Java基础知识学习笔记
目录
- 初识Java
-
- Java背景
-
- Java特性
- Java三大版本
- JDK、JRE、JVM
- hello world
- Mac中的一些IDEA快捷键
- Java基础语法
-
- 数据类型
-
- 基本类型
- 引用类型
- 变量
- 变量作用域
- 常量
- 变量命名规范
- 运算符
-
- 字符串连接符
- 三元运算符
- 进制转化
- 浮点数
- 字符
- 转义字符
- 类型转换
- 包机制
- JavaDoc
- 输入输出
- 基本结构
- 参数
-
- 命令行传参
- 可变参数
- 递归
- 数组
-
- 数组初始化
- 内存分析
- 数组的使用
- 多维数组
- 基础拓展
-
- Arrays类
- 冒泡排序
- 稀疏数组
- 面向对象
-
- 什么是面向对象
- 方法
-
- 方法调用
- 值传递
- 方法的重载
- 类与对象
-
- 创建对象
- 构造器
- Java三大属性
-
- 修饰符
-
- 方法的修饰
- 封装
-
- this
- 继承
-
- super注意点
- 方法重写
- 多态
-
- 类型转化
- static
- 抽象类
- 接口
-
- 接口作用:
- 内部类
- 异常机制
-
- 处理异常
- 自定义异常
- 实际应用中的经验总结
初识Java
主要学习资料 狂神说java
7月5日大致了解了Java的发展和基础语法
7月6日了解了面向对象的知识,对所有Java基础知识大致了解
7月7日归纳总结,结束Java基础模块的学习
Java背景
Java特性
- 简单性
- 面向对象
- 可移植性
- 高性能
- 分布式
- 动态性
- 多线程
- 安全性
- 健壮性
Java三大版本
- JavaSE 标准版
- JavaME 嵌入式开发
- JavaEE E企业级开发
JDK、JRE、JVM
- JDK。
- JRE java运行环境
- JVM 虚拟机
hello world
public class hello{
public static void main(String[] args){
Systerm.out.println("hello world");
}
}
注意大小写 IDEA中psvm可以自动生成第二行,psvm其实相当于c语言里的int main()
Mac中的一些IDEA快捷键
- 快速生成main方法:psvm+回车
- 快速生成打印方法:sout+回车
- 快速循环:100.for
- 遍历数组 itar
- 快速抽取变量:代码末尾加上.var+回车
- 大小写切换 cmd+shift+u
- 创建构造器/方法 cmd+n /control+enter
- 查询任何东西 shift+shift
- 进入一个类 cmd+b
- 展开继承关系 control+h
- 生成方法 control+i
- 接口方法 ==> 实现类方法:option+comand+B
- 实现类方法 ==> 接口方法:command+u
- surround with : cmd option t
- 进入源码 cmd+b
Java基础语法
数据类型
强类型语言:要求变量的使用要严格符合规定,所有变量都要先定义才能使用
基本类型
- byte 一个字节
- short 两个
- int 四个
- long 八个
- float 四个
- Double八个
- char 两个字节
- boolean
string不是关键字,类
什么是字节?
位(bit)字节(byte)
1B=8bit
引用类型
- 类
- 接口
- 数组
变量
每个变量都必须有类型
int num1=10;
long num2=30L;//long类型要在数字后面加个L
float num3=50.1F;
double num4=3.1666666;
string name="fangyijin";
//数据类型 变量名=值;
变量作用域
- 类变量
- 实例变量
- 局部变量
public class Demoo {
//类变量 static
static double salary=2500;
int age;
int name;
//实例变量:从属于对象,如果不进行初始化,这个变量默认值为0,布尔值默认为false
//除了基本类型其余默认值为null
public static void main(String[] args){
int i=10;
//局部变量必须声明和初始化值
System.out.println(i);
Demoo demoo=new Demoo();
System.out.println(demoo.age);
System.out.println(demoo.name);
System.out.println(salary);
}
}
常量
static final double PI=3.14;
//修饰符不存在先后顺序
//常量通常大写
变量命名规范
- 见名知义
- 首字母小写 驼峰原则
运算符
不同类型加减运算中,如果有long,结果为long,其余情况结果都为int。
- 逻辑运算符 &&与 || 或 !非
- 位运算符 <<*2 >> /2
- 拓展运算符。+= -=
a++ 先执行语句后自增
++a 先自增后执行语句
重点是执行时间
幂运算
Math.pow(3,2); //工具类运算
字符串连接符
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
int a=20;
int b=30;
System.out.println(""+a+b);
System.out.println(a+b+"");
}
}
//运算中有字符串就默认为字符串运算,注意以上两种区分
三元运算符
x?y=z 如果x==true,则结果为y,否则为z。
//x?y=z
int score=50;
String type=score<60 ?"不及格":"及格";
进制转化
- 二进制0b
- 八进制0
- 十六进制0x
浮点数
最好不要使用浮点数进行比较
银行业务用 BigDecimal比较
字符
所有的字符本质还是数字
char c1='a';
char c2='中';
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println((int)c1);
System.out.println(c2);
System.out.println((int)c2);
输出结果:
a
97
中
20013
转义字符
\n 换行
\t 制表符
类型转换
byte short char int long float double
//强制转换。(int) 高到低
//自动转换。 低到高
- 不能对布尔值转换
- 不能把对象类型转换为不相干类型
- 转换过程中可能遇到 内存溢出,或者精度问题
int money=10_0000_0000;
//数字之间可以用下划线分割
包机制
package用于区别类名的命名空间,写在类的最上面,包名倒着写;
定义包:package pkg1;
导入包:import pkg.classname;
import com.vickiww.*;
//导入包内所有类
JavaDoc
@author 作者名
@version 版本号
@since 指明需要最早使用的jdk版本
@param 参数名
@return 返回值情况
@throws 异常抛出情况
/** ➕回车
如何生成javadoc
- cd+空格+文件所在路径
- javadoc -encoding UTF-8 -charset UTF-8 Doc.java
- 只需点击名为index.html即可
也可直接在idea中主菜单里的tools里生成javadoc
输入输出
import java.util.Scanner; //导入输入包
Scanner scanner =new Scanner(System.in);//创建一个扫描器对象
if(scanner.hasNext()){
//判断有没有输入
String str=scanner.next();
System.out.println("输出内容为:"+str);
}
scanner.close();//关闭扫描器节约资源
-
next() 不能得到带有空格的字符串,对于输入有效字符之前遇到的空白,next()会将其去掉
-
nextline() 可以获得空白,以enter为结束符
-
hasNextInt () 输入整数
基本结构
- 顺序结构
- 选择结构 if switch
- 循环结构 for while
switch(grade){
case 'A':
System.out.println("良好");
break;
default:
System.out.println("未知");
}//jdk7开始,switch支持string类型
for(int i=1;i<=100;i++)
{
System.out.println(i);
}//100.for4自动生成循环语句
//九九乘法表
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <=i; j++) {
System.out.print(i+"*"+j+"="+i*j+"\t");
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}
//for循环遍历数组
int[] numbers={10,20,30,40};
for(int x:numbers)
{
System.out.println(x);
}
参数
命令行传参
package vickiww;
public class method {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { System.out.println("args["+i+"]:"+args[i]);
}
}
}
//在终端src目录下可调试 Java+文件名
可变参数
java支持同类型的可变参数给一个方法。
在方法声明中,在指定参数类型后加一个省略号
一个方法中只能指定一个可变参数,它必须是方法的最后一个参数
public class Method {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Method method=new Method();
method.test(1);
}
public void test(int...i){
System.out.println(i[0]);
}
}
递归
递归就是a方法调用a方法
//利用递归求阶乘
public class Method {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n=5;
System.out.println(f(n));
}
public static int f(int n){
if(n==1)return 1;
else return n*f(n-1);
}
}
数组
数组是相同类型数据的有序集合。数组的长度是确定的,不能改变。
数组元素必须是相同数据类型,不允许出现混合类型。数组变量属于引用类型,数组可以看作是对象。
数组的元素是通过索引访问的 ,数组索引从零开始。
下标合法区间[0,length-1]
数组初始化
int[] nums;//声明数组
int nums[];//另一种定义方式
nums=new int[10];//创建数组
int nums[]=new int[10];//声明和创建可以一起写
nums[0]=1;//数组的赋值
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
//nums.length获取数组长度
sum+=nums[i];
}
//静态初始化 创建+赋值
int[] a={1,2,3,4,5};
//动态初始化 包含默认初始化
int[] b=new int[10];
内存分析
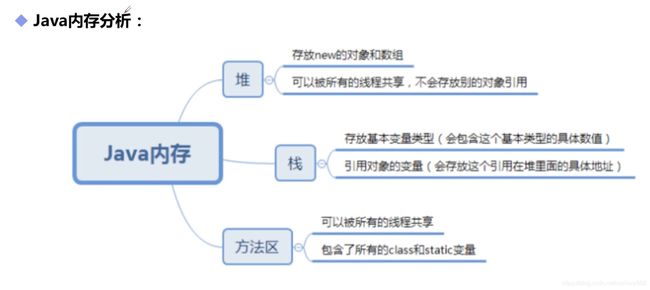
Java中对象是在堆中的,因此数组无论保存原始类型还是其他对象类型,数组对象本身是在堆中的。
数组的使用
//打印数组
int[] arrays={1,2,3,4,5};
for (int array : arrays) {
System.out.println(array);
}//for each循环
//反转数组
public static int[] reverse(int[] arrays){
int[] result=new int[arrays.length];
for(int i = 0, j=result.length-1;i<arrays.length;i++,j--){
result[j]=arrays[i];
}
return result;
}
多维数组
//打印二维数组
int[][] array={{1,2},{2,3},{3,4},{4,5}};
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < a[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(a[i][j]);
}
}
基础拓展
Arrays类
import java.util.Arrays;
//打印数组元素 [1,2,3,4,5]
System.out.println(Arrays.tostring(a));
//给数组赋值,全赋为4
Arrays.fill(a,4);
//数组排序,升序
Arrays.sort(a);
//二分查找指定元素索引值,数组一定要是排好序的
Arrays.binarySearch(a,3);
//比较两个数组元素是否相等
Arrays.equals(a,b);
//binarySearch的用法
int[] arr = {10,20,30,40,50};
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 30));
//输出:2 (下标索引值从0开始)
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 36));
//输出:-4 (找不到元素,返回-x,从-1开始数,如题,返回-4)
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 0,3,30));
//输出:2 (从0到3位(不包括)找30,找到了,在第2位,返回2)
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 0,3,40));
//输出:-4 (从0到3位(不包括)找40,找不到,从-1开始数,返回-4)
int[] arr = {3,2,1,5,4};
Arrays.sort(arr,0,3);//给第0位(0开始)到第3位(不包括)排序
冒泡排序
时间复杂度为o(n^2);
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Method {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a={3,11,9,7,8};
bubble(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
public static void bubble(int[] a){
for (int i = 0; i < a.length-1; i++) {
for(int j=i;j<a.length-1-i;j++){
if(a[j+1]<a[j]) {
int temp=0;
temp=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=a[j];
a[j]=temp;
}
}
}
}
}
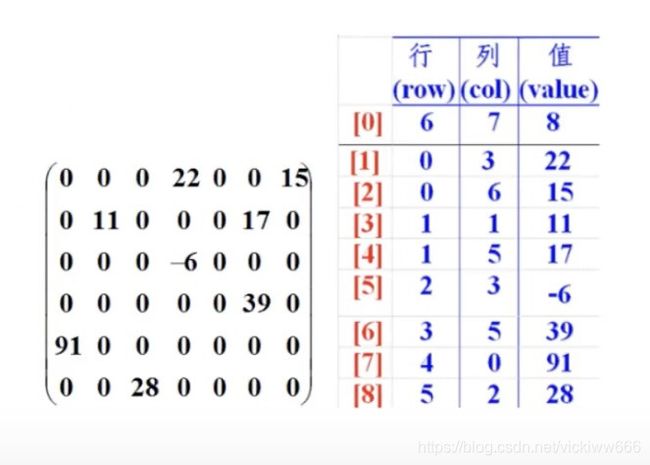
稀疏数组
面向对象
什么是面向对象
***OOP***面向对象编程
- 以类的方式组织代码,以对象的组织(封装)数据
- 抽象
- 三大特性:封装、继承、多态
- 从认识论角度 先有对象后有类。对象是具体的事物,类是抽象的
- 从代码运行角度 先有类后有对象。类是对象的模版。
方法
什么是方法?
Java方法是语句的集合,它们在一起执行一个功能,方法包含于类或对象中,在程序中被创建,在其他地方被引用(其实和***函数***差不多)。
int sum=add(1,2);//实参
public static int add(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}//形式参数
public static void test(){
System.out.println("hello world");
}
方法调用
- 直接调用
- 对象名.方法名
//静态方法
public class Student{
public static void say(){
System.out.println("我爱学习");
}
}
//静态方法调用
Student.say();
//非静态方法
public class Student{
public void say(){
System.out.println("我爱学习");
}
}
//非静态方法调用
Student student =new Student();//实例化这个类
student.say();
//new Student().say()
static是和类一起加载的,类实例化后才存在非静态方法
值传递
Java 中的基本类型,属于值传递。 Java 中的引用类型,属于“引用”传递(本质还是值传递)。
- 值传递:包括实实在在的值传递以及指针传递(指针传递参数本质上是值传递的方式,它所传递的是一个地址值),传递的都是实参的一个拷贝。
- 引用传递:数据类型 &变量名 = 变量名,用形参修饰实参
//c++中的定义
swap(a,b); //值传递
swap(&a,&b);//指针传递
int &b = a;//引用传递
public static void main(String[] args){
int a=1;
System.out.println(a); //输出为1
change(a);
System.out.println(a);//输出为1
}
public static void change(int a){
a=10;
}//这个方法返回值为空
public static void main(String[] args){
Person person=new Person();
person.name="vickiww";
System.out.println(person.name);//输出为vickiww
change(person);
System.out.println(person.name);//输出为vickiww666
}
public static void change(Person person){
person.name="vickiww666";
}
class Person{
String name;
}
方法的重载
一个类里有同名的方法,方法重载的规则:
- 方法名称必须相同
- 参数列表必须不同(类型不同或个数不同或参数排列顺序不同)
- 方法的返回值可以相同也可以不同
- 仅仅返回类型不同不足以成为方法的重载
方法名称相同的时候,编译器会根据参数列表来选择方法。
类与对象
- 类是一种抽象的数据类型,是对某一类事物整体描述/定义,但不能代表某一个具体的事物。
- 对象是抽象概念的具体实例。
创建对象
使用new关键词创建对象
public class application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Students xiaoming =new Students();//创建对象
xiaoming.age=18;
System.out.println(xiaoming.age);
}
}
public class Students {
string name;
int age; //类的属性
public void say(){
System.out.println("我爱学习");
}//类的方法
}//创建类
构造器
类中的构造器也称为构造方法
- 构造器和类名相同,没有返回值,也不能写void
- 一个类即使什么都不写,也会存在一个方法
- 使用new关键字,本质在调用构造器
- 构造器一般用来初始化值
- 一旦有了有参构造,无参就必须显示定义
- 构造器快捷键 control+enter(Mac) alt+insert(windows)
- this. 代表当前类
public class application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student xiaoming=new Student(18);
System.out.println(xiaoming.age);
}
}
public class Student {
String name;
int age;
public Student() {
}//无参构造
public Student(int age){
this.age=age;
}//有参构造
}
Java三大属性
修饰符
- public:具有最大的访问权限,可以访问任何一个classpath下的类、接口、异常等。它往往>>用于对外的情况,也就是对象或类对外的一种接口的形式。
- Protected:主要的作用就是用来保护子类的。它的含义在于子类可以用它修饰的成员,其他的不可以,它相当于传递给子类的一种继承的东西
- Default:有时候也称为friendly,它是针对本包访问而设计的,任何处于本包下的类、接口、异常等,都可以相互访问,即使是父类没有用protected修饰的成员也可以。
- private:访问权限仅限于类的内部,是一种封装的体现,例如,大多数成员变量都是修饰符为private的,它们不希望被其他任何外部的类访问。
public>Protected>Default>private
其实这四种修饰符表示的就是权限问题。即要遵循最小权限原则,则只要需要protected权限,绝不能使用public。
方法的修饰
- static是属于类,它不属于实例,非静态属于对象()
- final 常量 通过它修饰的没有子类
- private 不能继承
封装
- 该露的露,该藏的藏
- “高内聚,低耦合”。类的内部数据操作细节自己完成,不允许外部干涉;仅暴露少量的方法给外部使用。
- 封装(数据的隐藏)属性私有
- get/set
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student xiaoming=new Student();
xiaoming.setName("小明");
System.out.println(xiaoming.getName());
}
public class Student {
private String name;//对属性进行封装,不能直接调用了
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}//通过方法获取
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
if(age>120||age<3){
this.age = 3;
}else this.age=age;//可以设定属性是否合法
}
}
封装的好处:提高程序的安全性,保护数据
隐藏代码的实现细节 统一接口
提高系统可维护
this
- 本身调用者这个对象
- 没有继承关系也能使用
- this()本类的构造
继承
-
继承的本质是对某一批类的抽象
-
extends 扩展 子类是父类的扩展,子类继承了父类所有方法。
-
私有的无法被继承(把方法加上private就无法继承)
-
默认调用父辈的无参构造,调用父辈的构造器必须在子类第一行
-
Java类中只有单继承,没有多继承(一个儿子只能有一个爸爸,爸爸可以有多个儿子)
-
所有类都默认继承object类
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student xiaoming=new Student();
xiaoming.say();
xiaoming.test(16);
}
public class person {//person父类
protected int age=66;//受保护的属性
public void say(){
System.out.println("我爱吃饭");
}
public void print(){
System.out.println("我是人");
}
}
public class Student extends person{
private int age=16;
public void print(){
System.out.println("我是学生");
}
public void test(int age){
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println(this.age);
System.out.println(super.age);//super继承父类的属性
}
public void test1(){
print(); //调用自身方法
this.print();
super.print();//调用父类方法
}
}
//student是person的子类
super注意点
- super调用父辈的构造方法,必须在构造方法第一个
- super只能出现在子类的方法或构造方法中
- super和this不能同时调用构造方法
- super()父类的构造
方法重写
Override需要有继承关系,子类重写父类的方法,父类的引用指向子类。
- 方法名必须相同,参数列表必须相同
- 修饰符:范围可以扩大,不能缩小
- 重写都是方法的重写和属性无关
- 抛出的异常:范围可以缩小,但不能扩大
- 子类重写父类方法,执行子类方法
public class application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student xiaoming=new Student();
xiaoming.test();//输出结果:我是学生
person ren=new Student();//父类引用对象指向子类对象
ren.test();//输出结果:我是学生,如果类修饰符加上static,输出结果:我是人
}
}
public class Student extends person{
public void test(){
System.out.println("我是学生");
}
}
public class person {
public void test(){
System.out.println("我是人");
}
}
为什么要重写?
父类的功能子类不一定需要,或者不一定满足
多态
同一方法可根据发送对象不同而采取的多种不同的行为方式
一个对象的实际类型是确定的,但可以指向的引用对象类型有很多(父类,有关系的类)
- 多态是方法的多态,属性没有多态
- 子类能调用自己的和从父类继承的方法
- 父类可以引用子类,但不能调用子类独有的方法,可以执行重写的
- 存在条件 :继承,方法需要重写,父类引用指向子类对象
类型转化
//判断类型
Object object=new Student();
System.out.println(object instanceof Student);//true
System.out.println(object instanceof person);//true
System.out.println(object instanceof Object);//true
//有没有父子关系
//intanceof判断一个引用类型变量所指向的对象是否是一个类
//判断左边的对象是不是右边的实例
//高转低强制转换
person ren=new Student();//引用后只能使用子类重写方法
Student student=(Student) ren;//强制类型转化
student.run();//类型转换后可以使用子类特有方法
((student) ren).run();//前两步并一步
//低转高默认转化
Student student =new Student();
person ren=student;
//子类转化为父类,可能丢失一些方法,丢失子类独有的方法
static
public static void main(String[] args) {
person ren=new person();
System.out.println("========");
person ren1=new person();
}
}
public class person {
public person() {
System.out.println("构造代码块");
}//和对象同时产生
static {
System.out.println("静态代码块");
}//静态只执行一次
{
System.out.println("匿名代码块");
}
}
输出结果:
静态代码块
匿名代码块
构造代码块========
匿名代码块
构造代码块
//静态导入包
import static java.lang.Math.rangdom;
System.out.println(random());//静态导入包可以直接引用
抽象类
public abstract clss action{
public abstract void donothing();
}
- 抽象方法只有方法名字,没有方法实现
- 抽象类的所有方法,它的子类必须要实现它的方法
- 不能new抽象类,只能靠子类实现它
- 抽象类里可以写普通方法
- 抽象方法必须写在抽象类中
接口
接口的本质就是契约,用interface定义,接口都需要有实现类
//接口
public interface Service {
int AGE=99;//常量——public static final
void add();
void delete();
void update();
void query();
}
//实现类
public class ServiceImpl implements Service{
//快捷键 control+i 快速生成
@Override
public void add() {
}
@Override
public void delete() {
}
@Override
public void update() {
}
@Override
public void query() {
}
}
接口作用:
- 定义一些方法,让不同人实现
- implements可以实现多个接口
- 接口不能被实例化,接口中没有构造方法
- 必须要重写接口中的方法
内部类
- 成员内部类
- 静态内部类
- 局部内部类
- 匿名内部类
new Apple().eat();//没有名字初始化类,不用将实例保存到变量中
class Apple{
public void eat(){
System.out.println("我爱吃苹果");
}
}
public class application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Outer outer=new Outer();
Outer.Inner inner=outer.new Inner();
inner.getID();
}
}
public class Outer {
int id=10;//不管加什么修饰符,内部类都能获取
public void out(){
System.out.println("这是外部类的方法");
}
public class Inner{
public void in(){
System.out.println("这是内部类的方法");
}
public void getID(){
System.out.println(id);//内部类可以访问外部类的私有属性
}
}
}
异常机制
什么是异常?
Exception 程序出现异常问题
五个关键字:try catch finally throw throws
- 检查性异常
- 运行时异常 程序中可以选择捕获
- 错误ERROR 由Java虚拟机生成抛出 ,灾难性错误
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-c8s9vK1i-1625648187496)(/Users/fangyijin/Desktop/截屏2021-07-07 上午4.38.55.png)]
处理异常
try{//监控区域
System.out.println(a / b);
}catch (ArithmeticException e){//捕获异常
System.out.println("程序出现错误");
}finally{//处理善后工具
System.out.println("finally");
}
//catch(想要捕获的异常类型)
//假设要捕获多个异常,从小到大捕获
public void test(int a,int b){
if(b==0){
throw new ArithmeticException();//主动抛出异常,一般在方法中使用
}
}
//假设在方法中处理不了这个异常,方法上抛出异常
自定义异常
- 创建自定义异常类
public class MyException extends Exception{
private int detail;
public MyException(int a){
this.detail=a;
}
//tostring 异常的打印信息
public String tostring(){
return "MyException{ "+"detail="+detail+"}";
}
}
//可能会存在异常的方法
public class test{
static void test(int a) throws MyException{
System.out.println("传递的参数为:"+a);
if(a>10){
throw new MyException(a);
}
}
}