App自动化测试工具Airtest
AirtestProject是由网易游戏推出的一款跨平台的UI自动化测试框架,主要是面向游戏的UI自动化测试,比如Unity3D、cocos2dx-*游戏框架,也支持Android原生app、iOS app、微信小程序的UI测试。本文主要介绍如何使用AirtestProject进行Android APP自动化测试。
目录
- AirtestProject组件
- 下载安装
- Airtest使用
-
- 安装卸载apk
- 连接设备
- 打开、停止APP
- 元素操作方法
-
- touch点击操作
- swipe滑动操作
- text文本输入
- keyevent键盘输入
- snapshot截图
- wait等待出现
- exists检查目标是否出现
- 断言
-
- 断言目标是否存在
- 值是否相等
- Poco使用
-
- poco初始化
- UI元素定位
-
- 基本选择器
- 相对选择器
- 属性获取
- UI 元素操作
-
- click点击
- set_text文本输入
- swipe滑动
- drag_to拖到
- wait等待
- 截图
- 总结
- 系列文章
AirtestProject组件
AirtestProject包括一下组件:
- Airtest:基于图像识别的自动化测试框架,适用于游戏和App,图像识别主要使用opencv库。项目地址:https://github.com/AirtestProject/Airtest
- Poco:基于UI元素识别的测试框架,支持Unity3D/cocos2dx-*/Android原生app/iOS原生app/微信小程序。项目github地址:https://github.com/AirtestProject/Poco
- AirtestIDE:图形界面,内置了Airtest和Poco的相关插件。官网地址:http://airtest.netease.com/
- AirLab:真机自动化云测试平台。
下面介绍如何使用Airtest和Poco进行自动化测试。
下载安装
先安装一下AirtestIDE,主要用于截图、UI 元素查看以及脚本调试,下载地址:http://airtest.netease.com/
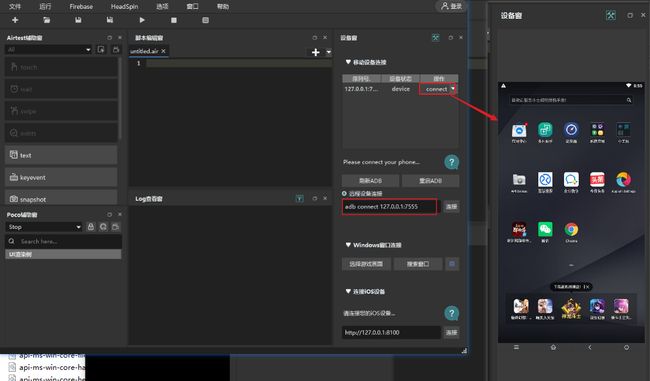
下载完成后解压,打开AirtestIDE.exe文件,连接一个模拟器,模拟器页面会实时显示在右边:
Python安装:
pip install -U airtest # airtest测试框架
pip install pocoui # poco测试框架
Airtest使用
安装卸载apk
install("path/to/your/apk") # 安装APK
uninstall("package_name_of_your_apk") # 卸载APK
连接设备
init_device(platform="Android",uuid="SNHVB20C18002195") # 连接android设备SNHVB20C18002195
init_device(platform="Windows",uuid="29563034") # uuid表示Android设备的序列号,Windows的句柄,iOS的uuid
connect_device('Android:///') # 本地android设备
connect_device('Android:///SNHVB20C18002195') # SNHVB20C18002195为手机序列号,可通过adb devices命令查看
connect_device("Android://127.0.0.1:7555")
connect_device("Windows:///") # 连接到windows桌面
connect_device("Windows:///29563034") # 连接到句柄29563034的windows应用
connect_device("iOS:///127.0.0.1:8100") # 连接iOS 设备
打开、停止APP
打开APP
start_app(package, activity=None)
停止APP:
stop_app(package)
元素操作方法
常用的元素操作方法主要包括下面5种:
touch点击操作
touch((100, 100), times=1) # 点击绝对坐标,times为点击次数,默认为1次
touch((100, 100), duration=2) # Android 和 Windows 平台应用可设置点击时间duration
touch((100, 100), right_click=True) # Windows右键点击
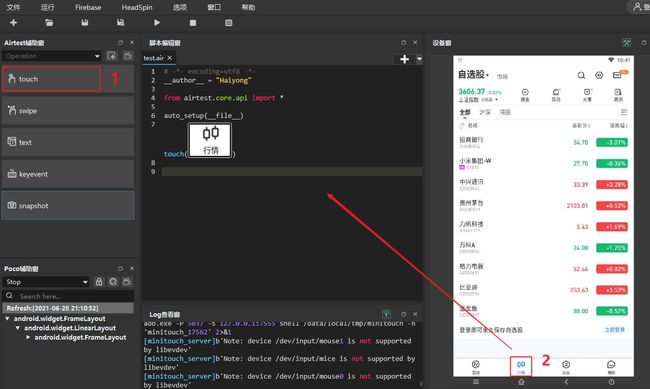
touch(Template(r"tpl1624889731448.png", record_pos=(-0.129, 0.832), resolution=(720, 1280))) # 点击图片中心,Template类包括了图片位置,手机分辨率,图片保存位置属性以及模板匹配,查找图片在手机的位置等方法
图片可以通过AirtestIDE来获取,点击Airtest辅助窗的touch方法,然后在设备窗中选择要操作的位置区域:
swipe滑动操作
swipe(v1, v2, vector=None) # 从v1滑动到v2,v1为起点,可以是Template类或者像素坐标
swipe((341,297), vector=[0.0131, 0.2495])
swipe(Template(r"tpl1624977188003.png", record_pos=(-0.015, -0.204), resolution=(720, 1280)), vector=[0.0011, 0.2826])
text文本输入
使用此方法时要确保输入框为活动状态,可以先点击一下输入框,然后再输入
text("test", enter=True) # 输入完成后,输入Enter键
keyevent键盘输入
keyevent(keyname) # 在Android中类似于执行 adb shell input keyevent KEYNAME
keyevent("HOME") # 或者 keyevent("3") HOME键
Android的按键可参考:https://developer.android.com/reference/android/view/KeyEvent
snapshot截图
snapshot(filename=None, msg="", quality=None, max_size=None) # 保存屏幕截图,filename:图像名,quality:图像质量(1-99),max_size:大小
wait等待出现
等待目标图片出现
wait(Template(r"tpl1624977188003.png"), timeout=None, interval=0.5, intervalfunc=None) # timeout:最大等待时间,interval:检查间隔时间
exists检查目标是否出现
检查当前界面是否出现指定目标
pos = exists(Template(r"tpl1624977188003.png")) # 如果找到目标,可以返回目标位置坐标
if pos:
touch(pos)
断言
断言目标是否存在
断言目标存在:assert_exists
assert_exists(Template(r"tpl1624977188003.png"))
断言目标不存在:assert_not_exists
assert_not_exists(Template(r"tpl1624977188003.png"))
值是否相等
assert_equal(first, second) # 断言两个值相等
assert_not_equal(first, second) # 断言两个值不相等
Poco使用
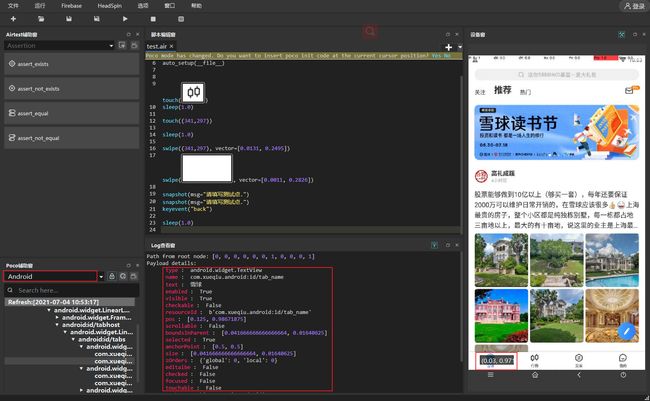
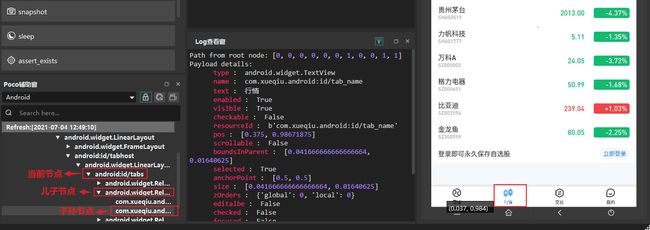
UI 元素可通过在AirtestIDE的Poco 辅助窗查看:
poco初始化
Android手机开启开发者模式,连接电脑,通过adb devices查看手机是否连接成功。
初始化:
from poco.drivers.android.uiautomation import AndroidUiautomationPoco
poco = AndroidUiautomationPoco(force_restart=False,use_airtest_input=True, screenshot_each_action=False)
poco.device.wake() # 执行唤醒:进入主页,启动Yosemite
UI元素定位
基本选择器
poco('node_name') # 默认第一个参数为节点名
# 也可以通过name 或者其它属性定位
poco(text='行情', type='android.widget.TextView')
相对选择器
和XPath的相对定位一样,poco可以根据父子关系、兄弟关系、祖孙关系来定位。
# select by direct child/offspring
poco("android:id/tabs").child("android.widget.RelativeLayout")[1].offspring(text="行情").click() # 具有多个元素的情况下,可以使用索引,索引从0开始。
兄弟节点定位:
poco("name").sibling("sibling_name")
父节点:
poco("name").parent("parent_name")
属性获取
获取UI对象属性
ele = poco(text='行情')
print(ele.attr('type')) # 属性
print(ele.attr('text')) # text属性
print(ele.get_bounds()) # 边界框
print(ele.get_position()) # 坐标
print(ele.get_size()) # UI 元素大小
print(ele.get_name()) # 元素名称
print(ele.get_text()) # 元素文本值,和ele.attr('text')一样
print(ele.exists()) # 元素是否存在
执行结果:
android.widget.TextView
行情
[0.978515625, 0.39583333333333337, 0.994921875, 0.3541666666666667]
[0.375, 0.98671875]
[0.041666666666666664, 0.01640625]
com.xueqiu.android:id/tab_name
行情
True
poco中的坐标采用百分比坐标,将x和y方向都缩放为0-1。
UI 元素操作
下面介绍几种常见poco元素操作方法
click点击
点击UI元素
poco('name').click() # 默认点击UI元素锚点(左上角)
poco('name').click('center') # 点击中心点
poco('name').click([0.5, 0.5]) # 点击中心点
poco('name').focus([0.5, 0.5]).click() # 点击中心点
点击坐标
poco.click([0.5, 0.5]) # 点击屏幕中心点
poco.long_click([0.5, 0.5], duration=3) # 长按
set_text文本输入
text = 'test'
poco('name').set_text(text) # 相文本框name输入文本
swipe滑动
swipe(direction, focus=None, duration=0.5)
-
direction : 滑动方向,可选up,down,left,right,也可传入向量坐标。
-
duration:滑动持续时间,时间越短,滑动速度就越快,滑动的距离就越长
ele = poco('name')
ele.swipe('up') # 向上滑动
ele.swipe([0,-0.1]) # 向上滑动
ele.swipe('down') # [0,0.1] 下滑
ele.swipe('left') # [-0.1,0] 左滑
ele.swipe('right')# [0.1,0] 右滑
ele.swipe([0.2, -0.2]) # 右上45度角滑动swipe sqrt(0.08) 单元距离
ele.swipe([0.2, -0.2], duration=0.5)
根据坐标滑动
poco.swipe(p1, p2=None, direction=None, duration=2.0)
从坐标 (100, 100) 滑动到 (100, 200) ,手机屏幕分辨率为1920×1080
poco.swipe([100/1920, 100/1080], [100/1920, 200/1080], duration=0.5)
# 或者
poco.swipe([100/1920, 100/1080], direction=[0, 100/1080], duration=0.5)
drag_to拖到
从一个UI元素拖到另一个UI元素
ele1 = poco('name1').focus([0.5,0.5])
ele2 = poco('name2').focus([0.5,0.5])
ele.drag_to(ele2)
wait等待
等待目标对象出现,返回目标对象
poco('name').wait(5).click() # 最多等待5秒,元素出现后点击
poco('name').wait(5).exists() # 最多等待5秒,返回元素是否出现
poco('name').wait_for_appearance(timeout=10) # 等待元素出现
poco("name").wait_for_disappearance(timeout=10) # 等待元素消失
ele1 = poco('name1')
ele2 = poco('name2')
poco.wait_for_all([ele1,ele2], timeout=10) # 等待2个UI元素标签全部出现
poco.wait_for_any([ele1,ele2], timeout=10) # 等待任意一个UI元素出现
截图
from base64 import b64decode
b64img, fmt = poco.snapshot(width=720)
open('screen.{}'.format(fmt), 'wb').write(b64decode(b64img))
总结
本文主要介绍了Airtest和poco的使用方法,Airtest的图片识别功能很好用,poco用于UI元素操作。可以将这它们结合起来使用,特别是在游戏的测试中,需要通过图标来定位。Airtest+poco还有一个优点就是app初始化启动速度要快于appium。
系列文章
1、Appium 介绍及环境安装
2、selenium/appium 等待方式介绍
3、App控件定位:Android 控件介绍及元素定位方法
4、Appium元素定位(一)
5、Appium元素定位(二):UiAutomator定位
6、Appium控件交互
7、Android WebView测试
8、AppCrawler自动遍历测试
9、自动遍历测试之Monkey工具
10、App自动化测试工具Uiautomator2
11、App自动化测试工具Airtest
12、Android手机管理平台搭建:STF和atxserver2
13、Windows上实现iOS APP自动化测试:tidevice + WDA + facebook-wda / appium
14、iOS APP自动化:predicate定位
15、iOS APP自动化:class chain定位方法
16、使用facebook-wda进行iOS APP自动化测试