React 学习笔记(一)
React 学习笔记(一)
学习资源:张天禹老师(尚硅谷 React 教程)
- 前置基础
-
this指向问题 -
ES6语法知识(class类) -
npm包管理器 - 原型与原型链
- 数组常用方法
- 模块化
-
1.1 React 历史
- 用于构建用户界面的开源
Javascript库 - 由
Facebook开发且开源Jordan Walke
1.2 为什么使用 React ?
1.2.1 原生缺点
- 原生操作
DOM相关的API来操作UI效率低 - 直接操作
DOM浏览器会产生大量的重绘重排 - 没有组件化思想
document.getElementById('app')
document.getquerySelector('#app')
document.getElementByTagName('div')
1.2.2 React 优势与特点
-
声明式编码便于提高开发效率和组件复用率
-
在
React Native可以使用React语法进行移动端开发 -
使用虚拟
DOM和优秀的Diffing算法,尽量减少与真实DOM的交互 -
...
1.2.3 需要了解与掌握的库
babel.min.js
ES6语法转成ES5语法jsx转成js
react.development.js(作为React核心库)
react-dom.development.js扩展库(用于操作DOM)
1.3 React 快速入门
1.3.1 React 使用示例
- 引入库的顺序
- 先引入
react核心库,再引入react-dom扩展库
<div id="app">div>
<script src="../js/react.development.js">script>
<script src="../js/react-dom.development.js">script>
<script src="../js/babel.min.js">script>
<script type="text/babel">
// 1.创建虚拟 DOM
const VDOM = <h1>Hello React</h1>
// 此处不写引号 因为不是字符串
// 2.渲染虚拟 DOM 到页面
// ReactDOM.render(虚拟 DOM,容器)
const app = document.getElementById('app')
ReactDOM.render(VDOM, app)
script>
- 虚拟
DOM的两种创建方式jsx与js创建方式比较
// jsx 方式创建
const VDOM = (
<h1 id="title">
<span>Hello React</span>
</h1>
)
// javascript 方式创建
// 如果 DOM 有多层嵌套 那么 javascript 书写结构非常复杂
/*
const VDOM = React.createElement('h1', { id: 'title' }, React.createElement('span', {}, 'Hello React'))
// createElement 为创建 DOM 元素
// createElement(标签元素,标签属性,标签体内容)
*/
// 2.渲染虚拟 DOM 到页面
const app = document.getElementById('app')
ReactDOM.render(VDOM, app)
1.3.2 什么是虚拟 DOM
Object类型对象- 最终会被
React转化为真实DOM呈现在页面中
const VDOM = (
<h1 id="title">
<span>Hello React</span>
</h1>
)
console.log(VDOM);
console.log(typeof VDOM)
console.log(VDOM instanceof Object);
1.3.3 什么是 JSX ?
- 全称为
JavaScript XML XML早期用于存储和传输数据
<student>
<name>Tomname>
<age>18age>
student>
jsx是React定义的一种类似于XML的JS扩展语法- 可以理解为
JS + XML的组合 - 本质是
React.createElement(component, prop, ...children)方法的语法糖
- 可以理解为
1.3.4 JSX 语法规则
- 定义虚拟
DOM不能写引号
const VDOM = 'Hello React
' // 无效写法
- 标签中需要混入
js表达式 - 需要使用 { }
注意区分:不是
Vue中的插值语法
const data = 'Hello React'
// 创建虚拟 DOM
const VDOM = (
<h1 id="title">
<span>{data}</span>
// 书写 js 表达式
<span>{data.toLowerCase()}</span>
</h1>
)
// 渲染虚拟 DOM 到页面
const app = document.getElementById('app')
ReactDOM.render(VDOM, app)
-
样式应用书写
- 样式类名指定需要使用
className而不是class - 内联样式需要使用
style = {{ key:value }}形式
- 样式类名指定需要使用
const VDOM = (
<div className="react-demo">
// 渲染时为 class="react-demo"
<div style={{color: 'pink'}}>
Hello React!
</div>
</div>
)
-
jsx不允许有多个根标签(只有一个根标签) -
标签必须闭合
-
标签首字符
- 若小写字母开头,则将标签转为
html同名元素,若html中无该标签对应的同名元素则,则报错 - 若大写字母开头,
React渲染对应的组件,若组件没有定义,则报错
- 若小写字母开头,则将标签转为
所以在
React中使用某种组件时需要其首字母大写!
const VDOM = (
<div>
<h1 id="title" className="pink">
<span style={{color: 'white', font-size: '29px'}}>{data}</span>
<span>{data.toLowerCase()}</span>
</h1>
<h1>Hello React</h1>
<input type="text" />
</div>
)
- 编写样式
<style>
.pink {
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
const data = 'Hello React'
// 创建虚拟 DOM
const VDOM = (
<h1 id="title" className="pink">
<span style={{color: 'white', font-size: '29px'}}>{data}</span>
<span>{data.toLowerCase()}</span>
</h1>
)
// todo: 渲染虚拟 DOM 到页面
注意
js表达式与js语句区分!
jsx注释{ /* ... */ }
const VDOM = (
<h1 id="title" className="pink">
<span>{data.toLowerCase()}</span>
{/*{data.toUpperCase()}*/}
</h1>
)
jsx小练习
使用
React渲染数据datas到页面中
//
// 注意写在 babel.min.js 中哦
// 模拟数据
const datas = ['Angular', 'React', 'Vue']
const renderDatas = datas.map((data, index) => <li key={index}> {data} </li>)
// console.log(renderDatas);
// 创建虚拟 DOM
const VDOM = (
<div>
<h1>前端 js 框架</h1>
<ul>
{renderDatas}
</ul>
</div>
)
// 渲染虚拟 DOM 到页面
ReactDOM.render(VDOM, document.getElementById('app'))
1.4 面向组件编程
1.4.1 模块与组件
- 模块化 | 组件化 | 工程化
1.4.2 使用 React 开发者工具调试
- 安装
React Developer Tools
1.4.3 React 面向组件编程
- 函数式组件
Function
// 1. 创建组件 函数式写法
function MyComponent() {
// 使用了严格模式 use strict 因为 babel 编译后默认开启严格模式
// console.log(this); // 函数内部 this 指向为 undefined
return <h1>函数定义的组件</h1>
}
// 2. 渲染组件到页面
// 第一个参数为自定义标签(函数式组件名称)
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent />, document.
getElementById('app'))
ReactDOM.render(...)做了什么?
- 简单来说,
ReactDOM会调用MyComponent函数,对于render函数的第一个参数,React解析为组件标签,然后会找到MyComponent组件 - 发现组件是使用函数定义的,随后调用该函数,将返回的虚拟
DOM转为真实DOM
- 类式组件
Class
// 1. 创建类式组件 均需要继承 React.component 父类
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
// render 为类 MyComponent 的原型对象上的方法,供实例使用
render() {
console.log(this); // MyComponent 的实例对象
return <h1>Hello React</h1>
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent />, document.getElementById('app'))
ReactDOM.render(...)做了什么?
React解析组件标签找到MyComponent组件- 发现组件是使用【类】定义的,随后调用
new创建该类的
实例,通过该实例调用原型上的render方法 - 将
render返回的虚拟DOM转为真实DOM随后呈现在页面上
1.4.4 state 概念及初始化
-
组件被称为状态机,通过更新组件的
state来更新对应的页面显示(重新渲染组件) -
state是组件对象最重要的属性,是对象-
可以包含多个
key-value的组合 -
state只能是object或null
-
class Weather extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
// 书写 constructor 后第一句需要写 super(...)
super(props)
// 初始化状态 state
this.state = { isHot: true }
}
render() {
// console.log(this);
// this 指向类 Weather 的实例对象 因为本质上是 Weather 类的实例对象调用 render 方法
return <h1>今天天气{this.state.isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'}</h1>
}
}
// todo: ReactDOM.render()
React 事件绑定
回顾原生实现事件绑定(点击事件…)
- 获取元素
- 使用
addEventListener监听事件
btn.addEventListener('click', callback)
- 为元素设置
onclick
btn.onclick = callback
// 或为 dom 元素设置属性
//
// function test () { //... }
React完成事件绑定
-
注意:类中的方法默认开启局部的严格模式
-
this指向问题
class Weather extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
// 初始化状态
this.state = { isHot: true }
}
demo() {
// 结果 this 为 undefined 而不是 Weather 实例对象
console.log(this)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{/* 注意是 onClick 【不是】 onclick */}
<h1 onClick={this.demo}>
今天天气{this.state.isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'}
</h1>
</div>
)
}
}
// todo: ReactDOM.render(...)
为什么
this为undefined?
// Example
var date = new Date();
date.getTime() // 1677578203663
var print = date.getTime;
print() // Uncaught TypeError: this is not a Date object.
- 上面代码中,我们将
date.getTime()方法赋给变量print,然后调用print()就报错了。这是因为getTime()方法内部的this,绑定Date对象的实例,赋给变量print以后,内部的this已经不指向Date对象的实例
this.demo也是同样的道理!内部的this不再指向组件实例对象!
- 改变
this指向- 使用
bind(不推荐,滥用原型链) - 使用箭头函数 √
- 使用
class Weather extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
// 初始化状态
this.state = { isHot: true }
// 改变 this 指向 使用 bind
// 在实例上添加 demo
this.demo = this.demo.bind(this)
}
demo() {
// demo 方法在类的原型对象上 供实例去使用
console.log(this)
}
/*
demo = () => {
// 通过 Weather 实例调用 demo demo 中的 this 指向 Weather 实例
// 只能写成箭头函数 不然 this 指向为 undefined
console.log(this);
}
*/
render() {
// console.log(this);
return (
<div>
<h1 onClick={this.demo}>今天天气{this.state.isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'}</h1>
</div>
)
}
}
setState的使用- 用于修改
state状态
- 用于修改
- 错误示例
- 不能直接修改
state
- 不能直接修改
class Weather extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
// 初始化状态
this.state = { isHot: true }
}
demo = () => {
console.log(this);
// 不起作用 但 state 值修改了【视图】没更新 DOM
this.state.isHot = !this.state.isHot
}
// todo render ...
}
// todo...
- 状态不能直接更改,需要使用
setState修改
class Weather extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
// 初始化状态
this.state = { isHot: true }
this.demo = this.demo.bind(this)
}
demo() {
const isHot = this.state.isHot
this.setState({
isHot: !isHot
})
}
// todo render ...
}
// todo...
注意事项
this.setState可合并多个状态操作Weather类构造器调用 1 次,成员方法render调用1 + n次- 1 为初始化,n 为状态更新的次数
state的简写方式
class Weather extends React.Component {
// 初始化状态
// 给实例添加属性 state
state = { isHot: true }
// 自定义方法
demo = () => {
console.log(this);
const { isHot } = this.state
this.setState({ isHot: !isHot })
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{/* this.demo 仅仅是保存的 demo 方法 实际上 this 发生改变 */}
<h1 onClick={this.demo}>今天天气
{this.state.isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'}</h1>
</div>
)
}
}
1.4.5 props 基本使用
// 创建组件
class Person extends React.Component {
render() {
// 实例内部使用 props 接受
const { name, sex, age } = this.props
return (
<ul>
<li>姓名 {name}</li>
<li>性别 {sex}</li>
<li>年龄 {age}</li>
</ul>
)
}
}
// 渲染组件 Person 标签内部传入属性
ReactDOM.render(<Person name="张三" age="20" sex="男" />, document.getElementById('app'))
批量传入 props
// 创建组件
class Person extends React.Component {
render() {
const { name, sex, age } = this.props
return (
<ul>
<li>姓名 {name}</li>
<li>性别 {sex}</li>
<li>年龄 {age}</li>
</ul>
)
}
}
const p = { name: "张三", age: 20, sex: "男" }
// 使用扩展运算符 ...
ReactDOM.render(<Person {...p} />, document.getElementById('app'))
限制 props
自
React v15.5起,React.PropTypes已移入另一个包中请使用prop-types库open in new window代替
// 引入 `props-types` 用于对组件的标签属性进行限制
<script src="../js/prop-types.js"></script>
// 创建组件
class Person extends React.Component {
render() {
const { name, sex, age } = this.props
return (
<ul>
<li>姓名 {name}</li>
<li>性别 {sex}</li>
<li>年龄 {age}</li>
</ul>
)
}
}
// 对标签属性进行类型与必要性的限制
Person.propTypes = {
// 限制 name 字符串且必传
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
// 限制 sayHello 为函数
sayHello: PropTypes.func
}
// 指定默认标签属性值
Person.defaultProps = {
sex: '男'
}
function sayHello() {
console.log('hello')
}
const p = { name: "张三", age: 20, sex: "男", sayHello }
// 使用扩展运算符 ...
ReactDOM.render(<Person {...p} />, document.getElementById('app'))
props的简写
使用扩展运算符
...
props的只读性- 组件无论是使用函数声明还是通过
class声明,都绝不能修改自身的props
- 组件无论是使用函数声明还是通过
// 创建组件
class Person extends React.Component {
render() {
const { name, sex, age } = this.props
return (
<ul>
<li>姓名 {name}</li>
<li>性别 {sex}</li>
<li>年龄 {age}</li>
</ul>
)
}
// 需要添加 static 关键字 作为静态属性
static propTypes = {
// 限制 name 字符串且必传
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
// 限制 sayHello 为函数
sayHello: PropTypes.func
}
// 指定默认标签属性值
static defaultProps = {
sex: '男'
}
}
function sayHello() {
console.log('hello')
}
const p = { name: "张三", age: 20, sex: "男", sayHello }
// 使用扩展运算符 ...
ReactDOM.render(<Person {...p} />, document.getElementById('app'))
1.4.6 类式组件中的构造器与 props
- 在
React中,通常情况下,构造函数仅用于以下两种情况:- 通过给
this.state赋值对象来初始化state。 - 为事件处理函数绑定实例(改变
this指向)
- 通过给
- 在
React组件挂载之前,会调用它的构造函数。在为React.Component子类实现构造函数时,应在其他语句之前调用super(props)。否则,this.props在构造函数中可能会出现未定义的bug。
class Person extends React.Component {
// 基本上少写 constructor
constructor(props) {
// 构造函数是否接受 props,是否传递给 super 取决于是否希望在构造器中通过 this 访问 props
// debugger
/*
实际调用
function Component(props) {
// this ==> Person
this.props = props
}
*/
super(props)
console.log(this.props)
}
}
1.4.7 函数式组件使用 props
function Person(props) {
const { name, sex } = props
return (
<ul>
<li>姓名 {name}</li>
<li>性别 {sex}</li>
</ul>
)
}
Person.propTypes = {
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
}
//指定默认标签属性值
Person.defaultProps = {
sex: '男',
}
const p = { name: '张三' }
ReactDOM.render(<Person {...p} />, document.getElementById('app'))
1.4.8 Ref 概念及基本使用
ref字符串形式(过时API)- 组件内的标签使用
ref标识自己
- 组件内的标签使用
class Demo extends React.Component {
showData = () => {
const input = this.refs.ipt1
// console.log(input) // 可用于获取真实 DOM
console.log(input.value)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<input ref="ipt1" type="text" />
<button onClick={this.showData}>点击</button>
</div>
)
}
}
// todo:ReactDOM.render(ref回调形式
class Demo extends React.Component {
showData = () => {
console.log(this.input1.value);
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{/* 保存 ref 到实例对象上的 input1 属性 */}
<input ref={(c) => this.input1 = c} type="text" />
<button onClick={this.showData}>点击</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Demo />, document.getElementById('app'))
-
ref回调形式调用次数问题 -
如果
ref回调函数是以内联函数的方式定义的,在更新过程中它会被执行两次,第一次传入参数null,然后第二次会传入参数DOM元素
// 创建组件
class Demo extends React.Component {
state = { isHot: false }
showData = () => {
console.log(this.input1.value);
}
changeWeather = () => {
const { isHot } = this.state
this.setState({ isHot: !isHot })
}
render() {
const { isHot } = this.state
return (
<div>
<h2>今天天气{isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'}</h2>
<input ref={(c) => { this.input1 = c; console.log('@', c); }} type="text" placeholder="点击提示" />
<button onClick={this.showData}>点击展示数据</button>
<button onClick={this.changeWeather}>点击切换天气</button>
</div>
)
}
}
// 每次点击切换天气按钮 ==> 重新渲染(更新)
// @ null
// @ input
-
因为在每次渲染时会创建一个新的函数实例,所以
React清空旧的ref并且设置新的ref -
通过将
ref的回调函数定义成class的绑定函数的方式可以避免上述问题,但是大多数情况下它是无关紧要的
// 创建组件
class Demo extends React.Component {
state = { isHot: false }
showData = () => {
console.log(this.input1.value);
}
changeWeather = () => {
const { isHot } = this.state
this.setState({ isHot: !isHot })
}
// 写在函数体内
saveInput = (c) => {
this.input1 = c
console.log('@', c);
// 只会输出一次
}
render() {
const { isHot } = this.state
return (
<div>
<h2>今天天气{isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'}</h2>
<input ref={this.saveInput} type="text" placeholder="点击提示" />
<button onClick={this.showData}>点击展示数据</button>
<button onClick={this.changeWeather}>点击切换天气</button>
</div>
)
}
}
createRef 的使用
- 创建
refsmyRef = React.createRef()
- 访问
refsthis.myRef.current
class Person extends React.Component {
// React.createRef 调用后返回一个容器 该容器可以存储 【被 ref 所标识】 的节点
myRef = React.createRef()
showData = () => {
// 获取 input
// console.log(this.myRef.current);
// 获取 input 框的值
console.log(this.myRef.current.value);
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{/*会将 ref 所在【标签节点】存储在 myRef*/}
<input ref={this.myRef} type="text" />
<button onClick={this.showData}>点击</button>
</div>
)
}
}
1.5 事件处理
1.5.1 概念与基础示例
-
通过
onXxx属性指定事件处理函数(注意大小写)-
React使用自定义(合成)事件,而不是使用原生的DOM事件 —— 兼容性 -
React中的事件是通过事件委托方式(基于冒泡)处理的(委托给组件最外层的元素)—— 高效
-
-
通过
event.target得到发生事件的DOM元素对象
注意:不要过度使用
ref
class Person extends React.Component {
showData = (e) => {
console.log(e.target.value)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<input onBlur={this.showData} />
</div>
)
}
}
1.5.2 React 中收集表单数据
- 包含表单的组件分类 : 受控组件和非受控组件
受控组件
类似于
vue的双向数据绑定
- 让
React中的state成为“唯一数据源”且使用setState()来更新,同时渲染表单的React组件还控制着用户输入过程中表单发生的操作,被React以这种方式控制取值的表单输入元素就叫做**“受控组件”**
// 创建组件
class Person extends React.Component {
// 初始化状态
state = {
username: '',
password: ''
}
handleSumbit = (e) => {
e.preventDefault() // 阻止表单提交
const { username, password } = this.state
alert(`用户名为 ${username} 密码为 ${password}`);
}
getUsername = (event) => {
// console.log(event.target.value);
this.setState({ username: event.target.value })
}
getPassword = (event) => {
this.setState({ password: event.target.value })
}
render() {
return (
<form onSubmit={this.handleSumbit}>
用户名: <input type="text" onChange={this.getUsername} name="username" />
密码: <input type="password" onChange={this.getPassword} name="password" />
<button>登录</button>
</form>
)
}
}
// todo: ReactDOM.render(非受控组件
- 受控组件使用
ref来从DOM节点获取表单数据
class Person extends React.Component {
handleSumbit = (e) => {
e.preventDefault() // 阻止表单提交
const { username, password } = this // 从实例上获取 username 与 password
alert(`用户名为 ${username.value} 密码为 ${password.value}`);
}
render() {
return (
<form onSubmit={this.handleSumbit} >
用户名: <input ref={c => this.username = c} type="text" name="username" />
密码: <input ref={c => this.password = c} type="password" name="password" />
<button>登录</button>
</form>
)
}
}
// todo: ReactDOM.render(知识扩展之函数式编程
- 高阶函数与柯里化应用
class Person extends React.Component {
//初始化状态
state = {
username: '',
password: ''
}
handleSumbit = (e) => {
e.preventDefault() // 阻止表单提交
const { username, password } = this.state
alert(`用户名为 ${username} 密码为 ${password}`);
}
saveFormData = (dataType) => {
// console.log(dataType);
// 注意:返回的箭头函数才是作为 onChange 事件的回调
// dataType 输入类型为字符串,需要【中括号】包裹
return (event) => {
this.setState({ [dataType]: event.target.value })
}
}
render() {
return (
<form onSubmit={this.handleSumbit}>
用户名: <input type="text" onChange={this.saveFormData('username')} name="username" />
密码: <input type="password" onChange={this.saveFormData('password')} name="password" />
<button>登录</button>
</form>
)
}
}
// todo: ReactDOM.render(- 上述示例中,
saveFormData返回一个箭头函数,作为onChange事件的监听函数,好处是通过函数调用继续返回函数的方式,实现多次接收参数最后统一处理的函数编码形式
- 其他做法
class Person extends React.Component {
// 初始化状态
state = {
username: '',
password: ''
}
handleSumbit = (e) => {
e.preventDefault() // 阻止表单提交
const { username, password } = this.state
alert(`用户名为 ${username} 密码为 ${password}`);
}
saveFormData = (event, dataType) => {
this.setState({ [dataType]: event.target.value })
}
render() {
return (
<form onSubmit={this.handleSumbit}>
用户名: <input type="text" onChange={(event) => this.saveFormData(event, 'username')} name="username" />
密码: <input type="password" onChange={(event) =>
this.saveFormData(event, 'password')} name="password" />
<button>登录</button>
</form>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Person />, document.getElementById('app'))
1.6 组件生命周期
- 使用示例
componentDidMount
- 简单理解其调用时机 : 组件挂载后(或节点插入
DOM树中)会立即调用
componentWillUnmount
- 调用时机 : 组件卸载及销毁之前立即调用
// 创建组件
class Life extends React.Component {
state = { opacity: 1 }
// 挂载 mount 卸载 unmount
demo = () => {
// 卸载组件 API (unmountComponentAtNode)
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById('app'))
}
// 组件挂载后(插入 DOM 树中)立即调用
// 实例会调用 所以 this 指向 组件实例
componentDidMount() {
this.timer = setInterval(() => {
let { opacity } = this.state
opacity -= 0.1
if (opacity < 0) opacity = 1
this.setState({ opacity })
}, 200)
}
// 组件卸载及销毁之前立即调用
componentWillUnmount() {
// 清楚定时器
clearInterval(this.timer)
}
// render 调用时机 初始化渲染与状态更新之后
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1 style={{ opacity: this.state.opacity }}>React</h1>
<button onClick={this.demo}>点击</button>
</div>
)
}
}
// 渲染组件
ReactDOM.render(<Life />, document.getElementById('app'))
React组件中包含一系列钩子函数(生命周期回调函数)会在特定的时刻调用- 在定义组件时,会在特定的生命周期回调函数中,完成特定的业务逻辑
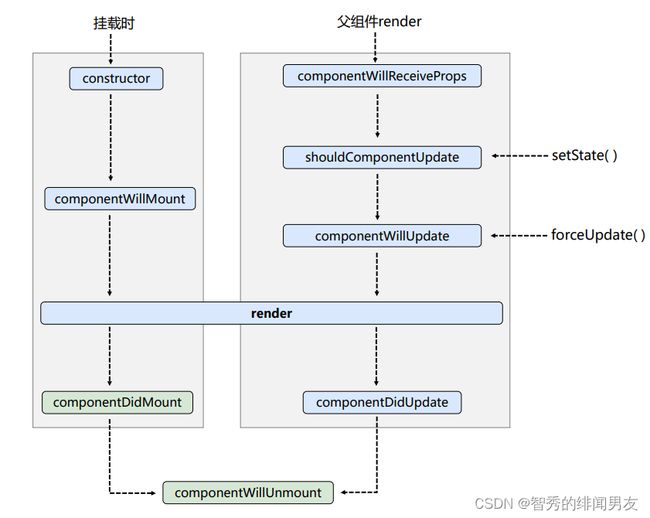
1.6.1 生命周期流程图(旧)
shouldComponentUpdate
- 如果
shouldComponentUpdate()返回false,则不会调用render(),默认为true
可以想象该生命周期钩子为
render“阀门”
forceUpdate()用于强制让组件重新渲染- 调用
forceUpdate()将致使组件调用render()方法,注意:此操作会跳过该组件的shouldComponentUpdate()
- 调用
// 创建组件
class Count extends React.Component {
// Count 构造器
constructor(props) {
console.log('1-constructor');
super(props)
// 初始化状态 state
this.state = { count: 0 }
}
add = () => {
const { count } = this.state
this.setState({ count: count + 1 })
}
// 强制更新按钮的回调
force = () => {
this.forceUpdate()
}
demo = () => {
// 卸载组件到对应的节点
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(document.getElementById('app'))
}
// 组件将要挂载的钩子
componentWillMount() {
console.log('2-componentWillMount');
}
// 组件挂载完毕的钩子
componentDidMount() {
console.log('4-componentDidMount');
}
// 组件将要卸载的钩子
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('5-componentWillUnmount');
}
// setState 触发 用于控制组件更新的阀门,一般不写默认返回 true
shouldComponentUpdate() {
console.log('shouldComponentUpdate');
// return false // 生命周期中断 render 不会调用
return true
}
// 组件将要更新的钩子
componentWillUpdate() {
console.log('componentWillUpdate');
}
// 组件更新完毕的钩子
componentDidUpdate() {
console.log('componentDidUpdate');
}
// render 调用时机 初始化渲染与状态更新之后
render() {
console.log('3-render');
return (
<div>
<h1>count 的值为 {this.state.count}</h1>
<button onClick={this.add}>+1</button>
<button onClick={this.demo}>卸载组件</button>
<button onClick={this.force}>强制重新渲染组件</button>
</div>
)
}
}
// 渲染组件
ReactDOM.render(<Count />, document.getElementById('app'))
- 父组件
render
// 父组件 A
// 简单说明如何形成父子组件,后续会深入
// 在类式组件 A 的 render 中声明子组件 B 即可
class A extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<div>A组件</div>
{/* 使用子组件 B */}
<B />
</div>
)
}
}
// 子组件 B
class B extends React.Component {
// 组件将要接收新的 props 的钩子
componentWillReceiveProps(props) {
console.log('B -- componentWillReceiveProps', props);
}
shouldComponentUpdate() {
console.log('shouldComponentUpdate');
return true
}
componentWillUpdate() {
console.log('componentWillUpdate');
}
componentDidUpdate() {
console.log('componentDidUpdate');
}
render() {
console.log('render')
return (
<div>B组件</div>
)
}
}
// 渲染组件
ReactDOM.render(<A />, document.getElementById('app'))
1.6.2 总结生命周期
1. 初始化阶段 : 由 ReactDOM.render() 触发(初次渲染)
constructor()
componentWillMount()
render()
componentDidMount()
2. 更新阶段 : 由组件内部 this.setSate() 或父组件重新 render 触发
shouldComponentUpdate()
componentWillUpdate()
render()
componentDidUpdate()
3. 卸载组件 : 由 ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode() 触发
componentWillUnmount()
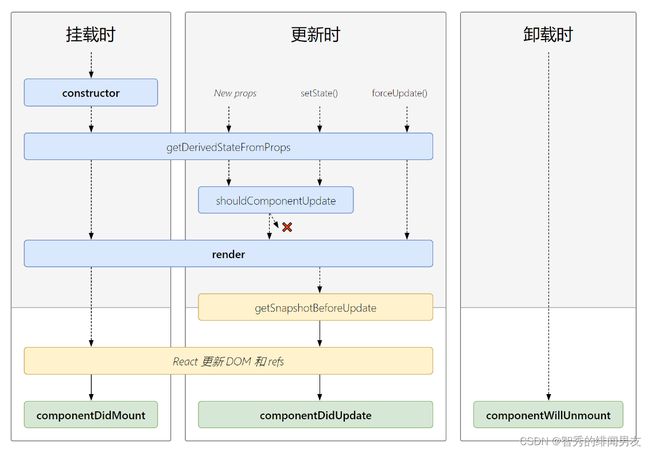
- 生命周期(新)
UNSAFE_name(即将废弃)UNSAFE_componentWillMount()UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate()UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps()
class Count extends React.Component {
// Count 构造器
constructor(props) {
}
// 强制更新按钮的回调
force = () => {
this.forceUpdate()
}
// 组件将要挂载的钩子
UNSAFE_componentWillMount() {
}
// 组件挂载完毕的钩子
componentDidMount() {
}
// 组件将要卸载的钩子
componentWillUnmount() {
}
// setState 触发 用于控制组件更新的阀门,一般不写默认返回 true
shouldComponentUpdate() {
// return false
return true
}
// 组件将要更新的钩子
UNSAFE_componentWillUpdate() {
}
// 组件更新完毕的钩子
componentDidUpdate() {
}
// render 调用时机 初始化渲染与状态更新之后
render() {
return (
<div>
{ /**/ }
</div>
)
}
}
- 在即将发布的版本中为这些生命周期添加
UNSAFE_前缀。 - 这里的
unsafe不是指安全性,而是表示使用这些生命周期的代码在React的未来版本(18.x)中更有可能出现bug,尤其是在启用异步渲染之后
1.6.3 生命周期流程图(新)
-
getDerivedStateFromProps- 适用于
state的值在任何时候都取决于props(使用场景较少)
- 适用于
-
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate- 可以在组件发送更改(新)之前从
DOM中捕获一些信息,此生命周期方法的任何返回值将作为参数传递给componentDidUpdate()
- 可以在组件发送更改(新)之前从
class Count extends React.Component {
// Count 构造器
constructor(props) {
console.log('constructor');
super(props)
// 初始化状态 state
this.state = { count: 0 }
}
add = () => {
const { count } = this.state
this.setState({ count: count + 1 })
}
// 强制更新按钮的回调
force = () => {
this.forceUpdate()
}
// 译为从 【Props】 中获取派生的 state 的钩子,需要声明成【静态】方法且必须返回 state object 或 null
static getDerivedStateFromProps(Props) {
console.log('getDerivedStateFromProps',Props);
return null
// return { count: 2 } // 会影响 state.count 的变更 永远是 2
}
// 需要返回一个 snapshot value 或 null
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate() {
console.log('getSnapshotBeforeUpdate');
return null
}
// 组件挂载完毕的钩子
componentDidMount() {
}
// 组件将要卸载的钩子
componentWillUnmount() {
}
// setState 触发 用于控制组件更新的阀门,一般不写默认返回 true
shouldComponentUpdate() {
}
// 组件更新完毕的钩子
componentDidUpdate(preProps, preState, snapShotValue) {
// preState 是先前的 state,preProp 是先前的 props
console.log('componentDidUpdate', preProps, preState, snapShotValue)
}
// render 调用时机 初始化渲染与状态更新之后
render() {
console.log('render');
return (
<div>
<h1>count 的值为 {this.state.count}</h1>
<button onClick={this.add}>+1</button>
<button onClick={this.force}>强制重新渲染组件</button>
</div>
)
}
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate的使用示例(使用场景较少)
class NewList extends React.Component {
// 初始化 state
state = { newsArr: [] }
// 在组件更新之前获取 DOM 数据
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate() {
// 传递给 componentDidUpdate 作为参数
return this.refs.list.scrollHeight
}
// 组件挂载完毕调用钩子
componentDidMount() {
setInterval(() => {
// 获取原 state
const { newsArr } = this.state
// 模拟生成新闻数据
const news = '新闻' + (newsArr.length + 1)
// 更新 state
this.setState({ newsArr: [news, ...newsArr] })
}, 1000)
}
componentDidUpdate(preProps, preState, height) {
this.refs.list.scrollTop += this.refs.list.scrollHeight - height
console.log(this.refs.list.scrollTop);
}
render() {
return (
<div className="list" ref="list">
{this.state.newsArr.map((item, index) => {
return <div className="news" key={index}>{item}</div>
})}
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<NewList />, document.getElementById('app'))
TO BE CONTINUE ...