4种实现JS深拷贝的方法
浅拷贝与深拷贝
浅拷贝是创建一个新对象,这个对象有着原始对象属性值的拷贝。如果属性是基本类型,拷贝的就是基本类型的值,如果属性是引用类型,拷贝的是内存地址 。
如果不进行深拷贝,其中一个对象改变了对象的值,就会影响到另一个对象的值。 深拷贝是将一个对象从内存中完整的拷贝一份出来,从堆内存中开辟一个新的区域存放新对象,且修改新对象不会影响原对象。
1、JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj))序列化和反序列
先将需要拷贝的对象进行JSON字符串化,然后再pase解析出来,赋给另一个变量,实现深拷贝。
let a = {a:1,b:2}
let b = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(a))
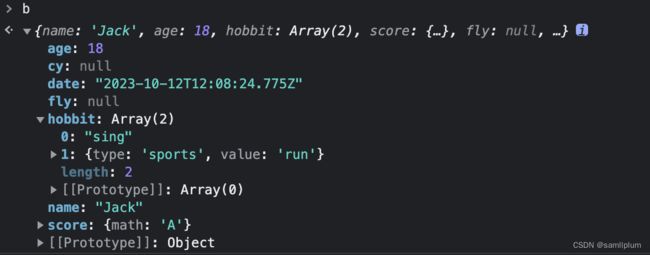
a.a = 111.1 JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj))深浅拷贝的缺陷
let a = {
name: 'Jack',
age: 18,
hobbit: ['sing', {type: 'sports', value: 'run'}],
score: {
math: 'A',
},
run: function() {},
walk: undefined,
fly: NaN,
cy: null,
date: new Date()
}
let b = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(a))
取不到值为 undefined 的 key;如果对象里有函数,函数无法被拷贝下来;无法拷贝copyObj对象原型链上的属性和方法;对象转变为 date 字符串。
2. Object.assign(target, source1, source2)
es6新增的方法,可用于对象合并,将源对象的所有可枚举属性,复制到目标对象上。
var data = {
a: "123",
b: 123,
c: true,
d: [43, 2],
e: undefined,
f: null,
g: function() { console.log("g"); },
h: new Set([3, 2, null]),
i: Symbol("fsd"),
k: new Map([ ["name", "张三"], ["title", "Author"] ])
};
var newData = Object.assign({},data)
console.log(newData) 可以看到这个API可以将源对象上的全部数据类型属性值完全复制到一个新的对象上,这难道就是我们所寻找的最完美的深拷贝方式了吗?答案是否,只能说是部分深拷贝,或者说就是浅拷贝,为什么这么说呢,接着往下看。
var test = { name: '张三' }
var data = {
a: 123,
b: test
}
var newData = Object.assign({},data)
console.log(newData)
// { a: 123, b: { name: '张三' }}
test.age = 18
console.log(newData)
// { a: 123, b: { name: '张三', age: 18 }}
结果很明显,这种方式的拷贝,如果源目标对象中某个属性值是对另一个对象的引用,那么这个属性的拷贝仍然是对引用的拷贝。
3、普通递归函数实现深拷贝
function deepClone(source) {
if (typeof source !== 'object' || source == null) {
return source;
}
const target = Array.isArray(source) ? [] : {};
for (const key in source) {
if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(source, key)) {
if (typeof source[key] === 'object' && source[key] !== null) {
target[key] = deepClone(source[key]);
} else {
target[key] = source[key];
}
}
}
return target;
}3.1、解决循环引用和symblo类型
function cloneDeep(source, hash = new WeakMap()) {
if (typeof source !== 'object' || source === null) {
return source;
}
if (hash.has(source)) {
return hash.get(source);
}
const target = Array.isArray(source) ? [] : {};
Reflect.ownKeys(source).forEach(key => {
const val = source[key];
if (typeof val === 'object' && val != null) {
target[key] = cloneDeep(val, hash);
} else {
target[key] = val;
}
})
return target;
}4. 迭代递归方法(解决闭环问题)
function deepCopy(data, hash = new WeakMap()) {
if(typeof data !== 'object' || data === null){
throw new TypeError('传入参数不是对象')
}
// 判断传入的待拷贝对象的引用是否存在于hash中
if(hash.has(data)) {
return hash.get(data)
}
let newData = {};
const dataKeys = Object.keys(data);
dataKeys.forEach(value => {
const currentDataValue = data[value];
// 基本数据类型的值和函数直接赋值拷贝
if (typeof currentDataValue !== "object" || currentDataValue === null) {
newData[value] = currentDataValue;
} else if (Array.isArray(currentDataValue)) {
// 实现数组的深拷贝
newData[value] = [...currentDataValue];
} else if (currentDataValue instanceof Set) {
// 实现set数据的深拷贝
newData[value] = new Set([...currentDataValue]);
} else if (currentDataValue instanceof Map) {
// 实现map数据的深拷贝
newData[value] = new Map([...currentDataValue]);
} else {
// 将这个待拷贝对象的引用存于hash中
hash.set(data,data)
// 普通对象则递归赋值
newData[value] = deepCopy(currentDataValue, hash);
}
});
return newData;
}
比之前的1.0版本多了个存储对象的容器WeakMap,思路就是,初次调用deepCopy时,参数会创建一个WeakMap结构的对象,这种数据结构的特点之一是,存储键值对中的健必须是对象类型。
- 首次调用时,weakMap为空,不会走上面那个if(hash.has())语句,如果待拷贝对象中有属性也为对象时,则将该待拷贝对象存入weakMap中,此时的健值和健名都是对该待拷贝对象的引用
- 然后递归调用该函数
- 再次进入该函数,传入了上一个待拷贝对象的对象属性的引用和存储了上一个待拷贝对象引用的weakMap,因为如果是循环引用产生的闭环,那么这两个引用是指向相同的对象的,因此会进入if(hash.has())语句内,然后return,退出函数,所以不会一直递归进栈,以此防止栈溢出。
总结
上述的几种方式不管优缺点如何,共同点是只能拷贝对象的可枚举属性,对于不可枚举或者原型上的属性,却不能拷贝,但对于基本的使用来说,已经足够了。