Golang性能分析工具PProf的使用
简介
pprof 是一个强大的性能分析工具,可以捕捉到多维度的运行状态的数据,能够非常方便的监控代码运行性能。
用法
性能分析基础数据的获取有三种方式:
- runtime/pprof 包
- net/http/pprof 包
- go test 时添加收集参数
性能调优的两个方向:CPU和内存
-
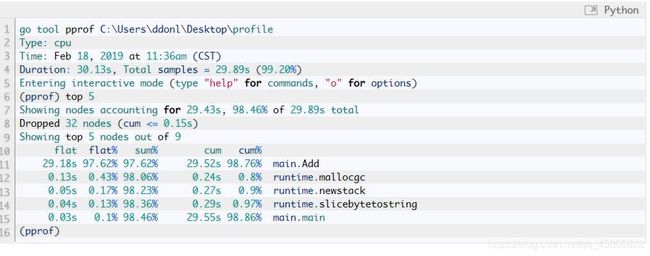
go tool pprof cpu.pprof
-
go tool pprof mem.pprof
runtime/pprof 包的使用[不推荐使用]
针对于应用程序,通过命令行的启动参数来生成prof文件,再使用go tool pprof工具进行分析,如
package main
import (
// "flag"
// "log"
// "os"
"runtime/pprof"
)
var cpuprofile = flag.String("cpuprofile", "", "write cpu profile to file")
func main() {
flag.Parse()
if *cpuprofile != "" {
f, err := os.Create(*cpuprofile)
// if err != nil {
// log.Fatal(err)
// }
err = pprof.StartCPUProfile(f)
// if err != nil {
// log.Fatal(err)
// }
defer pprof.StopCPUProfile()
}
// for {
// Add("test")
// }
}
// func Add(str string) string {
// data := []byte(str)
// sData := string(data)
// var sum = 0
// for i := 0; i < 10000; i++ {
// sum += i
// }
// return sData
// }
运行 ./app.exe -cpuprofile=cpu.prof
分析 go tool pprof cpu.prof
注意,实际测试时得到的cpu.prof文件总是为空,原因未知
net/http/pprof 包的使用[推荐]
net/http/pprof 对 runtime/pprof 进行了封装,并在http端口上暴露出来,入口为 IP:PORT/debug/pprof/
a>若应用为web服务器,只需引入包即可 _ “net/http/pprof”,会自动注册路由到/debug/pprof/
b>若为服务时程,可开启一个goroutine开启端口并监听,如
go func(){log.Println(http.ListenAndServe(":8080",nil))}()
package main
import (
"log"
"net/http"
_ "net/http/pprof"
)
func main() {
// 性能分析
go func() {
log.Println(http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil))
}()
// 实际业务代码
for {
Add("test")
}
}
func Add(str string) string {
data := []byte(str)
sData := string(data)
var sum = 0
for i := 0; i < 10000; i++ {
sum += i
}
return sData
}
访问 http://127.0.0.1:8080/debug/pprof/ 即可实时查看性能数据,业面如下:

其中 go tool trace 工具会打开 http://127.0.0.1:1089/ 通过网页方式显示结果
go test 时添加收集参数
需要创建测试文件
go test支持的参数非常多,如
-cpuprofile=cpu.prof
-memprofile=mem.prof
数据分析
命令行方式
对生成的profile文件,可使用go tool pprof profilename来分析,如
go tool pprof http://localhost:8080/debug/pprof/profile 默认采集需要30秒
go tool pprof http://localhost:8080/debug/pprof/heap
go tool pprof http://localhost:8080/debug/pprof/block
go tool pprof http://localhost:8080/debug/pprof/mutex
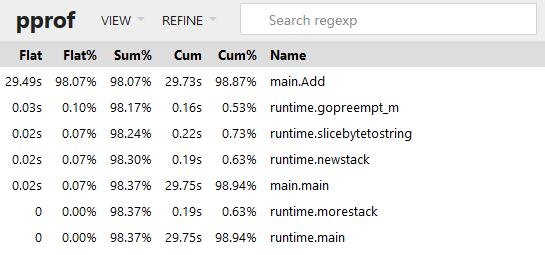
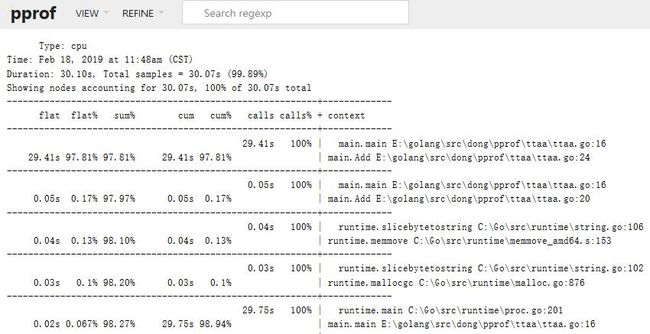
web可视化方式
在 go tool pprof 下输入 web 命令,注意默认端口为8080
go tool pprof -http=:8000 http://localhost:8080/debug/pprof/heap 查看内存使用
go tool pprof -http=:8000 http://localhost:8080/debug/pprof/profile 查看cpu占用
注意,需要提前安装 Graphviz 用于画图
下载地址:https://graphviz.gitlab.io/download/
windows:https://graphviz.gitlab.io/_pages/Download/windows/graphviz-2.38.zip
解压下,添加环境变量 Path下添加 C:\Go\graphviz\bin (这里我解压在 C:\Go\graphviz 目录)
测试:命令提示符下 dot -V # 打印版本信息
若是Linux,yum install graphviz # 默认安装版本为为2.30 依赖项较多
访问地址:http://localhost:8000/ui/
图形视图:面积超大,代表时间越长
top 视图:
火焰图
Peek:
代码视图:
简易指标输出 expvar
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
//"expvar"
//"net/http"
"fmt"
"runtime"
"time"
)
type Monitor struct {
Alloc uint64 `json:"堆内存"` // 堆内存字节分配数
TotalAlloc uint64 `json:"最大堆内存"` // 堆中分配最大字节数
Sys uint64 `json:"系统内存"` // 从系统中获得的总内存
Mallocs uint64 `json:"分配对象"` // 分配对象数
Frees uint64 `json:"释放对象"` // 释放对象数
LiveObjects uint64 `json:"存活对象"` // 存活对象数
PauseTotalNs uint64 `json:"GC时间"` // 总GC暂停时间
NumGC uint32 `json:"GC次数"`
NumGoroutine int `json:"协程数"` // goroutine数量
}
func NewMonitor(duration int) {
var m Monitor
var rtm runtime.MemStats
var interval = time.Duration(duration) * time.Second
//var goroutines = expvar.NewInt("num_goroutine")
for {
<-time.After(interval) // 时间间隔
// 读取内存状态信息
runtime.ReadMemStats(&rtm)
m.NumGoroutine = runtime.NumGoroutine()
//goroutines.Set(int64(m.NumGoroutine))
m.Alloc = rtm.Alloc
m.TotalAlloc = rtm.TotalAlloc
m.Sys = rtm.Sys
m.Mallocs = rtm.Mallocs
m.Frees = rtm.Frees
m.LiveObjects = m.Mallocs - m.Frees
m.PauseTotalNs = rtm.PauseTotalNs
m.NumGC = rtm.NumGC
b, _ := json.Marshal(m)
fmt.Println(string(b))
}
}
func main() {
go NewMonitor(1) // 性能数据
select {} // 业务逻辑
//http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil)
}
在正常程序中,添加 go NewMonitor(1) 每隔指定时间在控制台输出性能数据
此外,内置包 expvar 可以在/debug/vars 中输出cmdline、memstats的json数据,若要向其中添加输出内容,如输出 num_goroutine 用于显示协程数量,核心语句如下:
import "expvar"
var goroutines = expvar.NewInt("num_goroutine")
goroutines.Set(int64(m.NumGoroutine))
Go GC监控
GC 的认识
详细参考:https://github.com/qcrao/Go-Questions/blob/master/GC/GC.md
方式1:GODEBUG=gctrace=1
go build -o main
GODEBUG=gctrace=1 ./main
方式2:go tool trace
在代码中添加:
f, _ := os.Create(“trace.out”)
defer f.Close()
trace.Start(f)
defer trace.Stop()
然后运行程序,等程序运行完成,执行以下命令
go tool trace trace.out
需要等到程序执行完成 需要使用chrome浏览器(实测firefox有问题)
方式4:runtime.ReadMemStats
package main
import (
//"os"
//"runtime/trace"
"fmt"
"runtime"
"runtime/debug"
"time"
)
func allocate() {
_ = make([]byte, 1<<20)
}
// 以代码的方式实现对感兴趣指标的监控
func printGCStats() {
t := time.NewTicker(time.Second)
s := debug.GCStats{}
for {
select {
case <-t.C:
debug.ReadGCStats(&s)
fmt.Printf("gc %d last@%v, PauseTotal %v\n", s.NumGC, s.LastGC, s.PauseTotal)
}
}
}
// 直接通过运行时的内存相关的 API 进行监控
func printMemStats() {
t := time.NewTicker(time.Second)
s := runtime.MemStats{}
for {
select {
case <-t.C:
runtime.ReadMemStats(&s)
fmt.Printf("gc %d last@%v, next_heap_size@%vMB\n", s.NumGC, time.Unix(int64(time.Duration(s.LastGC).Seconds()), 0), s.NextGC/(1<<20))
}
}
}
func main() {
// 方式2:go tool trace
// f, _ := os.Create("trace.out")
// defer f.Close()
// trace.Start(f)
// defer trace.Stop()
// 方式3:debug.ReadGCStats
//go printGCStats()
// 方式4:runtime.ReadMemStats
go printMemStats()
for n := 1; n < 10000; n++ {
allocate()
}
}
文章转自:轻风博客 » Golang性能分析工具PProf的使用/Go GC监控