ARC4加密库
目录
介绍
库内容
用法
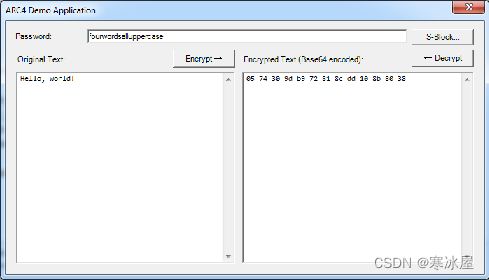
加解密数据示例
使用加密流的示例
形成密钥的示例
如何工作
S-block初始化
生成一个伪随机词K
密码算法
加密
解密
基于ARC4的随机字节生成器
线性同余随机
- 下载 DLL 文件 - 12.5 KB
- 下载源代码 - 17.7 KB
- 下载演示应用程序 - 24.9 KB
介绍
ARC4 Cryptography Provider Class Library是一个.NET项目的DLL文件,其中包括一个众所周知的对称加密算法的实现,该算法不存在于mscorlib库的System.Security.Cryptography命名空间中。
加密算法,称为ARC4(Alleged RC4),是一种流密码,广泛用于计算机网络上的各种信息安全系统(例如,SSL和TLS协议、WEP和WPA无线安全算法)。最初的RC4流密码由RSA Security的Ronald Rivest创建。七年来,密码一直是商业机密,算法的确切描述只有在签署保密协议后才提供,但在1994年9月,它的描述被匿名发送到Cypherpunks的邮件列表。
为了避免商标所有者的潜在索赔,密码有时被称为ARC4,意思是所谓的RC4(因为RSA Security没有正式发布该算法)。
尽管不推荐使用这种密码,但ARC4仍然很受欢迎,因为它的软件实现简单且运行速度快。另一个重要优势是可变密钥长度以及相同数量的加密和原始数据。
库内容
该库包含以下命名空间:
- System.Security.Cryptography包括算法的基类SymmetricAlgorithm和DeriveBytes的ARC4实现。
- System.IO包括使用ARC4算法包含加密数据的流的实现。
用法
ARC4Lib在自己的项目中有两种使用方式:
- 将下载的DLL文件复制到开发文件夹的自定义文件夹中。在Visual Studio IDE中创建一个项目。在解决方案资源管理器中,右键单击References或Dependencies节点并选择Add Project Reference,然后单击Browse按钮,选择要添加的文件ARC4Lib.dll,然后按OK。
- 将下载的源项目复制到开发文件夹的自定义文件夹中。在Visual Studio IDE中创建解决方案。将ARC4Lib.csproj添加到解决方案中。在解决方案资源管理器中,右键单击References或Dependencies节点并选择Add Project Reference然后单击Projects,选择要添加的文件ARC4Lib.csproj,然后按OK。这样,您可以根据需要进行修改ARC4Lib。
要为当前应用程序域注册算法映射名称,请尝试以下操作:
using System.Security.Cryptography;
// ...
ARC4.Register();加解密数据示例
using System.Security.Cryptography;
// ...
byte[] password = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("password");
byte[] data = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("secret");
byte[] encrypted, restored;
using (var arc4 = ARC4.Create(password)
{
using(var transform = arc4.CreateEncryptor()) // Encryption.
{
encrypted = transform.TransformFinalBlock(data, 0, data.Length);
}
using(var transform = arc4.CreateDecryptor()) // Decryption.
{
restored = transform.TransformFinalBlock(data, 0, data.Length);
}
}使用加密流的示例
using System.Security.Cryptography;
// ...
string password = "password";
string data = "secret";
string restored;
using (var memory = new MemoryStream())
{
// Encryption.
using (var stream = new ARC4Stream(memory, password))
{
using (var writer = new StreamWriter(stream))
{
writer.Write(data);
}
}
memory.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin); // Reset the memory position to start.
// Decryption.
using (var stream = new ARC4Stream(memory, password))
{
using (var reader = new StreamReader(stream))
{
restored = reader.ReadToEnd();
}
}
}形成密钥的示例
using System.Security.Cryptography;
// ...
const int KEY_LENGTH = 64;
string password = "password";
byte[] key;
byte[] salt;
using (var deriveBytes = new ARC4DeriveBytes(password))
{
key = deriveBytes.GetBytes(KEY_LENGTH);
salt = deriveBytes.Salt;
}如何工作
流密码算法的核心包括一个函数——一个伪随机比特(gamma)生成器,它产生一个密钥比特流(key stream, gamma, pseudo-random bit sequence)。然后它用于加密,使用按位异或将它们与原始数据结合; 解密以类似的方式执行(因为与给定数据的XOR是对合)。
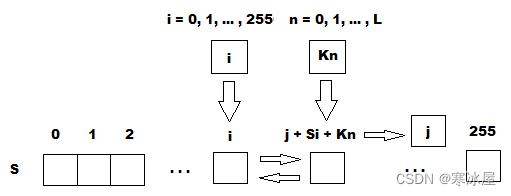
S-block初始化
该算法也称为密钥调度算法(KSA)。该算法使用用户输入的密钥,存储在Key中,长度为L个字节。初始化从填充数组(S-block)开始,然后这个数组被键定义的排列打乱。由于在S-block上只执行一个动作,因此必须声明S-block始终包含一组在初始化期间给出的值:S i =i。用户还可以使用初始化向量输入他自己的S-block版本或生成伪随机S-block。
byte[] sblock = new byte[256]; // The array contained S-block.
void CreateSBlock()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
sblock[i] = (byte)i; // S-block initialization.
}
}
void KeyScheduling() (byte[] key) // KSA
{
for (int i = 0, j = 0, l = key.Length; i < 256; i++)
{
j = (j + sblock[i] + key[i % l]) % 256;
Swap(sblock, i, j); // See below for "Swap" implementation ↓
}
}注意!默认情况下,在当前的ARC4.Create()实现中,s-block是用一个伪随机字节数组初始化的,该数组使用线性同余方法(LCR)和随机256字节的密钥。这与经典算法不太相符,在传递给PRGA之前,s-block被初始化为一个从0到255 (Si=i)的序列。如果需要经典行为,请使用ARC4.Create(key) 或传递ARC4SBlock.DefaultSBlock到作为初始化向量ARC4.Create(key,iv)。否则,您应该始终保留初始化向量以防止解密数据损坏,因为每次ARC4.Create()初始化引擎时加密数据都会不同。
如果您想使用自己的自定义S-block,将使用ValidBytes函数对其进行测试,以确保所有256个值不重复。
bool ValidBytes(byte[] bytes)
{
if (bytes == null || bytes.Length != 256)
{
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < 256; j++)
{
if (bytes[i] == bytes[j])
{
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
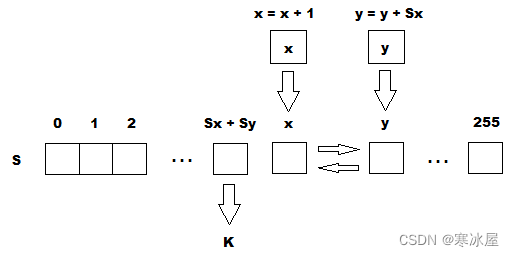
}生成一个伪随机词K
这部分算法称为伪随机生成算法(PRGA)。ARC4密钥流生成器置换存储在S-block中的值。在一个ARC4周期中,从密钥流中确定一个8位K词。以后将关键字与用户要加密的原文进行模二相加,得到密文。
函数NextByte 执行PRGA转换并返回单词K。
int x = 0, y = 0;
void Swap(byte[] array, int index1, int index2)
{
byte b = array[index1];
array[index1] = array[index2];
array[index2] = b;
}
byte NextByte() // PRGA
{
x = (x + 1) % 256;
y = (y + sblock[x]) % 256;
Swap(sblock, x, y);
return sblock[(sblock[x] + sblock[y]) % 256];
}密码算法
加密
该函数生成位序列K i。然后通过按位异或(⊕)操作将位序列与原始数据D i组合。结果是密码C i:
Ci = Di ⊕ Ki.
解密
密钥比特流(keystream)K i被重新创建(重新生成)。密钥的比特流与密码C i XOR操作相加。由于XOR操作的特性,输出是恢复的原始数据R i(使得所有i的R i = D i):
R i = C i ⊕ K i = (D i ⊕ K i ) ⊕ K i
函数Cipher使用ARC4算法执行对称加密和解密。
void Cipher(byte[] buffer, int offset, int count)
{
for (int i = offset; i < count; i++)
{
buffer[i] = unchecked((byte)(buffer[i] ^ NextByte()));
}
}基于ARC4的随机字节生成器
该类ARC4DeriveBytes实现了使用PRGA伪随机数生成器根据密码生成给定长度的密钥的功能。 首先,给定长度的数据数组由零值初始化,然后使用PRGA算法填充。
线性同余随机
LCR方法的本质是计算一个随机数序列X i,设置
X i+1 = (A • X i + C) MOD M,其中:
- M是模数(一个自然数M ≥ 2,相对于它计算除法的余数);
- A是因子(0 ≤ A < M);
- C为增量(0 ≤ C < M);
- X 0为初始值0 ≤ X 0 < M;
- 索引i在0 ≤ i < M范围内依次变化。
因此,LCR仅在以下情况下创建M个非重复伪随机值序列:
- 数字С和M互质;
- B = A -每个除以m的素数P的P的1倍;
- 如果M是4的倍数,则B是4的倍数。
为了在我们的案例中进行优化,预定义为:
- X i+1 = R (A • X i + C) MOD M,
- Xi ∈ (0, 256),
- X 0是随机的,
- R ∈ (0, 256)是随机常数,
- M = 256,
- A ∈ (9, 249)和A - 1可以被4整除,
- C ∈ (5, 251)并且C是一个素数。
可以使用以下方法获得的不同S-block数量的上限约为2亿个值。
byte[] _A = // An array of all values that A.
{
0x09, 0x0D, 0x11, 0x15, 0x19, 0x1D, 0x21, 0x25,
0x29, 0x2D, 0x31, 0x35, 0x39, 0x3D, 0x41, 0x45,
0x49, 0x4D, 0x51, 0x55, 0x59, 0x5D, 0x61, 0x65,
0x69, 0x6D, 0x71, 0x75, 0x79, 0x7D, 0x81, 0x85,
0x89, 0x8D, 0x91, 0x95, 0x99, 0x9D, 0xA1, 0xA5,
0xA9, 0xAD, 0xB1, 0xB5, 0xB9, 0xBD, 0xC1, 0xC5,
0xC9, 0xCD, 0xD1, 0xD5, 0xD9, 0xDD, 0xE1, 0xE5,
0xE9, 0xED, 0xF1, 0xF5, 0xF9
};
byte[] _C = // An array of all values that C.
{
0x05, 0x07, 0x0B, 0x0D, 0x11, 0x13, 0x17, 0x1D,
0x1F, 0x25, 0x29, 0x2B, 0x2F, 0x35, 0x3B, 0x3D,
0x43, 0x47, 0x49, 0x4F, 0x53, 0x59, 0x61, 0x65,
0x67, 0x6B, 0x6D, 0x71, 0x7F, 0x83, 0x89, 0x8B,
0x95, 0x97, 0x9D, 0xA3, 0xA7, 0xAD, 0xB3, 0xB5,
0xBF, 0xC1, 0xC5, 0xC7, 0xD3, 0xDF, 0xE3, 0xE5,
0xE9, 0xEF, 0xF1, 0xFB
};
void CreateRandomSBlock() // LCR
{
using (RNGCryptoServiceProvider rng = new RNGCryptoServiceProvider())
{
byte[] random = new byte[4];
rng.GetBytes(random);
int r = random[0]; // For best ranodimzation.
int x = random[1];
int a = _A[random[2] % _A.Length];
int c = _C[random[3] % _C.Length];
int m = 256;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
// S-block initialization.
sblock[i] = (byte) (r ^ (x = (a * x + c) % m));
}
}
}本文最初发布于GitHub - ng256/ARC4: ARC4 (Alleged RC4) cryptography provider class library.
https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/5319044/ARC4-Encryption-Library