BM85 验证IP地址
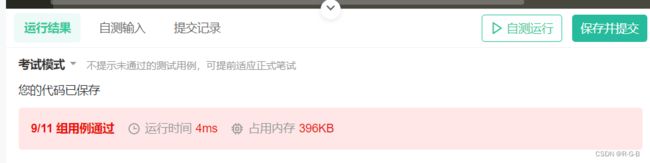
- 1 题目
- 2 实现
-
- 2.1 自己写
- 2.2 官解1 分割字符串比较法(推荐使用)
-
- 2.2.1 在a-f ,A-F范围 不在该范围表述
- 3 涉及函数讲解
-
- 3.1 string::find()函数和string::npos函数的介绍
- 3.2 erase()函数
- 3.3 字符串截取 s.substr()
- 3.4 字符是否为数字 isdigit(c)
- 3.5 n进制字符串转十进制 stoi()
1 题目
描述
编写一个函数来验证输入的字符串是否是有效的 IPv4 或 IPv6 地址
IPv4 地址由十进制数和点来表示,每个地址包含4个十进制数,其范围为 0 - 255, 用(“.”)分割。比如,172.16.254.1;
同时,IPv4 地址内的数不会以 0 开头。比如,地址 172.16.254.01 是不合法的。
IPv6 地址由8组16进制的数字来表示,每组表示 16 比特。这些组数字通过 (“:”)分割。比如, 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334 是一个有效的地址。而且,我们可以加入一些以 0 开头的数字,字母可以使用大写,也可以是小写。所以, 2001:db8:85a3:0:0:8A2E:0370:7334 也是一个有效的 IPv6 address地址 (即,忽略 0 开头,忽略大小写)。
然而,我们不能因为某个组的值为 0,而使用一个空的组,以至于出现 (: 的情况。 比如, 2001:0db8:85a3::8A2E:0370:7334 是无效的 IPv6 地址。
同时,在 IPv6 地址中,多余的 0 也是不被允许的。比如, 02001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334 是无效的。
说明: 你可以认为给定的字符串里没有空格或者其他特殊字符。
数据范围:字符串长度满足5≤n≤50
进阶:空间复杂度 O(n),时间复杂度 O(n)
2 实现
2.1 自己写
string solve(string IP) {
// write code here
int n = IP.size();
int point = 0;
int maohao = 0,k=0;
//长度超出、为0,不是IP
if(n > 39 || n < 7 || n == 0) return "Neither";
//IPv4
if(n >= 7 && n<= 15){//IPv4
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(IP[i] < '0') return "Neither";//
if(IP[i] == '.'){
point ++; k = 0;
if(IP[i - 1] == '.') return "Neither";//某字段长度为0
if(IP[i + 1] == '.') return "Neither";//某字段长度为0
}
else if(IP[i] != '.') {
++k;
//大于255,非零数字以0开头,不是IP
if(k == 3 && (IP[i] > '5' || IP[i-1] >'5' || IP[i - 2] > '2' || IP[i - 2] == '0')) return "Neither";
if(k == 2 && IP[i - 1] == '0') return "Neither";
if(k > 3) return "Neither";
}
}
if(point == 3)
return "IPv4";
}
//IPv6
if(n >15 && n<= 39){//IPv6
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(IP[i] < '0') return "Neither";
if(IP[i] == ':'){
maohao ++; k=0;
if(IP[i - 1] == ':') return "Neither";//某字段长度为0
if(IP[i + 1] == ':') return "Neither";
}
else if(IP[i] != ':') {
++k;
if(k > 4 ) return "Neither";
//不能出现a-fA-F以外的大小写字符
if(IP[i] < 'a' || IP[i] < 'A' || IP[i] > 'f' || IP[i] > 'F') return "Neither";
}
}
if(maohao == 7)
return "IPv6";
}
return "Neither";
}
2.2 官解1 分割字符串比较法(推荐使用)
思路:
我们可以先对IP字符串进行分割,然后依次判断每个分割是否符合要求。
具体做法:
step 1:写一个split函数(或者内置函数)。
step 2:遍历IP字符串,遇到.或者:将其分开储存在一个数组中。
step 3:遍历数组,对于IPv4,需要依次验证分组为4,分割不能缺省,没有前缀0或者其他字符,数字在0-255范围内。
step 4:对于IPv6,需要依次验证分组为8,分割不能缺省,每组不能超过4位,不能出现除数字小大写a-f以外的字符。
true的情况要多于false的情况的情况;
将true的情况都讨论了,剩下的就true;
若果,true和false混合都判断,,会有漏洞,部分不通过
string solve(string IP) {
// write code here
if(IP.size() == 0) return "Neither";
if(isIPv4(IP)) return "IPv4";
else if(isIPv6(IP)) return "IPv6";
return "Neither";
}
//对IP字符串进行分割, //将字符串从.或者:分割开
vector split(string str,string spliter){
int i;
vector res;
while((i = str.find(spliter)) && i != str.npos){ //如果找到了合法的分隔符,将分隔符前面的字段存入res
res.push_back(str.substr(0, i));
str = str.substr(i + 1);//从下一个位置开始到结尾,更新为新的str
}
//退出循环前,前三组已经存入res,第四组后面没有“:”,没得到
res.push_back(str);
return res;
}
//判断是否是IPv4
bool isIPv4(string str){
vector s = split(str,".");
//IPv4必定为4组
if(s.size() != 4)
return false;
//不可缺省,有一个分割为零,说明两个点相连
for(int i = 0;i < s.size(); i++){
//比较数字位数不为0,不超过3,不能有前缀零
if(s[i].size() <=0 || s[i].size() > 3 || (s[i][0] == '0' && s[i].size() > 1)) return false;
//遍历每个分割字符串,必须为数字
for(int j = 0; j < s[i].size(); j++)
if(!isdigit(s[i][j])) return false;
//转化为数字比较,0-255之间
if(stoi(s[i]) < 0 || stoi(s[i]) > 255) return false;
}
return true;
}
//判断是否是IPv6
bool isIPv6(string str){
vector s = split(str,":");
//IPv6必定为8组
if(s.size() != 8) return false;
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++){
//每个分割不能缺省,不能超过4位
if(s[i].size() == 0 || s[i].size() > 4 ) return false;
for(int j = 0; j < s[i].size(); j++){
//如果是字母,不能出现a-f A-F以外的大小写字符
if(!isdigit(s[i][j]))
if(!((s[i][j] >= 'a' && s[i][j] <= 'f') || (s[i][j] >= 'A' && s[i][j] <= 'F'))) return false;
// 下面if,判断字母不在a-f ,A-F范围内,,,写法严重错误,,,很久才发现,,
// A~Z对应 65~90,a~z对应97~122,,,
// < 'a' 或< 'A'为false,大写子字母全都是小于a的,都为false?
//if(!isdigit(s[i][j]) && (s[i][j] < 'a' || s[i][j] < 'A' || s[i][j] > 'f' || s[i][j] > 'F')) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
2.2.1 在a-f ,A-F范围 不在该范围表述
//如果是字母,不能出现a-f A-F以外的大小写字符
if(!isdigit(s[i][j]))
if(!((s[i][j] >= 'a' && s[i][j] <= 'f') || (s[i][j] >= 'A' && s[i][j] <= 'F'))) return false;
// 下面if,判断字母不在a-f ,A-F范围内,,,写法严重错误,,,很久才发现,,
// A~Z对应 6590,az对应97~122,,,
// < ‘a’ 或< 'A’为false,大写子字母全都是小于a的,都为false?
//if(!isdigit(s[i][j]) && (s[i][j] < 'a' || s[i][j] < 'A' || s[i][j] > 'f' || s[i][j] > 'F')) return false;
下面写法,也会有漏洞,部分不通过
if(!isdigit(s[i][j])) //是字母,且在a-f ,A-F范围内,true
if((s[i][j] >= 'a' && s[i][j] <= 'f') || (s[i][j] >= 'A' && s[i][j] <= 'F')) return true;
}
}
return true;
3 涉及函数讲解
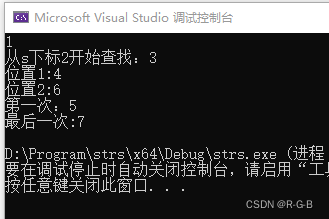
3.1 string::find()函数和string::npos函数的介绍
string::find()函数:是一个字符或字符串查找函数,该函数有唯一的返回类型,即string::size_type,即一个无符号整形类型,可能是整数也可能是长整数。
如果查找成功,返回按照查找规则找到的第一个字符或者子串的位置;
string::npos参数 —— npos 是一个常数,用来表示不存在的位置;
//如果字符串不存在包含关系,那么返回值就一定是npos
if(a.find(b)!=string::npos){
cout<<"yes"<string::size_type pos;
str.find(“字符串”) 返回值是字符在母串s中的下标位置;
str.find(“字符串”,9) 从s的下标9开始,查找字符串,返回字符串在s中的下标;
pos=s.find(str,pos) 查找s中str出现的所有位置。
pos=s.find_first_of(str) 返回str出现在母串s中的首次出现的位置
pos=s.find_last_of(str) 返回str出现在母串s中的最后一次出现的位置
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s("abcbcdcd");
string str="cd";
string::size_type pos;
pos=s.find("bc");
if(pos!=s.npos){
cout< 3.2 erase()函数
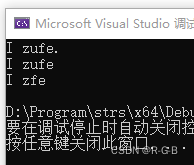
erase函数的原型如下:
(1)string& erase ( size_t pos = 0, size_t n = npos );
(2)iterator erase ( iterator position );
(3)iterator erase ( iterator first, iterator last );
也就是说有三种用法:
(1)erase(pos,n); 删除从pos开始的n个字符,比如erase(0,1)就是删除第一个字符
(2)erase(position);删除position处的一个字符(position是个string类型的迭代器)
(3)erase(first,last);删除从first到last之间的字符(first和last都是迭代器)
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s("I love zufe.");
string::iterator it;
s.erase(1,5);//删除从1开始的5个字符
cout< 3.3 字符串截取 s.substr()
substr有2种用法:
假设:string s = “0123456789”;
string sub1 = s.substr(5); //只有一个数字5表示从下标为5开始一直到结尾:sub1 = “56789”
string sub2 = s.substr(5, 3); //从下标为5开始截取长度为3位:sub2 = “567”
3.4 字符是否为数字 isdigit©
isdigit©是C语言中的一个函数,
isdigit()在ctype.h头文件中声明。
用于检查输入的字符是否为数字字符[0-9]。
如果是数字,则返回非零值,否则返回0。
cout << isdigit('9'); // Output: 1
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
char str[] = "hj;pq910js4";
int check;
cout << "The digit in the string are:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(str); i++) {
// check if str[i] is a digit
check = isdigit(str[i]);
if (check)
cout << str[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出
The digit in the string are:
9
1
0
4
3.5 n进制字符串转十进制 stoi()
使用之前要包含头文件#include< string >
(stoi就是string to int 的缩写)
stoi(字符串,起始位置,几进制);
stoi(str),将数字字符转化位int输出;
string str = "111111";
int a = stoi(str);
cout << a << endl;//输出111111