspect….(…)) | 匹配 com.wmx.aspect 包及其子包下任意类中的任意方法 |
| execution(* grp.pm…Controller.(…)) | 匹配 grp.pm 包下任意子孙包中以 “Controller” 结尾的类中的所有方法 |
| * com.wmx…Controller.*(…)) | com.wmx 包及其子包下面类名包含’Controller’的任意类中的任意方法 |
| * com.wmx..controller..*(…)) | 第一二层包名为 com.wmx ,第三层包名任意,第4层包名为 controller 下面的任意类中的任意方法 |
@Pointcut(“@annotation(xx)”) 拦截拥有指定注解的方法
/**
* @Pointcut :切入点声明,即切入到哪些目标方法。
* execution:可以用于指定具体类中的具体方法
* annotation:匹配拥有指定注解的方法; 只匹配实现类中有注解的方法,不会匹配接口中的注解方法; 如果注解是在类上,而不是方法上,并不会匹配类中的全部方法.
* 用于被下面的通知注解引用,这样通知注解只需要关联此切入点声明即可,无需再重复写切入点表达式
* @annotation 中的路径表示拦截特定注解
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.wmx.annotation.RedisLock)")
public void redisLockPC() {
}
常用注解
1.@Before:在切点方法前执行
- 前置通知:在方法执行之前执行的通知
- 在增强的方法上@Before(“execution(* 包名..(…))”)
- 上述表达式可使用pointcut或切入表达式,效果一致,之后不再赘述
- 切点方法没有形参与返回值
示例代码
@Aspect
public class AuthAspect {
//定义切点
@Pointcut("execution(* com.cnblogs.hellxz.service.*.*(..))")
public void pointCut() {}
//前置处理
@Before("pointCut()")
public void auth() {
System.out.println("模拟权限检查……");
}
}
2.@After:在切点方法后执行
- 后置通知:后置通知是在连接点完成之后执行的,即连接点返回结果或者抛出异常的时候
- 用法同@Before
3.@Around:在切点方法外环绕执行
-
环绕通知是所有通知类型中功能最为强大的,能够全面地控制连接点,甚至可以控制是否执行连接点。
对于环绕通知来说,连接点的参数类型必须是ProceedingJoinPoint。它是 JoinPoint的子接口,允许控制何时执行,是否执行连接点。 -
在环绕通知中需要明确调用ProceedingJoinPoint的proceed()方法来执行被代理的方法。如果忘记这样做就会导致通知被执行了,但目标方法没有被执行。
-
注意:环绕通知的方法需要返回目标方法执行之后的结果,即调用 joinPoint.proceed();的返回值,否则会出现空指针异常。
-
在增强的方法上@Around(“execution(* 包名.*(…))”)或使用切点@Around(“pointcut()”)
-
接收参数类型为ProceedingJoinPoint,必须有这个参数在切面方法的入参第一位
-
返回值为Object
-
需要执行
ProceedingJoinPoint对象的proceed方法,在这个方法前与后面做环绕处理,可以决定何时执行与完全阻止方法的执行 -
返回proceed方法的返回值
-
@Around相当于@Before和@AfterReturning功能的总和
-
可以改变方法参数,在proceed方法执行的时候可以传入Object[]对象作为参数,作为目标方法的实参使用。
-
如果传入Object[]参数与方法入参数量不同或类型不同,会抛出异常
-
通过改变proceed()的返回值来修改目标方法的返回值
示例代码
@Aspect
public class TxAspect {
//环绕处理
@Around("execution(* com.cnblogs.hellxz.service.*.*(..))")
Object auth(ProceedingJoinPoint point) {
Object object = null;
try {
System.out.println("事务开启……");
//放行
object = point.proceed();
System.out.println("事务关闭……");
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return object;
}
}
4.@AfterRetruning: 在方法返回之前,获取返回值并进行记录操作
- 返回通知:无论连接点是正常返回还是抛出异常,后置通知都会执行。如果只想在连接点返回的时候记录日志,应使用返回通知代替后置通知。
- 和上边的方法不同的地方是该注解除了切点,还有一个返回值的对象名
- 不同的两个注解参数:returning与pointcut,其中pointcut参数可以为切面表达式,也可为切点
- returning定义的参数名作为切面方法的入参名,类型可以指定。如果切面方法入参类型指定Object则无限制,如果为其它类型,- 则当且仅当目标方法返回相同类型时才会进入切面方法,否则不会
- 还有一个默认的value参数,如果指定了pointcut则会覆盖value的值
- 与@After类似,但@AfterReturning只有方法成功完成才会被织入,而@After不管结果如何都会被织入
- 虽然可以拿到返回值,但无法改变返回值
- 在返回通知中访问连接点的返回值
- 在返回通知中,只要将returning属性添加到@AfterReturning注解中,就可以访问连接点的返回值。该属性的值即为用来传入 返回值的参数名称
- 必须在通知方法的签名中添加一个同名参数。在运行时Spring AOP会通过这个参数传递返回值
- 原始的切点表达式需要出现在pointcut属性中
示例代码
@Aspect
public class AfterReturningAspect {
@AfterReturning(returning="rvt",
pointcut = "execution(* com.cnblogs.hellxz.service.*.*(..))")
//声明rvt时指定的类型会限定目标方法的返回值类型,必须返回指定类型或者没有返回值
//rvt类型为Object则是不对返回值做限制
public void log(Object rvt) {
System.out.println("获取目标返回值:"+ rvt);
System.out.println("假装在记录日志……");
}
/**
* 这个方法可以看出如果目标方法的返回值类型与切面入参的类型相同才会执行此切面方法
* @param itr
*/
@AfterReturning(returning="itr",
pointcut="execution(* com.cnblogs.hellxz.service.*.*(..))")
public void test(Integer itr) {
System.out.println("故意捣乱……:"+ itr);
}
}
5.@AfterThrowing: 在异常抛出前进行处理,比如记录错误日志
- 异常通知:只在连接点抛出异常时才执行异常通知
- 将throwing属性添加到@AfterThrowing注解中,也可以访问连接点抛出的异常。Throwable是所有错误和异常类的顶级父类,所 以在异常通知方法可以捕获到任何错误和异常。
- 如果只对某种特殊的异常类型感兴趣,可以将参数声明为其他异常的参数类型。然后通知就只在抛出这个类型及其子类的异常时才被执行
- 与@AfterReturning类似,同样有一个切点和一个定义参数名的参数——throwing
- 同样可以通过切面方法的入参进行限制切面方法的执行,e.g. 只打印IOException类型的异常, 完全不限制可以使用Throwable类型
- pointcut使用同@AfterReturning
- 还有一个默认的value参数,如果指定了pointcut则会覆盖value的值
- 如果目标方法中的异常被try catch块捕获,此时异常完全被catch块处理,如果没有另外抛出异常,那么还是会正常运行,不会进入AfterThrowing切面方法
示例代码
@Aspect
public class AfterThrowingAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.cnblogs.hellxz.test.*.*(..))")
public void pointcut() {}
/**
* 如果抛出异常在切面中的几个异常类型都满足,那么这几个切面方法都会执行
*/
@AfterThrowing(throwing="ex1",
pointcut="pointcut()")
//无论异常还是错误都会记录
//不捕捉错误可以使用Exception
public void throwing(Throwable ex1) {
System.out.println("出现异常:"+ex1);
}
@AfterThrowing(throwing="ex",
pointcut="pointcut()")
//只管IOException的抛出
public void throwing2(IOException ex) {
System.out.println("出现IO异常: "+ex);
}
}
pointcut定义的切点方法在@Before/@After/@Around需要写在双引号中,e.g. @Before(“pointCut()”)
JoinPoint和ProceedingJoinPoint的概念与方法说明
JoinPoint的概念与方法说明
概念
- 顾名思义,连接点,织入增强处理的连接点
- 程序运行时的目标方法的信息都会封装到这个连接点对象中
- 此连接点只读
方法说明 - Object[] getArgs():返回执行目标方法时的参数
- Signature getSignature():返回被增强方法的相关信息,e.g 方法名 etc
- Object getTarget():返回被织入增强处理的目标对象
- Object getThis():返回AOP框架目标对象生成的代理对象
使用 - 在@Before/@After/@AfterReturning/@AfterThrowing所修饰的切面方法的参数列表中加入JoinPoint对象,可以使用这个对象获得整个增强处理中的所有细节
- 此方法不适用于@Around, 其可用ProceedingJoinPoint作为连接点
ProceedingJoinPoint的概念与方法说明
概念
- 是JoinPoint的子类
- 与JoinPoint概念基本相同,区别在于是可修改的
- 使用@Around时,第一个入参必须为ProceedingJoinPoint类型
- 在@Around方法内时需要执行proceed()或proceed(Object[] args)方法使方法继续,否则会一直处于阻滞状态
方法说明 - ProceedingJoinPoint是JoinPoint的子类,包含其所有方法外,还有两个公有方法
- Object proceed():执行此方法才会执行目标方法
- Object proceed(Object[] args):执行此方法才会执行目标方法,而且会使用Object数组参数去代替实参,如果传入Object[]参数与方法入参数量不同或类型不同,会抛出异常
通过修改proceed方法的返回值来修改目标方法的返回值
编入(执行顺序)的优先级
优先级最高的会最先被织入,在退出连接点的时候,具有最高的优先级的最后被织入
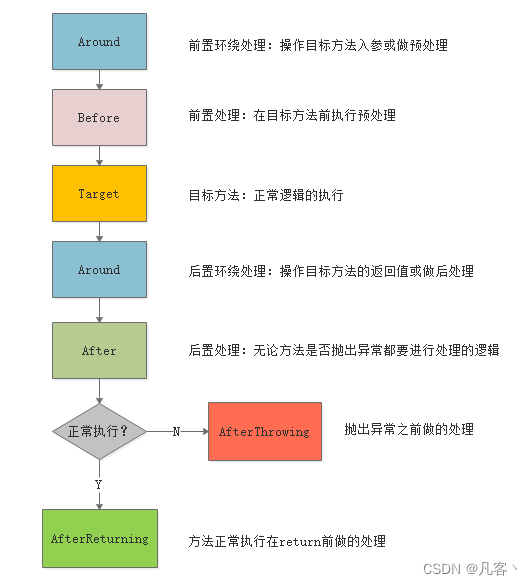
当不同切面中两个增强处理切入同一连接点的时候,Spring AOP 会使用随机织入的方式
如果想要指定优先级,那么有两种方案:
- 让切面类实现 org.springframework.core.Ordered接口,实现getOrder方法,返回要指定的优先级
- 切面类使用@Order修饰,指定一个优先级的值,值越小,优先级越高
示例代码
HelloService接口
package zhl.service;
public interface HelloService {
int add();
}
HelloServiceImpl接口
package zhl.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service("helloService")
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService{
@Override
public int add() {
System.out.println("运行的代码");
// int i = 1/0;
return 111;
}
LogAspect.java如下
package zhl.service;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogAspect {
// @Before("bean(helloService)")
// @Before("within(zhl.*)") zhl包下的子类
// @Before("within(zhl..*)") zhl包下的所有子孙类
// @Before("execution(public void zhl..*.*(..))") public 可以省略
@Pointcut("execution(* zhl..*.*(..))")
public void pointcut() {
}
@Before("pointcut()")
public void before(JoinPoint jointPoint){
Object[] args = jointPoint.getArgs();
String methodName = jointPoint.getSignature().getName();
Class<?> targetClass = jointPoint.getTarget().getClass();
System.out.println("[普通前置日志]:方法名称 "+methodName+" 目标对象的类型 "+
targetClass+" 参数 "+ Arrays.toString(args));
}
@AfterReturning(value = "pointcut()",returning = "result")
public void afterReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("[普通返回日志]:方法调用完成 方法名:"+methodName+"返回值信息:"+result);
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "pointcut()",throwing = "throwable")
public void throwable(JoinPoint jointPoint,Throwable throwable){
String methodName = jointPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("[普通异常日志] 方法调用异常 方法名:"+ methodName+"异常信息:"+throwable);
}
@After("pointcut()")
public void after() {
System.out.println("普通后置通知");
}
@Around("pointcut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint){
Object result = null;
try {
System.out.println("环绕前置通知");//类似于前置通知
result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕返回通知");//类似于返回通知
}catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("环绕异常通知"+throwable.getMessage());//类似于异常通知
}finally {
System.out.println("环绕后置通知");//类似于后置通知
}
return result;
}
}
无异常存在的执行顺序:环绕前置–> 普通前置–> 目标方法执行–> 普通返回 --> 普通后置–> 环绕返回 -->环绕后置
以下为代码运行结果
环绕前置通知
[普通前置日志]:方法名称 add 目标对象的类型 class zhl.service.HelloServiceImpl 参数 []
运行的代码
[普通返回日志]:方法调用完成 方法名:add返回值信息:111
普通后置通知
环绕返回通知
环绕后置通知
有异常存在的执行顺序:环绕前置–> 普通前置 --> 目标方法执行 -->普通异常 --> 普通后置
(1)目标方法有无输出与输出语句在异常语句上还是下决定,若一开始就出现异常则不会输出“运行的代码”

(2)出现异常由普通异常通知捕捉对其进行处理,异常通知与返回通知是互斥的,有异常无返回,有返回无异常
(3)因为异常已经被普通异常捕捉,环绕异常通知便不在执行
环绕前置通知
[普通前置日志]:方法名称 add 目标对象的类型 class zhl.service.HelloServiceImpl 参数 []
运行的代码
[普通异常日志] 方法调用异常 方法名:add异常信息:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
普通后置通知
访问目标方法的形参
除了使用JoinPoint或ProceedingJoinPoint来获取目标方法的相关信息外(包括形参),如果只是简单访问形参,那么还有一种方法可以实现
在pointcut的execution表达式之后加入&& args(arg0,arg1)这种方式
@Aspect
public class AccessInputArgs {
@Before("execution(* com.cnblogs.hellxz.test.*.*(..)) && args(arg0, arg1)")
public void access(String arg0, String arg1){
System.out.println("接收到的参数为arg0="+arg0+",arg1="+arg1);
}
}
注意:通过这种方式会只匹配到方法只有指定形参数量的方法,并且,在切面方法中指定的类型会限制目标方法,不符合条件的不会进行织入增强
切入点的使用
定义切入点
通过定义切入点,我们可以复用切点,减少重复定义切点表达式等
切入点定义包含两个部分:
- 切入点表达式
- 包含名字和任意参数的方法签名
使用@Pointcut注解进行标记一个无参无返回值的方法,加上切点表达式
@Pointcut("execution(* com.cnblogs.hellxz.test.*.*(..))")
public void pointcut(){}
切入点指示符
Spring AOP 支持10种切点指示符:execution、within、this、target、args、@target、@args、@within、@annotation、bean下面做下简记(没有写@Pointcut(),请注意):
-
execution: 用来匹配执行方法的连接点的指示符。
用法相对复杂,格式如下:execution(权限访问符 返回值类型 方法所属的类名包路径.方法名(形参类型) 异常类型)
e.g. execution(public String com.cnblogs.hellxz.test.Test.access(String,String))
权限修饰符和异常类型可省略,返回类型支持通配符,类名、方法名支持*通配,方法形参支持…通配 -
within: 用来限定连接点属于某个确定类型的类。
within(com.cnblogs.hellxz.test.Test)
within(com.cnblogs.hellxz.test.) //包下类
within(com.cnblogs.hellxz.test…) //包下及子包下 -
this和target: this用于没有实现接口的Cglib代理类型,target用于实现了接口的JDK代理目标类型
举例:this(com.cnblogs.hellxz.test.Foo) //Foo没有实现接口,使用Cglib代理,用this
实现了个接口public class Foo implements Bar{…}
target(com.cnblogs.hellxz.test.Test) //Foo实现了接口的情况 -
args: 对连接点的参数类型进行限制,要求参数类型是指定类型的实例。
args(Long) -
@target: 用于匹配类头有指定注解的连接点
@target(org.springframework.stereotype.Repository) -
@args: 用来匹配连接点的参数的,@args指出连接点在运行时传过来的参数的类必须要有指定的注解
@Pointcut("@args(org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody)")
public void methodsAcceptingEntities() {}
-
@within: 指定匹配必须包括某个注解的的类里的所有连接点
@within(org.springframework.stereotype.Repository) -
@annotation: 匹配那些有指定注解的连接点
@annotation(org.springframework.stereotype.Repository) -
bean: 用于匹配指定Bean实例内的连接点,传入bean的id或name,支持使用*通配符
切点表达式组合
使用&&、||、!、三种运算符来组合切点表达式,表示与或非的关系execution(* com.cnblogs.hellxz.test..(…)) && args(arg0, arg1)
案例
1:环绕通知 实现开关目标方法
1、比如某个方法只有管理员才有权限执行,而普通用户是没有权限
2、比如不符合条件的时候,需要终止(跳过)目标方法的执行
3、比如一个组件(Component)专门用于做校验,里面的方法是否校验可以配置在数据库中,当配置为启用时,则继续校验,否则不校验。
/**
* 环绕通知
* 1、@Around 的 value 属性:绑定通知的切入点表达式。可以关联切入点声明,也可以直接设置切入点表达式
* 2、Object ProceedingJoinPoint.proceed(Object[] args) 方法:继续下一个通知或目标方法调用,返回处理结果,如果目标方法发生异常,则 proceed() 会抛异常.
* 3、假如目标方法是控制层接口,则本方法的异常捕获与否都不会影响业务层方法的事务回滚
* 4、假如目标方法是控制层接口,本方法 try-catch 了异常后没有继续往外抛,则全局异常处理 @RestControllerAdvice 中不会再触发
*/
@Around(value = "aspectPointcut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
Object target = joinPoint.getTarget();
System.out.println("环绕通知=" + signature);
System.out.println("环绕通知=" + target);
// 是否继续校验
boolean validation = true;
if (validation) {
// 校验通过后执行目标方法
// 继续下一个切面通知或目标方法调用,返回处理结果,如果目标方法发生异常,则 proceed 会抛异常.
// 如果在调用目标方法或者下一个切面通知前抛出异常,则不会再继续往后走
return joinPoint.proceed(joinPoint.getArgs());
} else {
// 校验未通过时,不继续往后走,直接返回。
// 可以返回提示信息,但是必须保证返回的参数类型与目标方法的返回值类型一致,否则类型转换异常。
// 也可以直接抛异常。
return null;
}
}
2:自定义注解+切面实现统一日志处理
2.1 自定义日志注解
/**
* 自定义操作日志注解
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface OptLog {
/**
* 业务
* @return
*/
String business();
/**
* 操作类型,增删改查
* @return
*/
OptType optType();
}
2.2 声明日志切面组件
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.example.demo.annotation.OptLog;
import com.example.demo.annotation.OptType;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.core.LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Aspect
@Component
public class OptLogAspect {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(OptLogAspect.class);
/**
* 声明切入点,凡是使用该注解都经过拦截
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.example.demo.annotation.OptLog)")
public void OptLog() {
}
@Before("OptLog()")
public void doOptLogBefore(JoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) {
LOG.info("前置通知, 在方法执行之前执行...");
}
@After("OptLog()")
public void doOptLogAfter(JoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) {
LOG.info("后置通知, 在方法执行之后执行...");
}
@AfterReturning("OptLog()")
public void doOptLogAfterReturning(JoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) {
LOG.info("返回通知, 在方法返回结果之后执行...");
}
@AfterThrowing("OptLog()")
public void doOptLogAfterThrowing(JoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) {
LOG.info("异常通知, 在方法抛出异常之后执行...");
}
/**
* 设置环绕通知,围绕着方法执行
*
* @param proceedingJoinPoint
* @return
*/
@Around("OptLog()")
public Object optLogAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
Method method = ((MethodSignature) proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature()).getMethod();
if (method == null) {
return null;
}
// 获取方法名称
String methodName = proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName();
LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer discoverer = new LocalVariableTableParameterNameDiscoverer();
// 请求参数名称
String[] parameterNames = discoverer.getParameterNames(method);
// 请求参数值
Object[] paramValues = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs();
OptLog optLog = method.getAnnotation(OptLog.class);
this.handle(optLog.optType(), optLog.business(), methodName, parameterNames, paramValues);
return proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
}
/**
* 日志处理
*
* @param optType
* @param business
* @param methodName
* @param parameterNames
* @param paramValues
*/
public void handle(OptType optType, String business, String methodName,
String[] parameterNames, Object[] paramValues) {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();
if (parameterNames != null && parameterNames.length > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterNames.length; i++) {
jsonObject.put(parameterNames[i], paramValues[i]);
}
}
LOG.info("optType:" + optType + ",business:" + business + ", methodName:" + methodName + ", params:" + jsonObject);
}
}
2.3 控制层运行结果
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user/")
public class UserController {
@OptLog(optType = OptType.CREATE,business = "用户信息")
@RequestMapping("create")
public String createUser(String userName,int age,String address) {
System.out.println("方法执行中...");
return "success";
}
}
2.4 运行结果
15:32:49.494 [http-nio-8080-exec-2] INFO c.e.d.a.OptLogAspect - [handle,91] - optType:CREATE,business:用户信息, methodName:createUser, params:{"address":"广州市","userName":"阿杰","age":18}
15:32:49.494 [http-nio-8080-exec-2] INFO c.e.d.a.OptLogAspect - [doOptLogBefore,32] - 前置通知, 在方法执行之前执行...
方法执行中...
15:32:49.495 [http-nio-8080-exec-2] INFO c.e.d.a.OptLogAspect - [doOptLogAfterReturning,42] - 返回通知, 在方法返回结果之后执行...
15:32:49.495 [http-nio-8080-exec-2] INFO c.e.d.a.OptLogAspect - [doOptLogAfter,37] - 后置通知, 在方法执行之后执行...
3:自定义注解与切面类
3.1 创建自定义注解
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface TestAnnotation {
String name() default "默认值"; // 允许注解有参数
String age() default "15"; // 允许多个参数
}
3.2 创建一个类,定义方法后使用自定义注解
import com.yh.annotation.OperateLogAnnotation;
import com.yh.annotation.TestAnnotation;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestAOPController {
@RequestMapping("/show3")
@ResponseBody
@TestAnnotation(name = "我把值传进去", age = "24") // 加上自定义注解
public String getById() {
return "hello";
}
}
3.3 定义切面类进行,扫描自定义注解,并对切入点进行处理
import com.yh.annotation.TestAnnotation;
import com.yh.annotation.TestAnnotation;
//import javassist.bytecode.SignatureAttribute;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Aspect // FOR AOP
@Order(-99) // 控制多个Aspect的执行顺序,越小越先执行, 当然也可以不写这注解, 对于写和不写@order的两个切面, 有@order的优先于无@order的执行; 都有@order时, 越小越执先执行
@Component
public class TestAspect {
// 可以参考若依的自定义注解。自定义注解一般使用@annotation
// @Before可以有两种写法, @annotation(形参test),
@Before("@annotation(test)")// 拦截被TestAnnotation注解的方法;如果你需要拦截指定package指定规则名称的方法,可以使用表达式execution(...)
public void beforeTest(JoinPoint point, TestAnnotation test) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("beforeTest:" + test.name()); // 直接获取注解参数
//test.name()和test.age()
}
@After("@annotation(test)")
public void afterTest(JoinPoint point, TestAnnotation test) {
System.out.println("afterTest:" + test.name()); // 直接获取注解参数
}
// 可以控制方法运行, 同时修改入参和返回值
@Around("@annotation(test)") // test表示aroundTest方法中的test入参
public Object aroundTest(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, TestAnnotation test) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("aroundTest:" + test.value());
// 获取入参并修改
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
args[0] = "";
// 传入修改后的参数, 并继续执行
Object res = pjp.proceed(args);
// 修改返回值
return res.toString() + res.toString();
}
/*
// 指定切面
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.yh.annotation.TestAnnotation)")
public void annotationPointCut() {
}
// @Before可以有两者写法, @annotation(函数名annotationPointCut)
@Before("annotationPointCut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
MethodSignature sign = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = sign.getMethod();
TestAnnotation annotation = method.getAnnotation(TestAnnotation.class); // 获取指定注解实例
System.out.println("打印:" + annotation.name() + " 前置日志1"); // 获取注解实例的参数
}
@After("annotationPointCut()")
public void afterTTT(JoinPoint point) {
MethodSignature sign = (MethodSignature) point.getSignature();
Method method = sign.getMethod();
TestAnnotation annotation = method.getAnnotation(TestAnnotation.class); // 获取指定注解实例
System.out.println("打印自带参数:" + annotation.age() + " 后置日志1"); // 获取注解实例的参数
}
*/
}
4. After应用实例
4.1 使用After增强处理
Spring还提供了一个After增强处理,它与AfterReturning优点类似,但也有区别:
-
AfterReturning增强处理只有在目标方法正确完成后才会被织入
-
After增强处理不管目标方法如何结束(正确还是异常),它都会被织入
正是因为这个特点,因此After增强处理必须准备处理正常返回和异常返回两种情况,这种增强处理通常用于释放资源。使用@After注解标注一个方法,即可将该方法转换为After增强处理。使用@After注解是需要指定一个value属性,用于指定该增强处理的切入点,既可以是一个已有的切入点,也可以直接定义切入点表达式。
在com.abc.advice包下面增加AfterAdviceTest,这个类定义了一个After增强处理:
@Aspect
public class AfterAdviceTest {
@After(value="execution(* com.abc.servie.impl.*.afterAdvice*(..))")
public void releaseResource() {
System.out.println("模拟释放数据库连接");
}
}
并在AdviceManager类中增加以下内容:
//将被AfterAdvice的releaseResource方法匹配
public void afterAdvice() {
System.out.println("方法: afterAdvice");
}
上面定义了一个After增强处理,不管切入点的目标方法如何结束,该增强处理都会被织入。
4.2 使用Around增强处理
-
@Around注解用于标注Around增强处理,它近似等于Before增强处理和AfterReturning增强处理的总和,Around增强处理既可以在执行目标方法前织入增强动作,也可以在目标方法之后织入增强动作。
-
与@Before和@AfterReturning不同的是,@Around甚至可以决定目标方法在什么时候执行,如何执行,甚至可以完全阻止目标方法的执行。@Around可以修改目标方法的参数值,也可以修改目标方法的返回值。
-
@Around的功能虽然强大,但通常需要在线程安全的环境下使用,因此,如果使用普通的@Before和@AfterReturning就能解决的问题,就没有必要使用@Around了。如果需要目标方法执行之前和执行之后共享某种数据状态,则应该考虑使用@Around;尤其是需要使用增强处理阻止目标方法的执行,或者需要改变目标方法的参数和执行后的返回值时,就只能使用@Around了。
-
可以想象,使用@Around时,也需要指定一个value属性,这个属性依然是用于指定切入点。另外,当定义一个Around增强处理时,该方法的第一个形参必须是ProceedingJoinPoint类型(就是说至少包含一个形参),在增强处理方法体内,调用ProceedingJoinPoint的proceed()方法才会执行目标方法——这就是Around增强处理可以完全控制目标方法的执行时机、如何执行的关键,如果增强处理的方法体内没有调用这个proceed()方法,则目标方法不会执行。
-
调用proceed()方法时,还可以传入一个Object[]对象,该数组中的值将被传入目标方法作为执行方法的实参。因此我们可以通过这个参数,修改方法的参数值。
在com.abc.advice包下面增加AroundAdviceTest,这个类定义了一个Around增强处理:
package com.abc.advice;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
@Aspect
public class AroundAdviceTest {
@Around(value="execution(* com.abc.service.*.around*(..))")
public Object process(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("模拟执行目标方法前的增强处理:事务开始...");
//修改目标方法的参数
String[] params = new String[]{"param1"};
//执行目标方法,并保存目标方法执行后的返回值
Object returnValue = point.proceed(params);
System.out.println("模拟执行目标方法后的增强处理:事务结束...");
//返回修改后的返回值
return "方法实际返回值:" + returnValue + ",这是返回值的后缀";
}
}
上面定义了一个AroundAdviceTest切面,该切面包含了一个Around增强处理:process()方法,该方法中第一行代码用于模拟调用目标方法之前的处理,第二行修改了目标方法的第一个参数,接下来调用目标方法,后面模拟调用目标方法之后的处理和对返回值的修改。正如前面说的,通过这个process方法,我们可以增加类似于@Before和@AfterReturning的增强处理,可以决定什么时候执行目标方法,可以修改目标方法的参数值,还可以修改目标方法的返回值,真是想做什么就做什么啊!
在AdviceManager类中增加以下内容:
//将被AroundAdvice的process方法匹配
public String aroundAdvice(String param1) {
System.out.println("方法: aroundAdvice");
return param1;
}
在com.abc.main.AOPTest中加入方法的调用,触发切点:
String result = manager.aroundAdvice("param1");
System.out.println("返回值:" + result);
需要注意的是,当调用ProceedingJoinPoint的proceed()方法时,传入的Object[]参数值将作为目标方法的参数,如果这个数组长度与目标方法的参数个数不等,或者数组元素的类型和目标方法的参数类型不匹配,程序就会出现异常。