【MySQL操作练习】
※查询操作
Distinct用法
在mysql中,distinct关键字的主要作用就是对数据库表中一个或者多个字段重复的数据进行过滤,只返回其中的一条数据给用户,distinct只可以在select中使用
在使用distinct的过程中主要注意一下几点:
- 在对字段进行去重的时候,要保证distinct在所有字段的最前面
- 如果distinct关键字后面有多个字段时,则会对多个字段进行组合去重,只有多个字段组合起来的值是相等的才会被去重
Count函数


我们可以通过count(*) 和 count(列名) 之间的差别,来统计出0的个数:
select vend_id, count(prod_id) from Vendors left join Products using(vend_id)
group by vend_id
order by vend_id;
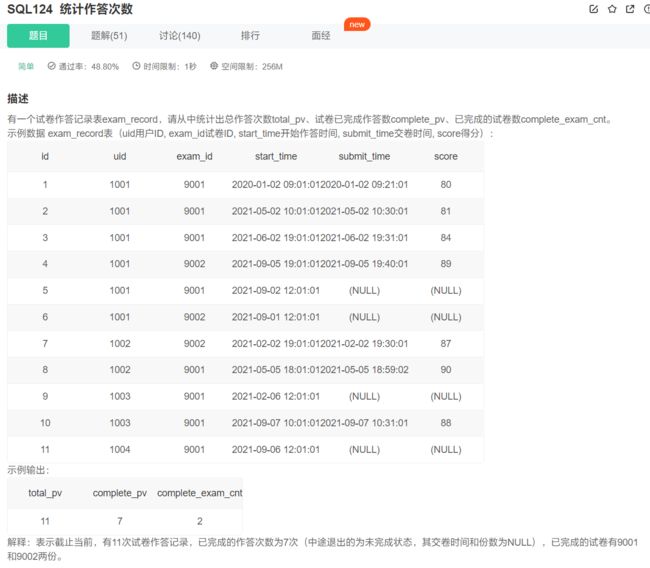
统计作答次数
select count(*) as total_pv, count(submit_time) as complete_pv,
count(distinct exam_id and score is not null) as complete_exam_cnt from exam_record;
也可以使用case when实现,关键点就在于count(列名)时,不会计算null行!
select
count(*) as total_pv,
count(case when score is not null then 1 else null end) as complete_pv,
count(distinct case when score is not null then exam_id else null end) as complete_exam_cnt
from exam_record ;
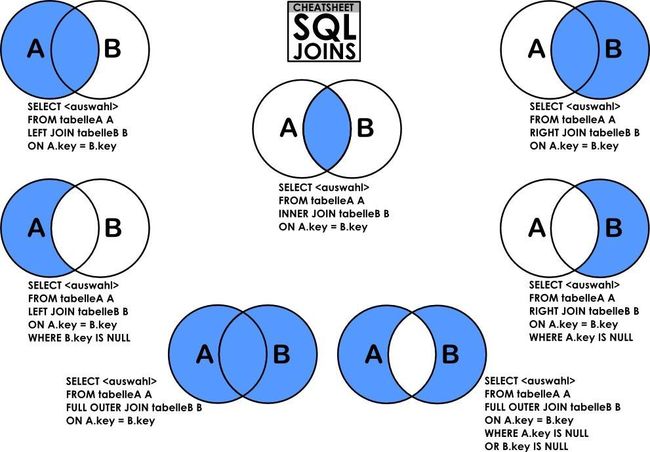
MySQL中的join用法
join的意思是连接,对于数据库来说,就是连接两个或以上的表。当什么时候需要连接查询两个表呢?当一个表中的内容不足以表达你需要的内容,而另一个与之相关联的表恰好有你所需的信息。所以join查询的目的就是补充你查询的表中没有的内容。
那怎么样将两个表关联起来呢?就需要两个表有相同的字段,即primary key和foreign key。
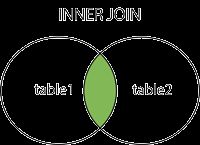
inner join / join
inner join/join级联查询两个表时,返回的结果是两个表中均存在的记录【查询出来的表中结果没有为null的数据】,可以理解是与关系。如下图所示:
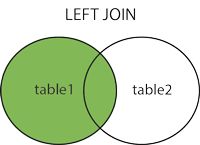
left join
left join级联查询两个表时,返回左表的所有记录以及两张表中均存在的记录,没有则返回null【因为是以左表为主,所以在left join时,新表中可能有多列没有数据,即为:null】。如下图所示:
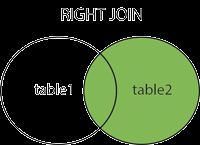
right join
full join / outer join
就是把(inner join、left join、right join)全都融合在了一起
由于mysql不支持full join,所以这里就不做full join的演示了。不过我们可以使用left join和right join来达到full join的目的。
select *
from user
left join orders on user.user_id = orders.user_id
union
select *
from user
right join orders on user.user_id = orders.user_id order by user_name;
using
MySQL中连接SQL语句中,ON子句的语法格式为:table1.column_name = table2.column_name。当模式设计对联接表的列采用了相同的命名样式时,就可以使用 USING 语法来简化 ON 语法,格式为:USING(column_name)。
所以,USING的功能相当于ON,区别在于USING指定一个属性名用于连接两个表【】,而ON指定一个条件【并不会去除重复的列】。
另外,SELECT 时,USING会去除USING指定的列,而ON不会。实例如下。
SELECT * from test t1 join test_copy1 tp1 on t1.id=tp1.id;
# 两张表通过相同的id列进行连接,最后只会保留一个id列,而使用on会出现两个id列
SELECT * from test t1 join test_copy1 tp1 USING(id);
natural join 与 nature/natura join
自然连接就是USING子句的简化版,它找出两个表中相同的列作为连接条件进行连接。
有左自然连接,右自然连接和普通自然连接之分。若两个表相同的列是id,所以会拿id作为连接条件【与使用on相比,连接后不会出现重复的列,例如以id进行连接,新表中只会出现一个id列!】
join on -> join using -> natural join,是一步步进行简化的
另外千万分清下面三条语句的区别 :
自然连接:SELECT * FROM t_blog NATURAL JOIN t_type;
笛卡尔积:SELECT * FROM t_blog NATURA JOIN t_type;
笛卡尔积:SELECT * FROM t_blog NATURE JOIN t_type;
笛卡尔积就是不管任何条件,将A表中的每一条数据,与B表中的每条数据进行连接,假设A表中有5条数据,B表中有10条数据,那么使用笛卡尔积共产生:5 * 10 = 50条数据
常见的时间函数
常见的有day、month、year获取相应的年月日,还可以使用date_format(),通过这个函数匹配’%Y%m%d’年份、月份和日期,大写的y是四位年份,还可以使用timestampdiff,求两段时间的时间差,需要在第一个参数的位置指定最后的时间单位。
使用last_day可以获取当前日期的最后一天,再配合day(),就可以获得当前月份的天数,特别的神奇!
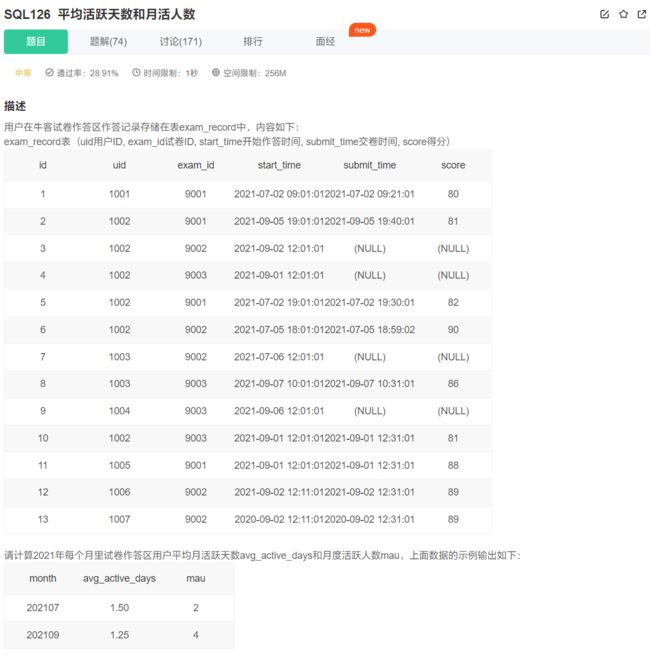
解释:2021年7月有2人活跃,共活跃了3天(1001活跃1天,1002活跃2天),平均活跃天数1.5;2021年9月有4人活跃,共活跃了5天,平均活跃天数1.25,结果保留2位小数。
注:此处活跃指有交卷行为。[也就是说submit_time is not null]
select date_format(submit_time, '%Y%m') as month,
# 通过 用户id + 提交日期 来计算出活跃天数
# 总人数就是看当前月份的不同用户id个数
round(count(distinct uid, date_format(submit_time, '%Y%m%d')) / count(distinct uid), 2) as avg_active_days,
count(distinct uid) as mau
from exam_record
where submit_time is not null
# 有了year 和 group by 的限制,就可以按照2021年的不同月份进行分组
and year(submit_time) = 2021
group by date_format(submit_time, '%Y%m');
round(a, b),可以对数值a进行四舍五入,保留b位小数。
※综合练习
(select
DATE_FORMAT(submit_time,"%Y%m") submit_month,count(uid) month_q_cnt,
# 这里必须要使用MAX(submit_time),否则转换出来的结果还是跟submit_time同样的一串数列
# 只有加上avg(),min()或max()运算才变成了一个数值作为分母使用
round(count(uid) /day(LAST_DAY(MAX(submit_time))),3) avg_day_q_cnt
from
practice_record
where year(submit_time)=2021
group by
DATE_FORMAT(submit_time,"%Y%m")
union ALL
select "2021汇总" submit_month, count(id) month_q_cnt, round(count(id)/31,3) avg_day_q_cnt
from
practice_record
where
year(submit_time)=2021
)
order by
submit_month;
多次排序
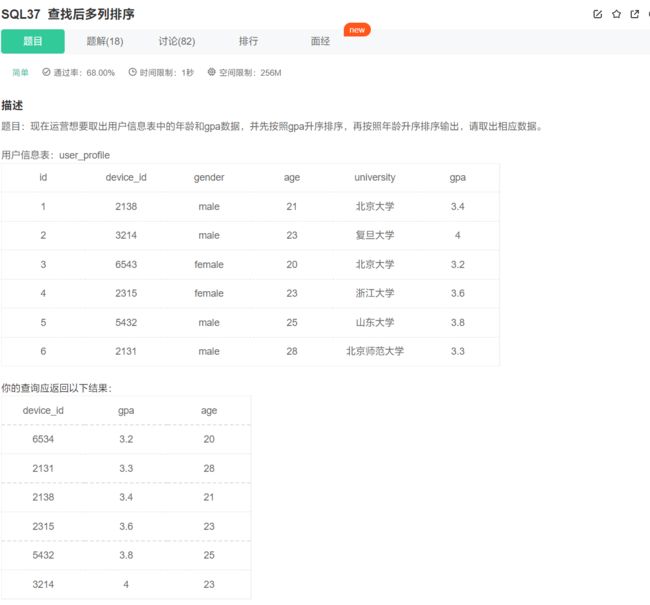
无论按照几列排序,都写在一个order by后面,降序或升序写在列名后,默认为asc升序
select device_id, gpa, age from user_profile
order by gpa asc, age asc;
select device_id, gpa, age from user_profile
order by gpa, age;
分组后过滤(having)
在where后不能使用聚合函数(例如:max、min、avg等),但在having后可以使用聚合函数进行过滤
select
university,
avg(question_cnt) as avg_question_cnt,
avg(answer_cnt) as avg_answer_cnt
from user_profile
where
avg_question_cnt < 5
or
avg_answer_cnt < 20
group by university;
注意过滤的条件,只有分组后拿到的平均值才能用于过滤,所以过滤应该在分组后,所以应该用having!
where可以看作是在数据分组前进行过滤,而having是在分组后进行过滤,所以where在group by之前,having在group by之后。
select 和 group by 列名的说明
如果在SELECT中的列,没有在GROUP BY中出现,那么这个SQL是不合法的,因为列不在GROUP BY从句中,也就是说查出来的列必须在group by后面出现否则就会报错,或者这个字段出现在聚合函数里面。
除了聚集函数,select中的所有列名,都必须出现在group by后!!!(聚集函数中使用到group by以外的列名也可以!)
第二次:(正解)
select
university,
avg(question_cnt) as avg_question_cnt,
avg(answer_cnt) as avg_answer_cnt
from user_profile
group by university
having avg_question_cnt < 5
or avg_answer_cnt < 20;
SQL语句书写顺序:select from where group by having order by limit
注意:order by 和 limit是最末尾的两个,因为这两个本质是在已经筛选出来的数据上进行调整,所以需要先把数据筛选出来
有明显的,需要使用聚合函数进行过滤的情况,那就得用having + 分组:
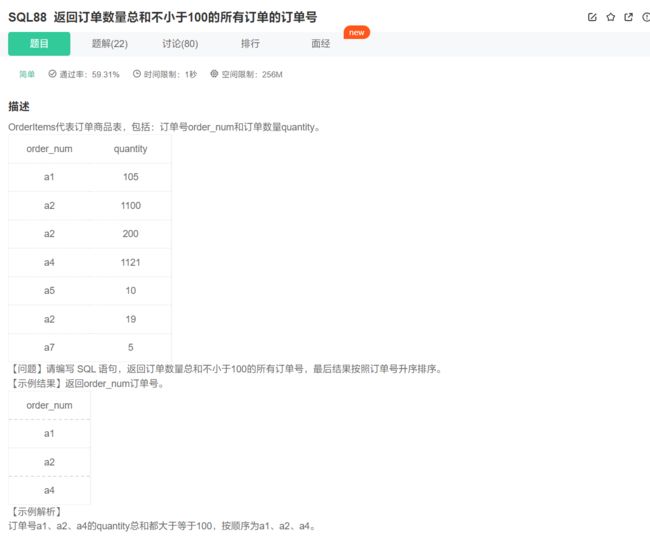
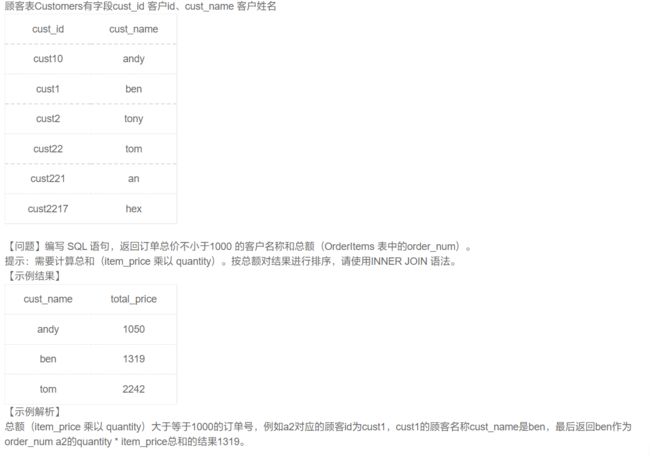
select distinct order_num from OrderItems group by order_num having(sum(quantity) >= 100) order by order_num;
注意,这里又需要使用聚合函数来协助判断,所以又需要分组 + having过滤:
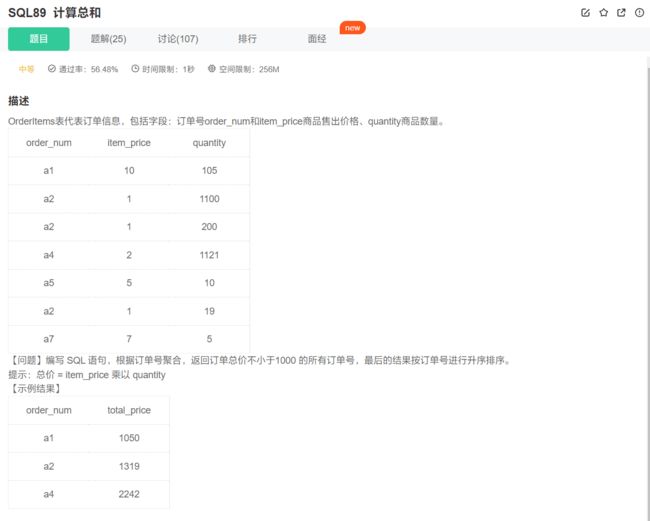
select order_num, sum(item_price * quantity) as total_price from OrderItems
group by order_num
having total_price >= 1000
order by order_num;
多表查询(子查询)
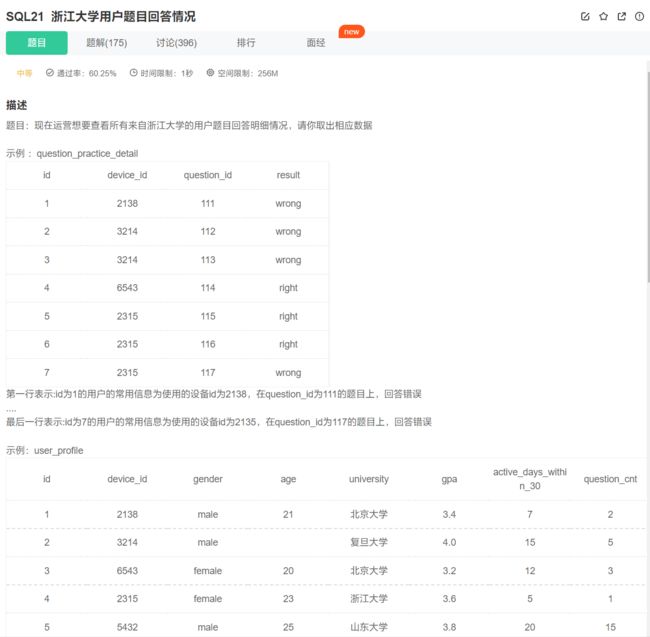
# 首先要查出浙江大学的用户
# 将查询出的浙江大学的用户的device_id作为第一张表查询的条件
select device_id, question_id, result from question_practice_detail
where device_id in (select distinct device_id from user_profile where university = '浙江大学');
多层子查询
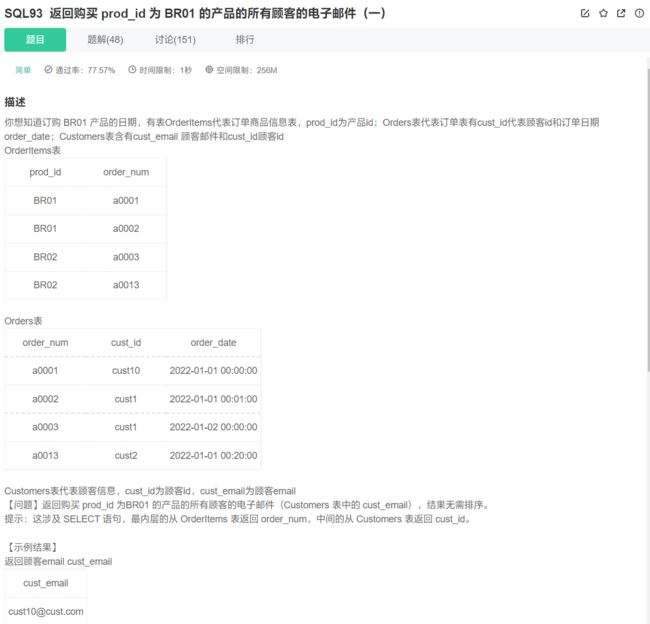
select cust_email from Customers where cust_id in (select cust_id from Orders where order_num in (select order_num from OrderItems where prod_id = 'BR01'));
第二种使用联结查询的写法:
select cust_email from Customers inner join Orders using(cust_id)
inner join OrderItems using(order_num)
where prod_id = 'BR01';
` ``
### 子查询和聚合函数的结合
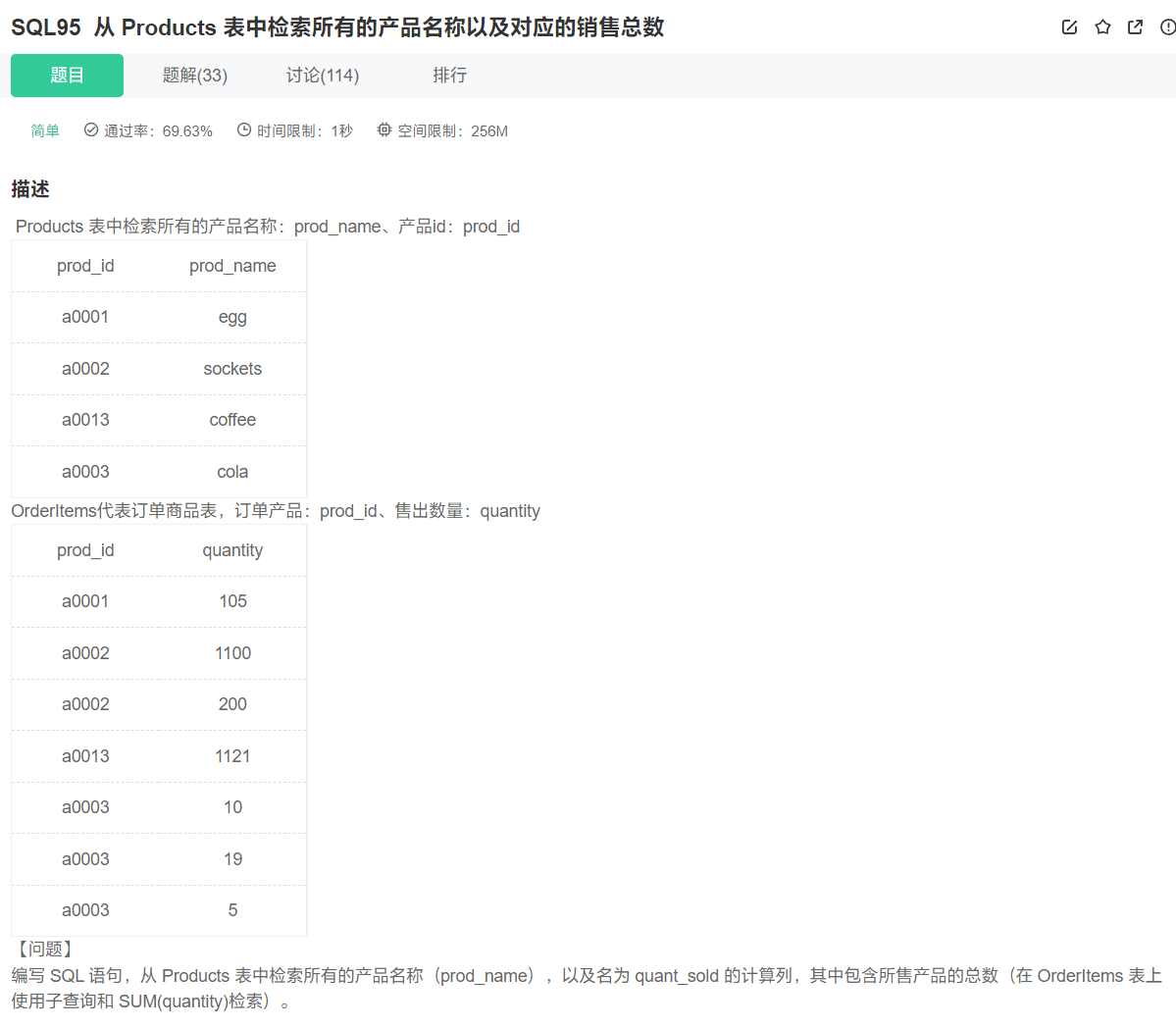
```sql
select prod_name, (select sum(quantity) from OrderItems as b where b.prod_id = a.prod_id) as quant_sold from Products as a;
链接查询(inner join、表别名)
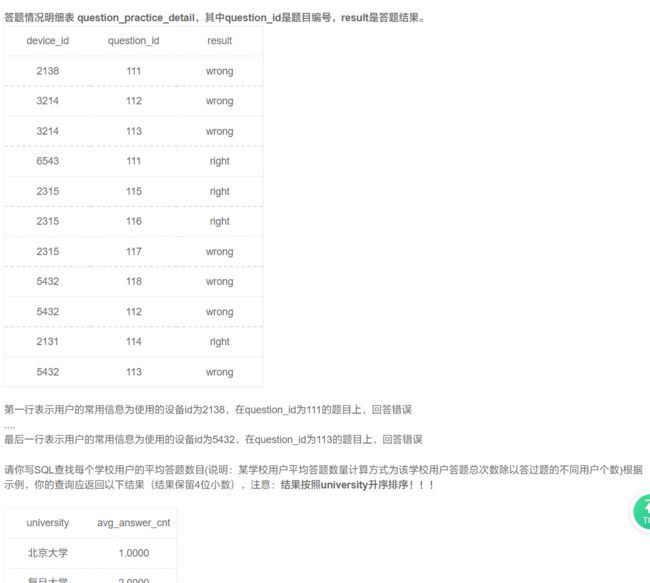
这里是将用户和题目分开进行存储,现在要统计用户的做题数,就需要将两张表联结,也就需要使用inner join,一定要清楚联结后的表格的样子:
select * from user_profile as up inner join question_practice_detail as qpd
on up.device_id = qpd.device_id;

因为device_id是唯一的,所以可以用它来作为联结两表的桥梁。
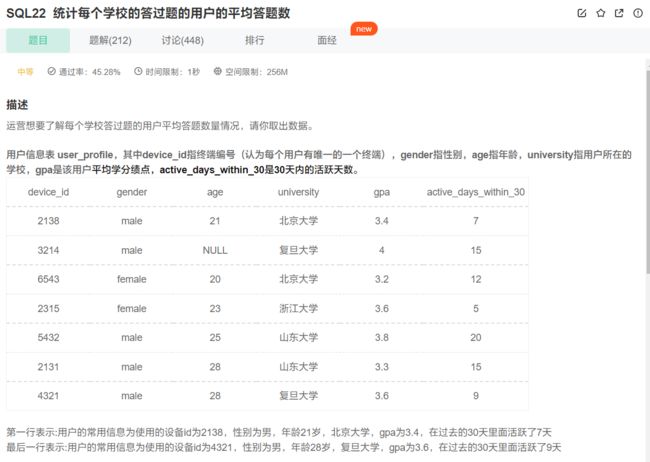
select university, count(question_id) / count(distinct qpd.device_id) as avg_answer_cnt
from user_profile as up
inner join question_practice_detail as qpd on up.device_id = qpd.device_id
group by university;
这道题用using也可以做,用using的前提是两张表中的联结列的列名要一致才行:
select university, count(question_id) / count(distinct device_id)
from user_profile as up inner join
question_practice_detail as qpd using(device_id)
group by university;
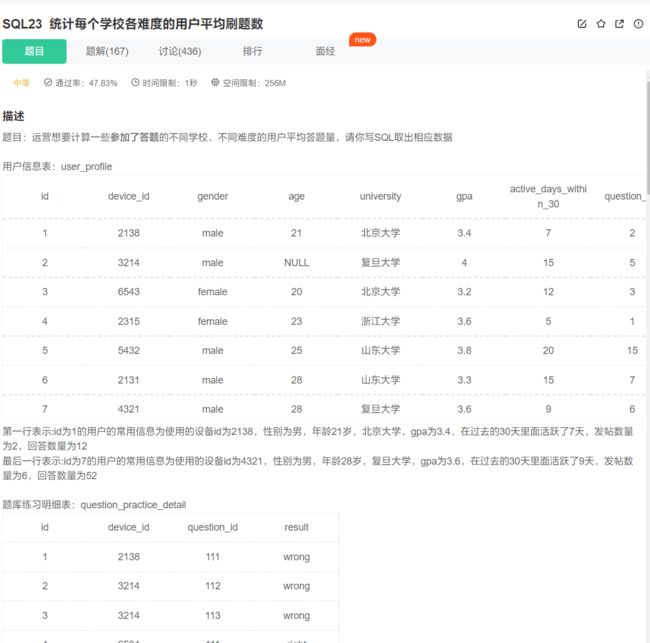
三张表联结
select
university,
difficult_level,
count(qpd.question_id) / count(distinct qpd.device_id) as avg_answer_cnt
from
question_practice_detail as qpd
inner join user_profile as up on up.device_id = qpd.device_id
inner join question_detail as qd on qd.question_id = qpd.question_id
group by
university,
difficult_level;
下面一种写法也可以,关键是要知道三张表之间联结的条件是什么?
select
university,
difficult_level,
count(qpd.question_id) / count(distinct qpd.device_id) as avg_answer_cnt
from
# 三张表的联结顺序可以不同,最终联结效果是一样的
user_profile as up
inner join question_practice_detail as qpd on up.device_id = qpd.device_id
inner join question_detail as qd on qd.question_id = qpd.question_id
group by
university,
difficult_level;
同样,上面count函数中写的哪个表并不重要,重要的是列,用其它表的相同列也可以,因为三张表已经联结起来了!
select
university,
difficult_level,
count(qd.question_id) / count(distinct up.device_id) as avg_answer_cnt # 可以用不同的列名
from
user_profile as up
inner join question_practice_detail as qpd on up.device_id = qpd.device_id
inner join question_detail as qd on qd.question_id = qpd.question_id
group by
university,
difficult_level;
select university, difficult_level, count(qpd.question_id) / count(distinct up.device_id) from
user_profile as up
inner join question_practice_detail as qpd on up.device_id = qpd.device_id
inner join question_detail as qd on qpd.question_id = qd.question_id
where university = '山东大学'
group by university, difficult_level;
因为一个顾客可能买多样物品,所以才需要按照顾客名进行分组!
select cust_name, sum(item_price * quantity) as total_price from Customers inner join Orders using(cust_id)
inner join OrderItems using(order_num)
group by cust_name
having total_price >= 1000
order by total_price;
组合查询(不去重)
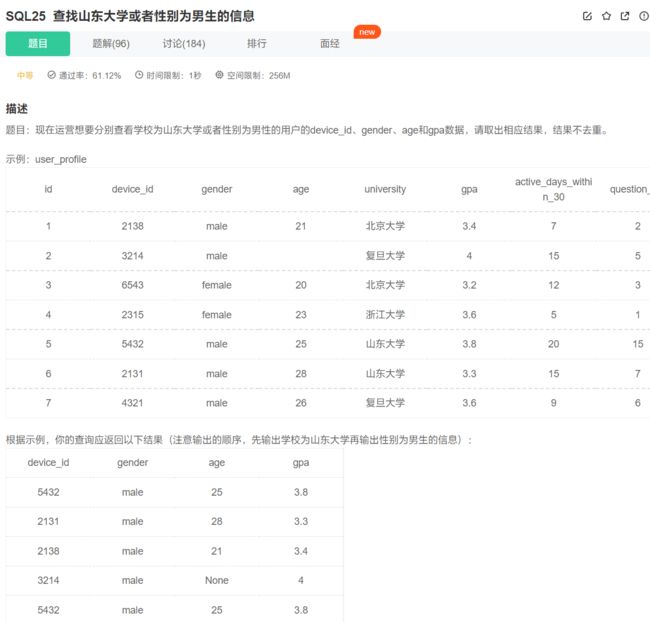
问题难点在于:选择出两个分别满足条件的数据后,不需要去重,直接放一起,怎么做?
限定条件:学校为山东大学或者性别为男性的用户:university=‘山东大学’, gender=‘male’;
分别查看&结果不去重:所以直接使用两个条件的or是不行的,直接用union也不行,要用union all,分别去查满足条件1的和满足条件2的,然后合在一起不去重
如果只使用union,默认是合并去重的,要加上all才不去重!
select
device_id, gender, age, gpa
from user_profile
where university='山东大学'
union all
select
device_id, gender, age, gpa
from user_profile
where gender='male'
常用函数——条件函数
case函数有两种用法:1、简单case函数 2、搜索case函数

在CASE结束后,要写上END,如果要另取别名,则需要使用as关键字。
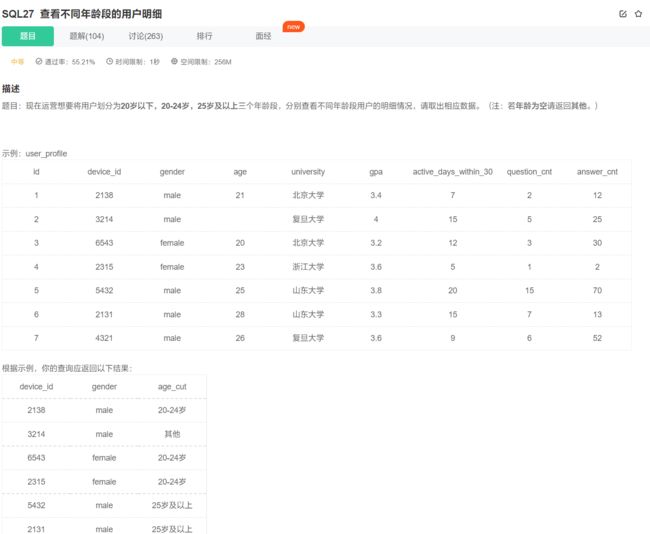
select
case
when age >= 25 then '25岁及以上'
when age < 25 or age is null then '25岁以下'
end as age_cut, count(*) as number
from user_profile
group by age_cut;
注意,case when 结束后末尾还有end!!
select device_id, gender,
case
when age < 20 then '20岁以下'
when age between 20 and 24 then '20-24岁'
when age >= 25 then '25岁及以上'
else '其他'
end
as age_cut
from user_profile;
常用函数——日期函数
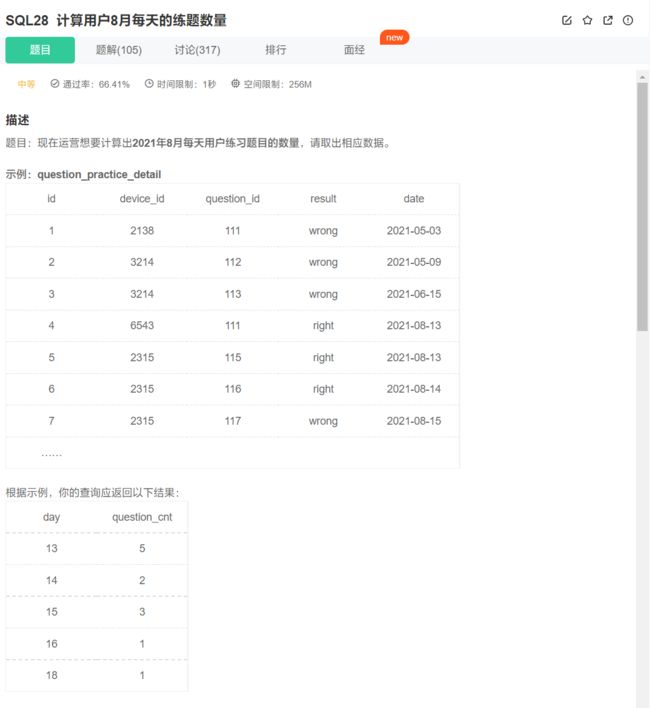
select day(date), count(*) from question_practice_detail
where year(date) = '2021' and month(date) = '8'
group by day(date);
select COUNT(distinct q2.device_id,q2.date)/count(DISTINCT q1.device_id,q1.date) as avg_ret
from question_practice_detail as q1 left join question_practice_detail as q2
on q1.device_id = q2.device_id and datediff(q2.date, q1.date) = 1;
首先,我们需要统计出总用户数,其次又需要统计出两天都来刷题的用户数,我们使用q1 left join q2,也就是说会保留q1中的每条数据,但q2连接过来可能会有列为null的情况。
因为left join导致q1没有none,所以去重计算出来的是用户总数,而q2部分没连接成功的为none,计算出来的是隔天有重复使用的用户的部分。
常用函数——文本函数
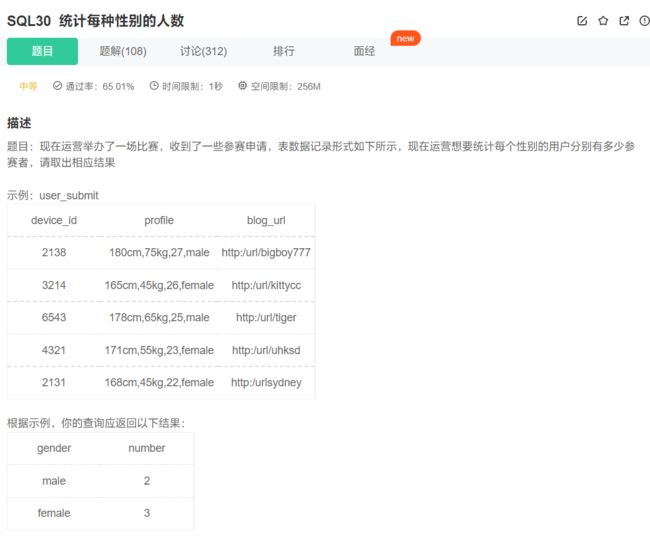
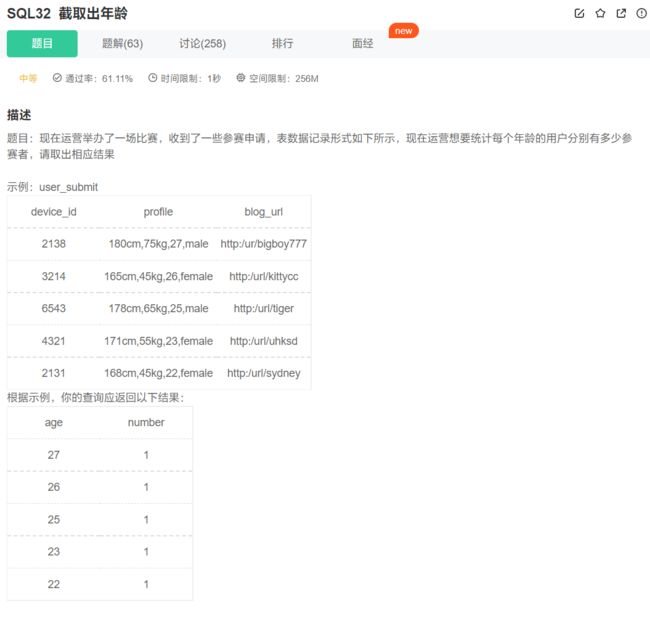
就是使用like函数去匹配字符串,_用于匹配单个字符,%用于匹配0个或多个字符:
select
case
when profile like '%,male' then 'male'
when profile like '%,female' then 'female'
end
as gender,
count(*)
from user_submit
group by gender;
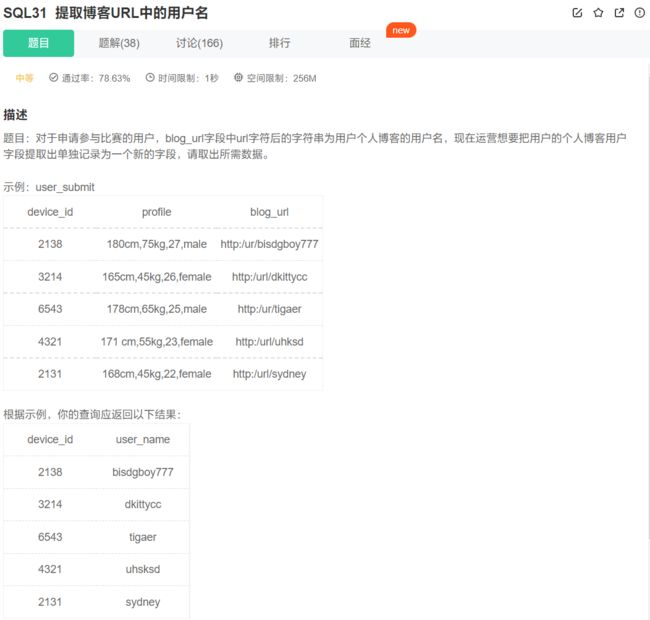
使用substring_index去获取字符串中的子串,同时还可以指定子串划分的标志,以及从第几个位置开始取子串取到末尾:
注意substring_index函数,取子串时,下标从1开始,而不是0
select
device_id,
substring_index(blog_url,'/',-1) as user_name
from user_submit;
select substring_index(substring_index(profile, ',', -2), ',', 1) as age, count(*)
from user_submit
group by age;
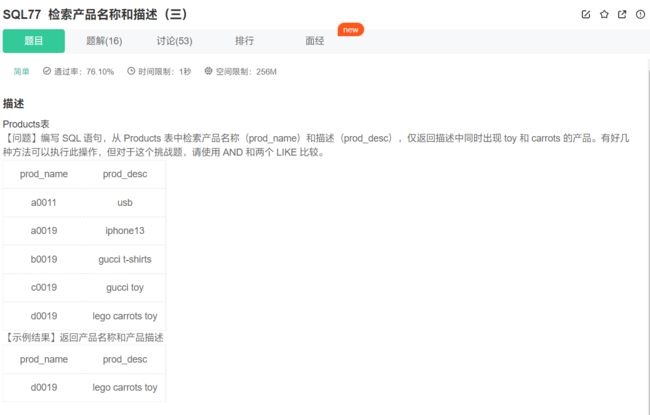
select prod_name, prod_desc from Products where prod_desc like '%toy%' and prod_desc like '%carrots%';
常用函数——窗口函数
SELECT
device_id,
university,
gpa
FROM
user_profile as u
WHERE
# 子查询,查询当前学校的最低gpa
gpa = (SELECT MIN(gpa) FROM user_profile WHERE university = u.university)
ORDER BY
university
如果子查询的执行依赖于外部查询,通常情况下都是因为子查询中的表用到了外部的表,并进行了条件关联,因此每执行一次外部查询,子查询都要重新计算一次,这样的子查询就称之为关联子查询。
相关子查询按照一行接一行的顺序执行,主查询的每一行都执行一次子查询。 注意,是主查询的每一行都要执行一次子查询!!!
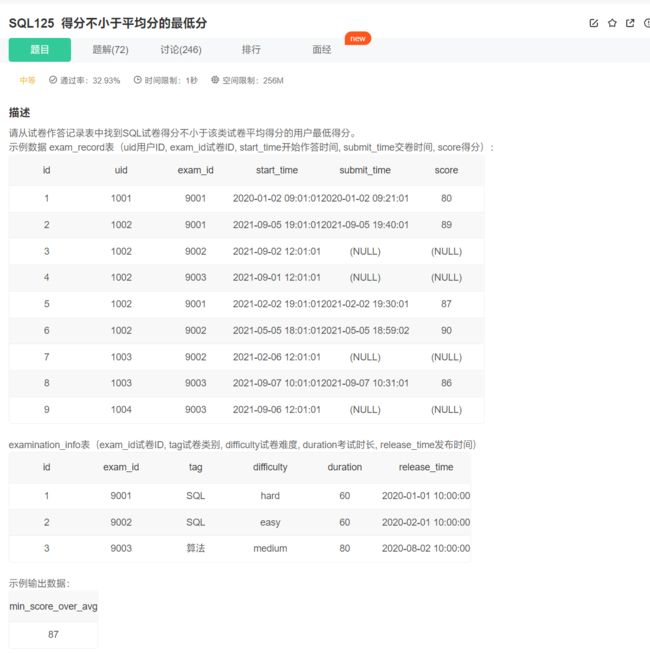
# SQL试卷得分不小于该类试卷平均得分的用户最低得分
select min(score) as min_score_over_avg from exam_record as er
join examination_info as ei using(exam_id)
where
tag = 'SQL'
and
score >=
(select avg(score) from exam_record join examination_info using(exam_id)
where tag = 'SQL'
);
如果想用聚合函数作为过滤条件,要么在where中使用子查询,要么在having中使用,对分组后数据进行过滤。
综合练习

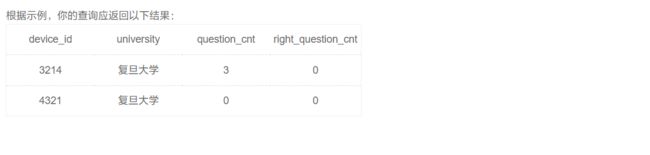
因为需要统计上没有答题的用户,所以应该采用left join,以用户所有数据为主体:
select
device_id, university,
count(qpd.question_id) as question_cnt,
sum(case when result = 'right' then 1 else 0 end) as right_question_cnt
from user_profile as up
left join question_practice_detail as qpd
using(device_id)
# 写上month is null,避免漏掉没有答题的同学
where university = '复旦大学' and (month(qpd.date) = 8 or month(qpd.date) is null)
group by device_id;
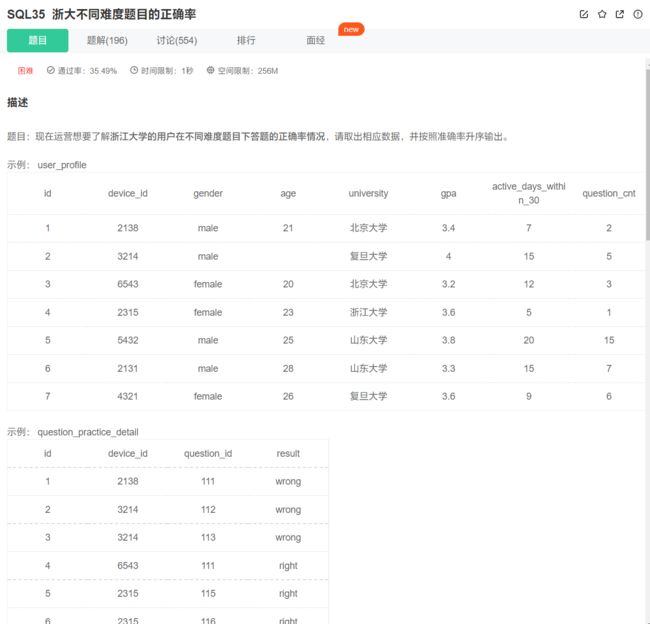
select difficult_level,
sum(case when result = 'right' then 1 else 0 end) / count(*) as correct_rate
from user_profile as up
join question_practice_detail as qpd using(device_id)
join question_detail as qd using(question_id)
where university = '浙江大学'
group by difficult_level
order by correct_rate;
注意case语句的妙用,使用case语句比if语句更简单易懂。
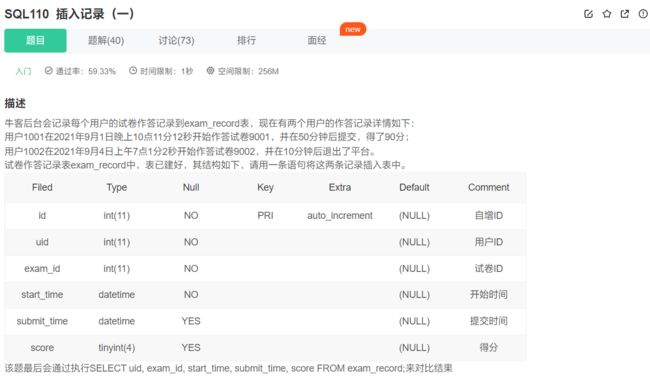
增删改
insert
两种insert方法:
insert into exam_record (uid, exam_id, start_time, submit_time, score)
values(1001, 9001, '2021-09-01 22:11:12', '2021-09-01 23:01:12', 90),
(1002, 9002, '2021-09-04 07:01:02', null, null);
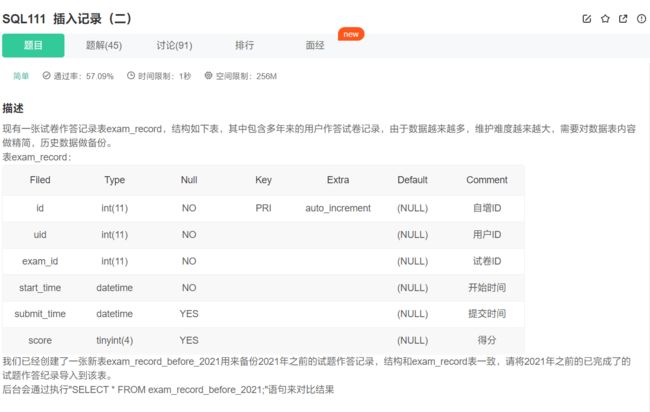
第二种是通过从其他地方select数据用于保存:
insert into exam_record_before_2021(uid, exam_id, start_time, submit_time, score) select uid, exam_id, start_time, submit_time, score
from exam_record where year(submit_time) < 2021;
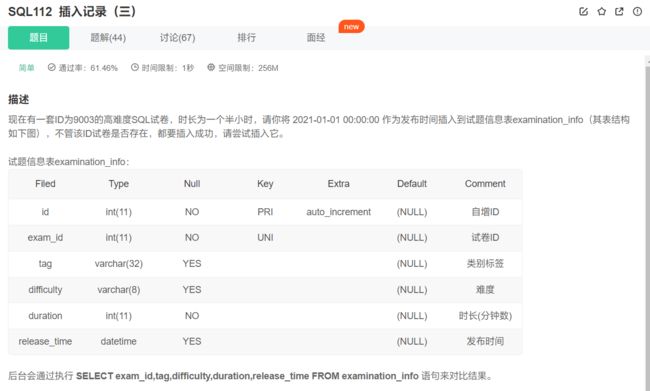
已有重复数据的插入?
replace into examination_info (exam_id, tag, difficulty, duration, release_time)
values(9003, 'SQL', 'hard', '90', '2021-01-01 00:00:00');
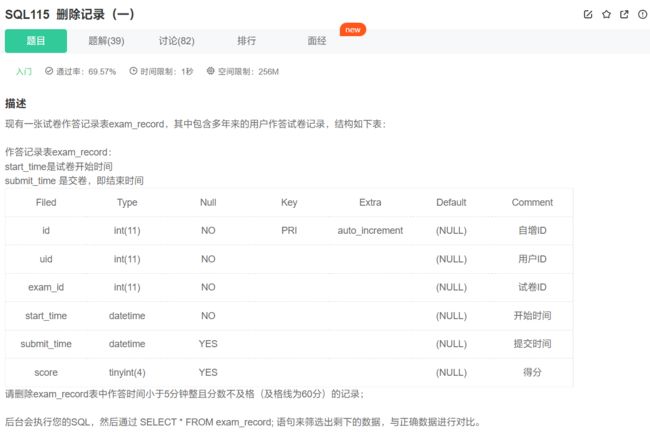
删除
timestampdiff求时间差
delete from exam_record where timestampdiff(MINUTE, start_time, submit_time) < 5 and score < 60;
使用order by + limit 返回top n 的数据
delete from exam_record where submit_time is null or timestampdiff(minute, start_time, submit_time) < 5 order by start_time limit 3;
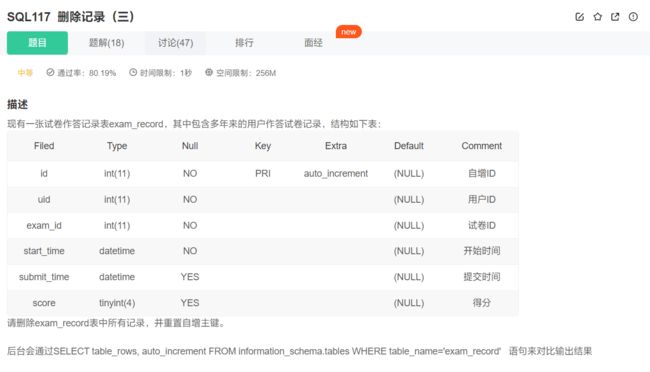
删除整张表的记录 并 重置自增型主键
truncate table exam_record;
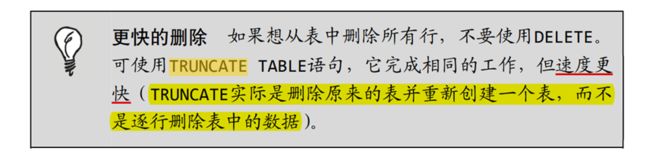
创建表
create table user_info_vip(
id int primary key auto_increment comment '自增ID',
uid int unique not null comment '用户ID',
nick_name varchar(64) comment '昵称',
achievement int default 0 comment '成就值',
level int comment '用户等级',
job varchar(32) comment '职业方向',
register_time datetime default current_timestamp comment '注册时间'
) default charset=utf8;
可以使用comment字段指定每一列的属性值