Android组件通信——Intent(二十三)
1. 认识Intent
1.1 知识点
(1)了解Intent的主要作用;
(2)掌握Activity程序对Intent操作的支持;
(3)可以使用Intent完成Activity程序间的跳转,也可以通过Intent接收返回数据
1.2 具体内容
以下用一个intent在Activity之间进行跳转的例子说明:
package com.example.intentproject;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class IntentActivity extends Activity {
Button but = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_intent_first);
but = (Button) super.findViewById(R.id.but_first);
but.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent(IntentActivity.this,SecondActivity.class);//创建Intent对象,并指定跳转的Activity
intent.putExtra("msg", "你好,我是来自毛栗子的第一个Activity");
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
}
package com.example.intentproject;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class SecondActivity extends Activity {
TextView tv = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_intent_second);
Intent intent = getIntent();//接收Intent对象
String msg = intent.getStringExtra("msg");
tv = (TextView) super.findViewById(R.id.tv_second);
tv.setText(msg);//显示信息
}
}
完成以上程序编写之后,不要忘记去主配文件当中去查看,新建的Activity是否已经注册。
package com.example.intentproject;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class IntentActivity extends Activity {
Button but = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_intent_first);
but = (Button) super.findViewById(R.id.but_first);
but.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent(IntentActivity.this,SecondActivity.class);//创建Intent对象,并指定跳转的Activity
intent.putExtra("msg", "你好,我是来自毛栗子的第一个Activity");
IntentActivity.this.startActivityForResult(intent, 1);//启动intent对象
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode,int resultCode,Intent data){
switch(resultCode){
case RESULT_OK:
TextView tv = (TextView) super.findViewById(R.id.tv_first);
tv.setText(data.getStringExtra("returnmsg"));
break;
case RESULT_CANCELED:
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
package com.example.intentproject;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class SecondActivity extends Activity {
TextView tv = null;
Button but = null;
Intent intent = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_intent_second);
Intent intent = getIntent();//接收Intent对象
String msg = intent.getStringExtra("msg");
tv = (TextView) super.findViewById(R.id.tv_second);
tv.setText(msg);//显示信息
but = (Button) super.findViewById(R.id.but_second);
but.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = SecondActivity.this.getIntent();
intent.putExtra("returnmsg", "你好,是卡哇伊吗?");
setResult(RESULT_OK,intent);
finish();
}
});
}
}
1.3 课程小结
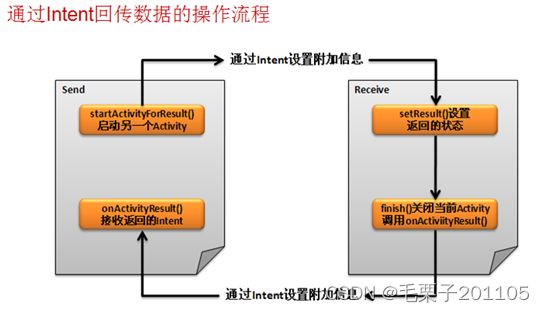
(1)Intent可以用于多个Activity间的跳转操作;
(2)使用Intent也可以接收Activity回传的数据。
2. Intent深入
2.1 知识点
(1)掌握内置Intent的调用操作。
2.2 具体内容
通过Intent跳转到网页:
package com.example.intentproject;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class IntentActivity extends Activity {
Button but = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_intent_first);
but = (Button) super.findViewById(R.id.but_first);
but.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Uri uri = Uri.parse("http://www.baidu.com");
Intent it =new Intent();
it.setAction(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);//指定action
it.setData(uri);//设置数据
startActivity(it);
}
});
}
}
以下使用Intent跳转到拨号页面:
package com.example.intentproject;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
public class IntentActivity extends Activity {
Button but = null;
EditText edt = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_intent_first);
but = (Button) super.findViewById(R.id.but_first);
edt = (EditText) super.findViewById(R.id.edt);
but.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
String num = edt.getText().toString().trim();
Uri uri = Uri.parse("tel:"+num);
Intent it =new Intent();
it.setAction(Intent.ACTION_CALL);//指定action
it.setData(uri);//设置数据
startActivity(it);
}
});
}
}
拨号还需要进行权限的配置:
通过intent发送短信:
package com.example.intentproject;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
public class IntentActivity extends Activity {
Button but = null;
EditText edt = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_intent_first);
but = (Button) super.findViewById(R.id.but_first);
edt = (EditText) super.findViewById(R.id.edt);
but.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
String num = edt.getText().toString().trim();
String note ="这是短信的内容";
Uri uri = Uri.parse("smsto:"+num);
Intent it =new Intent();
it.setAction(Intent.ACTION_SENDTO);//指定action
it.putExtra("sms_body", note);//指定附加信息
it.setType("vndd.android-dir/mms-sms");//设置MIME类型,对方手机将以短信形式打开我们这发生的信息
it.setData(uri);//设置数据
startActivity(it);
}
});
}
}
2.3 小结
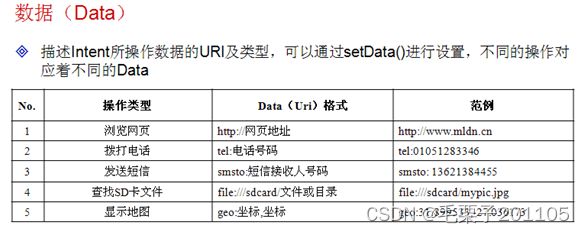
(1)在Android系统之中提供了多种Intent,用户只需要设置好URL以及附加的数据就可以完成这些Intent的操作。