CompletableFuture异步编程事务及多数据源配置问题(含gitee源码)
仓库地址: buxingzhe: 一个多数据源和多线程事务练习项目
小伙伴们在日常编码中经常为了提高程序运行效率采用多线程编程,在不涉及事务的情况下,使用dou.lea大神提供的CompletableFuture异步编程利器,它提供了许多优雅的api,我们可以很方便的进行异步多线程编程,速度杠杠的,在这里感谢大佬可怜我们广大码农的不易,提供了如此优秀的异步编程框架!
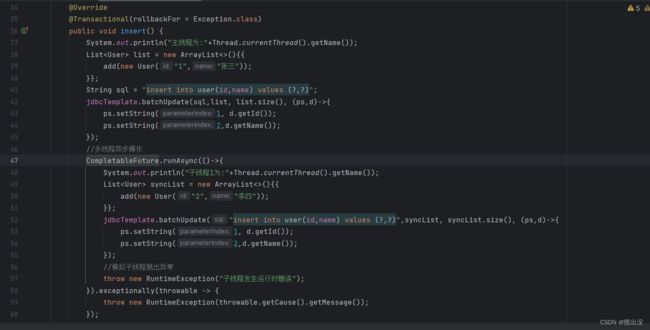
刚才说了,不涉及事务情况下,用着爽歪歪,一旦涉及到事务,没有遇到这种情况的就头疼了,多个线程之间发生异常,怎么回滚事务?因为很多业务场景使用了多线程编程,涉及到DML操作(select、update、insert、delete)中的增删改,必须要保持数据在业务上的一致性,比如修改A表,插入B表,这两步在业务上必须是原子的,有一个失败,对于另外表的操作都必须回滚,而spring中对不同线程的数据库连接是单独的,放在ThreadLocal中,多个线程之间不共享事务,下面通过几个浅显易懂的示例,来解释不同场景下的多线程报错以及处理办法。
可以看到,子线程中写了抛出异常代码,但是控制台没有打印出,主线程和子线程事务都未回滚,数据正常插入,主线程没有等子线程执行完就结束。对上面的例子修改下:
主线程中加入了join(),等待子线程执行,这时控制台打印了子线程抛出的异常如下:
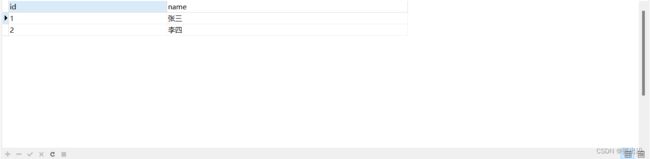
数据库数据如下:
我们看到,主线程方法上由于加了 @Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)声明式事务注解,事务回滚了,数据并没有插入。子线程虽然抛出异常,但是事务没有回滚,数据正常插入了!这不是我们想要的结果,再继续改进下:
先注入一个事务管理器
然后在子线程中加入编程式事务代码,手动管理子线程事务状态,发生异常后,回滚子线程事务,并抛出异常至主线程中(直接贴代码了,方便复制粘贴)
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void insert() {
System.out.println("主线程为:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
List list = new ArrayList<>(){{
add(new User("1","张三"));
}};
String sql = "insert into user(id,name) values (?,?)";
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql,list, list.size(), (ps,d)->{
ps.setString(1, d.getId());
ps.setString(2,d.getName());
});
//多线程异步操作
CompletableFuture future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
DefaultTransactionDefinition def = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
// 事物隔离级别,开启新事务,这样会比较安全些。
def.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW);
// 获得事务状态
TransactionStatus status = dataSourceTransactionManager.getTransaction(def);
try {
System.out.println("子线程1为:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
List syncList = new ArrayList<>(){{
add(new User("2","李四"));
}};
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate("insert into user(id,name) values (?,?)",syncList, syncList.size(), (ps,d)->{
ps.setString(1, d.getId());
ps.setString(2,d.getName());
});
//此异常必抛出,模拟抛出异常
if(1<2){
throw new RuntimeException("子线程发生异常");
}
//开启手动事务管理后,必须手动在逻辑结束时提交事务,否则会造成锁表,查询可以,增删改会卡住,除非重启服务断开与数据库的连接
dataSourceTransactionManager.commit(status);
}catch (Exception e){
//发生异常时手动回滚子线程事务
dataSourceTransactionManager.rollback(status);
//抛出异常供主线程捕获
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
}
}).exceptionally(throwable -> {
throw new RuntimeException(throwable.getCause().getMessage());
});
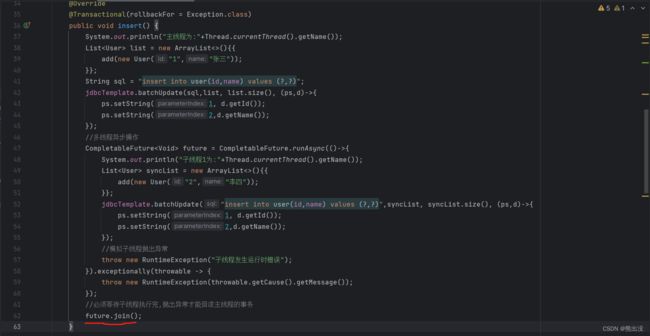
//必须等待子线程执行完,抛出异常才能回滚主线程的事务
future.join();
} 执行结果如下:
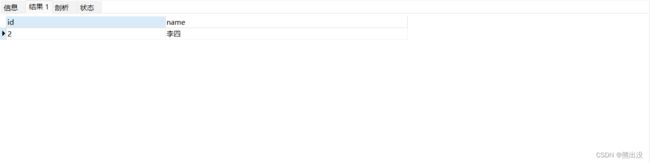
数据库数据如下:
可以看到主线程和子线程中的数据都回滚了!
以上都还是较为简单的场景,那如果异常是在主线程中发生或者在其他子线程发生,那所有线程中的事务如何回滚呢?请看示例
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void insert() {
System.out.println("主线程为:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
List list = new ArrayList<>(){{
add(new User("1","张三"));
}};
String sql = "insert into user(id,name) values (?,?)";
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql,list, list.size(), (ps,d)->{
ps.setString(1, d.getId());
ps.setString(2,d.getName());
});
//线程一抛出异常
CompletableFuture futureOne = getFutureOne();
//线程二无异常
CompletableFuture futureTwo = getFutureTwo();
//必须等待所有子线程执行完,抛出异常才能回滚主线程的事务
CompletableFuture.allOf(futureOne,futureTwo).join();
}
public CompletableFuture getFutureOne(){
return CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
DefaultTransactionDefinition def = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
// 事物隔离级别,开启新事务,这样会比较安全些。
def.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW);
// 获得事务状态
TransactionStatus status = dataSourceTransactionManager.getTransaction(def);
try {
System.out.println("子线程1为:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
List syncList = new ArrayList<>(){{
add(new User("2","李四"));
}};
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate("insert into user(id,name) values (?,?)",syncList, syncList.size(), (ps,d)->{
ps.setString(1, d.getId());
ps.setString(2,d.getName());
});
//此异常必抛出,模拟抛出异常
if(1<2){
throw new RuntimeException("子线程1发生异常");
}
//开启手动事务管理后,必须手动在逻辑结束时提交事务,否则会造成锁表,查询可以,增删改会卡住,除非重启服务,断开与数据库的连接
dataSourceTransactionManager.commit(status);
}catch (Exception e){
//发生异常时手动回滚子线程事务
dataSourceTransactionManager.rollback(status);
//抛出异常供主线程捕获
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
}
}).exceptionally(throwable -> {
throw new RuntimeException(throwable.getCause().getMessage());
});
}
public CompletableFuture getFutureTwo(){
return CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
DefaultTransactionDefinition def = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
// 事物隔离级别,开启新事务,这样会比较安全些。
def.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW);
// 获得事务状态
TransactionStatus status = dataSourceTransactionManager.getTransaction(def);
try {
System.out.println("子线程2为:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
List syncList = new ArrayList<>(){{
add(new User("3","王五"));
}};
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate("insert into user(id,name) values (?,?)",syncList, syncList.size(), (ps,d)->{
ps.setString(1, d.getId());
ps.setString(2,d.getName());
});
//开启手动事务管理后,必须手动在逻辑结束时提交事务,否则会造成锁表,查询可以,增删改会卡住,除非重启服务,断开与数据库的连接
dataSourceTransactionManager.commit(status);
}catch (Exception e){
//发生异常时手动回滚子线程事务
dataSourceTransactionManager.rollback(status);
//抛出异常供主线程捕获
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
}
}).exceptionally(throwable -> {
throw new RuntimeException(throwable.getCause().getMessage());
});
} 上面的代码中主线程调用了两个异步子线程,其中子线程一抛出异常,子线程二无异常,主线程阻塞等待两个子线程执行结果
可以看到异常打印在控制台,且只有主线程和线程一的数据回滚
下面再修改下,实现当子线程有异常抛出时,保证主线程和其他子线程也同步回滚:
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void insert() {
List statusList = new Vector<>();
try {
System.out.println("主线程为:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
List list = new ArrayList<>(){{
add(new User("1","张三"));
}};
String sql = "insert into user(id,name) values (?,?)";
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql,list, list.size(), (ps,d)->{
ps.setString(1, d.getId());
ps.setString(2,d.getName());
});
//线程一抛出异常
CompletableFuture futureOne = getFutureOne(statusList);
//线程二无异常
CompletableFuture futureTwo = getFutureTwo(statusList);
//必须等待所有子线程执行完,抛出异常才能回滚主线程的事务
CompletableFuture.allOf(futureOne,futureTwo).join();
statusList.forEach(dataSourceTransactionManager::commit);
}catch (Exception e){
statusList.forEach(dataSourceTransactionManager::rollback);
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
}
}
public CompletableFuture getFutureOne(List statusList){
return CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
DefaultTransactionDefinition def = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
// 事物隔离级别,开启新事务,这样会比较安全些。
def.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW);
// 获得事务状态
TransactionStatus status = dataSourceTransactionManager.getTransaction(def);
try {
System.out.println("子线程1为:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
List syncList = new ArrayList<>(){{
add(new User("2","李四"));
}};
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate("insert into user(id,name) values (?,?)",syncList, syncList.size(), (ps,d)->{
ps.setString(1, d.getId());
ps.setString(2,d.getName());
});
//此异常必抛出,模拟抛出异常
if(1<2){
throw new RuntimeException("子线程1发生异常");
}
//dataSourceTransactionManager.commit(status);
}catch (Exception e){
//抛出异常供主线程捕获
//dataSourceTransactionManager.rollback(status);
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
}finally {
statusList.add(status);
}
}).exceptionally(throwable -> {
throw new RuntimeException(throwable.getCause().getMessage());
});
}
public CompletableFuture getFutureTwo(List statusList){
return CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
DefaultTransactionDefinition def = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
// 事物隔离级别,开启新事务,这样会比较安全些。
def.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW);
// 获得事务状态
TransactionStatus status = dataSourceTransactionManager.getTransaction(def);
try {
System.out.println("子线程2为:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
List syncList = new ArrayList<>(){{
add(new User("3","王五"));
}};
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate("insert into user(id,name) values (?,?)",syncList, syncList.size(), (ps,d)->{
ps.setString(1, d.getId());
ps.setString(2,d.getName());
});
//dataSourceTransactionManager.commit(status);
}catch (Exception e){
//dataSourceTransactionManager.rollback(status);
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
}finally {
statusList.add(status);
}
}).exceptionally(throwable -> {
throw new RuntimeException(throwable.getCause().getMessage());
});
} 用线程安全的集合Vector收集子线程的事务状态,子线程不做commit和rollback,调用后报错如下:
No value for key [HikariDataSource (HikariPool-1)] bound to thread [main]
解释: 无法在当前线程绑定的threadLocal中寻找到HikariDataSource作为key,对应关联的资源对象ConnectionHolder
spring中一次事务的完成通常都是默认在当前线程内完成的,又因为一次事务的执行过程中,涉及到对当前数据库连接Connection的操作,因此为了避免将Connection在事务执行过程中来回传递,我们可以将Connextion绑定到当前事务执行线程对应的ThreadLocalMap内部,顺便还可以将一些其他属性也放入其中进行保存,在Spring中,负责保存这些ThreadLocal属性的实现类由TransactionSynchronizationManager承担。
TransactionSynchronizationManager类内部默认提供了下面六个ThreadLocal属性,分别保存当前线程对应的不同事务资源:
//保存当前事务关联的资源--默认只会在新建事务的时候保存当前获取到的DataSource和当前事务对应Connection的映射关系--当然这里Connection被包装为了ConnectionHolder
private static final ThreadLocal> resources =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Transactional resources");
//事务监听者--在事务执行到某个阶段的过程中,会去回调监听者对应的回调接口(典型观察者模式的应用)---默认为空集合
private static final ThreadLocal> synchronizations =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Transaction synchronizations");
//见名知意: 存放当前事务名字
private static final ThreadLocal currentTransactionName =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Current transaction name");
//见名知意: 存放当前事务是否是只读事务
private static final ThreadLocal currentTransactionReadOnly =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Current transaction read-only status");
//见名知意: 存放当前事务的隔离级别
private static final ThreadLocal currentTransactionIsolationLevel =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Current transaction isolation level");
//见名知意: 存放当前事务是否处于激活状态
private static final ThreadLocal actualTransactionActive =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Actual transaction active");
那么上面抛出的异常的原因也就很清楚了,无法在main线程找到当前事务对应的资源,原因如下:
主线程为:http-nio-5566-exec-2
子线程1为:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1
子线程2为:ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-2
开启新事务时,事务相关资源都被绑定到了http-nio-5566-exec-2线程对应的threadLocalMap内部,而当执行事务提交代码时,commit内部需要从TransactionSynchronizationManager中获取当前事务的资源,显然我们无法从main线程对应的threadLocalMap中获取到对应的事务资源,这就是异常抛出的原因。
下面介绍一种可用的多线程事务回滚方式,但是对编程顺序有要求,小伙伴们可以按需使用。
首先提供一个多线程事务管理类:
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionStatus;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.DefaultTransactionDefinition;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean;
/**
* 多线程事务管理器
* @Title: MultiThreadingTransactionManager
* @Description: TODO
* @author: hulei
* @date: 2023/8/7 11:36
* @Version: 1.0
*/
@Slf4j
public class MultiThreadingTransactionManager {
/**
* 事务管理器
*/
private final PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;
/**
* 超时时间
*/
private final long timeout;
/**
* 时间单位
*/
private final TimeUnit unit;
/**
* 一阶段门闩,(第一阶段的准备阶段),当所有子线程准备完成时(除“提交/回滚”操作以外的工作都完成),countDownLatch的值为0
*/
private CountDownLatch oneStageLatch = null;
/**
* 二阶段门闩,(第二阶段的执行执行),主线程将不再等待子线程执行,直接判定总的任务执行失败,执行第二阶段让等待确认的线程进行回滚
*/
private final CountDownLatch twoStageLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
/**
* 是否提交事务,默认是true(当任一线程发生异常时,isSubmit会被设置为false,即回滚事务)
*/
private final AtomicBoolean isSubmit = new AtomicBoolean(true);
/**
* 构造方法
*
* @param transactionManager 事务管理器
* @param timeout 超时时间
* @param unit 时间单位
*/
public MultiThreadingTransactionManager(PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
this.transactionManager = transactionManager;
this.timeout = timeout;
this.unit = unit;
}
/**
* 线程池方式执行任务,可保证线程间的事务一致性
*
* @param runnableList 任务列表
* @param executor 线程池
*/
public void execute(List runnableList, ExecutorService executor) {
// 排除null值
runnableList.removeAll(Collections.singleton(null));
// 属性初始化
innit(runnableList.size());
// 遍历任务列表并放入线程池
for (Runnable runnable : runnableList) {
// 创建线程
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
// 如果别的线程执行失败,则该任务就不需要再执行了
if (!isSubmit.get()) {
log.info("当前子线程执行中止,因为线程事务中有子线程执行失败");
oneStageLatch.countDown();
return;
}
// 开启事务
TransactionStatus transactionStatus = transactionManager.getTransaction(new DefaultTransactionDefinition());
try {
// 执行业务逻辑
runnable.run();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 执行体发生异常,设置回滚
isSubmit.set(false);
log.error("线程{}:业务发生异常,执行体:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName(), runnable);
}
// 计数器减一
oneStageLatch.countDown();
try {
//等待所有线程任务完成,监控是否有异常,有则统一回滚
twoStageLatch.await();
// 根据isSubmit值判断事务是否提交,可能是子线程出现异常,也有可能是子线程执行超时
if (isSubmit.get()) {
// 提交
transactionManager.commit(transactionStatus);
log.info("线程{}:事务提交成功,执行体:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName(), runnable);
} else {
// 回滚
transactionManager.rollback(transactionStatus);
log.info("线程{}:事务回滚成功,执行体:{}", Thread.currentThread().getName(), runnable);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("子线程抛出异常:{}",e.getMessage());
}
});
executor.execute(thread);
}
//主线程担任协调者,当第一阶段所有参与者准备完成,oneStageLatch的计数为0
//主线程发起第二阶段,执行阶段(提交或回滚)
try {
// 主线程等待所有线程执行完成,超时时间设置为五秒,超出等待时间则返回false,计数为0返回true
boolean timeOutFlag = oneStageLatch.await(timeout, unit);
long count = oneStageLatch.getCount();
// 主线程等待超时,子线程可能发生长时间阻塞,死锁
if (count > 0 || !timeOutFlag) {
// 设置为回滚
isSubmit.set(false);
log.info("主线线程等待超时,任务即将全部回滚");
throw new RuntimeException("主线线程等待超时,任务即将全部回滚");
}
twoStageLatch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error(e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
}
// 返回结果,是否执行成功,事务提交即为执行成功,事务回滚即为执行失败
boolean flag = isSubmit.get();
if(!flag){
log.info("有线程发生异常,事务全部回滚");
throw new RuntimeException("有线程发生异常,数据全部回滚");
}else{
log.info("主线程和子线程执行无异常,事务全部提交");
}
executor.shutdown();
}
/**
* 初始化属性
*
* @param size 任务数量
*/
private void innit(int size) {
oneStageLatch = new CountDownLatch(size);
}
}
看下调用代码示例
import com.hulei.studyproject.entity.User;
import com.hulei.studyproject.threadpool.ThreadPoolUtil;
import com.hulei.studyproject.transaction.MultiThreadingTransactionManager;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 测试多线程事务回滚
* @Title: UserServiceImpl
* @Description: TODO
* @author: hulei
* @date: 2023/7/31 17:41
* @Version: 1.0
*/
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService{
private final JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
private final PlatformTransactionManager platformTransactionManager;
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void insert() {
System.out.println("主线程为:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
List list = new ArrayList<>(){{
add(new User("1","张三"));
}};
String sql = "insert into user(id,name) values (?,?)";
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql,list, list.size(), (ps,d)->{
ps.setString(1, d.getId());
ps.setString(2,d.getName());
});
List runnableList = getRunnables();
MultiThreadingTransactionManager multiThreadingTransactionManager = new MultiThreadingTransactionManager(platformTransactionManager,5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = ThreadPoolUtil.getThreadPool();
multiThreadingTransactionManager.execute(runnableList,executor);
}
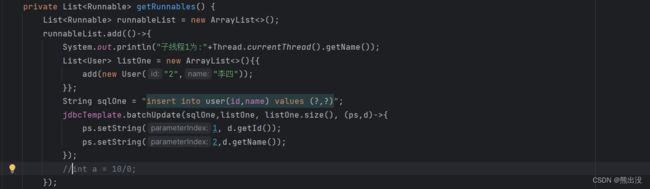
private List getRunnables() {
List runnableList = new ArrayList<>();
runnableList.add(()->{
System.out.println("子线程1为:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
List listOne = new ArrayList<>(){{
add(new User("2","李四"));
}};
String sqlOne = "insert into user(id,name) values (?,?)";
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sqlOne,listOne, listOne.size(), (ps,d)->{
ps.setString(1, d.getId());
ps.setString(2,d.getName());
});
int a = 10/0;
});
runnableList.add(()->{
System.out.println("子线程2为:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
List listTwo = new ArrayList<>(){{
add(new User("3","王五"));
}};
String sqlTwo = "insert into user(id,name) values (?,?)";
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sqlTwo,listTwo, listTwo.size(), (ps,d)->{
ps.setString(1, d.getId());
ps.setString(2,d.getName());
});
});
return runnableList;
}
}
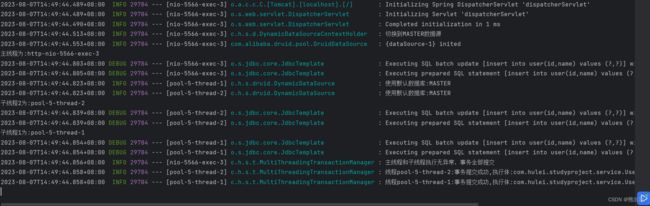
我们在其中一个子线程处手工写了一个会抛出异常的代码
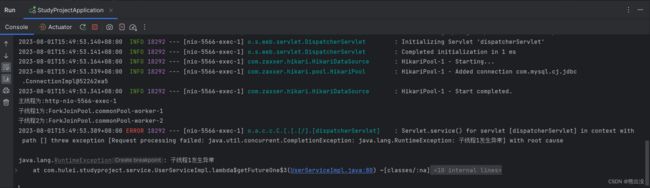
执行结果如下:
可以看到控制台报错,数据库执行结果如下:
主线程和子线程数据均未生成
把异常代码注释掉
无异常抛出,数据库结果如下:
可以看到子线程和主线程操作的数据均已回滚。
但是以上方法有一定局限性,即主线程如果再子线程执行后再抛出异常,则子线程无法回滚了,所以要求逻辑写在子线程执行之前
2处的代码必须放在方法最后写。