SpringBoot学习笔记——数据访问
目录
1、SQL
1.1、数据库连接
1.2、整合MyBatis操作
1.2.1、第一种:利用配置文件的形式整合
1.2.2、第二种:利用注解的形式整合
1.3、整合 MyBatis-Plus 操作
1、SQL
1.1、数据库连接
导入依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc
mysql
mysql-connector-java
修改配置项
spring:
datasource:
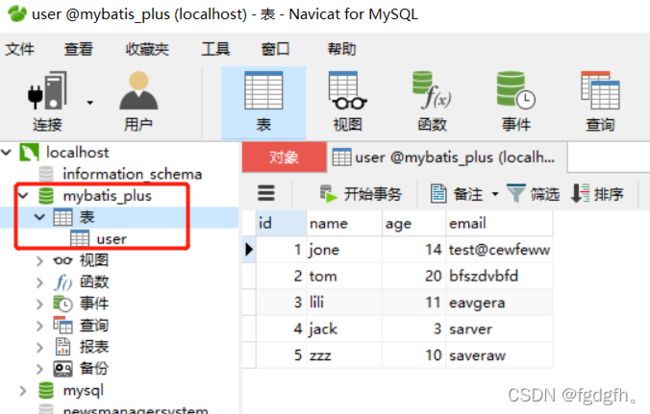
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus
username: root
password: 1017
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver测试
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot2WebApplicationTests {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
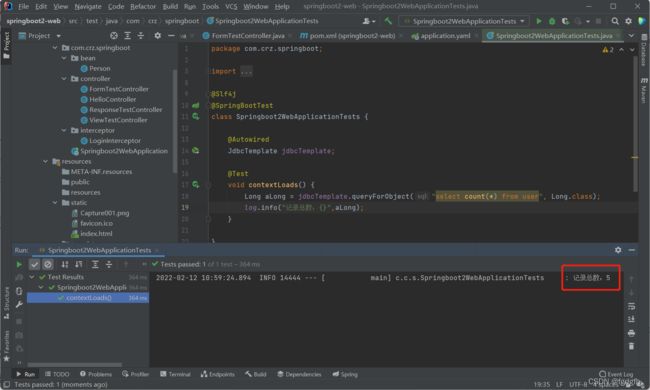
void contextLoads() {
Long aLong = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select count(*) from user", Long.class);
log.info("记录总数:{}",aLong);
}
}1.2、整合MyBatis操作
1.2.1、第一种:利用配置文件的形式整合
导入mybatis依赖
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
2.1.4
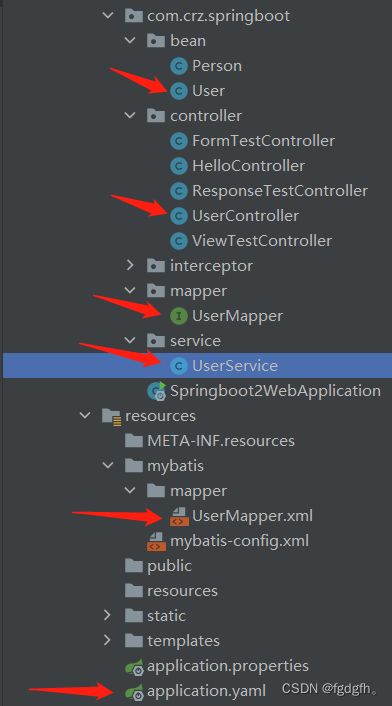
工程的目录结构如下
编写实体类User
@Data
public class User {
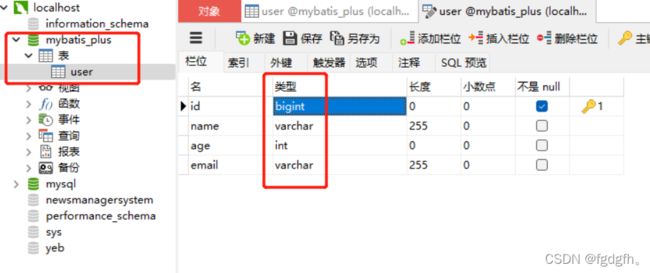
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}编写mapper接口层,标准@Mapper注解
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
/**
* @Description:根据id查询员工信息
* @Author:crz
* @Date:2022/2/12 13:33
*/
public User getUse(Integer id);
}编写sql映射文件并绑定mapper接口
在 application.yml 中进行相关配置
mybatis:
# 全局配置文件的位置
#config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml
# mapper sql映射文件的位置
mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true #开启驼峰命名法
#可以不写全局;配置文件,所有全局配置文件的配置都放在configuration配置项中即可编写 Service 层
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
public User getUserId(Integer id){
return userMapper.getUse(id);
}
}编写 Controller 层
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
@ResponseBody
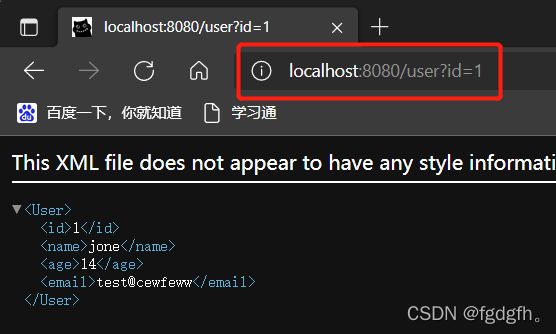
@GetMapping("/user")
public User getUser(@RequestParam("id") Integer id){
return userService.getUserId(id);
}
}测试
1.2.2、第二种:利用注解的形式整合
工程的目录结构如下
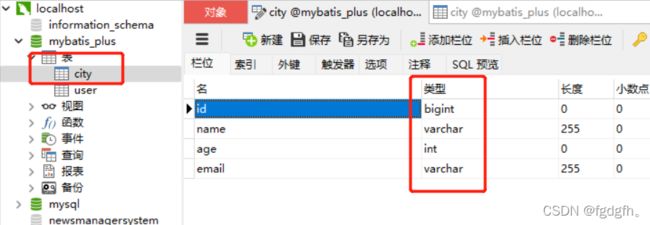
编写实体类City
@Data
public class City {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}编写mapper接口层,标准@Mapper注解
@Mapper
public interface CityMapper {
@Select("select * from city where id=#{id}")
public City getById(Integer id);
}编写 Service 层
@Service
public class CityService {
@Autowired
CityMapper cityMapper;
public City getById(Integer id){
return cityMapper.getById(id);
}
}编写 Controller 层
@Controller
public class CityController {
@Autowired
CityService cityService;
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/city")
public City getCityById(@RequestParam("id") Integer id){
return cityService.getById(id);
}
}测试
1.3、整合 MyBatis-Plus 操作
导入mybatis-plus依赖
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus-boot-starter
3.4.1
编写实体类User
@Data
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}编写mapper接口层,标准@Mapper注解
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper {
} 在com/crz/springboot/Springboot2WebApplicationTests.java文件进行测试
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
void testUserMapper(){
User user = userMapper.selectById(1L);
System.out.println("用户信息:"+user);
}测试
SpringBoot2学习笔记