SpringMVC系列-3 拦截器
背景
本文作为 SpringMVC系列 的第三篇,以SpringMVC系列-2 HTTP请求调用链为基础,介绍Spring MVC的拦截器。
1.拦截器
SpringMVC的核心实现是DispatcherServlet,本质是一个Servlet实现类,拦截器位于DispatcherServlet逻辑中;Filter是Servlet规范,且过滤器和拦截器发挥作用的时机不同,需要注意不要将二者混淆。一个HTTP请求的执行路径可以表示为:
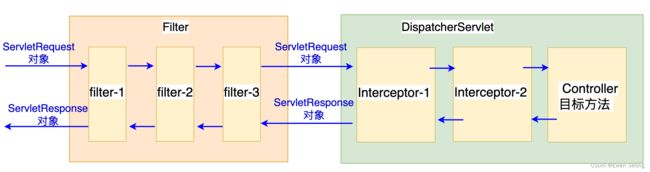
请求依次经过各Filter,然后进入DispatcherServlet。在DispatcherServlet中先经过拦截器逻辑再调用Controller目标方法,即拦截器逻辑发在请求被服务器真实处理前后,因此常用于进行操作日志记录、鉴权等。
2.使用方式
2.1自定义HandlerInterceptor接口的实现类:
@Slf4j
public class MyHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
LOGGER.info("-------[Interceptor] preHandle-------");
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
LOGGER.info("-------[Interceptor] postHandle-------");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
LOGGER.info("-------[Interceptor] afterCompletion-------");
}
}
HandlerInterceptor中的声明的preHandle/postHandle/afterCompletion为default类型的接口,可以随意选择是否实现。
preHandle接口若返回false, 会跳过Controller方法的执行,流程可参考SpringMVC系列-2 HTTP请求调用链
2.2 通过WebMvcConfigurer将拦截器注册到框架中:
注册拦截器的时候,可以选择将其注册为HandlerInterceptor或MappedInterceptor,二者注册方式和生效场景略有不同。
HandlerInterceptor对所有请求生效,MappedInterceptor对URL满足匹配要求的请求生效。
注册为HandlerInterceptor
@Configuration
public class MyInterceptorConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new MyHandlerInterceptor());
}
}
此时HandlerInterceptor对所有的HTTP请求生效。
注册为MappedInterceptor
@Configuration
public class MyInterceptorConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new MyHandlerInterceptor())
.addPathPatterns("/**")
.excludePathPatterns("/static/**");
}
}
在注册拦截器时,如果通过addPathPatterns添加白名单或者excludePathPatterns添加黑名单时,框架会自动将该拦截器包装成MappedInterceptor。
匹配过程涉及三个变量:匹配器、路径黑名单、路径白名单;
【1】匹配器
可通过registry.pathMatcher(new MyAntPathMatcher());方法注册匹配器。
一般不会直接自定义匹配器,而是使用既有的匹配器,按照其匹配规则配置UR L的黑/白名单(如上述案例所示)。
框架默认的配置器AntPathMatcher,该匹配器实现的匹配规则如下:
?匹配一个字符
* 匹配0个或多个字符
** 匹配0个或多个目录
如:"/**"表示匹配所有的Http请求路径,"/abc/api/**"表示匹配以/abc/api/开头的URL。
【2】路径黑名单、白名单
public boolean matches(String lookupPath, PathMatcher pathMatcher) {
PathMatcher pathMatcherToUse = (this.pathMatcher != null ? this.pathMatcher : pathMatcher);
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.excludePatterns)) {
for (String pattern : this.excludePatterns) {
if (pathMatcherToUse.match(pattern, lookupPath)) {
return false;
}
}
}
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.includePatterns)) {
return true;
}
for (String pattern : this.includePatterns) {
if (pathMatcherToUse.match(pattern, lookupPath)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
优先匹配黑名单:
step1: 如果路径被任一黑名单匹配,则返回false—表示匹配失败;
step2: 如果匹配任一白名单(或白名单为空),则返回true—表示匹配成功;
step3: 如果所有白名单均不匹配,则返回false—表示失败。
这种黑白名单规则一般也适用于业务场景,需求设计时也可参考。
另外,对于MappedInterceptor类型的拦截器除了使用WebMvcConfigurer方式将其注册到框架外,还可通过向IOC容器中注册Bean对象的方式实现,如下所示:
@Configuration
public class MyInterceptorConfig {
@Bean
public MappedInterceptor myMappedInterceptor() {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = new MappedInterceptor(new String[]{"/**"}, new String[]{"/static/**"}, new MyHandlerInterceptor());
mappedInterceptor.setPathMatcher(new AntPathMatcher());
return mappedInterceptor;
}
}
2.3 Controller测试案例:
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/info")
public class MyController {
@GetMapping("/name")
public String getName() {
LOGGER.info("[Controller] getName has called.");
return "success";
}
}
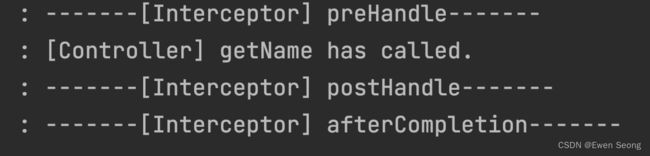
2.4 执行结果
3.实现原理
本章节以SpringBoot+SpringMVC为框架背景,结合SpringMVC框架源码介绍项目启动过程拦截器的注册和Controller被调用过程拦截器的收集和执行原理。
3.1 启动过程
SpringBoot自动装配机制在启动时向容器注册WebMvcAutoConfiguration这个配置类, 其内部引入的EnableWebMvcConfiguration配置类中(以及其父类WebMvcConfigurationSupport)使用@Bean注解方式向IOC容器中注册了RequestMappingHandlerMapping、ViewControllerHandlerMapping、BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping、RouterFunctionMapping、ResourceHandlerMapping、WelcomePageHandlerMapping这些Bean对象, 这些Bean对象注册到IOC容器前,调用getInterceptors方法获取拦截器数组并对其进行了属性设置。
获取拦截器的逻辑如下:
protected final Object[] getInterceptors(FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService, ResourceUrlProvider mvcResourceUrlProvider) {
if (this.interceptors == null) {
InterceptorRegistry registry = new InterceptorRegistry();
addInterceptors(registry);
registry.addInterceptor(new ConversionServiceExposingInterceptor(mvcConversionService));
registry.addInterceptor(new ResourceUrlProviderExposingInterceptor(mvcResourceUrlProvider));
this.interceptors = registry.getInterceptors();
}
return this.interceptors.toArray();
}
其中用户自定义的拦截器通过addInterceptors(registry);逻辑获取:
protected void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
this.configurers.addInterceptors(registry);
}
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
for (WebMvcConfigurer delegate : this.delegates) {
delegate.addInterceptors(registry);
}
}
其中,delegate包含了IOC容器中WebMvcConfigurer类型的对象,即包含了章节2中的MyInterceptorConfig。
EnableWebMvcConfiguration(DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration的子类)对象在属性设置阶段会获取IOC中所有WebMvcConfigurer类型的Bean对象作为如参,并调用setConfigurers方法,:
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
@Autowired(required = false)
public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);
}
}
}
根据调用链:
public void addWebMvcConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
this.delegates.addAll(configurers);
}
}
因此,delegate包含了IOC容器中WebMvcConfigurer类型的对象。
当将各类型(包括RequestMappingHandlerMapping)的HandlerMapping注册到IOC容器时,其interceptors属性已包含了拦截器对象。
3.2 收集拦截器
如SpringMVC系列-2 HTTP请求调用链中所述,当调栈进入doDispatch方法时,会经历收集拦截器、调用拦截器preHandle方法、调用目标方法、调用拦截器postHandle方法、调用拦截器的afterCompletion方法。
其中收集拦截器的逻辑如下:
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request, LOOKUP_PATH);
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}
拦截器数组来源于this.adaptedInterceptors属性,如果是MappedInterceptor类型,则判断请求的URL是否匹配,如果匹配则将拦截器加入到调用链中;如果是HandlerInterceptor类型,则直接加入到调用链中。
而this.adaptedInterceptors属性来源于章节 3.1 中的interceptors属性,以及IOC容器中MappedInterceptor类型的Bean对象:
protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
extendInterceptors(this.interceptors);
detectMappedInterceptors(this.adaptedInterceptors);
initInterceptors();
}
其中:detectMappedInterceptors方法逻辑如下:
protected void detectMappedInterceptors(List<HandlerInterceptor> mappedInterceptors) {
mappedInterceptors.addAll(
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(
obtainApplicationContext(), MappedInterceptor.class, true, false).values());
}
从IOC容器中获取所有MappedInterceptor类型的Bean对象。
而initInterceptors方法将interceptors属性集合包含的拦截器添加到this.adaptedInterceptors属性中:
protected void initInterceptors() {
if (!this.interceptors.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.interceptors.size(); i++) {
Object interceptor = this.interceptors.get(i);
if (interceptor == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Entry number " + i + " in interceptors array is null");
}
this.adaptedInterceptors.add(adaptInterceptor(interceptor));
}
}
}
3.3 调用拦截器
参考SpringMVC系列-2 HTTP请求调用链文章。