java零基础Ⅲ-- 8.算法优化体验课-骑士周游问题
java零基础Ⅲ-- 8.算法优化体验课-骑士周游问题
- 算法优化意义
- 经典算法面试题 - 骑士周游问题
-
- 马踏棋盘算法介绍和游戏演示
- 代码实现
- 优化 - 贪心算法
连接视频
算法优化意义
1、算法是程序员的灵魂,为什么有些程序可以在海量数据计算时,依然保持高速计算?
2、拿实际工作经历来说,在 Unix下开发服务器程序,功能是要支持上千万人同时在线,在上线前,做内测,一切OK,可上线后,服务器就支撑不住了,公司的CTO对代码进行优化,再次上线,坚如磐石。那一瞬间,你就能感受到程序是有灵魂的,就是算法。
3、编程中算法很多,比如 八大排序算法(冒泡、选择、插入、快排、归并、希尔、基数、推排序)、查找算法、分治算法、动态规划算法、KMP算法、贪心算法、普里姆算法、克鲁斯卡尔算法、迪杰斯特拉算法、佛洛伊德算法
4、以骑士周游问题为例,体验算法优化程序的意义
经典算法面试题 - 骑士周游问题
马踏棋盘算法介绍和游戏演示
1、马踏棋盘算法也称为 骑士周游问题
2、将马随机放在国际象棋的 8x8 棋盘Board[0-7][0-7]的某个方格中,马按走棋规则(马走日字)进行移动。要求每个格子只进入一次,走遍棋盘上全部64个方格
3、游戏演示:
https://u.ali213.net/games/horsesun/index.html?game_code=403
4、会使用到图的遍历算法(DFS) + 贪心算法优化
5、马踏棋盘问题(骑士周游问题)实际上是图的深度优先搜索(DFS)的应用
6、如果使用回溯(就是深度优先搜索)来解决,假如马儿踏了53个点,走了到了第53个,坐标(1,0),发现已经走到尽头,没办法,那就只能回退了,查看其他的路径,就在棋盘上不停的回溯… ,思路分析 + 代码实现
7、先用基本方式来解决,然后使用贪心算法(greedyalgorithm)进行优化。解决马踏棋盘问题,体会到不同的算法对程序效率的影响
8、使用前面游戏来验证算法是否正确

注意:马儿走的策略不同,则得到的结果也不一样,效率也不一样。
代码实现
package com.zzpedu;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class HorseChessBoard {
//定义属性
private static int X = 6;// 表示col 列
private static int Y = 6;// 表示row 行
private static int[][] chessBoard = new int[Y][X];//棋盘
private static boolean[] visited = new boolean[X*Y];//记录某个位置是否走过
private static boolean finished = false;//记录马儿遍历完棋盘
public static void main(String[] args) {
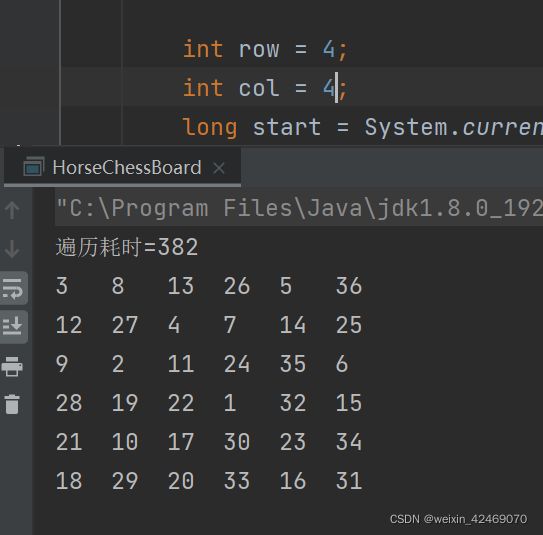
int row = 4;
int col = 4;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//测试一把
traversalChessBoard(chessBoard,row - 1,col -1,1);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("遍历耗时=" + (end - start));
//输出当前这个棋盘的情况
for(int[] rows : chessBoard){
for(int step : rows){//step 表示 该位置是马儿应该走的第几步
System.out.print(step + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//**编写最核心算法** ,遍历棋盘,如果遍历成功,就把 finished 设置成true
//并且,将马儿走的每一步,记录到 chessBoard
public static void traversalChessBoard(int[][] chessBoard,int row,int col,int step){
//先把 step 记录到 chessBoard
chessBoard[row][col] = step;
//把这个位置,设置为已经访问
visited[row * X + col] = true;
//获取当前这个位置可以走的下一个位置有哪些
ArrayList<Point> ps = next(new Point(col, row));// col => x , row => y
//遍历
while (!ps.isEmpty()){
//取出当前这个ps 第一个位置(点)
Point p = ps.remove(0);
//判断该位置是否走过,如果没有走过,我们就递归遍历
if(!visited[p.y * X + p.x]){//没有走过
//递归遍历
traversalChessBoard(chessBoard,p.y,p.x,step+1);
}
}
//当退出while,看看是否遍历成功,如果没有成功,就重置响应的值,然后进行回溯
if(step < X*Y && !finished){
//重置
chessBoard[row][col] = 0;
visited[row * X + col] = false;
}else {
finished = true;
}
}
//编写方法,可以获取当前位置,可以走的下一步位置(Point表示x,y)
public static ArrayList<Point> next(Point curPoint){
//先创建一个ArrayList
ArrayList<Point> ps = new ArrayList<>();
//创建一个Point对象(点/位置),准备放入到 ps
Point p1 = new Point();
//判断在 curPoint 是否可以走如下位置,如果可以走,就将该点(Point)放入到 ps
//判断是否可以走5位置
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x - 2) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 1) >= 0 ) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));//这里一定要new Point 否则重复
}
//判断是否可以走6位置
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x - 1) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 2) >= 0 ) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//判断是否可以走7位置
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x + 1) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 2) >= 0 ) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//判断是否可以走0位置
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x + 2) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 1) >= 0 ) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//判断是否可以走1位置
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x + 2) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 1) < Y ) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//判断是否可以走2位置
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x + 1) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 2) < Y ) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//判断是否可以走3位置
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x - 1) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 2) < Y ) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//判断是否可以走4位置
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x - 2) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 1) < Y ) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
return ps;
}
}
但 row、col =2 耗时太长了,需要优化
优化 - 贪心算法
public class HorseChessBoard {
//定义属性
private static int X = 6;// 表示col 列
private static int Y = 6;// 表示row 行
private static int[][] chessBoard = new int[Y][X];//棋盘
private static boolean[] visited = new boolean[X*Y];//记录某个位置是否走过
private static boolean finished = false;//记录马儿遍历完棋盘
public static void main(String[] args) {
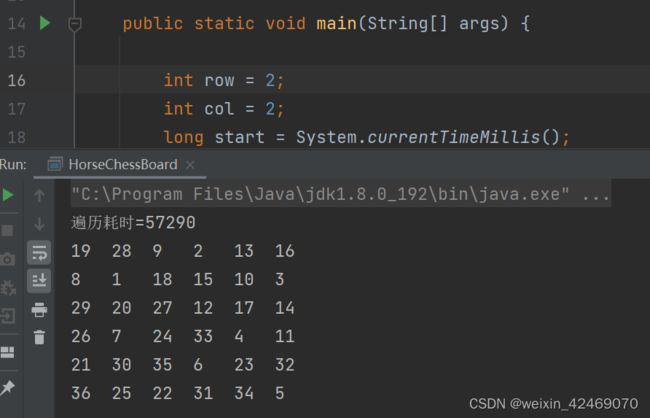
int row = 2;
int col = 2;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//测试一把
traversalChessBoard(chessBoard,row - 1,col -1,1);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("遍历耗时=" + (end - start));
//输出当前这个棋盘的情况
for(int[] rows : chessBoard){
for(int step : rows){//step 表示 该位置是马儿应该走的第几步
System.out.print(step + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//写一个方法,对ps的各个位置,可以走的下一个位置次数进排序,把可能走的下一个位置从小到大排序
public static void sort(ArrayList<Point> ps){
ps.sort(new Comparator<Point>() {
@Override
public int compare(Point o1, Point o2) {
return next(o1).size() - next(o2).size();
}
});
}
//**编写最核心算法** ,遍历棋盘,如果遍历成功,就把 finished 设置成true
//并且,将马儿走的每一步,记录到 chessBoard
public static void traversalChessBoard(int[][] chessBoard,int row,int col,int step){
//先把 step 记录到 chessBoard
chessBoard[row][col] = step;
//把这个位置,设置为已经访问
visited[row * X + col] = true;
//获取当前这个位置可以走的下一个位置有哪些
ArrayList<Point> ps = next(new Point(col, row));// col => x , row => y
sort(ps);//排序
//遍历
while (!ps.isEmpty()){
//取出当前这个ps 第一个位置(点)
Point p = ps.remove(0);
//判断该位置是否走过,如果没有走过,我们就递归遍历
if(!visited[p.y * X + p.x]){//没有走过
//递归遍历
traversalChessBoard(chessBoard,p.y,p.x,step+1);
}
}
//当退出while,看看是否遍历成功,如果没有成功,就重置响应的值,然后进行回溯
if(step < X*Y && !finished){
//重置
chessBoard[row][col] = 0;
visited[row * X + col] = false;
}else {
finished = true;
}
}
//编写方法,可以获取当前位置,可以走的下一步位置(Point表示x,y)
public static ArrayList<Point> next(Point curPoint){
//先创建一个ArrayList
ArrayList<Point> ps = new ArrayList<>();
//创建一个Point对象(点/位置),准备放入到 ps
Point p1 = new Point();
//判断在 curPoint 是否可以走如下位置,如果可以走,就将该点(Point)放入到 ps
//判断是否可以走5位置
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x - 2) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 1) >= 0 ) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));//这里一定要new Point 否则重复
}
//判断是否可以走6位置
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x - 1) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 2) >= 0 ) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//判断是否可以走7位置
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x + 1) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 2) >= 0 ) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//判断是否可以走0位置
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x + 2) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 1) >= 0 ) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//判断是否可以走1位置
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x + 2) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 1) < Y ) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//判断是否可以走2位置
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x + 1) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 2) < Y ) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//判断是否可以走3位置
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x - 1) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 2) < Y ) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
//判断是否可以走4位置
if ((p1.x = curPoint.x - 2) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 1) < Y ) {
ps.add(new Point(p1));
}
return ps;
}
}
执行效果: