2-5编写算法,在单链表中查找第一值为x的结点,并输出其前驱和后继的存储位置
#include
#include
typedef int DataType;
struct Node
{
DataType data;
struct Node* next;
};
typedef struct Node *PNode;
typedef struct Node *LinkList;
LinkList SetNullList_Link()
{
LinkList head = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if (head != NULL) head->next = NULL;
else printf("alloc failure");
return head;
}
void CreateList_Tail(struct Node* head)
{
PNode p = NULL;
PNode q = head;
DataType data;
scanf("%d", &data);
while (data != -1)
{
p = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
p->data = data;
p->next = NULL;
q->next = p;
q = p;
scanf("%d", &data);
}
}
int Inserch_num(LinkList head,int x)
{
LinkList p;
int i=0;
p=head->next;
while(p)
{
if(i==0&&p->data==x)
{
printf("The Prodrove node is head,the position of the rear node is at position 2 of the linked list\n");
return 0;
}
if(p->data==x&&p->next==NULL)
{
printf("The Prodrove node is %d,there is no rear node\n ",i);
return 0;
}
if(p->data==x)
{
printf("The Prodrove node is %d,he rear node is %d\n",i,i+2);
return 0;
}
i++;
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
void print(LinkList head)
{
PNode p = head->next;
while (p)
{
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
}
void DestoryList_Link(LinkList head)
{
PNode pre = head;
PNode p = pre->next;
while (p)
{
free(pre);
pre = p;
p = pre->next;
}
free(pre);
}
int main()
{
LinkList head = NULL;
int x=0,a=0;
head = SetNullList_Link();
CreateList_Tail(head);
print(head);
printf("\n");
printf("Please input the number you find:");
scanf("%d",&x);
a=x;
Inserch_num(head,a);
DestoryList_Link(head);
return 0;
}

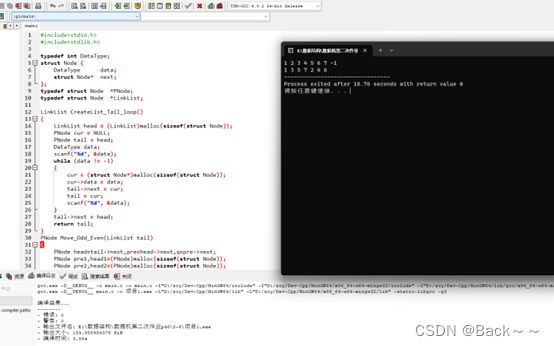
2-6在单循环链表中,编写算法实现将链表中数据域为奇数的结点移至表头,将链表中数据域为偶数的结点移至表尾
#include
#include
typedef int DataType;
struct Node {
DataType data;
struct Node* next;
};
typedef struct Node *PNode;
typedef struct Node *LinkList;
LinkList CreateList_Tail_loop()
{
LinkList head = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
PNode cur = NULL;
PNode tail = head;
DataType data;
scanf("%d", &data);
while (data != -1)
{
cur = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
cur->data = data;
tail->next = cur;
tail = cur;
scanf("%d", &data);
}
tail->next = head;
return tail;
}
PNode Move_Odd_Even(LinkList tail)
{
PNode head=tail->next,pre=head->next,q=pre->next;
PNode pre1,head1=(PNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
PNode pre2,head2=(PNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
pre1=head1;
pre2=head2;
while(q!=head->next)
{
if(pre->data%2==0)
{
pre->next=pre1->next;
pre1->next=pre;
pre1=pre;
}
else
{
pre->next=pre2;
pre2->next=pre;
pre2=pre;
}
pre=q;
q=q->next;
}
head1=head1->next;
pre2->next=head1;
pre1->next=head2;
return pre1;
}
void print(LinkList tail)
{
PNode head = tail->next;
PNode p = head->next;
while (p != head)
{
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
}
void DestoryList_Link(LinkList tail)
{
PNode pre = tail->next;
PNode p = pre->next;
while (p != tail)
{
free(pre);
pre = p;
p = pre->next;
}
free(pre);
free(tail);
}
int main()
{
LinkList tail = NULL;
LinkList p = NULL;
tail = CreateList_Tail_loop();
p = Move_Odd_Even(tail);
print(p);
DestoryList_Link(tail);
return 0;
}
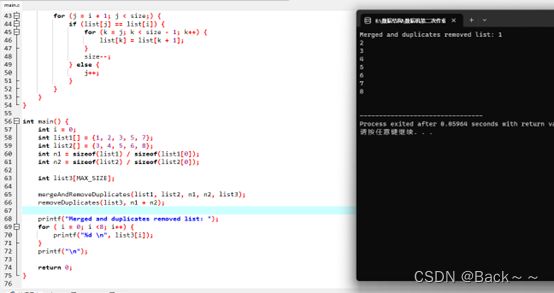
2-7将两个有序线性表LIST1=(a1,a2,…,an)和LIST2=(b1,b2,…,bn)链接成一个有序线性链表LIST3,并删除LIST3链表中相同的结点,即链接中若有多个结点具有相同的数据域,只保留一个结点,使得顺序表中所有结点的数据域都不相同。在采用顺序表和单链表两种形式下分别设计算法实现上述功能
#include
#include
#define MAX_SIZE 100
void mergeAndRemoveDuplicates(int list1[], int list2[], int n1, int n2, int list3[]) {
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while (i < n1 && j < n2) {
if (list1[i] < list2[j]) {
list3[k] = list1[i];
i++;
k++;
} else if (list1[i] > list2[j]) {
list3[k] = list2[j];
j++;
k++;
} else {
list3[k] = list1[i];
i++;
j++;
k++;
}
}
while (i < n1) {
list3[k] = list1[i];
i++;
k++;
}
while (j < n2) {
list3[k] = list2[j];
j++;
k++;
}
}
void removeDuplicates(int list[], int size) {
int i, j, k;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
for (j = i + 1; j < size;) {
if (list[j] == list[i]) {
for (k = j; k < size - 1; k++) {
list[k] = list[k + 1];
}
size--;
} else {
j++;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int i = 0;
int list1[] = {1, 2, 3, 5, 7};
int list2[] = {3, 4, 5, 6, 8};
int n1 = sizeof(list1) / sizeof(list1[0]);
int n2 = sizeof(list2) / sizeof(list2[0]);
int list3[MAX_SIZE];
mergeAndRemoveDuplicates(list1, list2, n1, n2, list3);
removeDuplicates(list3, n1 + n2);
printf("Merged and duplicates removed list: ");
for ( i = 0; i <8; i++) {
printf("%d \n", list3[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
#include
#include
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
struct ListNode* createNode(int val) {
struct ListNode* newNode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
newNode->val = val;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
struct ListNode* mergeAndRemoveDuplicates(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {
struct ListNode* p = list1;
struct ListNode* q = list2;
struct ListNode* list3 = NULL;
struct ListNode* tail = NULL;
while (p && q) {
if (p->val < q->val) {
if (list3 == NULL) {
list3 = tail = createNode(p->val);
} else {
tail->next = createNode(p->val);
tail = tail->next;
}
p = p->next;
} else if (p->val > q->val) {
if (list3 == NULL) {
list3 = tail = createNode(q->val);
} else {
tail->next = createNode(q->val);
tail = tail->next;
}
q = q->next;
} else {
if (list3 == NULL) {
list3 = tail = createNode(p->val);
} else {
tail->next = createNode(p->val);
tail = tail->next;
}
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
}
while (p) {
tail->next = createNode(p->val);
tail = tail->next;
p = p->next;
}
while (q) {
tail->next = createNode(q->val);
tail = tail->next;
q = q->next;
}
struct ListNode* cur = list3;
while (cur && cur->next) {
if (cur->val == cur->next->val) {
struct ListNode* temp = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
free(temp);
} else {
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return list3;
}
void printList(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur != NULL) {
printf("%d ", cur->val);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
struct ListNode* list1 = createNode(1);
list1->next = createNode(2);
list1->next->next = createNode(3);
list1->next->next->next = createNode(5);
list1->next->next->next->next = createNode(7);
struct ListNode* list2 = createNode(3);
list2->next = createNode(4);
list2->next->next = createNode(5);
list2->next->next->next = createNode(6);
list2->next->next->next->next = createNode(8);
struct ListNode* list3 = mergeAndRemoveDuplicates(list1, list2);
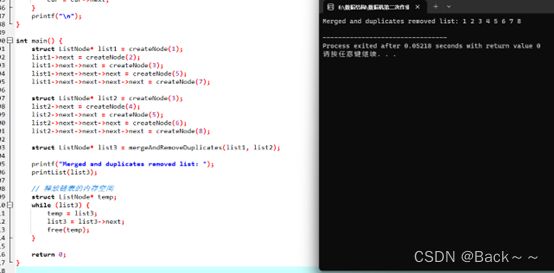
printf("Merged and duplicates removed list: ");
printList(list3);
struct ListNode* temp;
while (list3) {
temp = list3;
list3 = list3->next;
free(temp);
}
return 0;
}
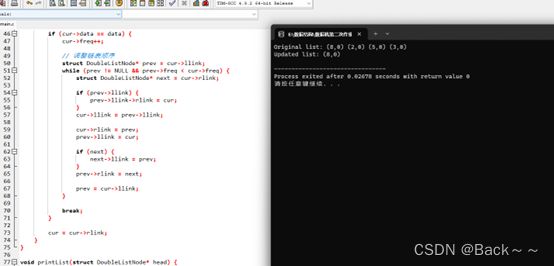
2-8设双链表中的结点包括4个部分:前驱指针llink,后继指针rlink,数据域data,访问频度freq,初始时将各结点的freq设置为0。当对某结点访问时使该结点的freq增加1,并且将链表按照访问freq递减的顺序进行排序。请编写算法实现以上功能
#include
#include
struct DoubleListNode {
int data;
int freq;
struct DoubleListNode* llink;
struct DoubleListNode* rlink;
};
struct DoubleListNode* createNode(int data) {
struct DoubleListNode* newNode = (struct DoubleListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct DoubleListNode));
if (newNode == NULL) {
printf("Memory allocation failed.\n");
exit(1);
}
newNode->data = data;
newNode->freq = 0;
newNode->llink = NULL;
newNode->rlink = NULL;
return newNode;
}
void insertNode(struct DoubleListNode** head, int data) {
struct DoubleListNode* newNode = createNode(data);
if (*head == NULL) {
*head = newNode;
return;
}
newNode->rlink = *head;
(*head)->llink = newNode;
*head = newNode;
}
void increaseFreq(struct DoubleListNode** head, int data) {
if (*head == NULL) {
return;
}
struct DoubleListNode* cur = *head;
while (cur != NULL) {
if (cur->data == data) {
cur->freq++;
struct DoubleListNode* prev = cur->llink;
while (prev != NULL && prev->freq < cur->freq) {
struct DoubleListNode* next = cur->rlink;
if (prev->llink) {
prev->llink->rlink = cur;
}
cur->llink = prev->llink;
cur->rlink = prev;
prev->llink = cur;
if (next) {
next->llink = prev;
}
prev->rlink = next;
prev = cur->llink;
}
break;
}
cur = cur->rlink;
}
}
void printList(struct DoubleListNode* head) {
struct DoubleListNode* cur = head;
while (cur != NULL) {
printf("(%d,%d) ", cur->data, cur->freq);
cur = cur->rlink;
}
printf("\n");
}
void freeList(struct DoubleListNode* head) {
struct DoubleListNode* cur = head;
while (cur != NULL) {
struct DoubleListNode* temp = cur;
cur = cur->rlink;
free(temp);
}
}
int main() {
struct DoubleListNode* head = NULL;
insertNode(&head, 3);
insertNode(&head, 5);
insertNode(&head, 2);
insertNode(&head, 8);
printf("Original list: ");
printList(head);
increaseFreq(&head, 2);
increaseFreq(&head, 5);
increaseFreq(&head, 3);
printf("Updated list: ");
printList(head);
freeList(head);
return 0;
}