Jdk1.7之HashMap源码总结
文章目录
- 一、HashMap属性
-
- 1. 默认容量16
- 2. 最大容量
- 3. 加载因子
- 4. EMPTY_TABLE
- 5. TABLE(数组)
- 6. SIZE(元素个数)
- 7. 阈值(与加载因子有关)
- 8. 加载因子
- 二、HashMap重要方法
-
- 1. HashMap无参构造方法
- 2. HashMap有参构造方法
- 3. HashMap#put方法
-
- 3.1 初始化table#inflateTable
- 3.2 putForNullKey方法
- 3.3 hash方法
- 3.4 indexFor方法
- 3.5 addEntry方法
- 3.5.1 resize扩容方法(多线程死循环)
-
- 3.5.1.1 hash种子
-
- 3.5.1.1.1 Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD
- 3.5.1.2 转移元素
- 3.5.2 createEntry
-
- 3.5.2.1 Entry结构
- 4. HashMap#get方法
-
- 4.1 getForNullKey方法
- 4.2 getEntry方法
一、HashMap属性
1. 默认容量16
/**
* The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
2. 最大容量
/**
* The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified
* by either of the constructors with arguments.
* MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30.
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
3. 加载因子
/**
* The load factor used when none specified in constructor.
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
4. EMPTY_TABLE
/**
* An empty table instance to share when the table is not inflated.
*/
static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {};
5. TABLE(数组)
/**
* The table, resized as necessary. Length MUST Always be a power of two.
*/
transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
6. SIZE(元素个数)
/**
* The number of key-value mappings contained in this map.
*/
transient int size;
7. 阈值(与加载因子有关)
/**
* The next size value at which to resize (capacity * load factor).
* @serial
*/
// If table == EMPTY_TABLE then this is the initial capacity at which the
// table will be created when inflated.
int threshold;
8. 加载因子
/**
* The load factor for the hash table.
*
* @serial
*/
final float loadFactor;
二、HashMap重要方法
1. HashMap无参构造方法
public HashMap() {
//调用有两个参数的构造方法
//默认初始容量16,加载因子是 0.75
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
2. HashMap有参构造方法
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
//如果初始容量小于0抛出异常
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
//如果初始容量大于最大容量,则初始容量设置为最大值1 << 30
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
//如果加载因子小于0 或者 加载因子不是数值型,则抛异常
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
//设置负载因子和初始容量
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = initialCapacity;
init();
}
init在hashmap中是没有实现的
void init() {}
3. HashMap#put方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
//如果当前table属性等于空(EMPTY_TABLE),最开始就是空的
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
//threshold如果不手动设置,默认0.75
inflateTable(threshold);
}
//如果key等于null(从这里可以看出key是支持null的)
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
//根据key算出一个hash值
int hash = hash(key);
//拿hash值以及数组的长度计算得到一个下标
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
//key相同需要覆盖value,从链表的头结点table[i]开始遍历,直到链表的最后一个结点
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//如果hash值相等 并且key是否相等
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
//如果相等取出覆盖之前的值
V oldValue = e.value;
//将传进来的value进行赋值
e.value = value;
//空方法
e.recordAccess(this);
//返回之前的值
return oldValue;
}
}
//默认0,每次put modCount都会加1,,remove时也会加1(快速失败,fail-fast 并发中的一种容错机制)
//modCount代表修改次数,如果使用for循环边遍历边修改(添加或修改元素)会报错的,与expectedModCount对应
//解决方法就是使用迭代器Iterator,迭代器每次遍历的时候是每次都会重新赋值
//expectedModCount = modCount,这样下次循环的时候就不会报错了
modCount++;
//构建Entry对象,头插法
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
注意:✈这里头插法效率其实并不太能提高性能,因为针对同一个桶位在key不冲突的情况下,每次都要遍历到链表的尾部。✈
3.1 初始化table#inflateTable
/**
* Inflates the table.
*/
private void inflateTable(int toSize) {
// Find a power of 2 >= toSize
//找到一个大于等于传进来的最接近2次幂的数,如果传入的是10,会返回16
int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize);
threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
//创建一个Entry数组,赋值给hashmap的table属性
table = new Entry[capacity];
initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity);
}
private static int roundUpToPowerOf2(int number) {
// assert number >= 0 : "number must be non-negative";
//如果number大于最大值,则设置为最大值
//否则如果number是大于1的数则调用Integer.highestOneBit(),否则返回1
return number >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
: (number > 1) ? Integer.highestOneBit((number - 1) << 1) : 1;
}
//调用该方法会返回一个小于等于2的幂次方数
public static int highestOneBit(int i) {
// HD, Figure 3-1
i |= (i >> 1);
i |= (i >> 2);
i |= (i >> 4);
i |= (i >> 8);
i |= (i >> 16);
return i - (i >>> 1);
}
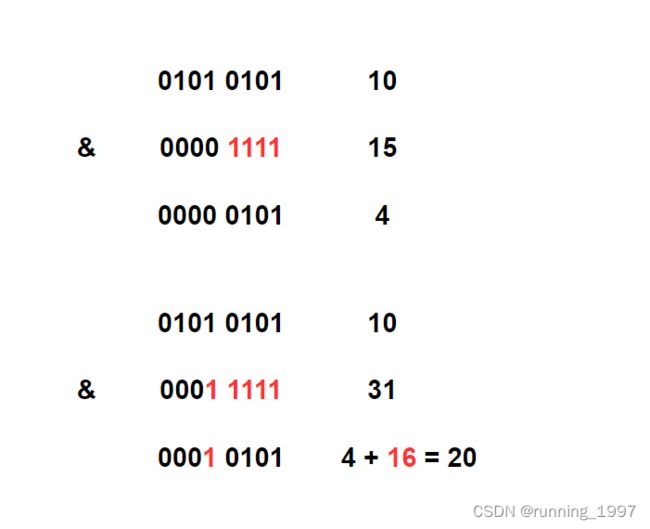
注意:所有的数转换为2进制,如果是2的次幂都有一个特点就是2进制为只有一个1,其余都是 0
调用 highestOneBit 方法会返回一个小于等于2的幂次方数
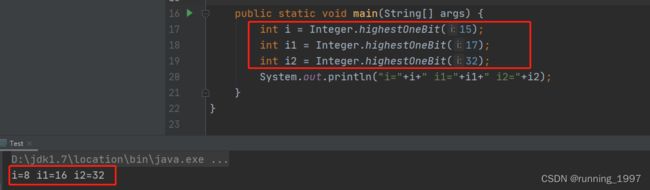
尝试找几个数字测试后发现,可以看出与我们想要的结果相反,我们想要的是找到一个大于等于的。
所以假设调用roundUpToPowerOf2(int number)方法传入的是18,则返回的是32。(先乘2再找小于2的次幂的数)
3.2 putForNullKey方法
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
//遍历数组下标的第1一个桶位
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null) {
//如果存在key等于null,覆盖并返回旧值
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
//如果key等于null,则放在hashmap的第0个位置
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
}
注意:✨key为null的值放在数组的第1个桶位,并不代表只有为null的key,还包括其他元素✨
3.3 hash方法
final int hash(Object k) {
//这里hash种子默认等于0
int h = hashSeed;
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
//调用key的hashcode方法(0和hashcode做异或运算也会改变)
h ^= k.hashCode();
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
//进行一系列右移和异或运算
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
为啥hashcode这里要进行这么多运算?
- 因为hashcode是一个32的数,如果不进行右移以及异或操作,生效的就是对应数组长度-1的低位为1的数,这样即使hashcode可以保证随机,但是高位即使每次产生的不一样,其实也是没有效果的,结果还是不会改变的。
- 所以该方法进行一系列右移和异或运算的目的就是让高位也参与到运算中来,保证随机性。
3.4 indexFor方法
计算数组下标
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
// assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2";
//注意这里用的是&操作,length必须是2的次幂才可以这么使用
//因为2的次幂-1后对应二进制低位都是1 比如16-1=15 对应二进制是1111
//最后结果其实就是受对应低位的影响
return h & (length-1);
}
注意:这里不难看出,为啥 hashmap数组的容量一定是2的次幂,因为只有是2的次幂才能使用&运算,计算时效率更加高效。
3.5 addEntry方法
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//size大于等于阈值 && 当前桶位不为空
//threshold = table.length * 0.75 (1.8这里没有第二个条件)
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
//成倍扩容
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
//创建Entry
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
注意:扩容条件:(size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])(jdk1.7)
3.5.1 resize扩容方法(多线程死循环)
void resize(int newCapacity) {
//记录老数组
Entry[] oldTable = table;
//记录老数组的容量
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
//是否等于最大值
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
//设置最大值
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//直接返回,不扩容了
return;
}
//每个线程过来调用put方法到这里都会创建一个新的数组(对数组进行卡扩容)
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
//转移元素
//因为扩容时,容量发生变化,肯定要重新hash,hash种子默认0,当然我们也可以通过设置环境变量来修改
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
//将新的数组赋值给table属性
table = newTable;
//针对新的数组容量重新算一个新的阈值
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
3.5.1.1 hash种子
final boolean initHashSeedAsNeeded(int capacity) {
//hashSeed 默认为0,一开始这里currentAltHashing 肯定为false,因为hashSeed 默认为0
boolean currentAltHashing = hashSeed != 0;
//useAltHashing 为true的前提是虚拟机启动并且数组容量大于等于
boolean useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() &&
(capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD);
//^代表不相等时返回true,相等返回false
//只有switching 等于 true hash种子才会改变(全局)
//由第一行currentAltHashing 一开始为false,只有useAltHashing为true,推出switching 为false,hashSeed 才会改变
boolean switching = currentAltHashing ^ useAltHashing;
if (switching) {
hashSeed = useAltHashing
? sun.misc.Hashing.randomHashSeed(this)
: 0;
}
return switching;
}
总结:hash种子其实就是让你的hash值更加散列,默认0
如果我们有需要,当数组容量capacity 超过某个值需要改变hash种子,让其更加散列,可以设置这个值通过配置环境变量【jdk.map.althashing.threshold】
3.5.1.1.1 Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD
在 HashMap 里全局搜素定位ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD变量赋值位置
private static class Holder {
/**
* Table capacity above which to switch to use alternative hashing.
*/
static final int ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD;
static {
String altThreshold = java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new sun.security.action.GetPropertyAction(
"jdk.map.althashing.threshold"));
int threshold;
try {
threshold = (null != altThreshold)
? Integer.parseInt(altThreshold)
: ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD_DEFAULT;
// disable alternative hashing if -1
if (threshold == -1) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
if (threshold < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("value must be positive integer.");
}
} catch(IllegalArgumentException failed) {
throw new Error("Illegal value for 'jdk.map.althashing.threshold'", failed);
}
ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD = threshold;
}
}
发现ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD = threshold,说明threshold变量赋的值,那threshold又是哪里来的,往上找会发现jdk.map.althashing.threshold,如果配置了该环境变量,就可以取到对应的值赋值给threshold ,如果没有配置该变量就取一个int 最大值 threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE
3.5.1.2 转移元素
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
//遍历旧数组的每一个元素
while(null != e) {
//遍历每个桶位上的元素,也就是链表
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
//默认等于false
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
//根据新的容量重新计算数组下标
//同样的元素在扩容后下标存放位置要么是老位置保持不变,要么是原来位置+老数组容量,见图 3.5.1
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
//将旧数组的引用指向新数组的起始位置(把一个元素插入链表表头)
e.next = newTable[i];
//头插法,插入新数组对应链表的第一个位置(将新插入的元素作为链表头部)
newTable[i] = e;
//把引用重新指向老数组对应桶位链表要转移的下一个元素
e = next;
//下一次循环一样的道理
}
}
}
扩容后我们会发现在同一个桶位上,新数组与原来数组对应链表上元素的存放顺序反了
死循环问题分析:
- 因为key对应的value是放在堆内存的,是共享的。
- 假设当两个线程同时触发扩容条件,此时老数组对应下标2位置有三个元素,1,2,3,注意顺序是1->2->3。
- 如果线程1先进行扩容,扩容后的新数组在下标为2或2+老数组容量位置上的元素顺序就会变成3->2->1。
- 那么假设线程2扩容前e指向的是1,next指向的是2,再开始扩容时会发现,死循环了。
️♀️注意:多线程同时扩容的情况下会出现循环链表,也即死循环问题(头插法导致扩容死循环)。️♀️
死循环会导致调get方法或put方法的时候,正好落在出现产生循环链表对应的桶位时,那么就会围绕链表一直循环下去。
3.5.2 createEntry
头插法
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//定义一个引用e指向当前桶位的第一个元素
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
//创建一个Entry对象,插入table[bucketIndex]的前面
//把Entry对象,对象赋值给table[bucketIndex] 头插法
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
//hashmap中的元素加1
size++;
}
3.5.2.1 Entry结构
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
int hash;
}
4. HashMap#get方法
public V get(Object key) {
//如果key等于null
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key);
//获取entry对象中的value
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
4.1 getForNullKey方法
private V getForNullKey() {
if (size == 0) {
//元素个数为0,直接返回null
return null;
}
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
//遍历数组下标第1个桶位,如果找到,则返回对应entry对象的value
if (e.key == null)
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
4.2 getEntry方法
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
//元素个数为0,直接返回null
return null;
}
//如果key等于null,返回0
//否则,针对key算出一个hash值,与put时的hash方法对应
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
//调用indexFor算出数组下标,遍历对应桶位上的链表
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
//判断hash和key是否相等,如果相等,找到直接返回entry对象
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}