数据库基础篇二
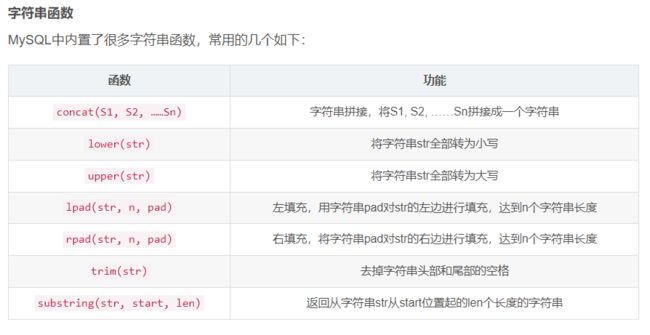
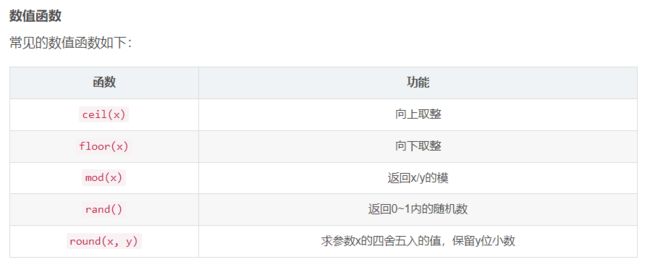
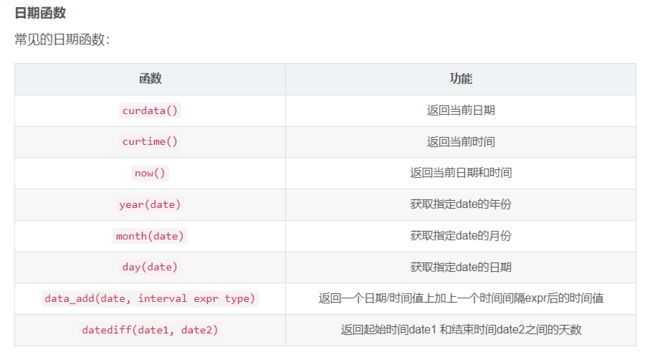
函数
约束
概述
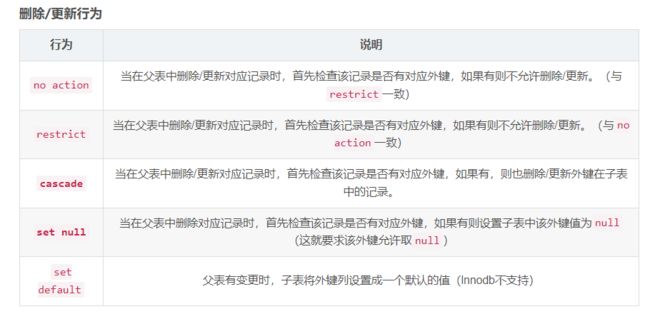
外键约束
外键用来让两张表的数据之间建立连接,从而保证数据的一致性和完整性。
添加外键
alter table 表名 add constraint 外键名称 foreign key(外键字段名) references 主表(主表列名);
删除外键
alter table 表名 drop foreign key 外键名称;
多表查询
内连接
- 隐式内连接
select 字段列表 from 表1,表2 where 条件……;- 显式内连接
select 字段列表 from 表1 [inner] join 表2 on 连接条件……;外连接
外连接查询语法:
左外连接
select 字段列表 from 表1 left [outer] join 表2 on 条件……;
相当于查询字段1(左表)的所有数据包含表1和表2交集部分的数据
右外连接
select 字段列表 from 表1 right [outer] join 表2 on 条件……;
相当于查询表2(右表)的所有数据包含表1和表2交集部分数据
自连接
自连接查询语法:
select 字段列表 from 表A 别名A join 表名A 别名B on 条件……;
自连接查询,可以是内连接,也可以是外连接查询。一定要起别名
联合查询 - union,union all(集合查询)
select 字段列表 from 表A ……
union [all]
select 字段列表 from 表B ……;
子查询
概念:SQL语句中嵌套select语句,称为嵌套语句,又称子查询。
select * from t1 where column1 = (select column1 from t2);
子查询外部的语句可以使insert / update / delete / select 的任何一个。
根据子查询结果不同,分为:
标量子查询(子查询结果为单个值)
列子查询(子查询结果为一列)
行子查询(子查询结果为一列)
表子查询(子查询结果为多行多列)
根据子查询位置,分为: where之后、from之后、select之后。
标量子查询
子查询返回的结果是单个值(数字、字符串、日期等),最简单地形式,这种子查询称为标量子查询
常用的操作符:= <> > >= < <=
# a. 查询”销售部“部门ID
select id from dept where name = '销售部';
# b. 根据销售部门ID,查询员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id = 4;
select * from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '销售部');
列子查询
子查询返回的结果是一列(可以是多行),这种查询称为列子查询
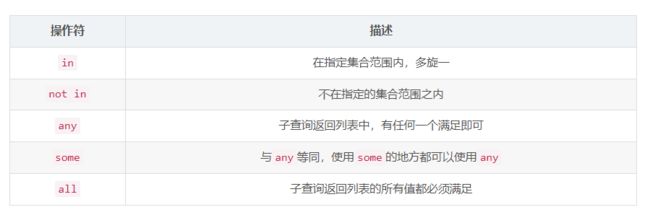
常用的操作符: in、 not in、 any 、some 、all
# 查询 销售部 和 市场部 的部门ID
select id from dept where name = '销售部' or name = '市场部';
# 根据部门ID,查询员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id in (select id from dept where name = '市场部' or name = '销售部');
行子查询
子查询返回的结果是一行(可以是多列),这种子查询称为行子查询。
常用的操作符:= 、 <> 、 in、 not in
# 行子查询
# 查询 张无忌 的薪资及直属领导相同的员工信息
select salary, managerid from emp where name = '张无忌';
# 查询与 张无忌 的薪资及直属领导相同的员工信息
select * from emp where (salary, managerid) = (select salary, managerid from emp where name = '张无忌');
表子查询
子查询返回的结果是多行多列,这种子查询称为表子查询。
常用的操作符:in
# 表子查询
# 查询 鹿杖客、宋远桥 的职位和薪资
select job, salary from emp where name = '鹿杖客' or name = '宋远桥';
# 查询与 鹿杖客、宋远桥 的职位和薪资相同的员工信息
select * from emp where (job, salary) in (select job, salary from emp where name = '鹿杖客' or name = '宋远桥');