Filebeat之input和output(包含Elasticsearch Output 、Logstash Output、 Redis Output、 File Output和 Console Ou...
Filebeat啊,根据input来监控数据,根据output来使用数据!!!
Filebeat的input
通过paths属性指定要监控的数据
Filebeat的output
1、Elasticsearch Output (Filebeat收集到数据,输出到es里。默认的配置文件里是有的,也可以去官网上去找)
2、Logstash Output (Filebeat收集到数据,输出到logstash里。默认的配置文件里是有的,也可以得去官网上去找)
3、Redis Output (Filebeat收集到数据,输出到redis里。默认的配置文件里是没有的,得去官网上去找)
4、File Output (Filebeat收集到数据,输出到file里。默认的配置文件里是有的,也可以去官网上去找)
5、Console Output (Filebeat收集到数据,输出到console里。默认的配置文件里是有的,也可以去官网上去找)
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/1.3/filebeat-configuration-details.html
手把手教你看官网(如何查找并配置为自己的,以Redis Output为例)
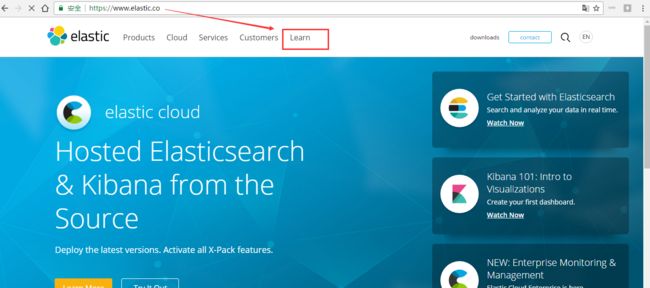
第一步: https://www.elastic.co/
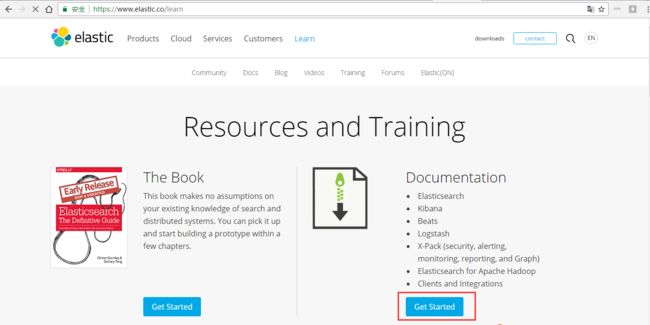
第二步:https://www.elastic.co/learn
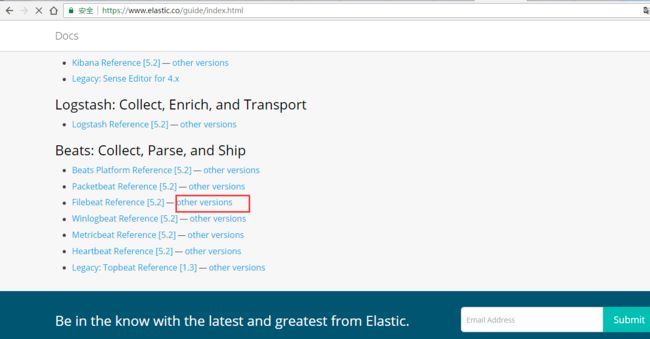
第三步: https://www.elastic.co/guide/index.html
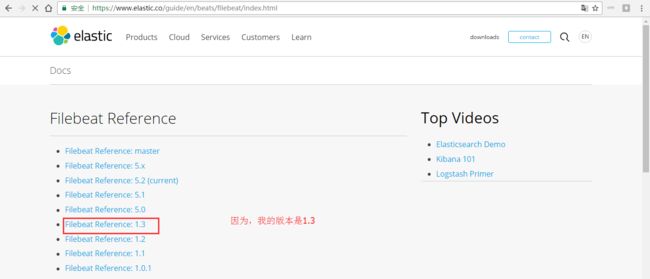
第四步: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/index.html
第五步:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/1.3/index.html
第六步:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/1.3/redis-output.html
output: redis: # Set the host and port where to find Redis. host: "localhost" port: 6379 # Uncomment out this option if you want to store the topology in Redis. # The default is false. save_topology: true # Optional index name. The default is filebeat and generates filebeat keys. index: "filebeat" # Optional Redis database number where the events are stored # The default is 0. db: 0 # Optional Redis database number where the topology is stored # The default is 1. It must have a different value than db. db_topology: 1 # Optional password to authenticate with. By default, no # password is set. # password: "" # Optional Redis initial connection timeout in seconds. # The default is 5 seconds. timeout: 5 # Optional interval for reconnecting to failed Redis connections. # The default is 1 second. reconnect_interval: 1
第七步:以上是官网提供的例子。
比如我的机器情况是:
HadoopMaster 安装了 Elasticsearch Logstash Kibana Filebeat
HadoopSlave1 安装了 Elasticsearch Filebeat
HadoopSlave2 安装了 Elasticsearch Filebeat redis
所以,我最后的
output: redis: # Set the host and port where to find Redis. host: "192.168.80.12" port: 6379 # Uncomment out this option if you want to store the topology in Redis. # The default is false. save_topology: true # Optional index name. The default is filebeat and generates filebeat keys. index: "filebeat" # Optional Redis database number where the events are stored # The default is 0. db: 0 # Optional Redis database number where the topology is stored # The default is 1. It must have a different value than db. db_topology: 1 # Optional password to authenticate with. By default, no # password is set. # password: "" # Optional Redis initial connection timeout in seconds. # The default is 5 seconds. timeout: 5 # Optional interval for reconnecting to failed Redis connections. # The default is 1 second. reconnect_interval: 1
总结
1、Elasticsearch Output
启动redis
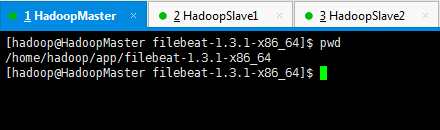
[hadoop@HadoopMaster filebeat-1.3.1-x86_64]$ pwd
/home/hadoop/app/filebeat-1.3.1-x86_64
[hadoop@HadoopMaster filebeat-1.3.1-x86_64]$ ./filebeat -c filebeat_es.yml
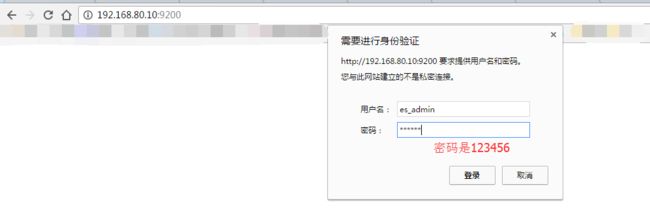
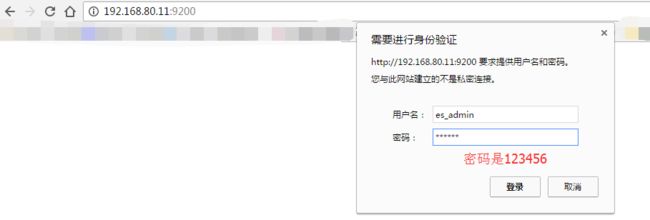
因为,我之前,在Elasticsearch里,进行过sheield权限插件的安装,虽然目前是30天试用期(因为这个插件是商业化的)。但是到期后先卸载,重新安装即可。很简单。
Elasticsearch之shield(权限)插件安装之后的浏览详解
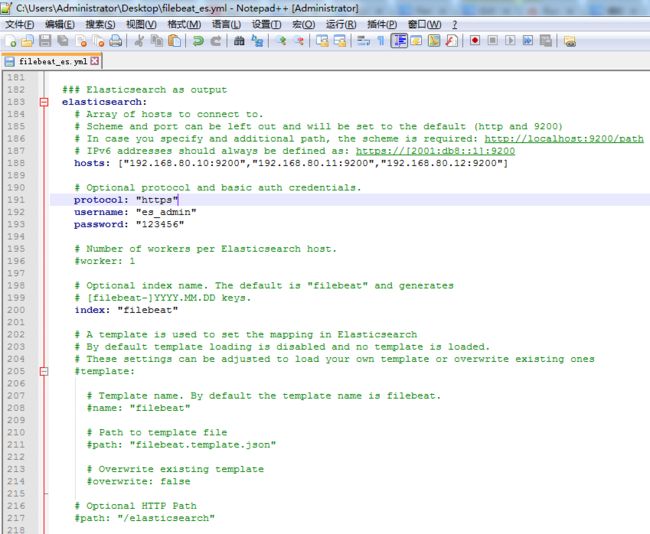
所以,我的自定义filebeat_es.yml才会如下。
################### Filebeat Configuration Example ######################### ############################# Filebeat ###################################### filebeat: # List of prospectors to fetch data. prospectors: # Each - is a prospector. Below are the prospector specific configurations - # Paths that should be crawled and fetched. Glob based paths. # To fetch all ".log" files from a specific level of subdirectories # /var/log/*/*.log can be used. # For each file found under this path, a harvester is started. # Make sure not file is defined twice as this can lead to unexpected behaviour. paths: - /home/hadoop/app.log #- c:\programdata\elasticsearch\logs\* # Configure the file encoding for reading files with international characters # following the W3C recommendation for HTML5 (http://www.w3.org/TR/encoding). # Some sample encodings: # plain, utf-8, utf-16be-bom, utf-16be, utf-16le, big5, gb18030, gbk, # hz-gb-2312, euc-kr, euc-jp, iso-2022-jp, shift-jis, ... #encoding: plain # Type of the files. Based on this the way the file is read is decided. # The different types cannot be mixed in one prospector # # Possible options are: # * log: Reads every line of the log file (default) # * stdin: Reads the standard in input_type: log # Exclude lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It drops the lines that are # matching any regular expression from the list. The include_lines is called before # exclude_lines. By default, no lines are dropped. # exclude_lines: ["^DBG"] # Include lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It exports the lines that are # matching any regular expression from the list. The include_lines is called before # exclude_lines. By default, all the lines are exported. # include_lines: ["^ERR", "^WARN"] # Exclude files. A list of regular expressions to match. Filebeat drops the files that # are matching any regular expression from the list. By default, no files are dropped. # exclude_files: [".gz$"] # Optional additional fields. These field can be freely picked # to add additional information to the crawled log files for filtering #fields: # level: debug # review: 1 # Set to true to store the additional fields as top level fields instead # of under the "fields" sub-dictionary. In case of name conflicts with the # fields added by Filebeat itself, the custom fields overwrite the default # fields. #fields_under_root: false # Ignore files which were modified more then the defined timespan in the past. # In case all files on your system must be read you can set this value very large. # Time strings like 2h (2 hours), 5m (5 minutes) can be used. #ignore_older: 0 # Close older closes the file handler for which were not modified # for longer then close_older # Time strings like 2h (2 hours), 5m (5 minutes) can be used. #close_older: 1h # Type to be published in the 'type' field. For Elasticsearch output, # the type defines the document type these entries should be stored # in. Default: log #document_type: log # Scan frequency in seconds. # How often these files should be checked for changes. In case it is set # to 0s, it is done as often as possible. Default: 10s #scan_frequency: 10s # Defines the buffer size every harvester uses when fetching the file #harvester_buffer_size: 16384 # Maximum number of bytes a single log event can have # All bytes after max_bytes are discarded and not sent. The default is 10MB. # This is especially useful for multiline log messages which can get large. #max_bytes: 10485760 # Mutiline can be used for log messages spanning multiple lines. This is common # for Java Stack Traces or C-Line Continuation #multiline: # The regexp Pattern that has to be matched. The example pattern matches all lines starting with [ #pattern: ^\[ # Defines if the pattern set under pattern should be negated or not. Default is false. #negate: false # Match can be set to "after" or "before". It is used to define if lines should be append to a pattern # that was (not) matched before or after or as long as a pattern is not matched based on negate. # Note: After is the equivalent to previous and before is the equivalent to to next in Logstash #match: after # The maximum number of lines that are combined to one event. # In case there are more the max_lines the additional lines are discarded. # Default is 500 #max_lines: 500 # After the defined timeout, an multiline event is sent even if no new pattern was found to start a new event # Default is 5s. #timeout: 5s # Setting tail_files to true means filebeat starts readding new files at the end # instead of the beginning. If this is used in combination with log rotation # this can mean that the first entries of a new file are skipped. #tail_files: false # Backoff values define how agressively filebeat crawls new files for updates # The default values can be used in most cases. Backoff defines how long it is waited # to check a file again after EOF is reached. Default is 1s which means the file # is checked every second if new lines were added. This leads to a near real time crawling. # Every time a new line appears, backoff is reset to the initial value. #backoff: 1s # Max backoff defines what the maximum backoff time is. After having backed off multiple times # from checking the files, the waiting time will never exceed max_backoff idenependent of the # backoff factor. Having it set to 10s means in the worst case a new line can be added to a log # file after having backed off multiple times, it takes a maximum of 10s to read the new line #max_backoff: 10s # The backoff factor defines how fast the algorithm backs off. The bigger the backoff factor, # the faster the max_backoff value is reached. If this value is set to 1, no backoff will happen. # The backoff value will be multiplied each time with the backoff_factor until max_backoff is reached #backoff_factor: 2 # This option closes a file, as soon as the file name changes. # This config option is recommended on windows only. Filebeat keeps the files it's reading open. This can cause # issues when the file is removed, as the file will not be fully removed until also Filebeat closes # the reading. Filebeat closes the file handler after ignore_older. During this time no new file with the # same name can be created. Turning this feature on the other hand can lead to loss of data # on rotate files. It can happen that after file rotation the beginning of the new # file is skipped, as the reading starts at the end. We recommend to leave this option on false # but lower the ignore_older value to release files faster. #force_close_files: false # Additional prospector #- # Configuration to use stdin input #input_type: stdin # General filebeat configuration options # # Event count spool threshold - forces network flush if exceeded #spool_size: 2048 # Enable async publisher pipeline in filebeat (Experimental!) #publish_async: false # Defines how often the spooler is flushed. After idle_timeout the spooler is # Flush even though spool_size is not reached. #idle_timeout: 5s # Name of the registry file. Per default it is put in the current working # directory. In case the working directory is changed after when running # filebeat again, indexing starts from the beginning again. #registry_file: .filebeat # Full Path to directory with additional prospector configuration files. Each file must end with .yml # These config files must have the full filebeat config part inside, but only # the prospector part is processed. All global options like spool_size are ignored. # The config_dir MUST point to a different directory then where the main filebeat config file is in. #config_dir: ############################################################################### ############################# Libbeat Config ################################## # Base config file used by all other beats for using libbeat features ############################# Output ########################################## # Configure what outputs to use when sending the data collected by the beat. # Multiple outputs may be used. output: ### Elasticsearch as output elasticsearch: # Array of hosts to connect to. # Scheme and port can be left out and will be set to the default (http and 9200) # In case you specify and additional path, the scheme is required: http://localhost:9200/path # IPv6 addresses should always be defined as: https://[2001:db8::1]:9200 hosts: ["192.168.80.10:9200","192.168.80.11:9200","192.168.80.12:9200"] # Optional protocol and basic auth credentials. protocol: "https" username: "es_admin" password: "123456" # Number of workers per Elasticsearch host. #worker: 1 # Optional index name. The default is "filebeat" and generates # [filebeat-]YYYY.MM.DD keys. index: "filebeat" # A template is used to set the mapping in Elasticsearch # By default template loading is disabled and no template is loaded. # These settings can be adjusted to load your own template or overwrite existing ones #template: # Template name. By default the template name is filebeat. #name: "filebeat" # Path to template file #path: "filebeat.template.json" # Overwrite existing template #overwrite: false # Optional HTTP Path #path: "/elasticsearch" # Proxy server url #proxy_url: http://proxy:3128 # The number of times a particular Elasticsearch index operation is attempted. If # the indexing operation doesn't succeed after this many retries, the events are # dropped. The default is 3. #max_retries: 3 # The maximum number of events to bulk in a single Elasticsearch bulk API index request. # The default is 50. #bulk_max_size: 50 # Configure http request timeout before failing an request to Elasticsearch. #timeout: 90 # The number of seconds to wait for new events between two bulk API index requests. # If `bulk_max_size` is reached before this interval expires, addition bulk index # requests are made. #flush_interval: 1 # Boolean that sets if the topology is kept in Elasticsearch. The default is # false. This option makes sense only for Packetbeat. #save_topology: false # The time to live in seconds for the topology information that is stored in # Elasticsearch. The default is 15 seconds. #topology_expire: 15 # tls configuration. By default is off. tls: # List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/root/ca.pem"] # Certificate for TLS client authentication certificate: "/etc/pki/client/cert.pem" # Client Certificate Key certificate_key: "/etc/pki/client/cert.key" # Controls whether the client verifies server certificates and host name. # If insecure is set to true, all server host names and certificates will be # accepted. In this mode TLS based connections are susceptible to # man-in-the-middle attacks. Use only for testing. #insecure: true # Configure cipher suites to be used for TLS connections #cipher_suites: [] # Configure curve types for ECDHE based cipher suites #curve_types: [] # Configure minimum TLS version allowed for connection to logstash #min_version: 1.0 # Configure maximum TLS version allowed for connection to logstash #max_version: 1.2 ### Logstash as output #logstash: # The Logstash hosts #hosts: ["localhost:5044"] # Number of workers per Logstash host. #worker: 1 # The maximum number of events to bulk into a single batch window. The # default is 2048. #bulk_max_size: 2048 # Set gzip compression level. #compression_level: 3 # Optional load balance the events between the Logstash hosts #loadbalance: true # Optional index name. The default index name depends on the each beat. # For Packetbeat, the default is set to packetbeat, for Topbeat # top topbeat and for Filebeat to filebeat. #index: filebeat # Optional TLS. By default is off. #tls: # List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications #certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/root/ca.pem"] # Certificate for TLS client authentication #certificate: "/etc/pki/client/cert.pem" # Client Certificate Key #certificate_key: "/etc/pki/client/cert.key" # Controls whether the client verifies server certificates and host name. # If insecure is set to true, all server host names and certificates will be # accepted. In this mode TLS based connections are susceptible to # man-in-the-middle attacks. Use only for testing. #insecure: true # Configure cipher suites to be used for TLS connections #cipher_suites: [] # Configure curve types for ECDHE based cipher suites #curve_types: [] ### File as output #file: # Path to the directory where to save the generated files. The option is mandatory. #path: "/tmp/filebeat" # Name of the generated files. The default is `filebeat` and it generates files: `filebeat`, `filebeat.1`, `filebeat.2`, etc. #filename: filebeat # Maximum size in kilobytes of each file. When this size is reached, the files are # rotated. The default value is 10 MB. #rotate_every_kb: 10000 # Maximum number of files under path. When this number of files is reached, the # oldest file is deleted and the rest are shifted from last to first. The default # is 7 files. #number_of_files: 7 ### Console output #console: # Pretty print json event #pretty: false ############################# Shipper ######################################### shipper: # The name of the shipper that publishes the network data. It can be used to group # all the transactions sent by a single shipper in the web interface. # If this options is not defined, the hostname is used. #name: # The tags of the shipper are included in their own field with each # transaction published. Tags make it easy to group servers by different # logical properties. #tags: ["service-X", "web-tier"] # Uncomment the following if you want to ignore transactions created # by the server on which the shipper is installed. This option is useful # to remove duplicates if shippers are installed on multiple servers. #ignore_outgoing: true # How often (in seconds) shippers are publishing their IPs to the topology map. # The default is 10 seconds. #refresh_topology_freq: 10 # Expiration time (in seconds) of the IPs published by a shipper to the topology map. # All the IPs will be deleted afterwards. Note, that the value must be higher than # refresh_topology_freq. The default is 15 seconds. #topology_expire: 15 # Internal queue size for single events in processing pipeline #queue_size: 1000 # Configure local GeoIP database support. # If no paths are not configured geoip is disabled. #geoip: #paths: # - "/usr/share/GeoIP/GeoLiteCity.dat" # - "/usr/local/var/GeoIP/GeoLiteCity.dat" ############################# Logging ######################################### # There are three options for the log ouput: syslog, file, stderr. # Under Windos systems, the log files are per default sent to the file output, # under all other system per default to syslog. logging: # Send all logging output to syslog. On Windows default is false, otherwise # default is true. to_syslog: false # Write all logging output to files. Beats automatically rotate files if rotateeverybytes # limit is reached. to_files: true # To enable logging to files, to_files option has to be set to true files: # The directory where the log files will written to. path: /home/hadoop/mybeat # The name of the files where the logs are written to. name: mybeat # Configure log file size limit. If limit is reached, log file will be # automatically rotated rotateeverybytes: 10485760 # = 10MB # Number of rotated log files to keep. Oldest files will be deleted first. keepfiles: 7 # Enable debug output for selected components. To enable all selectors use ["*"] # Other available selectors are beat, publish, service # Multiple selectors can be chained. #selectors: [ ] # Sets log level. The default log level is error. # Available log levels are: critical, error, warning, info, debug level: debug
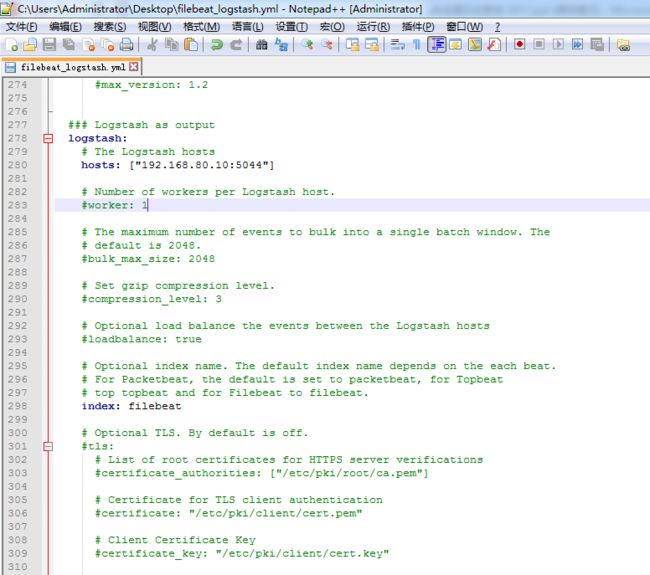
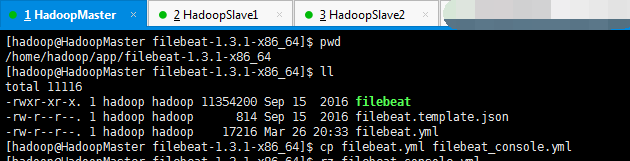
2、Logstash Output
启动redis
[hadoop@HadoopMaster filebeat-1.3.1-x86_64]$ pwd
/home/hadoop/app/filebeat-1.3.1-x86_64
[hadoop@HadoopMaster filebeat-1.3.1-x86_64]$ ./filebeat -c filebeat_logstash.yml
因为,我这里,安装Logstash,在192.168.80.10上,具体,请移步
Logstash安装(图文详解)(多节点的ELK集群安装在一个节点就好)
################### Filebeat Configuration Example ######################### ############################# Filebeat ###################################### filebeat: # List of prospectors to fetch data. prospectors: # Each - is a prospector. Below are the prospector specific configurations - # Paths that should be crawled and fetched. Glob based paths. # To fetch all ".log" files from a specific level of subdirectories # /var/log/*/*.log can be used. # For each file found under this path, a harvester is started. # Make sure not file is defined twice as this can lead to unexpected behaviour. paths: - /home/hadoop/app.log #- c:\programdata\elasticsearch\logs\* # Configure the file encoding for reading files with international characters # following the W3C recommendation for HTML5 (http://www.w3.org/TR/encoding). # Some sample encodings: # plain, utf-8, utf-16be-bom, utf-16be, utf-16le, big5, gb18030, gbk, # hz-gb-2312, euc-kr, euc-jp, iso-2022-jp, shift-jis, ... #encoding: plain # Type of the files. Based on this the way the file is read is decided. # The different types cannot be mixed in one prospector # # Possible options are: # * log: Reads every line of the log file (default) # * stdin: Reads the standard in input_type: log # Exclude lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It drops the lines that are # matching any regular expression from the list. The include_lines is called before # exclude_lines. By default, no lines are dropped. # exclude_lines: ["^DBG"] # Include lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It exports the lines that are # matching any regular expression from the list. The include_lines is called before # exclude_lines. By default, all the lines are exported. # include_lines: ["^ERR", "^WARN"] # Exclude files. A list of regular expressions to match. Filebeat drops the files that # are matching any regular expression from the list. By default, no files are dropped. # exclude_files: [".gz$"] # Optional additional fields. These field can be freely picked # to add additional information to the crawled log files for filtering #fields: # level: debug # review: 1 # Set to true to store the additional fields as top level fields instead # of under the "fields" sub-dictionary. In case of name conflicts with the # fields added by Filebeat itself, the custom fields overwrite the default # fields. #fields_under_root: false # Ignore files which were modified more then the defined timespan in the past. # In case all files on your system must be read you can set this value very large. # Time strings like 2h (2 hours), 5m (5 minutes) can be used. #ignore_older: 0 # Close older closes the file handler for which were not modified # for longer then close_older # Time strings like 2h (2 hours), 5m (5 minutes) can be used. #close_older: 1h # Type to be published in the 'type' field. For Elasticsearch output, # the type defines the document type these entries should be stored # in. Default: log #document_type: log # Scan frequency in seconds. # How often these files should be checked for changes. In case it is set # to 0s, it is done as often as possible. Default: 10s #scan_frequency: 10s # Defines the buffer size every harvester uses when fetching the file #harvester_buffer_size: 16384 # Maximum number of bytes a single log event can have # All bytes after max_bytes are discarded and not sent. The default is 10MB. # This is especially useful for multiline log messages which can get large. #max_bytes: 10485760 # Mutiline can be used for log messages spanning multiple lines. This is common # for Java Stack Traces or C-Line Continuation #multiline: # The regexp Pattern that has to be matched. The example pattern matches all lines starting with [ #pattern: ^\[ # Defines if the pattern set under pattern should be negated or not. Default is false. #negate: false # Match can be set to "after" or "before". It is used to define if lines should be append to a pattern # that was (not) matched before or after or as long as a pattern is not matched based on negate. # Note: After is the equivalent to previous and before is the equivalent to to next in Logstash #match: after # The maximum number of lines that are combined to one event. # In case there are more the max_lines the additional lines are discarded. # Default is 500 #max_lines: 500 # After the defined timeout, an multiline event is sent even if no new pattern was found to start a new event # Default is 5s. #timeout: 5s # Setting tail_files to true means filebeat starts readding new files at the end # instead of the beginning. If this is used in combination with log rotation # this can mean that the first entries of a new file are skipped. #tail_files: false # Backoff values define how agressively filebeat crawls new files for updates # The default values can be used in most cases. Backoff defines how long it is waited # to check a file again after EOF is reached. Default is 1s which means the file # is checked every second if new lines were added. This leads to a near real time crawling. # Every time a new line appears, backoff is reset to the initial value. #backoff: 1s # Max backoff defines what the maximum backoff time is. After having backed off multiple times # from checking the files, the waiting time will never exceed max_backoff idenependent of the # backoff factor. Having it set to 10s means in the worst case a new line can be added to a log # file after having backed off multiple times, it takes a maximum of 10s to read the new line #max_backoff: 10s # The backoff factor defines how fast the algorithm backs off. The bigger the backoff factor, # the faster the max_backoff value is reached. If this value is set to 1, no backoff will happen. # The backoff value will be multiplied each time with the backoff_factor until max_backoff is reached #backoff_factor: 2 # This option closes a file, as soon as the file name changes. # This config option is recommended on windows only. Filebeat keeps the files it's reading open. This can cause # issues when the file is removed, as the file will not be fully removed until also Filebeat closes # the reading. Filebeat closes the file handler after ignore_older. During this time no new file with the # same name can be created. Turning this feature on the other hand can lead to loss of data # on rotate files. It can happen that after file rotation the beginning of the new # file is skipped, as the reading starts at the end. We recommend to leave this option on false # but lower the ignore_older value to release files faster. #force_close_files: false # Additional prospector #- # Configuration to use stdin input #input_type: stdin # General filebeat configuration options # # Event count spool threshold - forces network flush if exceeded #spool_size: 2048 # Enable async publisher pipeline in filebeat (Experimental!) #publish_async: false # Defines how often the spooler is flushed. After idle_timeout the spooler is # Flush even though spool_size is not reached. #idle_timeout: 5s # Name of the registry file. Per default it is put in the current working # directory. In case the working directory is changed after when running # filebeat again, indexing starts from the beginning again. #registry_file: .filebeat # Full Path to directory with additional prospector configuration files. Each file must end with .yml # These config files must have the full filebeat config part inside, but only # the prospector part is processed. All global options like spool_size are ignored. # The config_dir MUST point to a different directory then where the main filebeat config file is in. #config_dir: ############################################################################### ############################# Libbeat Config ################################## # Base config file used by all other beats for using libbeat features ############################# Output ########################################## # Configure what outputs to use when sending the data collected by the beat. # Multiple outputs may be used. output: ### Elasticsearch as output #elasticsearch: # Array of hosts to connect to. # Scheme and port can be left out and will be set to the default (http and 9200) # In case you specify and additional path, the scheme is required: http://localhost:9200/path # IPv6 addresses should always be defined as: https://[2001:db8::1]:9200 #hosts: ["localhost:9200"] # Optional protocol and basic auth credentials. #protocol: "https" #username: "admin" #password: "s3cr3t" # Number of workers per Elasticsearch host. #worker: 1 # Optional index name. The default is "filebeat" and generates # [filebeat-]YYYY.MM.DD keys. #index: "filebeat" # A template is used to set the mapping in Elasticsearch # By default template loading is disabled and no template is loaded. # These settings can be adjusted to load your own template or overwrite existing ones #template: # Template name. By default the template name is filebeat. #name: "filebeat" # Path to template file #path: "filebeat.template.json" # Overwrite existing template #overwrite: false # Optional HTTP Path #path: "/elasticsearch" # Proxy server url #proxy_url: http://proxy:3128 # The number of times a particular Elasticsearch index operation is attempted. If # the indexing operation doesn't succeed after this many retries, the events are # dropped. The default is 3. #max_retries: 3 # The maximum number of events to bulk in a single Elasticsearch bulk API index request. # The default is 50. #bulk_max_size: 50 # Configure http request timeout before failing an request to Elasticsearch. #timeout: 90 # The number of seconds to wait for new events between two bulk API index requests. # If `bulk_max_size` is reached before this interval expires, addition bulk index # requests are made. #flush_interval: 1 # Boolean that sets if the topology is kept in Elasticsearch. The default is # false. This option makes sense only for Packetbeat. #save_topology: false # The time to live in seconds for the topology information that is stored in # Elasticsearch. The default is 15 seconds. #topology_expire: 15 # tls configuration. By default is off. #tls: # List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications #certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/root/ca.pem"] # Certificate for TLS client authentication #certificate: "/etc/pki/client/cert.pem" # Client Certificate Key #certificate_key: "/etc/pki/client/cert.key" # Controls whether the client verifies server certificates and host name. # If insecure is set to true, all server host names and certificates will be # accepted. In this mode TLS based connections are susceptible to # man-in-the-middle attacks. Use only for testing. #insecure: true # Configure cipher suites to be used for TLS connections #cipher_suites: [] # Configure curve types for ECDHE based cipher suites #curve_types: [] # Configure minimum TLS version allowed for connection to logstash #min_version: 1.0 # Configure maximum TLS version allowed for connection to logstash #max_version: 1.2 ### Logstash as output logstash: # The Logstash hosts hosts: ["192.168.80.10:5044"] # Number of workers per Logstash host. #worker: 1 # The maximum number of events to bulk into a single batch window. The # default is 2048. #bulk_max_size: 2048 # Set gzip compression level. #compression_level: 3 # Optional load balance the events between the Logstash hosts #loadbalance: true # Optional index name. The default index name depends on the each beat. # For Packetbeat, the default is set to packetbeat, for Topbeat # top topbeat and for Filebeat to filebeat. index: filebeat # Optional TLS. By default is off. #tls: # List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications #certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/root/ca.pem"] # Certificate for TLS client authentication #certificate: "/etc/pki/client/cert.pem" # Client Certificate Key #certificate_key: "/etc/pki/client/cert.key" # Controls whether the client verifies server certificates and host name. # If insecure is set to true, all server host names and certificates will be # accepted. In this mode TLS based connections are susceptible to # man-in-the-middle attacks. Use only for testing. #insecure: true # Configure cipher suites to be used for TLS connections #cipher_suites: [] # Configure curve types for ECDHE based cipher suites #curve_types: [] ### File as output #file: # Path to the directory where to save the generated files. The option is mandatory. #path: "/tmp/filebeat" # Name of the generated files. The default is `filebeat` and it generates files: `filebeat`, `filebeat.1`, `filebeat.2`, etc. #filename: filebeat # Maximum size in kilobytes of each file. When this size is reached, the files are # rotated. The default value is 10 MB. #rotate_every_kb: 10000 # Maximum number of files under path. When this number of files is reached, the # oldest file is deleted and the rest are shifted from last to first. The default # is 7 files. #number_of_files: 7 ### Console output #console: # Pretty print json event #pretty: false ############################# Shipper ######################################### shipper: # The name of the shipper that publishes the network data. It can be used to group # all the transactions sent by a single shipper in the web interface. # If this options is not defined, the hostname is used. #name: # The tags of the shipper are included in their own field with each # transaction published. Tags make it easy to group servers by different # logical properties. #tags: ["service-X", "web-tier"] # Uncomment the following if you want to ignore transactions created # by the server on which the shipper is installed. This option is useful # to remove duplicates if shippers are installed on multiple servers. #ignore_outgoing: true # How often (in seconds) shippers are publishing their IPs to the topology map. # The default is 10 seconds. #refresh_topology_freq: 10 # Expiration time (in seconds) of the IPs published by a shipper to the topology map. # All the IPs will be deleted afterwards. Note, that the value must be higher than # refresh_topology_freq. The default is 15 seconds. #topology_expire: 15 # Internal queue size for single events in processing pipeline #queue_size: 1000 # Configure local GeoIP database support. # If no paths are not configured geoip is disabled. #geoip: #paths: # - "/usr/share/GeoIP/GeoLiteCity.dat" # - "/usr/local/var/GeoIP/GeoLiteCity.dat" ############################# Logging ######################################### # There are three options for the log ouput: syslog, file, stderr. # Under Windos systems, the log files are per default sent to the file output, # under all other system per default to syslog. logging: # Send all logging output to syslog. On Windows default is false, otherwise # default is true. to_syslog: false # Write all logging output to files. Beats automatically rotate files if rotateeverybytes # limit is reached. to_files: true # To enable logging to files, to_files option has to be set to true files: # The directory where the log files will written to. path: /home/hadoop/mybeat # The name of the files where the logs are written to. name: mybeat # Configure log file size limit. If limit is reached, log file will be # automatically rotated rotateeverybytes: 10485760 # = 10MB # Number of rotated log files to keep. Oldest files will be deleted first. keepfiles: 7 # Enable debug output for selected components. To enable all selectors use ["*"] # Other available selectors are beat, publish, service # Multiple selectors can be chained. #selectors: [ ] # Sets log level. The default log level is error. # Available log levels are: critical, error, warning, info, debug level: debug
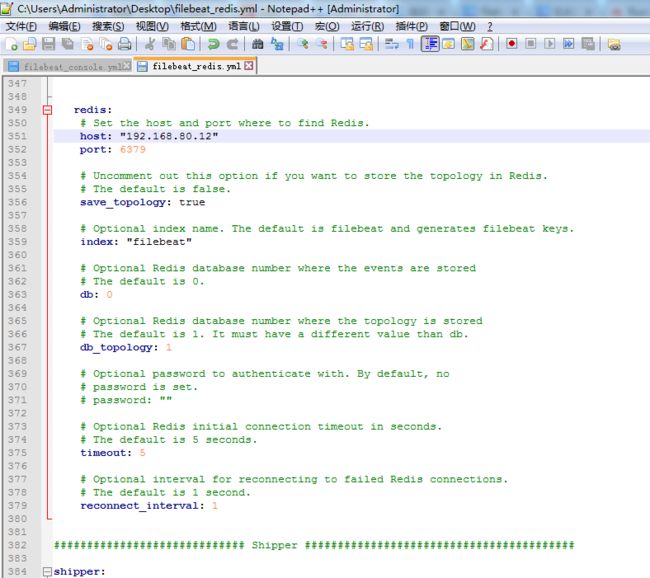
3、Redis Output(Filebeat收集到数据,输出到redis里。默认的配置文件里是没有的,得去官网上去找)
启动redis
[hadoop@HadoopMaster filebeat-1.3.1-x86_64]$ pwd /home/hadoop/app/filebeat-1.3.1-x86_64 [hadoop@HadoopMaster filebeat-1.3.1-x86_64]$ ./filebeat -c filebeat_redis.yml
################### Filebeat Configuration Example ######################### ############################# Filebeat ###################################### filebeat: # List of prospectors to fetch data. prospectors: # Each - is a prospector. Below are the prospector specific configurations - # Paths that should be crawled and fetched. Glob based paths. # To fetch all ".log" files from a specific level of subdirectories # /var/log/*/*.log can be used. # For each file found under this path, a harvester is started. # Make sure not file is defined twice as this can lead to unexpected behaviour. paths: - /home/hadoop/app.log #- c:\programdata\elasticsearch\logs\* # Configure the file encoding for reading files with international characters # following the W3C recommendation for HTML5 (http://www.w3.org/TR/encoding). # Some sample encodings: # plain, utf-8, utf-16be-bom, utf-16be, utf-16le, big5, gb18030, gbk, # hz-gb-2312, euc-kr, euc-jp, iso-2022-jp, shift-jis, ... #encoding: plain # Type of the files. Based on this the way the file is read is decided. # The different types cannot be mixed in one prospector # # Possible options are: # * log: Reads every line of the log file (default) # * stdin: Reads the standard in input_type: log # Exclude lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It drops the lines that are # matching any regular expression from the list. The include_lines is called before # exclude_lines. By default, no lines are dropped. # exclude_lines: ["^DBG"] # Include lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It exports the lines that are # matching any regular expression from the list. The include_lines is called before # exclude_lines. By default, all the lines are exported. # include_lines: ["^ERR", "^WARN"] # Exclude files. A list of regular expressions to match. Filebeat drops the files that # are matching any regular expression from the list. By default, no files are dropped. # exclude_files: [".gz$"] # Optional additional fields. These field can be freely picked # to add additional information to the crawled log files for filtering #fields: # level: debug # review: 1 # Set to true to store the additional fields as top level fields instead # of under the "fields" sub-dictionary. In case of name conflicts with the # fields added by Filebeat itself, the custom fields overwrite the default # fields. #fields_under_root: false # Ignore files which were modified more then the defined timespan in the past. # In case all files on your system must be read you can set this value very large. # Time strings like 2h (2 hours), 5m (5 minutes) can be used. #ignore_older: 0 # Close older closes the file handler for which were not modified # for longer then close_older # Time strings like 2h (2 hours), 5m (5 minutes) can be used. #close_older: 1h # Type to be published in the 'type' field. For Elasticsearch output, # the type defines the document type these entries should be stored # in. Default: log #document_type: log # Scan frequency in seconds. # How often these files should be checked for changes. In case it is set # to 0s, it is done as often as possible. Default: 10s #scan_frequency: 10s # Defines the buffer size every harvester uses when fetching the file #harvester_buffer_size: 16384 # Maximum number of bytes a single log event can have # All bytes after max_bytes are discarded and not sent. The default is 10MB. # This is especially useful for multiline log messages which can get large. #max_bytes: 10485760 # Mutiline can be used for log messages spanning multiple lines. This is common # for Java Stack Traces or C-Line Continuation #multiline: # The regexp Pattern that has to be matched. The example pattern matches all lines starting with [ #pattern: ^\[ # Defines if the pattern set under pattern should be negated or not. Default is false. #negate: false # Match can be set to "after" or "before". It is used to define if lines should be append to a pattern # that was (not) matched before or after or as long as a pattern is not matched based on negate. # Note: After is the equivalent to previous and before is the equivalent to to next in Logstash #match: after # The maximum number of lines that are combined to one event. # In case there are more the max_lines the additional lines are discarded. # Default is 500 #max_lines: 500 # After the defined timeout, an multiline event is sent even if no new pattern was found to start a new event # Default is 5s. #timeout: 5s # Setting tail_files to true means filebeat starts readding new files at the end # instead of the beginning. If this is used in combination with log rotation # this can mean that the first entries of a new file are skipped. #tail_files: false # Backoff values define how agressively filebeat crawls new files for updates # The default values can be used in most cases. Backoff defines how long it is waited # to check a file again after EOF is reached. Default is 1s which means the file # is checked every second if new lines were added. This leads to a near real time crawling. # Every time a new line appears, backoff is reset to the initial value. #backoff: 1s # Max backoff defines what the maximum backoff time is. After having backed off multiple times # from checking the files, the waiting time will never exceed max_backoff idenependent of the # backoff factor. Having it set to 10s means in the worst case a new line can be added to a log # file after having backed off multiple times, it takes a maximum of 10s to read the new line #max_backoff: 10s # The backoff factor defines how fast the algorithm backs off. The bigger the backoff factor, # the faster the max_backoff value is reached. If this value is set to 1, no backoff will happen. # The backoff value will be multiplied each time with the backoff_factor until max_backoff is reached #backoff_factor: 2 # This option closes a file, as soon as the file name changes. # This config option is recommended on windows only. Filebeat keeps the files it's reading open. This can cause # issues when the file is removed, as the file will not be fully removed until also Filebeat closes # the reading. Filebeat closes the file handler after ignore_older. During this time no new file with the # same name can be created. Turning this feature on the other hand can lead to loss of data # on rotate files. It can happen that after file rotation the beginning of the new # file is skipped, as the reading starts at the end. We recommend to leave this option on false # but lower the ignore_older value to release files faster. #force_close_files: false # Additional prospector #- # Configuration to use stdin input #input_type: stdin # General filebeat configuration options # # Event count spool threshold - forces network flush if exceeded #spool_size: 2048 # Enable async publisher pipeline in filebeat (Experimental!) #publish_async: false # Defines how often the spooler is flushed. After idle_timeout the spooler is # Flush even though spool_size is not reached. #idle_timeout: 5s # Name of the registry file. Per default it is put in the current working # directory. In case the working directory is changed after when running # filebeat again, indexing starts from the beginning again. #registry_file: .filebeat # Full Path to directory with additional prospector configuration files. Each file must end with .yml # These config files must have the full filebeat config part inside, but only # the prospector part is processed. All global options like spool_size are ignored. # The config_dir MUST point to a different directory then where the main filebeat config file is in. #config_dir: ############################################################################### ############################# Libbeat Config ################################## # Base config file used by all other beats for using libbeat features ############################# Output ########################################## # Configure what outputs to use when sending the data collected by the beat. # Multiple outputs may be used. output: ### Elasticsearch as output #elasticsearch: # Array of hosts to connect to. # Scheme and port can be left out and will be set to the default (http and 9200) # In case you specify and additional path, the scheme is required: http://localhost:9200/path # IPv6 addresses should always be defined as: https://[2001:db8::1]:9200 #hosts: ["localhost:9200"] # Optional protocol and basic auth credentials. #protocol: "https" #username: "admin" #password: "s3cr3t" # Number of workers per Elasticsearch host. #worker: 1 # Optional index name. The default is "filebeat" and generates # [filebeat-]YYYY.MM.DD keys. #index: "filebeat" # A template is used to set the mapping in Elasticsearch # By default template loading is disabled and no template is loaded. # These settings can be adjusted to load your own template or overwrite existing ones #template: # Template name. By default the template name is filebeat. #name: "filebeat" # Path to template file #path: "filebeat.template.json" # Overwrite existing template #overwrite: false # Optional HTTP Path #path: "/elasticsearch" # Proxy server url #proxy_url: http://proxy:3128 # The number of times a particular Elasticsearch index operation is attempted. If # the indexing operation doesn't succeed after this many retries, the events are # dropped. The default is 3. #max_retries: 3 # The maximum number of events to bulk in a single Elasticsearch bulk API index request. # The default is 50. #bulk_max_size: 50 # Configure http request timeout before failing an request to Elasticsearch. #timeout: 90 # The number of seconds to wait for new events between two bulk API index requests. # If `bulk_max_size` is reached before this interval expires, addition bulk index # requests are made. #flush_interval: 1 # Boolean that sets if the topology is kept in Elasticsearch. The default is # false. This option makes sense only for Packetbeat. #save_topology: false # The time to live in seconds for the topology information that is stored in # Elasticsearch. The default is 15 seconds. #topology_expire: 15 # tls configuration. By default is off. #tls: # List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications #certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/root/ca.pem"] # Certificate for TLS client authentication #certificate: "/etc/pki/client/cert.pem" # Client Certificate Key #certificate_key: "/etc/pki/client/cert.key" # Controls whether the client verifies server certificates and host name. # If insecure is set to true, all server host names and certificates will be # accepted. In this mode TLS based connections are susceptible to # man-in-the-middle attacks. Use only for testing. #insecure: true # Configure cipher suites to be used for TLS connections #cipher_suites: [] # Configure curve types for ECDHE based cipher suites #curve_types: [] # Configure minimum TLS version allowed for connection to logstash #min_version: 1.0 # Configure maximum TLS version allowed for connection to logstash #max_version: 1.2 ### Logstash as output #logstash: # The Logstash hosts #hosts: ["localhost:5044"] # Number of workers per Logstash host. #worker: 1 # The maximum number of events to bulk into a single batch window. The # default is 2048. #bulk_max_size: 2048 # Set gzip compression level. #compression_level: 3 # Optional load balance the events between the Logstash hosts #loadbalance: true # Optional index name. The default index name depends on the each beat. # For Packetbeat, the default is set to packetbeat, for Topbeat # top topbeat and for Filebeat to filebeat. #index: filebeat # Optional TLS. By default is off. #tls: # List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications #certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/root/ca.pem"] # Certificate for TLS client authentication #certificate: "/etc/pki/client/cert.pem" # Client Certificate Key #certificate_key: "/etc/pki/client/cert.key" # Controls whether the client verifies server certificates and host name. # If insecure is set to true, all server host names and certificates will be # accepted. In this mode TLS based connections are susceptible to # man-in-the-middle attacks. Use only for testing. #insecure: true # Configure cipher suites to be used for TLS connections #cipher_suites: [] # Configure curve types for ECDHE based cipher suites #curve_types: [] ### File as output #file: # Path to the directory where to save the generated files. The option is mandatory. #path: "/tmp/filebeat" # Name of the generated files. The default is `filebeat` and it generates files: `filebeat`, `filebeat.1`, `filebeat.2`, etc. #filename: filebeat # Maximum size in kilobytes of each file. When this size is reached, the files are # rotated. The default value is 10 MB. #rotate_every_kb: 10000 # Maximum number of files under path. When this number of files is reached, the # oldest file is deleted and the rest are shifted from last to first. The default # is 7 files. #number_of_files: 7 ### Console output #console: # Pretty print json event #pretty: false redis: # Set the host and port where to find Redis. host: "192.168.80.12" port: 6379 # Uncomment out this option if you want to store the topology in Redis. # The default is false. save_topology: true # Optional index name. The default is filebeat and generates filebeat keys. index: "filebeat" # Optional Redis database number where the events are stored # The default is 0. db: 0 # Optional Redis database number where the topology is stored # The default is 1. It must have a different value than db. db_topology: 1 # Optional password to authenticate with. By default, no # password is set. # password: "" # Optional Redis initial connection timeout in seconds. # The default is 5 seconds. timeout: 5 # Optional interval for reconnecting to failed Redis connections. # The default is 1 second. reconnect_interval: 1 ############################# Shipper ######################################### shipper: # The name of the shipper that publishes the network data. It can be used to group # all the transactions sent by a single shipper in the web interface. # If this options is not defined, the hostname is used. #name: # The tags of the shipper are included in their own field with each # transaction published. Tags make it easy to group servers by different # logical properties. #tags: ["service-X", "web-tier"] # Uncomment the following if you want to ignore transactions created # by the server on which the shipper is installed. This option is useful # to remove duplicates if shippers are installed on multiple servers. #ignore_outgoing: true # How often (in seconds) shippers are publishing their IPs to the topology map. # The default is 10 seconds. #refresh_topology_freq: 10 # Expiration time (in seconds) of the IPs published by a shipper to the topology map. # All the IPs will be deleted afterwards. Note, that the value must be higher than # refresh_topology_freq. The default is 15 seconds. #topology_expire: 15 # Internal queue size for single events in processing pipeline #queue_size: 1000 # Configure local GeoIP database support. # If no paths are not configured geoip is disabled. #geoip: #paths: # - "/usr/share/GeoIP/GeoLiteCity.dat" # - "/usr/local/var/GeoIP/GeoLiteCity.dat" ############################# Logging ######################################### # There are three options for the log ouput: syslog, file, stderr. # Under Windos systems, the log files are per default sent to the file output, # under all other system per default to syslog. logging: # Send all logging output to syslog. On Windows default is false, otherwise # default is true. to_syslog: false # Write all logging output to files. Beats automatically rotate files if rotateeverybytes # limit is reached. to_files: true # To enable logging to files, to_files option has to be set to true files: # The directory where the log files will written to. path: /home/hadoop/mybeat # The name of the files where the logs are written to. name: mybeat # Configure log file size limit. If limit is reached, log file will be # automatically rotated rotateeverybytes: 10485760 # = 10MB # Number of rotated log files to keep. Oldest files will be deleted first. keepfiles: 7 # Enable debug output for selected components. To enable all selectors use ["*"] # Other available selectors are beat, publish, service # Multiple selectors can be chained. #selectors: [ ] # Sets log level. The default log level is error. # Available log levels are: critical, error, warning, info, debug level: debug
4、File Output
启动redis
[hadoop@HadoopMaster filebeat-1.3.1-x86_64]$ pwd
/home/hadoop/app/filebeat-1.3.1-x86_64
[hadoop@HadoopMaster filebeat-1.3.1-x86_64]$ ./filebeat -c filebeat_file.yml
我这里,就以官网,提供的默认路径了,当然自己可以修改。
################### Filebeat Configuration Example ######################### ############################# Filebeat ###################################### filebeat: # List of prospectors to fetch data. prospectors: # Each - is a prospector. Below are the prospector specific configurations - # Paths that should be crawled and fetched. Glob based paths. # To fetch all ".log" files from a specific level of subdirectories # /var/log/*/*.log can be used. # For each file found under this path, a harvester is started. # Make sure not file is defined twice as this can lead to unexpected behaviour. paths: - /home/hadoop/app.log #- c:\programdata\elasticsearch\logs\* # Configure the file encoding for reading files with international characters # following the W3C recommendation for HTML5 (http://www.w3.org/TR/encoding). # Some sample encodings: # plain, utf-8, utf-16be-bom, utf-16be, utf-16le, big5, gb18030, gbk, # hz-gb-2312, euc-kr, euc-jp, iso-2022-jp, shift-jis, ... #encoding: plain # Type of the files. Based on this the way the file is read is decided. # The different types cannot be mixed in one prospector # # Possible options are: # * log: Reads every line of the log file (default) # * stdin: Reads the standard in input_type: log # Exclude lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It drops the lines that are # matching any regular expression from the list. The include_lines is called before # exclude_lines. By default, no lines are dropped. # exclude_lines: ["^DBG"] # Include lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It exports the lines that are # matching any regular expression from the list. The include_lines is called before # exclude_lines. By default, all the lines are exported. # include_lines: ["^ERR", "^WARN"] # Exclude files. A list of regular expressions to match. Filebeat drops the files that # are matching any regular expression from the list. By default, no files are dropped. # exclude_files: [".gz$"] # Optional additional fields. These field can be freely picked # to add additional information to the crawled log files for filtering #fields: # level: debug # review: 1 # Set to true to store the additional fields as top level fields instead # of under the "fields" sub-dictionary. In case of name conflicts with the # fields added by Filebeat itself, the custom fields overwrite the default # fields. #fields_under_root: false # Ignore files which were modified more then the defined timespan in the past. # In case all files on your system must be read you can set this value very large. # Time strings like 2h (2 hours), 5m (5 minutes) can be used. #ignore_older: 0 # Close older closes the file handler for which were not modified # for longer then close_older # Time strings like 2h (2 hours), 5m (5 minutes) can be used. #close_older: 1h # Type to be published in the 'type' field. For Elasticsearch output, # the type defines the document type these entries should be stored # in. Default: log #document_type: log # Scan frequency in seconds. # How often these files should be checked for changes. In case it is set # to 0s, it is done as often as possible. Default: 10s #scan_frequency: 10s # Defines the buffer size every harvester uses when fetching the file #harvester_buffer_size: 16384 # Maximum number of bytes a single log event can have # All bytes after max_bytes are discarded and not sent. The default is 10MB. # This is especially useful for multiline log messages which can get large. #max_bytes: 10485760 # Mutiline can be used for log messages spanning multiple lines. This is common # for Java Stack Traces or C-Line Continuation #multiline: # The regexp Pattern that has to be matched. The example pattern matches all lines starting with [ #pattern: ^\[ # Defines if the pattern set under pattern should be negated or not. Default is false. #negate: false # Match can be set to "after" or "before". It is used to define if lines should be append to a pattern # that was (not) matched before or after or as long as a pattern is not matched based on negate. # Note: After is the equivalent to previous and before is the equivalent to to next in Logstash #match: after # The maximum number of lines that are combined to one event. # In case there are more the max_lines the additional lines are discarded. # Default is 500 #max_lines: 500 # After the defined timeout, an multiline event is sent even if no new pattern was found to start a new event # Default is 5s. #timeout: 5s # Setting tail_files to true means filebeat starts readding new files at the end # instead of the beginning. If this is used in combination with log rotation # this can mean that the first entries of a new file are skipped. #tail_files: false # Backoff values define how agressively filebeat crawls new files for updates # The default values can be used in most cases. Backoff defines how long it is waited # to check a file again after EOF is reached. Default is 1s which means the file # is checked every second if new lines were added. This leads to a near real time crawling. # Every time a new line appears, backoff is reset to the initial value. #backoff: 1s # Max backoff defines what the maximum backoff time is. After having backed off multiple times # from checking the files, the waiting time will never exceed max_backoff idenependent of the # backoff factor. Having it set to 10s means in the worst case a new line can be added to a log # file after having backed off multiple times, it takes a maximum of 10s to read the new line #max_backoff: 10s # The backoff factor defines how fast the algorithm backs off. The bigger the backoff factor, # the faster the max_backoff value is reached. If this value is set to 1, no backoff will happen. # The backoff value will be multiplied each time with the backoff_factor until max_backoff is reached #backoff_factor: 2 # This option closes a file, as soon as the file name changes. # This config option is recommended on windows only. Filebeat keeps the files it's reading open. This can cause # issues when the file is removed, as the file will not be fully removed until also Filebeat closes # the reading. Filebeat closes the file handler after ignore_older. During this time no new file with the # same name can be created. Turning this feature on the other hand can lead to loss of data # on rotate files. It can happen that after file rotation the beginning of the new # file is skipped, as the reading starts at the end. We recommend to leave this option on false # but lower the ignore_older value to release files faster. #force_close_files: false # Additional prospector #- # Configuration to use stdin input #input_type: stdin # General filebeat configuration options # # Event count spool threshold - forces network flush if exceeded #spool_size: 2048 # Enable async publisher pipeline in filebeat (Experimental!) #publish_async: false # Defines how often the spooler is flushed. After idle_timeout the spooler is # Flush even though spool_size is not reached. #idle_timeout: 5s # Name of the registry file. Per default it is put in the current working # directory. In case the working directory is changed after when running # filebeat again, indexing starts from the beginning again. #registry_file: .filebeat # Full Path to directory with additional prospector configuration files. Each file must end with .yml # These config files must have the full filebeat config part inside, but only # the prospector part is processed. All global options like spool_size are ignored. # The config_dir MUST point to a different directory then where the main filebeat config file is in. #config_dir: ############################################################################### ############################# Libbeat Config ################################## # Base config file used by all other beats for using libbeat features ############################# Output ########################################## # Configure what outputs to use when sending the data collected by the beat. # Multiple outputs may be used. output: ### Elasticsearch as output #elasticsearch: # Array of hosts to connect to. # Scheme and port can be left out and will be set to the default (http and 9200) # In case you specify and additional path, the scheme is required: http://localhost:9200/path # IPv6 addresses should always be defined as: https://[2001:db8::1]:9200 #hosts: ["localhost:9200"] # Optional protocol and basic auth credentials. #protocol: "https" #username: "admin" #password: "s3cr3t" # Number of workers per Elasticsearch host. #worker: 1 # Optional index name. The default is "filebeat" and generates # [filebeat-]YYYY.MM.DD keys. #index: "filebeat" # A template is used to set the mapping in Elasticsearch # By default template loading is disabled and no template is loaded. # These settings can be adjusted to load your own template or overwrite existing ones #template: # Template name. By default the template name is filebeat. #name: "filebeat" # Path to template file #path: "filebeat.template.json" # Overwrite existing template #overwrite: false # Optional HTTP Path #path: "/elasticsearch" # Proxy server url #proxy_url: http://proxy:3128 # The number of times a particular Elasticsearch index operation is attempted. If # the indexing operation doesn't succeed after this many retries, the events are # dropped. The default is 3. #max_retries: 3 # The maximum number of events to bulk in a single Elasticsearch bulk API index request. # The default is 50. #bulk_max_size: 50 # Configure http request timeout before failing an request to Elasticsearch. #timeout: 90 # The number of seconds to wait for new events between two bulk API index requests. # If `bulk_max_size` is reached before this interval expires, addition bulk index # requests are made. #flush_interval: 1 # Boolean that sets if the topology is kept in Elasticsearch. The default is # false. This option makes sense only for Packetbeat. #save_topology: false # The time to live in seconds for the topology information that is stored in # Elasticsearch. The default is 15 seconds. #topology_expire: 15 # tls configuration. By default is off. #tls: # List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications #certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/root/ca.pem"] # Certificate for TLS client authentication #certificate: "/etc/pki/client/cert.pem" # Client Certificate Key #certificate_key: "/etc/pki/client/cert.key" # Controls whether the client verifies server certificates and host name. # If insecure is set to true, all server host names and certificates will be # accepted. In this mode TLS based connections are susceptible to # man-in-the-middle attacks. Use only for testing. #insecure: true # Configure cipher suites to be used for TLS connections #cipher_suites: [] # Configure curve types for ECDHE based cipher suites #curve_types: [] # Configure minimum TLS version allowed for connection to logstash #min_version: 1.0 # Configure maximum TLS version allowed for connection to logstash #max_version: 1.2 ### Logstash as output #logstash: # The Logstash hosts #hosts: ["localhost:5044"] # Number of workers per Logstash host. #worker: 1 # The maximum number of events to bulk into a single batch window. The # default is 2048. #bulk_max_size: 2048 # Set gzip compression level. #compression_level: 3 # Optional load balance the events between the Logstash hosts #loadbalance: true # Optional index name. The default index name depends on the each beat. # For Packetbeat, the default is set to packetbeat, for Topbeat # top topbeat and for Filebeat to filebeat. #index: filebeat # Optional TLS. By default is off. #tls: # List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications #certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/root/ca.pem"] # Certificate for TLS client authentication #certificate: "/etc/pki/client/cert.pem" # Client Certificate Key #certificate_key: "/etc/pki/client/cert.key" # Controls whether the client verifies server certificates and host name. # If insecure is set to true, all server host names and certificates will be # accepted. In this mode TLS based connections are susceptible to # man-in-the-middle attacks. Use only for testing. #insecure: true # Configure cipher suites to be used for TLS connections #cipher_suites: [] # Configure curve types for ECDHE based cipher suites #curve_types: [] ### File as output file: # Path to the directory where to save the generated files. The option is mandatory. path: "/tmp/filebeat" # Name of the generated files. The default is `filebeat` and it generates files: `filebeat`, `filebeat.1`, `filebeat.2`, etc. filename: filebeat # Maximum size in kilobytes of each file. When this size is reached, the files are # rotated. The default value is 10 MB. rotate_every_kb: 10000 # Maximum number of files under path. When this number of files is reached, the # oldest file is deleted and the rest are shifted from last to first. The default # is 7 files. number_of_files: 7 ### Console output #console: # Pretty print json event #pretty: false ############################# Shipper ######################################### shipper: # The name of the shipper that publishes the network data. It can be used to group # all the transactions sent by a single shipper in the web interface. # If this options is not defined, the hostname is used. #name: # The tags of the shipper are included in their own field with each # transaction published. Tags make it easy to group servers by different # logical properties. #tags: ["service-X", "web-tier"] # Uncomment the following if you want to ignore transactions created # by the server on which the shipper is installed. This option is useful # to remove duplicates if shippers are installed on multiple servers. #ignore_outgoing: true # How often (in seconds) shippers are publishing their IPs to the topology map. # The default is 10 seconds. #refresh_topology_freq: 10 # Expiration time (in seconds) of the IPs published by a shipper to the topology map. # All the IPs will be deleted afterwards. Note, that the value must be higher than # refresh_topology_freq. The default is 15 seconds. #topology_expire: 15 # Internal queue size for single events in processing pipeline #queue_size: 1000 # Configure local GeoIP database support. # If no paths are not configured geoip is disabled. #geoip: #paths: # - "/usr/share/GeoIP/GeoLiteCity.dat" # - "/usr/local/var/GeoIP/GeoLiteCity.dat" ############################# Logging ######################################### # There are three options for the log ouput: syslog, file, stderr. # Under Windos systems, the log files are per default sent to the file output, # under all other system per default to syslog. logging: # Send all logging output to syslog. On Windows default is false, otherwise # default is true. to_syslog: false # Write all logging output to files. Beats automatically rotate files if rotateeverybytes # limit is reached. to_files: true # To enable logging to files, to_files option has to be set to true files: # The directory where the log files will written to. path: /home/hadoop/mybeat # The name of the files where the logs are written to. name: mybeat # Configure log file size limit. If limit is reached, log file will be # automatically rotated rotateeverybytes: 10485760 # = 10MB # Number of rotated log files to keep. Oldest files will be deleted first. keepfiles: 7 # Enable debug output for selected components. To enable all selectors use ["*"] # Other available selectors are beat, publish, service # Multiple selectors can be chained. #selectors: [ ] # Sets log level. The default log level is error. # Available log levels are: critical, error, warning, info, debug level: debug
5、Console Output (Filebeat收集到数据,输出到console里。为了测试,默认的配置文件里是有的)
启动redis
[hadoop@HadoopMaster filebeat-1.3.1-x86_64]$ pwd
/home/hadoop/app/filebeat-1.3.1-x86_64
[hadoop@HadoopMaster filebeat-1.3.1-x86_64]$ ./filebeat -c filebeat_console.yml
最终的filebeat_console.yml(我自己改名的,为了区别和方便)
################### Filebeat Configuration Example ######################### ############################# Filebeat ###################################### filebeat: # List of prospectors to fetch data. prospectors: # Each - is a prospector. Below are the prospector specific configurations - # Paths that should be crawled and fetched. Glob based paths. # To fetch all ".log" files from a specific level of subdirectories # /var/log/*/*.log can be used. # For each file found under this path, a harvester is started. # Make sure not file is defined twice as this can lead to unexpected behaviour. paths: - /home/hadoop/app.log #- c:\programdata\elasticsearch\logs\* # Configure the file encoding for reading files with international characters # following the W3C recommendation for HTML5 (http://www.w3.org/TR/encoding). # Some sample encodings: # plain, utf-8, utf-16be-bom, utf-16be, utf-16le, big5, gb18030, gbk, # hz-gb-2312, euc-kr, euc-jp, iso-2022-jp, shift-jis, ... #encoding: plain # Type of the files. Based on this the way the file is read is decided. # The different types cannot be mixed in one prospector # # Possible options are: # * log: Reads every line of the log file (default) # * stdin: Reads the standard in input_type: log # Exclude lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It drops the lines that are # matching any regular expression from the list. The include_lines is called before # exclude_lines. By default, no lines are dropped. # exclude_lines: ["^DBG"] # Include lines. A list of regular expressions to match. It exports the lines that are # matching any regular expression from the list. The include_lines is called before # exclude_lines. By default, all the lines are exported. # include_lines: ["^ERR", "^WARN"] # Exclude files. A list of regular expressions to match. Filebeat drops the files that # are matching any regular expression from the list. By default, no files are dropped. # exclude_files: [".gz$"] # Optional additional fields. These field can be freely picked # to add additional information to the crawled log files for filtering #fields: # level: debug # review: 1 # Set to true to store the additional fields as top level fields instead # of under the "fields" sub-dictionary. In case of name conflicts with the # fields added by Filebeat itself, the custom fields overwrite the default # fields. #fields_under_root: false # Ignore files which were modified more then the defined timespan in the past. # In case all files on your system must be read you can set this value very large. # Time strings like 2h (2 hours), 5m (5 minutes) can be used. #ignore_older: 0 # Close older closes the file handler for which were not modified # for longer then close_older # Time strings like 2h (2 hours), 5m (5 minutes) can be used. #close_older: 1h # Type to be published in the 'type' field. For Elasticsearch output, # the type defines the document type these entries should be stored # in. Default: log #document_type: log # Scan frequency in seconds. # How often these files should be checked for changes. In case it is set # to 0s, it is done as often as possible. Default: 10s #scan_frequency: 10s # Defines the buffer size every harvester uses when fetching the file #harvester_buffer_size: 16384 # Maximum number of bytes a single log event can have # All bytes after max_bytes are discarded and not sent. The default is 10MB. # This is especially useful for multiline log messages which can get large. #max_bytes: 10485760 # Mutiline can be used for log messages spanning multiple lines. This is common # for Java Stack Traces or C-Line Continuation #multiline: # The regexp Pattern that has to be matched. The example pattern matches all lines starting with [ #pattern: ^\[ # Defines if the pattern set under pattern should be negated or not. Default is false. #negate: false # Match can be set to "after" or "before". It is used to define if lines should be append to a pattern # that was (not) matched before or after or as long as a pattern is not matched based on negate. # Note: After is the equivalent to previous and before is the equivalent to to next in Logstash #match: after # The maximum number of lines that are combined to one event. # In case there are more the max_lines the additional lines are discarded. # Default is 500 #max_lines: 500 # After the defined timeout, an multiline event is sent even if no new pattern was found to start a new event # Default is 5s. #timeout: 5s # Setting tail_files to true means filebeat starts readding new files at the end # instead of the beginning. If this is used in combination with log rotation # this can mean that the first entries of a new file are skipped. #tail_files: false # Backoff values define how agressively filebeat crawls new files for updates # The default values can be used in most cases. Backoff defines how long it is waited # to check a file again after EOF is reached. Default is 1s which means the file # is checked every second if new lines were added. This leads to a near real time crawling. # Every time a new line appears, backoff is reset to the initial value. #backoff: 1s # Max backoff defines what the maximum backoff time is. After having backed off multiple times # from checking the files, the waiting time will never exceed max_backoff idenependent of the # backoff factor. Having it set to 10s means in the worst case a new line can be added to a log # file after having backed off multiple times, it takes a maximum of 10s to read the new line #max_backoff: 10s # The backoff factor defines how fast the algorithm backs off. The bigger the backoff factor, # the faster the max_backoff value is reached. If this value is set to 1, no backoff will happen. # The backoff value will be multiplied each time with the backoff_factor until max_backoff is reached #backoff_factor: 2 # This option closes a file, as soon as the file name changes. # This config option is recommended on windows only. Filebeat keeps the files it's reading open. This can cause # issues when the file is removed, as the file will not be fully removed until also Filebeat closes # the reading. Filebeat closes the file handler after ignore_older. During this time no new file with the # same name can be created. Turning this feature on the other hand can lead to loss of data # on rotate files. It can happen that after file rotation the beginning of the new # file is skipped, as the reading starts at the end. We recommend to leave this option on false # but lower the ignore_older value to release files faster. #force_close_files: false # Additional prospector #- # Configuration to use stdin input #input_type: stdin # General filebeat configuration options # # Event count spool threshold - forces network flush if exceeded #spool_size: 2048 # Enable async publisher pipeline in filebeat (Experimental!) #publish_async: false # Defines how often the spooler is flushed. After idle_timeout the spooler is # Flush even though spool_size is not reached. #idle_timeout: 5s # Name of the registry file. Per default it is put in the current working # directory. In case the working directory is changed after when running # filebeat again, indexing starts from the beginning again. #registry_file: .filebeat # Full Path to directory with additional prospector configuration files. Each file must end with .yml # These config files must have the full filebeat config part inside, but only # the prospector part is processed. All global options like spool_size are ignored. # The config_dir MUST point to a different directory then where the main filebeat config file is in. #config_dir: ############################################################################### ############################# Libbeat Config ################################## # Base config file used by all other beats for using libbeat features ############################# Output ########################################## # Configure what outputs to use when sending the data collected by the beat. # Multiple outputs may be used. output: ### Elasticsearch as output #elasticsearch: # Array of hosts to connect to. # Scheme and port can be left out and will be set to the default (http and 9200) # In case you specify and additional path, the scheme is required: http://localhost:9200/path # IPv6 addresses should always be defined as: https://[2001:db8::1]:9200 #hosts: ["localhost:9200"] # Optional protocol and basic auth credentials. #protocol: "https" #username: "admin" #password: "s3cr3t" # Number of workers per Elasticsearch host. #worker: 1 # Optional index name. The default is "filebeat" and generates # [filebeat-]YYYY.MM.DD keys. #index: "filebeat" # A template is used to set the mapping in Elasticsearch # By default template loading is disabled and no template is loaded. # These settings can be adjusted to load your own template or overwrite existing ones #template: # Template name. By default the template name is filebeat. #name: "filebeat" # Path to template file #path: "filebeat.template.json" # Overwrite existing template #overwrite: false # Optional HTTP Path #path: "/elasticsearch" # Proxy server url #proxy_url: http://proxy:3128 # The number of times a particular Elasticsearch index operation is attempted. If # the indexing operation doesn't succeed after this many retries, the events are # dropped. The default is 3. #max_retries: 3 # The maximum number of events to bulk in a single Elasticsearch bulk API index request. # The default is 50. #bulk_max_size: 50 # Configure http request timeout before failing an request to Elasticsearch. #timeout: 90 # The number of seconds to wait for new events between two bulk API index requests. # If `bulk_max_size` is reached before this interval expires, addition bulk index # requests are made. #flush_interval: 1 # Boolean that sets if the topology is kept in Elasticsearch. The default is # false. This option makes sense only for Packetbeat. #save_topology: false # The time to live in seconds for the topology information that is stored in # Elasticsearch. The default is 15 seconds. #topology_expire: 15 # tls configuration. By default is off. #tls: # List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications #certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/root/ca.pem"] # Certificate for TLS client authentication #certificate: "/etc/pki/client/cert.pem" # Client Certificate Key #certificate_key: "/etc/pki/client/cert.key" # Controls whether the client verifies server certificates and host name. # If insecure is set to true, all server host names and certificates will be # accepted. In this mode TLS based connections are susceptible to # man-in-the-middle attacks. Use only for testing. #insecure: true # Configure cipher suites to be used for TLS connections #cipher_suites: [] # Configure curve types for ECDHE based cipher suites #curve_types: [] # Configure minimum TLS version allowed for connection to logstash #min_version: 1.0 # Configure maximum TLS version allowed for connection to logstash #max_version: 1.2 ### Logstash as output #logstash: # The Logstash hosts #hosts: ["localhost:5044"] # Number of workers per Logstash host. #worker: 1 # The maximum number of events to bulk into a single batch window. The # default is 2048. #bulk_max_size: 2048 # Set gzip compression level. #compression_level: 3 # Optional load balance the events between the Logstash hosts #loadbalance: true # Optional index name. The default index name depends on the each beat. # For Packetbeat, the default is set to packetbeat, for Topbeat # top topbeat and for Filebeat to filebeat. #index: filebeat # Optional TLS. By default is off. #tls: # List of root certificates for HTTPS server verifications #certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/root/ca.pem"] # Certificate for TLS client authentication #certificate: "/etc/pki/client/cert.pem" # Client Certificate Key #certificate_key: "/etc/pki/client/cert.key" # Controls whether the client verifies server certificates and host name. # If insecure is set to true, all server host names and certificates will be # accepted. In this mode TLS based connections are susceptible to # man-in-the-middle attacks. Use only for testing. #insecure: true # Configure cipher suites to be used for TLS connections #cipher_suites: [] # Configure curve types for ECDHE based cipher suites #curve_types: [] ### File as output #file: # Path to the directory where to save the generated files. The option is mandatory. #path: "/tmp/filebeat" # Name of the generated files. The default is `filebeat` and it generates files: `filebeat`, `filebeat.1`, `filebeat.2`, etc. #filename: filebeat # Maximum size in kilobytes of each file. When this size is reached, the files are # rotated. The default value is 10 MB. #rotate_every_kb: 10000 # Maximum number of files under path. When this number of files is reached, the # oldest file is deleted and the rest are shifted from last to first. The default # is 7 files. #number_of_files: 7 ### Console output console: # Pretty print json event pretty: false ############################# Shipper ######################################### shipper: # The name of the shipper that publishes the network data. It can be used to group # all the transactions sent by a single shipper in the web interface. # If this options is not defined, the hostname is used. #name: # The tags of the shipper are included in their own field with each # transaction published. Tags make it easy to group servers by different # logical properties. #tags: ["service-X", "web-tier"] # Uncomment the following if you want to ignore transactions created # by the server on which the shipper is installed. This option is useful # to remove duplicates if shippers are installed on multiple servers. #ignore_outgoing: true # How often (in seconds) shippers are publishing their IPs to the topology map. # The default is 10 seconds. #refresh_topology_freq: 10 # Expiration time (in seconds) of the IPs published by a shipper to the topology map. # All the IPs will be deleted afterwards. Note, that the value must be higher than # refresh_topology_freq. The default is 15 seconds. #topology_expire: 15 # Internal queue size for single events in processing pipeline #queue_size: 1000 # Configure local GeoIP database support. # If no paths are not configured geoip is disabled. #geoip: #paths: # - "/usr/share/GeoIP/GeoLiteCity.dat" # - "/usr/local/var/GeoIP/GeoLiteCity.dat" ############################# Logging ######################################### # There are three options for the log ouput: syslog, file, stderr. # Under Windos systems, the log files are per default sent to the file output, # under all other system per default to syslog. logging: # Send all logging output to syslog. On Windows default is false, otherwise # default is true. to_syslog: false # Write all logging output to files. Beats automatically rotate files if rotateeverybytes # limit is reached. to_files: true # To enable logging to files, to_files option has to be set to true files: # The directory where the log files will written to. path: /home/hadoop/mybeat # The name of the files where the logs are written to. name: mybeat # Configure log file size limit. If limit is reached, log file will be # automatically rotated rotateeverybytes: 10485760 # = 10MB # Number of rotated log files to keep. Oldest files will be deleted first. keepfiles: 7 # Enable debug output for selected components. To enable all selectors use ["*"] # Other available selectors are beat, publish, service # Multiple selectors can be chained. #selectors: [ ] # Sets log level. The default log level is error. # Available log levels are: critical, error, warning, info, debug level: debug
扩展延伸(进一步建议学习,更贴近生产)
本文转自大数据躺过的坑博客园博客,原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/zlslch/p/6623106.html,如需转载请自行联系原作者