图像特征描述子之BRISK
原文站点:https://senitco.github.io/2017/07/12/image-feature-brisk/
BRISK(Binary Robust Invariant Scalable Keypoints)是BRIEF算法的一种改进,也是一种基于二进制编码的特征描述子,而且对噪声鲁棒,具有尺度不变性和旋转不变性。
特征点检测
BRISK主要利用FAST算法进行特征点检测,为了满足尺度不变性,BRISK构造图像金字塔在多尺度空间检测特征点。
构建尺度空间
尺度空间包含n个octave( ci 表示)和n个intro-octave( di 表示),原论文中n=4。 c0 是原始图像, ci+1 是 ci 的降采样图像,缩放因子为2,即 ci+1 的宽高分别为 ci 的1/2; d0 是相对于原图缩放因子为1.5的降采样图像,同样, di+1 是 di 的2倍降采样。 ci 、 di 与原图像的大小关系如下表所示。
| image | c0 | d0 | c1 | d1 | c2 | d2 | c3 | d3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| width | w | 2w/3 | w/2 | w/3 | w/4 | w/6 | w/8 | w/12 |
| height | h | 2h/2 | h/2 | h/3 | h/4 | h/6 | h/8 | h/12 |
由于n = 4,一共可以得到8张不同尺度的图像。在多尺度空间中,利用FAST9-16检测算子定位特征点,即在特征点邻域边界圆上的16个像素,至少有9个连续像素与特征点的灰度差值大于给定阈值T。此外,对原图像进行一次FAST5-8角点检测,作为 d_−1 层,方便后续在做非极大值抑制处理时,可以对相邻尺度空间的图像特征点进行比对。在前面博文中已详细介绍FAST角点检测。
非极大值抑制
对多尺度空间的9幅图像进行非极大值抑制,与SIFT算法类似,在特征点的图像空间(8邻域)和尺度空间(上下两层18邻域)共26个邻域点做比较,FAST响应值须取得极大值,否则不能作为特征点。由于是在离散坐标空间中,特征点的位置比较粗糙,还需进一步精确定位。
亚像素精确定位
得到图像特征点的坐标和尺度信息后,在极值点所在层及其上下层所对应的位置,对3个相应关键点的FAST响应进行二维二次函数插值(x,y方向),得到二维平面精确的极值点位置和响应值后,再对尺度方向进行一维插值,得到特征点所对应的精确尺度。

特征点描述
给定一组特征点(包含亚像素图像位置和浮点型尺度值),BRISK通过比较邻域Patch内像素点对的灰度值,并进行二进制编码得到特征描述子。为了满足旋转不变性,需要选取合适的特征点主方向。
采样模式和旋转估计
特征点邻域的采样模式如下图所示,以特征点为中心,构建不同半径的同心圆,在每个圆上获取一定数目的等间隔采样点,所有采样点包括特征点一共有 N 个。由于这种采样模式会引起混叠效应,需要对所有采样点进行高斯滤波,滤波半径r和高斯方差 σ 成正比,同心圆半径越大,采样点滤波半径也越大。

N 个采样点两两组合共有N(N−1)2个点对,用集合 A 表示, I(pi,σi) 为像素灰度值, σ 表示尺度,用 g(pi,pj) 表示特征点局部梯度值,其计算公式为
采样点对的集合表示为
定义短距离点对子集 S 和长距离点对子集 L
式中,阈值分别设置为 σmax=9.57t,σmin=13.67t , t 是特征点所在的尺度。特征点的主方向计算如下(此处仅用到了长距离点对子集):
长距离的点对均参与了运算,基于本地梯度互相抵消的假设,全局梯度的计算是不必要的。
生成描述子
要解决旋转不变性,需要对特征点周围的采样区域旋转至主方向,得到新的采样区域,采样模式同上。采样点集合中包含 N(N−1)2 个采样点对,考虑其中短距离点对子集中的512个点对,进行二进制编码,编码方式如下:
pαi 表示旋转角度 α 后的采样点。由此得到512bit也就是64Byte的二进制编码(BRISK64)。
特征点匹配
BRISK特征匹配和BRIEF一样,都是通过计算特征描述子的Hamming距离来实现。
算法特点
简单总结,BRISK算法具有较好的尺度不变性、旋转不变性,以及抗噪性能。在图像特征点的检测与匹配中,计算速度优于SIFT、SURF,而次于FREAK、ORB。对于较模糊的图像,能够取得较为出色的匹配结果。
Experiment & Result
OpenCV实现BRISK特征检测与描述
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//Load Image
Mat c_src1 = imread( "1.png");
Mat c_src2 = imread("2.png");
Mat src1 = imread( "1.png", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
Mat src2 = imread( "2.png", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
if( !src1.data || !src2.data )
{
cout<< "Error reading images " << std::endl;
return -1;
}
//feature detect
BRISK detector;
vector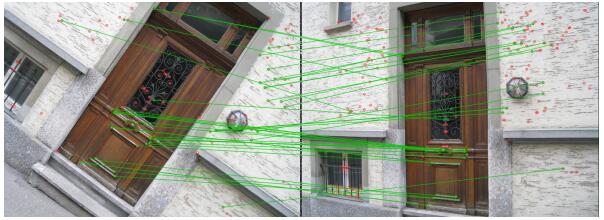
OpenCV中BRISK算法的部分源码实现
// construct the image pyramids
void BriskScaleSpace::constructPyramid(const cv::Mat& image)
{
// set correct size:
pyramid_.clear();
// fill the pyramid:
pyramid_.push_back(BriskLayer(image.clone()));
if (layers_ > 1)
{
pyramid_.push_back(BriskLayer(pyramid_.back(), BriskLayer::CommonParams::TWOTHIRDSAMPLE));
}
const int octaves2 = layers_;
for (uchar i = 2; i < octaves2; i += 2)
{
pyramid_.push_back(BriskLayer(pyramid_[i - 2], BriskLayer::CommonParams::HALFSAMPLE));//
pyramid_.push_back(BriskLayer(pyramid_[i - 1], BriskLayer::CommonParams::HALFSAMPLE));//
}
}
//extract the feature points
void BriskScaleSpace::getKeypoints(const int threshold_, std::vectorreference
- Paper: BRISK: Binary Robust Invariant Scalable Keypoints
- http://blog.csdn.net/jinxueliu31/article/details/18556855
- http://blog.csdn.net/hujingshuang/article/details/47045497
- http://blog.csdn.net/luoshixian099/article/details/50731801
- http://www.cnblogs.com/ronny/p/4260167.html