多线程案例2--阻塞队列
文章目录
-
- 阻塞队列
-
- 阻塞队列的特点
- 阻塞队列的应用场景
-
- 生产者消费者模型
- 利于代码解耦合
- 削峰填谷
- 阻塞队列的具体使用
-
- 标准库里的阻塞队列
- 自己实现阻塞队列
提到队列首先就会想到先进先出,但是并不是所有的队列都是先进先出的
PriorityQueue:优先级队列 元素会有优先级,入列和出列都按照优先级进行
消息队列也不是先进先出的, 消息队列入列没什么区别,但是出列会指定某个特定的类型先出
补充一下: 一般会把纤细队列单独实现成一个程序,并且部署在一组服务器上,使之变成一个"消息队列服务器",也就是"MQ",这是一种常见的"中间件"
中间件–一类通用的服务器的统称,有些程序是"专用的", 和具体业务相关
还有一些程序是通用的, 例如数据存储,这是十分通用的,所以MySQL也算是一种中间件
阻塞队列
阻塞队列的特点
阻塞队列是一种特殊的队列,它是先进先出的
线程安全
带有阻塞的功能
1)如果队列满了,还要继续入列,入列操作就会阻塞, 直到队列有位置, 才能进行入列
2)如果队列空了,还要集训出列,出列操作就会阻塞, 直到队列不为空,才难继续出列
阻塞队列的应用场景
生产者消费者模型
生产者线程: "生产"产品,并把产品方放到一个队列中
消费者模型: "消费"产品
一旦有了这个阻塞队列,生产者只管生产,消费者只管消费,这样子各个线程做自己的事,很好的解决了锁竞争的问题, 效率就会很高
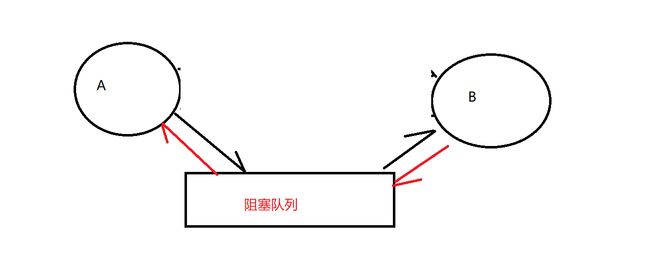
利于代码解耦合
现在有两段代码A和B,要是A和B进行直接通信,要是A出了问题,B也会跟着有问题,两者的耦合性就会很强,这不符合"低耦合"的思想
使用阻塞队列就能有效地降低耦合性
A和阻塞队列交互, B和阻塞队列交互,这就降低了耦合性
削峰填谷
要是没有生产者消费者模型,流量的压力会直接压到每一台服务器,一旦服务器的抗压能力不太行,就会挂掉
为什么服务器提同一时刻收到很多的请求就很容易挂掉?
服务器每处理一个请求,都要消耗一定的硬件资源(包括但不限于CPU 内存 硬盘 带宽),同一时刻的请求越多,小号的资源也就越多, 可是一台主机上的资源是有限的,一旦某一个资源耗尽了,服务器也就挂了
有了阻塞队列,就能承担部分流量的,使其他的一些程序正常运行
阻塞队列的具体使用
阻塞队列有三个基本的操作: 入队列 出队列 取出队首元素
标准库里的阻塞队列
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class Demo23 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<Integer> blockingQueue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(100);//给定100个大小
//put方法是带有阻塞功能的入队列方法,offer方法就没有阻塞功能,所以要用put
blockingQueue.put(10);
blockingQueue.put(20);
blockingQueue.put(30);
//take是带有阻塞功能的出队列
int ret = blockingQueue.take();
System.out.println(ret);
ret = blockingQueue.take();
System.out.println(ret);
ret = blockingQueue.take();
System.out.println(ret);
}
}
要是再使用 take 取一次,就会发现程序会先打印10 20 30 之后不会结束,会一直开在 take 那一行
以上就是java提供的阻塞队列,使用是很简单的
自己实现阻塞队列
实现步骤:
- 先实现一个普通队列
- 加上线程安全
- 加上阻塞的实现
基于数组的循环队列
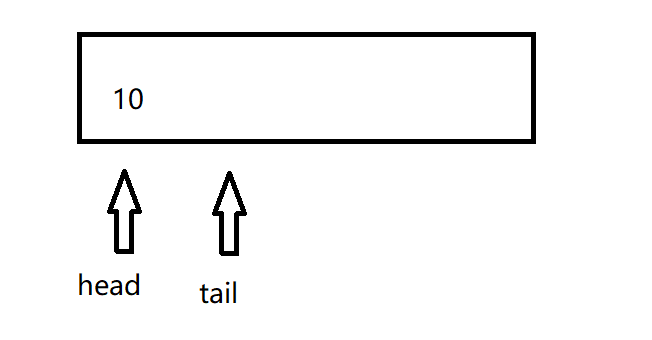
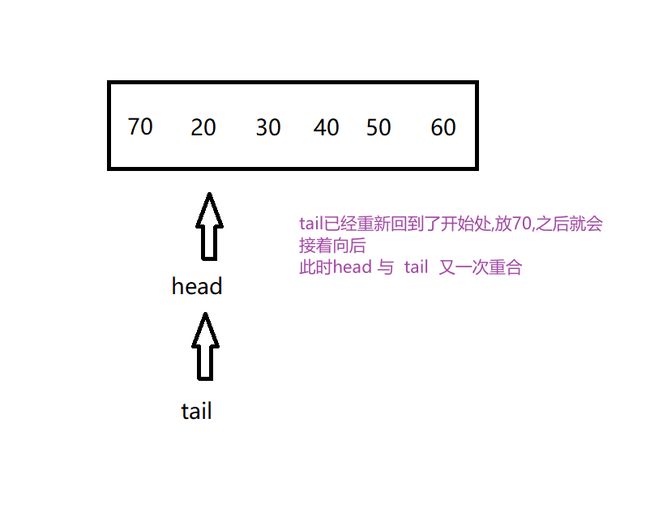
实现思路: 使用双指针法,定义两个指针在数组的开始处,只要放一个数字进去,tail就向后走一步,head保持不动,直到tail 走到最后,数组放满了,tail就重新回到开始处,要是取出元素就将head向后走一步,直到head走到最后就重新回到开始处, 循环队列在逻辑上是一个环
class MyBlockingQueue{
int[] arr = new int[1000]; //数组的最大容量
private int head = 0;
private int tail = 0;
private int size = 0;//队列元素的个数
public void put(int elem) {
//判断队列是否满了
if (size == arr.length) {
return;
}
arr[tail] = elem;
tail++;
if (tail >= arr.length) {
tail = 0;
}
//这里的if语句还能写成这样: tail = tail % arr.length;
//当tail == arr.length时,tail就变成了0,也能达到一样的效果
size++;
}
public Integer take() {
//判断队列是否为空
if (size == 0) {
return null;//要是为空就直接返回null,要是返回值是int的话,类型就不匹配,所以返回值是Ingeter
}
int ret = arr[head];
head++;
if (head >= arr.length) {
head = 0;
}
size--;
return ret;
}
}
//测试一下
public class Demo24 {
public static void main(String[] args){
MyBlockingQueue myBlockingQueue = new MyBlockingQueue();
myBlockingQueue.put(1);
myBlockingQueue.put(2);
myBlockingQueue.put(3);
int ret = myBlockingQueue.take();
System.out.println(ret);
ret = myBlockingQueue.take();
System.out.println(ret);
ret = myBlockingQueue.take();
System.out.println(ret);
Integer ret2 = myBlockingQueue.take();//此时队列已经是空了,所以返回的就是Integer类型的null
System.out.println(ret2);//输出null
}
}
//保证线程安全:
//加锁synchronized
//加上volatile
class MyBlockingQueue{
int[] arr = new int[1000]; //数组的最大容量
//一个小技巧: shift + alt + insert 进行列编辑,很适合这里加volatile
private volatile int head = 0;
private volatile int tail = 0;
private volatile int size = 0;
public void put(int elem) {
synchronized (this){
//判断队列是否满了
if (size == arr.length) {
return;
}
arr[tail] = elem;
tail++;
if (tail >= arr.length) {
tail = 0;
}
size++;
}
}
public Integer take() {
synchronized (this){
//判断队列是否为空
if (size == 0) {
return null;//要是为空就直接返回null,要是返回值是int的话,类型就不匹配,所以返回值是Ingeter
}
int ret = arr[head];
head++;
if (head >= arr.length) {
head = 0;
}
size--;
return ret;
}
}
}
要想加上阻塞功能, 就要使用wait notify
//加上阻塞功能
class MyBlockingQueue{
int[] arr = new int[1000]; //数组的最大容量
//一个小技巧: shift + alt + insert 进行列编辑,很适合这里加volatile
private volatile int head = 0;
private volatile int tail = 0;
private volatile int size = 0;
public void put(int elem) throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this){
//判断队列是否满了
// 要是队列满了就阻塞,直到队列腾出了位置,才会被唤醒
if (size == arr.length) {
this.wait();
}
arr[tail] = elem;
tail++;
if (tail >= arr.length) {
tail = 0;
}
size++;
this.notify();
}
}
public Integer take() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this){
//判断队列是否为空
if (size == 0) {
//要是队列为空,就阻塞,直到队列不为空
this.wait();
}
int ret = arr[head];
head++;
if (head >= arr.length) {
head = 0;
}
size--;
this.notify();
return ret;
}
}
}
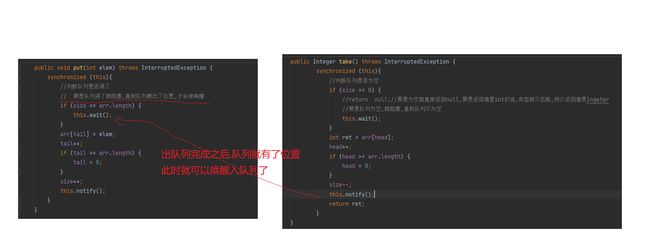
注意: 这里的队列是不会出现同时阻塞的, 因为两个阻塞的if 是完全不一样的
但是还是有问题的,take里面的 if 是发现队列为空就阻塞,等待put唤醒,但是不能保证唤醒之后队列就不为空了! (万一其他线程调用了interrupt, 这个线程就有可能被提前唤醒,) 所以还是有风险的,所以要进行再次判断是否为空,为了保险起见,直接使用while进行多次判断是最好的办法
加上while之后,要是发现队列还是空,就接着wait等待
总结阻塞队列的实现:
- 实现一个简单的循环队列
- 保证线程安全 synchronized volatile
- 加上阻塞的功能 wait notify while循环判断
class MyBlockingQueue{
int[] arr = new int[1000]; //数组的最大容量
//一个小技巧: shift + alt + insert 进行列编辑,很适合这里加volatile
private volatile int head = 0;
private volatile int tail = 0;
private volatile int size = 0;
public void put(int elem) throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this){
//判断队列是否满了
// 要是队列满了就阻塞,直到队列腾出了位置,才会被唤醒
if (size == arr.length) {
this.wait();
}
arr[tail] = elem;
tail++;
if (tail >= arr.length) {
tail = 0;
}
size++;
this.notify();
}
}
public Integer take() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this){
//判断队列是否为空
if (size == 0) {
//return null;//要是为空就直接返回null,要是返回值是int的话,类型就不匹配,所以返回值是Ingeter
//要是队列为空,就阻塞,直到队列不为空
this.wait();
}
int ret = arr[head];
head++;
if (head >= arr.length) {
head = 0;
}
size--;
this.notify();
return ret;
}
}
}
public class Demo24 {
public static void main(String[] args){
MyBlockingQueue queue = new MyBlockingQueue();
Thread producer = new Thread (()->{
int n = 1;
while (true) {
try {
queue.put(n);
System.out.println("生产元素 " + n);
n++;
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
Thread customer = new Thread(()->{
while (true) {
try {
int n = queue.take();
System.out.println("消费元素 "+ n);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
producer.start();
customer.start();
}
}