研发必会-异步编程利器之CompletableFuture(上)
微信公众号访问地址:
近期热推文章:
1、springBoot对接kafka,批量、并发、异步获取消息,并动态、批量插入库表;
2、SpringBoot用线程池ThreadPoolTaskExecutor异步处理百万级数据;
3、基于Redis的Geo实现附近商铺搜索(含源码)
4、基于Redis实现关注、取关、共同关注及消息推送(含源码)
5、SpringBoot整合多数据源,并支持动态新增与切换(详细教程)
6、基于Redis实现点赞及排行榜功能
一些业务场景我们需要使用多线程异步执行任务,加快任务执行速度。
CompletableFuture实现了Future接口。
一、Future简介
JDK5新增了Future接口,它提供了一种异步并行计算的功能。若主线程要执行一个很耗时的计算任务,我们就可以通过future,把这个任务放到异步线程中去执行。主线程继续处理其他任务,异步线程处理完成后,再通过Future获取计算结果。
方法1:
@Testpublic void testFuture() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);Futurefuture = executorService.submit(() -> { Thread.sleep(2000);return "hello";});System.out.println(future.get());System.out.println("end");}
但是,Future无法解决多个异步任务需要相互依赖的场景,简单点说就:主线程需要等待子线程任务执行完毕之后再进行执行,这个时候你可能想到了CountDownLatch,没错确实可以解决,代码如下:第一个通过用户id获取用户信息,第二个通过商品id获取商品信息。
方法2:
@Testpublic void testCountDownLatch() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);CountDownLatch downLatch = new CountDownLatch(2);long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();FutureuserFuture = executorService.submit(() -> { //模拟查询商品耗时500毫秒Thread.sleep(500);downLatch.countDown();return "用户A";});FuturegoodsFuture = executorService.submit(() -> { //模拟查询商品耗时500毫秒Thread.sleep(400);downLatch.countDown();return "商品A";});downLatch.await();//模拟主程序耗时时间Thread.sleep(600);System.out.println("获取用户信息:" + userFuture.get());System.out.println("获取商品信息:" + goodsFuture.get());System.out.println("总共用时" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms");}
运行结果:
获取用户信息:用户A获取商品信息:商品A总共用时1110ms
从运行结果可以看出结果都已经获取,而且如果我们不用异步操作,执行时间应该是:500+400+600 = 1500,用异步操作后实际只用1110。可以发现,future+线程池异步配合,提高了程序的执行效率。
但是Future对于结果的获取,不是很友好,只能通过阻塞或者轮询的方式得到任务的结果。
1、Future.get():阻塞调用,在线程获取结果之前get方法会一直阻塞。
2、Future提供了一个isDone方法,可以在程序中轮询这个方法查询执行结果。
虽然 Future 以及相关使用方法提供了异步执行任务的能力,但是对于结果的获取却是很不方便。阻塞的方式和异步编程的设计理念相违背,而轮询的方式会耗费无谓的CPU资源。
因此,JDK8设计出CompletableFuture。CompletableFuture提供了一种观察者模式类似的机制,可以让任务执行完成后通知监听的一方。
二、CompletableFuture简介
2.1、使用场景
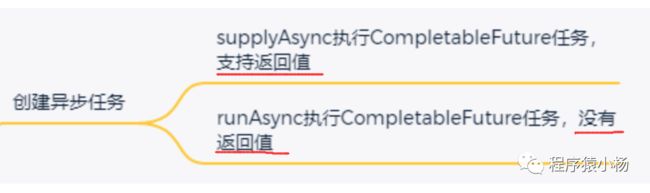
2.2、创建异步任务
2.2.1、常见的有4种创建方式:
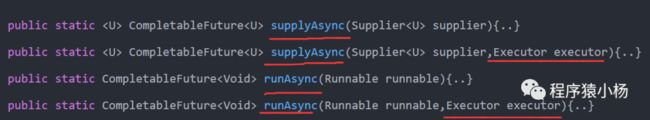
「supplyAsync」:执行任务,支持返回值;
「runAsync」:执行任务,没有返回值。
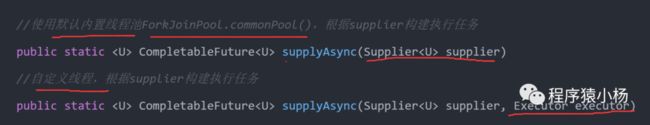
1、supplyAsync方法
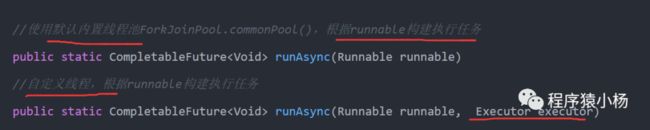
2、runAsync方法
2.2.2、结果获取4种方式
//方式一 在Future中就已经提供了public T get()//方式二 如果在指定时间内未获取结果将抛出超时异常public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)//方式三 立即获取结果不阻塞,结果计算已完成将返回结果或计算过程中的异常,//如果未计算完成将返回设定的valueIfAbsent值public T getNow(T valueIfAbsent)//方式四 方法里不会抛出异常public T join()
2.2.3、案例如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {//自定义线程池ExecutorService executor= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();//1、supplyAsync的使用CompletableFuturesupplyAsync=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ log.info("使用supplyAsync方法实现异步");return "java成长之路"; },executor);//supplyAsync的future,有返回值 join方法测试log.info("输出返回结果为:"+supplyAsync.join());//getNow方法测试log.info("getNow方法测试结果:"+supplyAsync.getNow("java成长之路02"));//2、runAsync的使用CompletableFuturerunAsync=CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> log.info("使用runAsync方法实现异步"),executor);//runAsync的future没有返回值,输出nulllog.info("输出返回结果为:"+runAsync.join());//最后关闭线程池executor.shutdown();//3、get方法测试CompletableFuturecp3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync((() -> 1 / 0)); log.info("get方法测试返回结果为:"+cp3.get());}
输出结果:
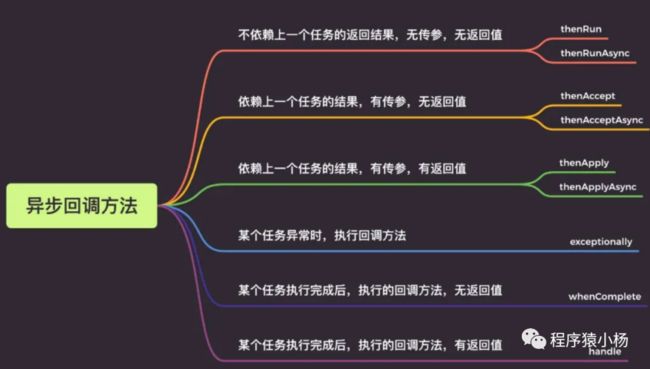
2.3、异步回调方法
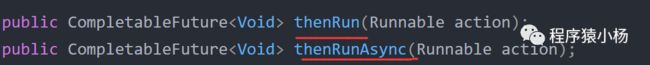
2.3.1、thenRun/thenRunAsync
做完第一个任务后,再做第二个任务。某个任务执行完成后,执行回调方法;但是前后两个任务没有参数传递,第二个任务也没有返回值。
代码案例:
/*** 功能描述:异步回调方法 testThenRun* @MethodName: testThenRun* @MethodParam: []* @Return: void* @Author: yyalin* @CreateDate: 2023/10/10 17:51*/public void testThenRun() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();CompletableFuturerunAsyncRes= CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{ try {//执行任务1log.info("任务1开始睡眠600ms。。。。");Thread.sleep(600);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});//做完第一个任务后,再做第二个任务 运行第二个任务//thenRun是没有开启异步的CompletableFuturethenRunRes=runAsyncRes.thenRunAsync(()->{ try {//执行任务2log.info("任务2开始睡眠400ms。。。。");Thread.sleep(400);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});//使用get方式获取thenRunRes的返回结果log.info("使用get方式获取thenRunRes的返回结果:"+thenRunRes.get());//模拟主程序耗时时间Thread.sleep(600);log.info("总共用时" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms");}
输出结果:
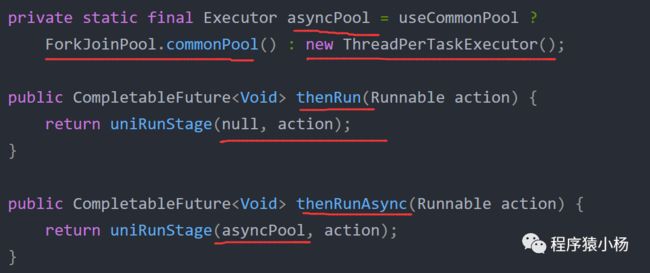
区别:是否共用线程池
执行第一个任务的时候,传入了一个自定义线程池:
1、调用thenRun方法执行第二个任务时,则第二个任务和第一个任务是共用同一个线程池;
2、调用thenRunAsync方法执行第二个任务时,则第一个任务使用的是你自己传入的线程池,第二个任务使用的是ForkJoin线程池。
2.3.2.thenAccept/thenAcceptAsync
第一个任务执行完成后,执行第二个回调方法任务,会将第一个任务的执行结果,作为第二个任务的入参,传递到回调方法中,但是回调方法是没有返回值的。(任务有返回结果,对应回调方法有入参无返回值)
代码案例:
/*** 功能描述:测试thenAccept/thenAcceptAsync* @MethodName: testThenRun* @MethodParam: []* @Return: void* @Author: yyalin* @CreateDate: 2023/10/10 18:19*/public void testThenAccept() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {//执行任务1并返回结果CompletableFuturesupplyAsyncRes=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ return "res01";});//执行任务1的回调方法 任务1的执行结果作为回调方法的入参CompletableFuturethenAccptRes=supplyAsyncRes.thenAccept((res)->{ log.info("任务1返回结果为:"+res);});//回调方法没有返回值log.info("回调任务返回结果:"+thenAccptRes.get());}
2.3.3、thenApply/thenApplyAsync
第一个任务执行完成后,执行第二个回调方法任务,会将第一个任务的执行结果,作为第二个任务的入参,传递到回调方法中,并且回调方法是有返回值的。(任务有返回结果,对应回调方法有入参有返回值)。
代码案例:
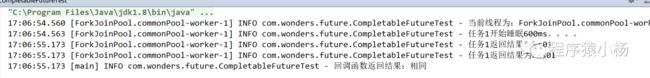
/*** 功能描述:测试thenApply/thenApplyAsync* @MethodName: testThenAccept* @MethodParam: []* @Return: void* @Author: yyalin* @CreateDate: 2023/10/11 9:26*/public void testThenApply() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {//执行任务并将结果传参给回调方法且返回回调结果CompletableFuturesupplyAsyncRes=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ return "res";}).thenApply((a)->{if(Objects.equals(a,"res")){return "相同";}return "不同";});log.info("回调任务返回结果:"+supplyAsyncRes.get());}
结果:
下面是异常回调:
2.3.4、exceptionally
某个任务执行异常时,执行的回调方法;并且有抛出异常作为参数,传递到回调方法。(回调方法有返回值)
代码案例:
/*** 功能描述:exceptionally* @MethodName: testExceptionally* @MethodParam: []* @Return: void* @Author: yyalin* @CreateDate: 2023/10/11 9:36*/public void testExceptionally() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuturelog.info("当前线程为:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());throw new RuntimeException();}).exceptionally((e)->{log.info("返回异常e:"+e);return "程序异常.......";});log.info("回调任务返回结果:"+exceptionallyRes.get());}
结果:
2.3.5、whenComplete方法
某个任务执行完成后,执行的回调方法,无返回值;并且whenComplete方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是上个任务的结果。(回调方法无返回值)
当CompletableFuture的任务不论是正常完成还是出现异常它都会调用 「whenComplete」这回调函数。
-
「正常完成」:whenComplete返回结果和上级任务一致,异常为null;
-
「出现异常」:whenComplete返回结果为null,异常为上级任务的异常;
即调用get()时,正常完成时就获取到结果,出现异常时就会抛出异常,需要你处理该异常。
代码案例:
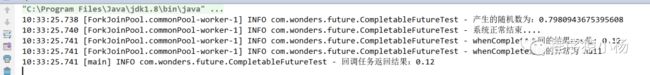
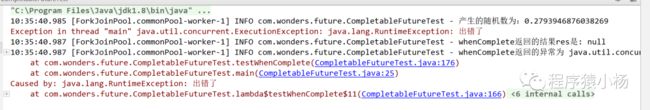
/*** 功能描述:whenComplete方法* @MethodName: testExceptionally* @MethodParam: []* @Return: void* @Author: yyalin* @CreateDate: 2023/10/11 9:48*/public void testWhenComplete() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {//执行任务CompletableFuturefutureRes=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ double math=Math.random();log.info("产生的随机数为:"+math);if(math<0.1){throw new RuntimeException("出错了");}log.info("系统正常结束....");return 0.12;});//异常回调方法CompletableFuturewhenCompleteRes=futureRes.whenComplete((res, throwable)->{ log.info("whenComplete返回的结果res是: "+res);log.info("whenComplete返回的异常为 "+throwable);});log.info("回调任务返回结果:"+whenCompleteRes.get().toString());}
正常返回,没有异常时候:
出现异常,返回结果为空,并回调方法返回异常:
与 exceptionally结合示例:
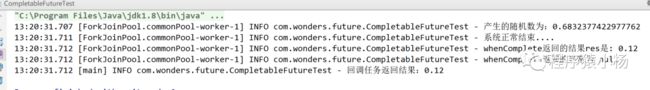
/*** 功能描述:whenComplete方法* @MethodName: testExceptionally* @MethodParam: []* @Return: void* @Author: yyalin* @CreateDate: 2023/10/11 9:48*/public void testWhenComplete() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {//1、执行任务CompletableFuturefutureRes=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ double math=Math.random();log.info("产生的随机数为:"+math);if(math<0.6){throw new RuntimeException("出错了");}log.info("系统正常结束....");return 0.12;}).whenComplete((res, throwable)->{ //2、任务执行异常回调方法log.info("whenComplete返回的结果res是: "+res);log.info("whenComplete返回的异常为 "+throwable);}).exceptionally((throwable)->{ //3、异常捕获log.info("系统出现异常,需要处理:"+throwable.getMessage());return 0.0; //返回默认值});log.info("回调任务返回结果:"+futureRes.get());}
返回结果:当出现异常时,exceptionally中会捕获该异常,给出默认返回值0.0
2.3.6、handle方法
某个任务执行完成后,执行回调方法,并且是有返回值的;并且handle方法返回的CompletableFuture的result是回调方法执行的结果。(回调方法有返回值)
代码案例:
/*** 功能描述:handle方法* @MethodName: testWhenComplete* @MethodParam: []* @Return: void* @Author: yyalin* @CreateDate: 2023/10/11 16:55*/public void testHandle() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {//任务1返回结果CompletableFuturefutureRes=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ log.info("当前线程为:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());try {//执行任务1log.info("任务1开始睡眠600ms。。。。");Thread.sleep(600);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "res01";});//回调函数CompletableFuturehandleRes=futureRes.handle((res,throwable)->{ log.info("任务1返回结果:"+res);if(res.equals("res01")){log.info("任务1返回结果为res01");return "相同";}return "不同";}).exceptionally(throwable -> {log.info("系统出现异常,需要处理:"+throwable.getMessage());return "异常"; //返回默认值});log.info("回调函数返回结果:"+handleRes.get());}
返回结果:
如果大家对相关文章感兴趣,可以关注微信公众号"程序猿小杨",会持续更新优秀文章!欢迎大家 分享、收藏、点赞、在看,您的支持就是我坚持下去的最大动力!谢谢!
参考网站:
https://blog.csdn.net/ThinkWon/article/details/123390393
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/shjANruBk6VL492JaWLTEg