相交链表-python
leetCode第160题 相交链表
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:

题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
自定义评测:
评测系统 的输入如下(你设计的程序 不适用 此输入):
intersectVal - 相交的起始节点的值。如果不存在相交节点,这一值为 0
listA - 第一个链表
listB - 第二个链表
skipA - 在 listA 中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数
skipB - 在 listB 中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数
评测系统将根据这些输入创建链式数据结构,并将两个头节点 headA 和 headB 传递给你的程序。如果程序能够正确返回相交节点,那么你的解决方案将被 视作正确答案 。
示例 1:
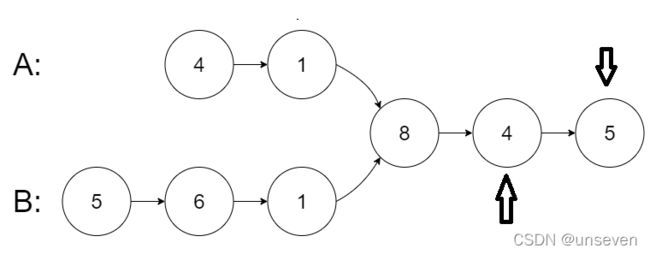
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Intersected at ‘8’
解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,6,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例2:
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Intersected at ‘2’
解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [1,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。
由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。
提示:
listA 中节点数目为 m
listB 中节点数目为 n
1 <= m, n <= 3 * 104
1 <= Node.val <= 105
0 <= skipA <= m
0 <= skipB <= n
如果 listA 和 listB 没有交点,intersectVal 为 0
如果 listA 和 listB 有交点,intersectVal == listA[skipA] == listB[skipB]
进阶:你能否设计一个时间复杂度 O(m + n) 、仅用 O(1) 内存的解决方案?
分析此题,如果没有思绪,不妨想想暴力法,直接将A的所有结点挨个带入B,如果找到了一样的,那么证明二者相交
class Solution: def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode: if headA == None or headB == None: return None while headA != None: tempB = headB while tempB != None: if headA != tempB: tempB = tempB.next else: return tempB headA = headA.next return None这样时间复杂度达到了O(n*m),势必会导致超时
不妨引入hash map ,在这个地方不用python的字典来实现hash map,应该用集合来实现
先将A的所有结点存入hash map
遍历B的每一个结点,如果在hash map出现了,那么证明这个就是交点
## python3
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
hash_map = set()
if headA == None or headB == None:
return None
while headA != None:
hash_map.add(headA)
headA = headA.next
while headB != None:
if headB in hash_map:
return headB
else:
headB = headB.next
return None
进阶中要求我们设计一个时间复杂度 O(m + n) 、仅用 O(1) 内存的解决方案。那么hash map的引入使得空间复杂度不满足要求。
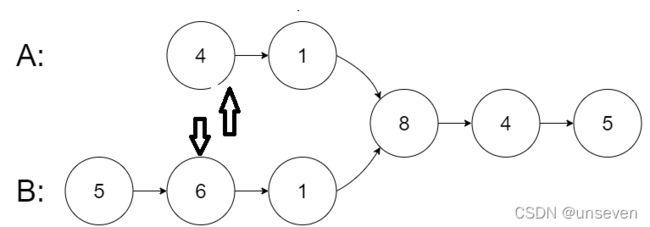
这时不妨采用双指针法,在A和B的开始处设立一个指针。
然后同时移动指针,那么会有一端先遍历完
将A的指针移动到B的开头,继续遍历,之后B也会被遍历完
将B移动到A的开头
此时两指针会在同一位置,继续移动指针,找到汇合的结点即可。
这其实是一个很简单的数学推理,因为如果长短有差距,那么一个结点多走的步刚好就是链表长度的差。
# python3
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if headA == None or headB == None:
return None
tempA = headA
tempB = headB
while tempA != tempB:
tempA = headB if tempA == None else tempA.next
tempB = headA if tempB == None else tempB.next
return tempA
当然我们也可以直接求出两个链表的长度,计算长度的差值,让长链表先走完那些多出来的结点,然后找到汇聚的结点
## python3
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if headA == None or headB == None:
return None
len1 = 0
len2 = 0
diff = 0
tempA = headA
tempB = headB
while headA != None:
len1 += 1
tempA = tempA.next
while headB != None:
len2 += 1
tempB = tempB.next
if len1 < len2: ## 使tempA 指向更长的链表,方便后续移动
tempA = headB
tempB = headA
diff = len2 - len1
else:
tempA = headA
tempB = headB
diff = len1 - len2
for i in range(diff):
tempA = tempA.next
while tempA != None and tempB != None:
if tempA == tempB:
return tempA
else:
headA = headA.next
headB = headB.next
return None