Java经典算法
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/e6da97caaa47
https://blog.csdn.net/YaoChung/article/details/80793691
总结:算法的主要思想:
1、穷举
2、递归
3、建模
流程:数据结构+算法
常用的数据结构是数组,也可以是其他的,可自己斟酌
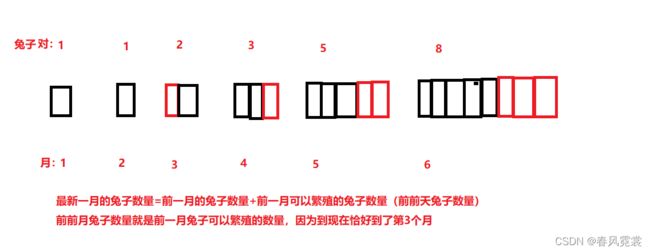
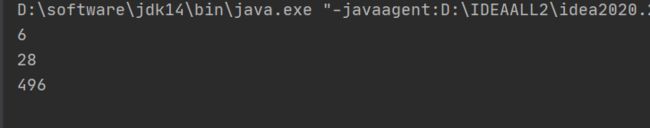
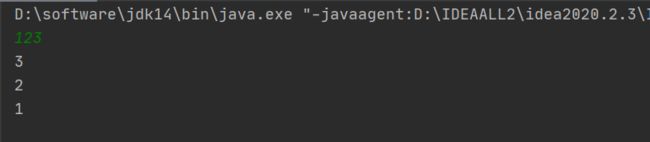
【程序1】 题目:古典问题:有一对兔子,从出生后第3个月起每个月都生一对兔子,小兔子长到第四个月后每个月又生一对兔子,假如兔子都不死,问每个月的兔子总数为多少?
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
/**
*【程序1】 题目:古典问题:有一对兔子,从出生后第3个月起每个月都生一对兔子,
* 小兔子长到第四个月后每个月又生一对兔子,假如兔子都不死,问每个月的兔子总数为多少?
*
* */
public class RabbitTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
for(i = 1; i < 20; i++){
System.out.println(f(i));
}
}
public static int f(int x){
if(x == 1 || x ==2){
return 1;
}else {
// 这里使用递归,递归加法:妙处在于可以从现在为起点,一直往回递归的加,直到递归到x==1和x==2才跳出递归
return f(x-1)+f(x-2);
}
}
}
【程序2】
题目:判断101-200之间有多少个素数,并输出所有素数。
程序分析:判断素数的方法:用一个数分别去除2到sqrt(这个数),如果能被整除, 则表明此数不是素数,反之是素数。
素数又叫质数,素数是指在大于1的自然数中,除了1和它本身以外,不能被其他自然数整除的数。
程序分析:
1、首先明白什么是素数,只能被1和本身整除的数,用循环遍历101-200之间的数,然后用101200间的书整出2到该数前面一个数,比如是113,我们113整除2112之间的数,只要这里的数整出都不等于0,则可以判断这个数是素数;
2、另一种是用一个数分别去除2到sqrt(这个数),如果能被整除,则表明此数不是素数,反之是素数。 这种方法效率更高,循环的次数更少。(就是2 * 5和5 * 2是一个意思,但被运行了两次,所以只用到开方这个数的数值就能判断了)
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
/**
* 判断101-200之间有多少个素数,并输出所有素数。
*
* */
public class Iszhishu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i, j;
int count = 0;
for (i = 101; i <= 200; i++) {
//若是用sqrt取整,必须要加一,要不然还是会少取值,会算多,介意还是从头遍历到尾更严谨,不介意用平方差的方式
int k = (int)Math.sqrt(i+1);
// System.out.println("k====="+k);
for (j = 2; j < i; j++) {
//只需要判断2到sqrt(这个数)这个范围类的就行
// for (j = 2; j < k; j++) {
// 如果j能被i整出在跳出循环
if (i % j == 0)
break;
}
// 判断循环是否提前跳出,如果j
if (j >= i) {
// if (j >= k) {
count++;
System.out.println(i);
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
【程序3】 题目:打印出所有的 "水仙花数 ",所谓 "水仙花数 "是指一个三位数,其各位数字立方和等于该数本身。例如:153是一个 "水仙花数 ",因为153=1的三次方+5的三次方+3的三次方。
.程序分析:利用for循环控制100-999个数,每个数分解出个位,十位,百位。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
public class ShuixianhuaTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i =0;
for(i = 100; i <= 999; i++){
if( shuixianhua(i)){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
public static boolean shuixianhua(int x){
int i,j,k;
i = x/100;//得到百位数
j = (x % 100)/10;//得到十位数
k = x % 10;//得到个位数
if(x == i*i*i+j*j*j+k*k*k){
System.out.println("x=="+x);
System.out.println("i="+i+"j="+j+"k="+k+"||i*i*i+j*j*j+k*k*k===="+(i*i*i+j*j*j+k*k*k));
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
【程序4】 题目:将一个正整数分解质因数。例如:输入90,打印出 90 = 2 ∗ 3 ∗ 3 ∗ 5
程序分析:
分解质因数的思路就是用该数n不断除以一个递增的数i(该数初始为2,递增至n)若能整除i,则当前i就为n的因子之一,然后将n用该因子缩小,即n=n/i再重复执行上述操作,若n = i则说明分解因子结束了
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FengjieTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入:");
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = input.nextInt();
fengjie(num);
}
public static void fengjie(int n){
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
while (n != i){// 执行的条件必须是n与i不等,若相等则分解结束了
if(n % i == 0){// 若能整除则i为n的因子之一
System.out.println("i="+i);// 输出因子
n = n /i;// 找到了一个因子i,则n/i缩小n继续寻找
}else {
break;// 不能整除则跳出本次循环,递增i进行下一轮
}
}
}
System.out.println("n="+n);
}
}
【程序5】 题目:利用条件运算符的嵌套来完成此题:学习成绩> =90分的同学用A表示,60-89分之间的用B表示,60分以下的用C表示。
1.程序分析:(a> b)?a:b这是条件运算符的基本例子。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FenshuABCTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入:");
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = input.nextInt();
System.out.println(scoreGrade(num));
}
public static String scoreGrade(int n){
return (n>=90? "A":(n>=60? "B" : "C"));
}
}
【程序6】 题目:输入两个正整数m和n,求其最大公约数和最小公倍数。
1.程序分析:利用辗除法。
最大公因数定义:
(最大公约数、最大公因子):指两个或多个整数共有约数中最大的一个。

最小公倍数定义:
两个或多个整数公有的倍数叫做它们的公倍数,其中除0以外最小的一个公倍数就叫做这几个整数的最小公倍数。

为什么最大公因数和最小公倍数的积等于两个数的积?
设A=a×c,B=b×c,a、b互质。
A和B的最小公倍数是a×b×c,A和B的最大公约数是c。
A和B的最小公倍数×A和B的最大公约数=a×b×c×c。
A×B= a×c×b×c。
由以上可得:两个数的最大公因数和最小公倍数的乘积等于这两个数的积。
辗转相除法:
-
最大公约数:具体做法是:用较小数除较大数,再用出现的余数(第一余数)去除除数,
再用出现的余数(第二余数)去除第一余数,如此反复,直到最后余数是0为止。
如果是求两个数的最大公约数,那么最后的除数就是这两个数的最大公约数。把这些数相乘就是最小公倍数。 -
最小公倍数就等于两个数乘积除以最大公约数
辗转相除法证明:
为什么除数和余数的最大公约数就是被除数和除数的最大
设a、b为正整数,且a>b,a=bq+r,q、r也为正整数,且0<r<b;这里,a为被除数、b为除数、q为商、r为余数;
设a与b的最大公约数为d,即(a,b)=d,
试证(b,r)=(a,b)=d;
证明:由于(a,b)=d,
所以可设a=md、b=nd,m、n为正整数,且(m,n)=1;
r=a-bq=md-ndq=d(m-qn),
所以d能整除r,即d|r;
得到:辗转相除法中得到的余数,是一个能被两个数的最大公约数整除的值
由于d|b,(因为d是ab的公约数)
所以d|(b,r)①;
假设(b,r)=D>d②,
则D|(bq+r),即D|a,(两个数都能被D整除,则它们的和也能被整除,乘除法的本质是加减法:eg:90和6都能被3或6整除,那么它们的和96一定也能被整除)
所以D|(a,b),
所以D≦(a,b),即D≦d,这和②矛盾!
结合①可知(b,r)=d,即(b,r)=(a,b)。
得到:辗转相除法中得到的余数,是一个能被两个数的最大公约数整除的值,所以可以用这个余数去得到最大公约数
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
/**辗转相除法:
* 1、最大公约数:具体做法是:用较小数除较大数,再用出现的余数(第一余数)去除除数,
* 再用出现的余数(第二余数)去除第一余数,如此反复,直到最后余数是0为止。
* 如果是求两个数的最大公约数,那么最后的除数就是这两个数的最大公约数。
* 把这些数相乘就是最小公倍数。
*
* 得到:辗转相除法中得到的余数,是一个能被两个数的最大公约数整除的值
*
*2、最小公倍数就等于两个数乘积除以最大公约数
* */
public class YueshuBeiShuTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a =90; int b = 6;
int c = gcd(a,b);
System.out.println("最小公倍数:"+ a*b/c + "最大公约数:" + c);
}
// 得到最大公约数后,最小公倍数就等于两个数乘积除以最大公约数
public static int gcd(int m, int n){
while (true){
if((m = m % n) == 0){
return n;
}
if((n = n % m) == 0){
return m;
}
}
}
}
【程序7】 题目:输入一行字符,分别统计出其中英文字母、空格、数字和其它字符的个数。
正则表达式
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
public class StatisticsStrTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "as df 124 说看见啊";
statisticsStr(str);
}
public static void statisticsStr(String str){
int abccount=0;
int spacecount=0;
int numcount=0;
int othercount=0;
// 匹配英文字母
String E1 = "[a-zA-Z]";
// 匹配空格
String E2 = "\\s*";
// 匹配数字
String E3 = "[0-9]";
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
// 将char变成string 类型才能用正则
String[] arrStr = new String[chars.length];
for(int i =0; i < chars.length; i++){
arrStr[i] = String.valueOf(chars[i]);
}
// 进行正则匹配
for(String cha : arrStr){
if(cha.matches(E1)){
abccount++;
}else
if(cha.matches(E2)){
spacecount++;
}else
if(cha.matches(E3)){
numcount++;
}else {
othercount++;
}
}
System.out.println("英文字母个数:"+abccount);
System.out.println("空格个数:"+spacecount);
System.out.println("数字个数:"+numcount);
System.out.println("其他字符的个数:"+othercount);
}
}
【程序8】 题目:求s=a+aa+aaa+aaaa+aa…a的值,其中a是一个数字。例如2+22+222+2222+22222(此时共有5个数相加),几个数相加有键盘控制。
1.程序分析:关键是计算出每一项的值。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class AddTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("请输入a的值:");
try {
String a = br.readLine();
System.out.println("请输入a的个数:");
String count = br.readLine();
String aa = a;
int sum = 0;
for(int i =1; i<=Integer.parseInt(count); i++){
int b = Integer.parseInt(a);
sum += b;
a += aa;
System.out.println("a===="+a);
}
System.out.println(sum);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
【程序9】 题目:一个数如果恰好等于它的因子之和,这个数就称为 "完数 "。例如6=1+2+3.编程 找出1000以内的所有完数。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
/**
* 一个数如果恰好等于它的因子之和,这个数就称为 "完数 "。例如6=1+2+3.编程 找出1000以内的所有完数。
*
* */
public class WanshuTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int s;
for(int i=1; i <= 1000; i++){
s=0;
for(int j=1; j < i; j++){
if(i % j == 0){
s = s + j;
}
}
if(s == i){
System.out.println(i + " ");
}
}
}
}
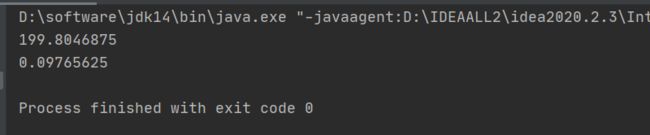
【程序10】 题目:一球从100米高度自由落下,每次落地后反跳回原高度的一半;再落下,求它在 第10次落地时,共经过多少米?第10次反弹多高?
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
public class BollTrapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double s = 0;
double t =100;
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){
s += t;
t = t/2;
}
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println(t);
}
}
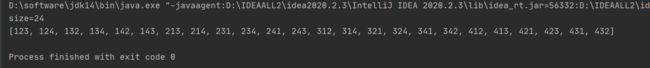
【程序11】 题目:有1、2、3、4个数字,能组成多少个互不相同且无重复数字的三位数?都是多少?
1.程序分析:可填在百位、十位、个位的数字都是1、2、3、4。组成所有的排列后再去 掉不满足条件的排列。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class NoRepetitionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=1; i < 5; i++){
for(int j =1; j < 5; j++){
for(int k=1; k < 5; k++){
if(i != j && j != k && k != i){
list.add(i * 100 + j * 10 + k);
}
}
}
}
System.out.println("size="+list.size());
System.out.println(list);
}
}
【程序12】 题目:企业发放的奖金根据利润提成。利润(I)低于或等于10万元时,奖金可提10%;利润高于10万元,低于20万元时,低于10万元的部分按10%提成,高于10万元的部分,可可提成7.5%;20万到40万之间时,高于20万元的部分,可提成5%;40万到60万之间时高于40万元的部分,可提成3%;60万到100万之间时,高于60万元的部分,可提成1.5%,高于100万元时,超过100万元的部分按1%提成,从键盘输入当月利润I,求应发放奖金总数?
1.程序分析:请利用数轴来分界,定位。注意定义时需把奖金定义成长整型。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ProfitTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入当月利润(单位:万):");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
double x = scanner.nextDouble();
double y = 0;
if(x>0 && x <=10){
y = x * 0.1;
}else if(x > 10 && x<20){
y = 10*0.1 + (x - 10)*0.075;
}else if (x>20&&x<=40) {
y=10*0.1+10*0.075+(x-20)*0.05;
}else if (x>40&&x<=60) {
y=10*0.1+10*0.075+20*0.05+(x-40)*0.03;
} else if (x>60&&x<=100) {
y=10*0.1+10*0.075+20*0.05+20*0.03+(x-60)*0.015;
}else if (x>100) {
y=10*0.1+10*0.075+20*0.05+20*0.03+40*0.015+(x-100)*0.01;
}
System.out.println("应发的奖金是(单位:万):"+y);
}
}
【程序13】
题目:一个整数,它加上100后是一个完全平方数,再加上168又是一个完全平方数,请问该数是多少?
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
public class PingFangTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0 ; i<10000; i++){
if(Math.sqrt(i+100)%1==0 && Math.sqrt(i+168)%1==0){
System.out.println("i="+i);
System.out.println("i+100="+(i+100)+" | Math.sqrt(i+100)="+Math.sqrt(i+100));
System.out.println("i+168="+(i+168)+" | Math.sqrt(i+168)="+Math.sqrt(i+168));
}
}
}
}
【程序14】
题目:输入某年某月某日,判断这一天是这一年的第几天?
判断闰年和平年决定2月的天数:
1、普通闰年:能被4整除但不能被100整除的年份为普通闰年。(如2004年就是闰年,1999年不是闰年);
2、世纪闰年:能被400整除的为世纪闰年。(如2000年是世纪闰年,1900年不是世纪闰年)。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class YearDayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int year,month,day;
int days = 0;
int d = 0;
int e;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
do {
e = 0;
System.out.println("输入年:");
year = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("输入月:");
month = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("输入天:");
day = scanner.nextInt();
if(year < 0 || month <0 || month >12 || day < 0 || day > 31){
System.out.println("输入错误,请重新输入!");
e = 1;
}
}while (e ==1);
for(int i =1; i < month; i++){
switch (i){
case 1:
case 3:
case 5:
case 7:
case 8:
case 10:
case 12:
days = 31;
break;
case 4:
case 6:
case 9:
case 11:
days = 30;
break;
case 2:
if((year % 400 == 0) || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0)){
days = 29;
}else {
days = 28;
}
break;
}
d += days;
}
System.out.println(year + "-" + month + "-" + day + "是这年的第" + (d + day) + "天。");
}
}
【程序15】
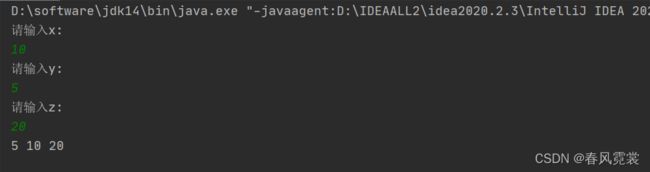
题目:输入三个整数x,y,z,请把这三个数由小到大输出。
思路,只需要一个空杯子t,就可以移动三个数了!
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 输入三个整数x,y,z,请把这三个数由小到大输出。
* */
public class SortTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入x:");
int x = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入y:");
int y = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入z:");
int z = scanner.nextInt();
int t = 0;
if(x > y){
t = x;
x = y;
y = t;
}
if(y > z){
t = z;
z = y;
y = t;
}
if(x > y){
t = x;
x = y;
y = t;
}
System.out.println(x + " " + y + " " + z );
}
}
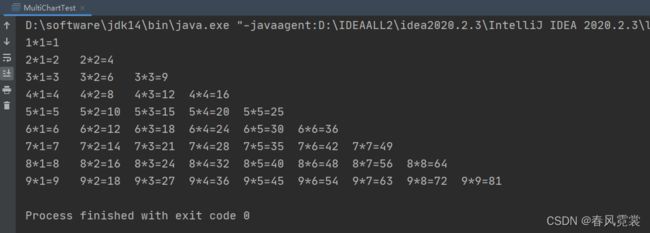
【程序16】 题目:输出9*9口诀。
上三角和下三角的区别在与第二个循环的初始值和结束条件,初始值从1开始,判断条件为小于i的为下三角初始值为i判断条件为小于9的为上三角
三角诀窍:两个循环,
内循环用print()输出
外循环用println()换行
两个条件和初始化:
一个(如i<9)判断条件为小于9,
一个则小于参数(如:j < i)
三角换位则是变化初始化和判断条件的值
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
public class MultiChartTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// multiChart01();
// 下三角
// multiChart02();
// 上三角
multiChart03();
}
// 直接得到
public static void multiChart01(){
for(int i = 1; i <= 9; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= i; j++){
System.out.println(i + "*" + j + "=" + i*j + "\t");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
// 下三角
public static void multiChart02(){
for(int i=1; i <= 9; i++){
for(int j=1; j <= i; j++){
// print()是只输出不换行
System.out.print(i + "*" + j + "=" + i*j + "\t");
// System.out.print(i + "*" + j + "=" + i*j + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// 上三角
/**
* 上三角和下三角的区别在与第二个循环的初始值和结束条件,初始值从1开始,判断条件为小于i的为下三角
* 初始值为i判断条件为小于9的为上三角
* */
public static void multiChart03(){
for(int i = 1; i <= 9; i++){
for(int j=i; j<= 9;j++){
System.out.print(i+"*"+j+"="+i*j+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
【程序17】 题目:猴子吃桃问题:猴子第一天摘下若干个桃子,当即吃了一半,还不瘾,又多吃了一个 第二天早上又将剩下的桃子吃掉一半,又多吃了一个。以后每天早上都吃了前一天剩下 的一半零一个。到第10天早上想再吃时,见只剩下一个桃子了。求第一天共摘了多少。
分析: 前一天的数量就是后一天加1后乘2
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
/**
* 猴子吃桃问题:猴子第一天摘下若干个桃子,当即吃了一半,还不瘾,又多吃了一个 第二天早上又将剩下的桃子吃掉一半,
* 又多吃了一个。以后每天早上都吃了前一天剩下 的一半零一个。到第10天早上想再吃时,见只剩下一个桃子了。求第一天共摘了多少。
* 作者:CoderBigBear
* 链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/e6da97caaa47
* 来源:简书
* 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
*
* */
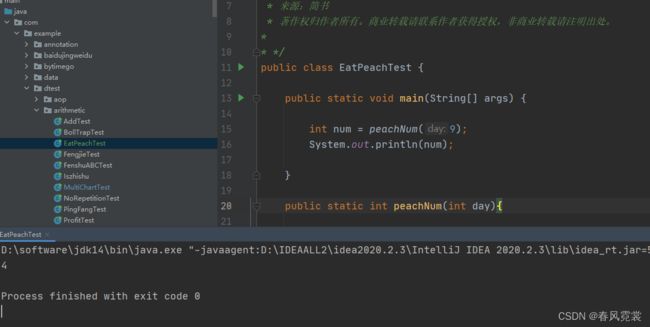
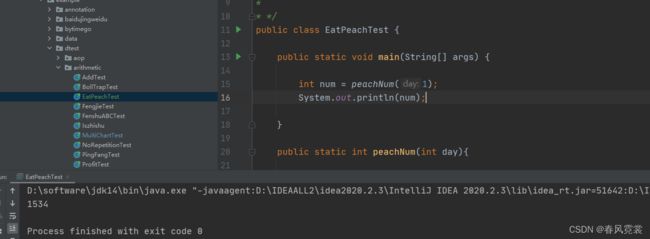
public class EatPeachTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = peachNum(9);
System.out.println(num);
}
public static int peachNum(int day){
if(day == 10){
return 1;
}else {
// 前一天的数量就是后一天加1后乘2
return (peachNum(day+1)+1)*2;
}
}
}
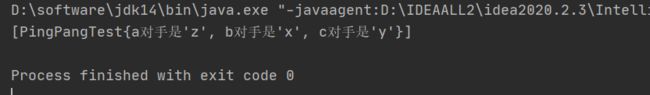
【程序18】 题目:两个乒乓球队进行比赛,各出三人。甲队为a,b,c三人,乙队为x,y,z三人。已抽签决定比赛名单。有人向队员打听比赛的名单。a说他不和x比,c说他不和x,z比,请编程序找出三队赛手的名单。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* 两个乒乓球队进行比赛,各出三人。甲队为a,b,c三人,乙队为x,y,z三人。
* 已抽签决定比赛名单。有人向队员打听比赛的名单。a说他不和x比,c说他不和x,z比,请编程序找出三队赛手的名单。
*
* */
public class PingPangTest {
String a,b,c;
public PingPangTest(String a, String b, String c){
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PingPangTest{" +
"a对手是'" + a + '\'' +
", b对手是'" + b + '\'' +
", c对手是'" + c + '\'' +
'}';
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// String[] abc = new String[3];
// 创建数组来遍历:
String[] op = {"x","y","z"};
ArrayList<PingPangTest> arrayList = new ArrayList<PingPangTest>();
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){
for(int k = 0; k < 3; k++){
// 创建对象来作容器
PingPangTest p = new PingPangTest(op[i],op[j],op[k]);
if(
!p.a.equals(p.b)&&
!p.a.equals(p.c)&&
!p.b.equals(p.c)&&
!p.a.equals("x")&&
!p.c.equals("x")&&
!p.c.equals("z")){
arrayList.add(p);
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(arrayList);
}
}
【程序19】
题目:打印出如下图案(菱形)
星星增长是按照奇数1、3、5、7,而空格是按顺序!

package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
public class LingXingTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
linxin(7);
dengyaosanjiaoxin(7);
}
/**
* 菱形就是两个上下等腰三角形
* */
public static void linxin(int num){
if(num % 2 == 0){
System.out.println("请输入奇数");
return;
}
// int H =7,W = 7;//高和宽必须是相等的
int H =num,W = num;//高和宽必须是相等的
for(int i=0; i < (H+1)/2; i++){
for(int j=0; j<W/2-i; j++){
System.out.print(" ");
}
for(int k=1; k<(i+1)*2; k++){
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println("");
}
for(int i=1; i<=H/2; i++){
for(int j=1; j<=i; j++){
System.out.print(" ");
}
for(int k=1; k<=W-i*2; k++){
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
public static void dengyaosanjiaoxin(int num){
// 等腰三角形,就是菱形截下的被
// 让高和宽必须是相等的,且必须是基数
if(num % 2 == 0){
System.out.println("请输入奇数");
return;
}
int H = num;
int W = num;
// 外层循环判断高的值到哪里
for(int i=0; i < (H+1)/2; i++){
// 空格值:每层空格左边增加 (宽度/2-i)值 (i=循环次数减一,从0开始)
for(int j=1;j <= W/2-i; j++){
System.out.print(" ");
}
// *符号个数:每层*值增加:(i+1)*2-1的数量
for(int k=1;k < (i+1)*2; k++){
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
}
【程序20】 题目:有一分数序列:2/1,3/2,5/3,8/5,13/8,21/13…求出这个数列的前20项之和。
1.程序分析:请抓住分子与分母的变化规律。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
public class FenShuHeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
float fm = 1;
float fz = 1;
float temp;
float sum = 0;
for(int i=0; i < 20; i++){
temp = fm;
// 把分子的值给分母:
fm = fz;
// 分子重新赋值:
fz = fz + temp;
sum += fz/fm;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
【程序21】 题目:求1+2!+3!+…+20!的和
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
/**
* 题目:求1+2!+3!+...+20!的和
* */
public class JieChenAddTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long sum = 0;
long fac = 1;
for(int i=1; i<=20; i++){
fac = fac * i;
sum += fac;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
【程序22】 题目:利用递归方法求5!。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
/**
* 利用递归方法求5!。
* */
public class DiGuiTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(fac(5));
}
public static int fac(int n){
if(n == 1){
return 1;
}else {
return n * fac(n-1);
}
}
}
【程序23】 题目:有5个人坐在一起,问第五个人多少岁?他说比第4个人大2岁。问第4个人岁数,他说比第3个人大2岁。问第三个人,又说比第2人大两岁。问第2个人,说比第一个人大两岁。最后问第一个人,他说是10岁。请问第五个人多大?
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
public class AgeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=1; i <=5; i++){
System.out.println("第"+i+"个的年龄为:"+getAge(i));
}
}
public static int getAge(int n){
if(n == 1){
return 10;
}else {
return 2 + getAge(n-1);
}
}
}
【程序24】
题目:给一个不多于5位的正整数,要求:一、求它是几位数,二、逆序打印出各位数字。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class numPrintTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = scanner.nextLine();
char[] num = str.toCharArray();
System.out.println(num.length);
for(int i=num.length-1; i>0; i--){
System.out.println(num[i-1]);
}
}
}
【程序25】 题目:一个5位数,判断它是不是回文数。即12321是回文数,个位与万位相同,十位与千位相同。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class HuiWenTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入一个5位数:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = scanner.nextInt();
if(!(9999 < num && num < 100000)){
System.out.println("输入错误:请输入一个5位数:");
num = scanner.nextInt();
}
int wan = num/10000;
int qian = num%10000/1000;
int bai = num%1000/100;
int shi = num%100/10;
int ge = num%10;
if(wan == ge && qian == shi){
System.out.println(num+"是回文数");
}else {
System.out.println(num+"不是回文数");
}
}
}
【程序26】 题目:请输入星期几的第一个字母来判断一下是星期几,如果第一个字母一样,则继续 判断第二个字母。
英文星期一到星期天:
星期一(Monday)
星期二(Tuesday)
星期三(Wednesday)
星期四(Thursday)
星期五(Friday)
星期六(Saturday)
星期日(Sunday)
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class XinqiTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入星期的第一个大写字母:");
char ch = getChar();
switch (ch){
case 'M':
System.out.println("Monday:星期一");
break;
case 'W':
System.out.println("Wednesday:星期三");
break;
case 'F':
System.out.println("Friday:星期五");
case 'T':
System.out.println("请输入星期的第二个字母");
char ch2 = getChar();
if(ch2 == 'u'){
System.out.println("Tuesday:星期二");
}else
if(ch2 == 'h'){
System.out.println("Thursday:星期四");
}else {
System.out.println("无此写法!");
}
break;
case 'S':
System.out.println("请输入星期的第二个字母");
char ch3 = getChar();
if(ch3 == 'u'){
System.out.println("Sunday:星期日");
}else
if(ch3 == 'a'){
System.out.println("Saturday:星期六");
}else {
System.out.println("无此写法!");
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("无此写法!");
}
}
public static char getChar(){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = scanner.nextLine();
char ch = str.charAt(0);
if(!((ch>='A'&&ch<='Z')||(ch>='a'&&ch<='z'))){
System.out.println("输入错误,请重新输入:");
ch = getChar();
}
return ch;
}
}
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
public class ShushuTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 因为从3开始算,所有直接输出2
System.out.println(2);
boolean flag = false;
int i,j;
for(i=3;i < 100; i++){
for(j=2; j <=i; j++){
if(i%j == 0){
break;
}
}
// 很重要:判断循环是否提前跳出,如果j
if(j >= i){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
}
【程序28】 题目:对10个数进行排序
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.*;
public class PaiXunum10Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] nums = new Integer[10];
Random random = new Random();
for(int i=0; i< 10; i++){
//得到10个100以内的整数(random范围:0-0.9999999)
nums[i] = random.nextInt(100)+1;
// System.out.println(nums[i]);
}
// 冒泡排序
paixu00(nums);
// 数组自带排序工具
paixu01(nums);
// set排序
paixu02(nums);
// list排序
paixu03(nums);
}
public static void paixu00(Integer[] nums){
// 冒泡排序法升序:
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
for(int j=i;j<nums.length;j++){
if(nums[i] > nums[j]){
// 重要: 不光赋值,还要换位
Integer t = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = t;
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
System.out.println(nums[i]);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------------------");
// 冒泡排序法降序:
for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++){
for(int j=i; j<nums.length; j++){
if(nums[i] < nums[j]){
// 重要: 不光赋值,还要换位
Integer t = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = t;
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
System.out.println(nums[i]);
}
}
public static void paixu01(Integer[] nums){
// 数组默认工具,从小到大排列:
Arrays.sort(nums);
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
System.out.println(nums[i]);
}
System.out.println("------------------------------");
// 若要自定义,需添加匿名内部类
Arrays.sort(nums,new Comparator<Integer>(){
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
/**
* 当o1
if(o1 < o2){
return 1;
}else if(o1 > o2){
return -1;
}else {
return 0;
}
}
});
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
System.out.println(nums[i]);
}
}
public static void paixu02(Integer[] nums){
// 默认升序
Set<Integer> set = new TreeSet<>();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
set.add(nums[i]);
}
System.out.println("set====="+set);
System.out.println("---------------------");
// 自定义降序
Set<Integer> setZiDing = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
if(o1 < o2){
return 1;
}else if(o1 > o2){
return -1;
}else {
return 0;
}
}
});
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
setZiDing.add(nums[i]);
}
System.out.println("setZiDing==="+setZiDing);
}
public static void paixu03(Integer[] nums){
List<Integer> integerList = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i< nums.length; i++){
integerList.add(nums[i]);
}
// 升序:
Collections.sort(integerList, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
if(o1 < o2){
return 1;
}else if(o1 > o2){
return -1;
}else {
return 0;
}
}
});
System.out.println(integerList);
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
// 降序:
Collections.sort(integerList, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
if(o1 < o2){
return -1;
}else if(o1 > o2){
return 1;
}else {
return 0;
}
}
});
System.out.println(integerList);
}
}
【程序29】 题目:求一个3*3矩阵对角线元素之和
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
public class JuZhenDuiJiaoTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// System.out.println("请输出3*3的矩阵元素");
// int[][] arr = new int[3][3];
int[][] arr = {{1,2,3},{4,5,6},{7,8,9}};
// arr.length:横排数
// arr[0].length:竖排数
System.out.println("arr.length===="+arr.length);
System.out.println("arr.length===="+arr[0].length);
for(int i = 0; i< arr.length;i++){
for(int j=0; j<arr[i].length;j++){
System.out.print(arr[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
matrixValueSum(arr);
}
public static void matrixValueSum(int[][] arr){
int sum1 = 0;
int sum2 = 0;
for(int i=0; i< arr.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<arr[i].length;j++){
if(i == j){
sum1 += arr[i][j];
}
if(j == arr.length - i-1){
System.out.println("ij=="+i+j);
sum2 += arr[i][j];
}
}
}
System.out.println("sum1="+sum1+"sum2="+sum2);
}
}
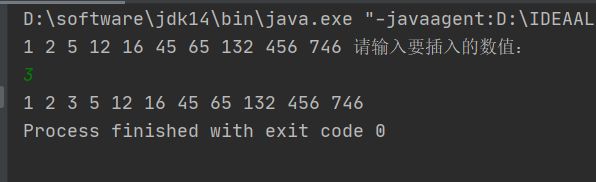
【程序30】 题目:有一个已经排好序的数组。现输入一个数,要求按原来的规律将它插入数组中。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrChaRuTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// System.out.println("请输入是个数值:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// int[] arr = new int[10];
// for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
// arr[i] = scanner.nextInt();
// }
int[] arr = {1,5,45,12,65,
746,132,456,2,16};
Arrays.sort(arr);//默认升序排序
for(int i=0; i<arr.length;i++){
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
// 请输入要插入的数值:
System.out.println("请输入要插入的数值:");
int x = scanner.nextInt();
arr = sort(arr, x);
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
public static int[] sort(int[] a,int b){
int[] c = new int[a.length+1];
boolean flag = true;
for(int i=0; i<a.length; i++){
if(flag){
if(a[i] < b){
c[i] = a[i];
}else {
c[i] = b;
flag = false;
//参数依次意义:要复制的源数组;要源数组开始索引;要复制到的目标数组;目标数组的开始索引;要复制的长度
System.arraycopy(a,i,c,i+1,a.length-i);
}
}else {
break;
}
}
return c;
}
}
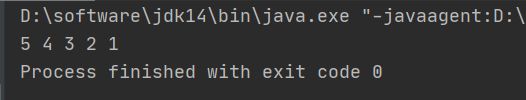
【程序31】 题目:将一个数组逆序输出。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
public class NiXuTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
for(int i=arr.length-1; i >= 0; i--){
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
}
【程序32】 题目:取一个整数a从右端开始的4~7位。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class JieQuTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入7位长度的数:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = scanner.nextLine();
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
int j = chars.length;
if(chars.length < 7){
System.out.println("error!");
}
// 第一种:字符数组
System.out.println(chars[j-7]+""+chars[j-6]+""+chars[j-5]+""+chars[j-4]);
// 第二种:字符串截取:
System.out.println(str.substring(str.length()-7,str.length()-4+1));
}
}
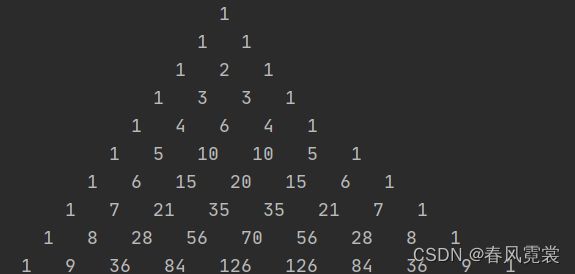
杨辉三角形
【程序33】
题目:打印出杨辉三角形(要求打印出10行如下图)
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
public class YangHuiSanJiaoTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] a = new int[10][10];
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
a[i][i] = 1;//每一行最后一个数是1
a[i][0] = 1;//每一行的第一个数是1
}
for(int i=2; i<10;i++){
for(int j=1; j<i; j++){
// 每一行中间值,等于上一行相邻中间值相加
a[i][j] = a[i - 1][j - 1] + a[i - 1][j];
}
}
for(int i=0; i< 10; i++){
// 第一行前面有循环长度的两倍才会在中间,因为上下的每个数都是在空隙中间而不是对齐的
// 之后就随着i值增加,空隙也成2倍减少
// 减一是上图从左边最边开始,不减最后一排是从左边第2个开始
for(int k=0; k< (10-i)*2-1; k++){
// for(int k=0; k< (10-i)*2; k++){
System.out.print(" ");
}
for(int j = 0 ;j<= i; j++){
// 空格为3个,会让上一行的数落在下一行的中间位置
System.out.print(a[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
【程序34】 题目:输入3个数a,b,c,按大小顺序输出。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class DaXiaoTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] arr = new int[3];
for(int i=0; i<3;i++){
System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"个数");
arr[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
paixu01(arr);
}
public static void paixu01(int[] arr){
// 升序排序
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
// 这里循环必须是j=i,才不会将之前比对过的再比对后交换
for(int j=i;j<arr.length;j++){
if(arr[i] > arr[j]){
int t = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = t;
}
}
}
for(int a:arr){
System.out.print(a+" ");
}
System.out.println("升序!");
}
}
题目:输入数组,最大的与第一个元素交换,最小的与最后一个元素交换,输出数组。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PaiXuMaxMin {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] a = new int[5];
for(int i=0; i < a.length; i++){
System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"个值:");
a[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
for(int i=0; i < a.length; i++){
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// 找出最大值
int maxi = 0;
int max = a[maxi];
for(int i =1; i< a.length; i++){
if(max < a[i]){
max = a[i];
maxi = i;
}
}
// 将第一个和最大值交换值i
int t = a[0];
a[0] = a[maxi];
a[maxi] = t;
// 找出最小值
int mini = 0;
int min = a[mini];
for(int i = 0; i< a.length; i++){
if(min > a[i]){
min = a[i];
mini = i;
}
}
// 将最小值和最后一位交换
int k = a[a.length -1];
a[a.length -1] = a[mini];
a[mini] = k;
for(int j: a){
System.out.print(j+ " ");
}
}
}

【程序36】
题目:有n个整数,使其前面各数顺序向后移m个位置,最后m个数变成最前面的m个数
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class HouYiTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = 10;
int[] a = new int[N];
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入10个整数:");
for(int i=0; i < N; i++){
a[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("你输入的数组为: ");
for(int i=0; i < N; i++){
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println("请输入向后移动的位数: ");
int m = scanner.nextInt();
int[] b = new int[m];
// 将要m个末尾数据取出
for(int i=0;i < m; i++){
b[i] = a[N - m + i];
System.out.println("bi====="+b[i]);
}
// 将移动m个数,将前面的m个数赋值到后面
for(int i=N-1;i>=m;i--){
a[i] = a[i-m];
}
// 将b[i]保存的末尾m个数添加到最前面上去
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
a[i] = b[i];
}
System.out.println("位移后的数组是: ");
for(int i=0; i < N; i++){
System.out.print(a[i]+ " ");
}
}
}
【程序38】
题目:写一个函数,求一个字符串的长度,在main函数中输入字符串,并输出其长度。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Zhifucd {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入字符串:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println(str.length());
}
}
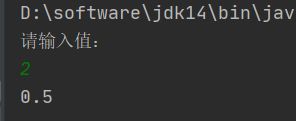
【程序39】
题目:编写一个函数,输入n为偶数时,调用函数求1/2+1/4+…+1/n,当输入n为奇数时,调用函数1/1+1/3+…+1/n(利用指针函数)
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Fenshujia {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入值:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println(sum(n));
}
public static double sum(int n){
double sum = 0;
if(n % 2 == 0){
for(int i=2; i<= n; i+=2){
sum += (double)1/i;
}
}else {
for(int i=1; i<=n; i+=2){
sum += (double)1/i;
}
}
return sum;
}
}
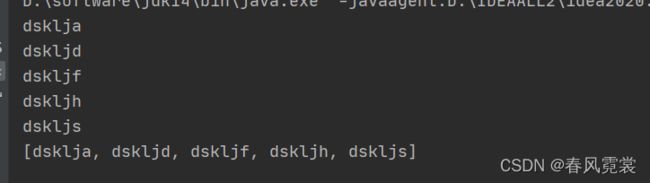
题目:字符串排序。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class StrPaixu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] str = new String[5];
str[0] = "dsklja";
str[1] = "dskljf";
str[2] = "dskljh";
str[3] = "dskljs";
str[4] = "dskljd";
compar01(str);
compar02(str);
}
public static boolean compare(String s1,String s2){
boolean flag = true;
for(int i=0; i < s1.length() && i< s2.length() ; i++){
if(s1.charAt(i) > s2.charAt(i)){
flag = false;
break;
// 如果前面的小于后面的,返回true,默认升序
}else if(s1.charAt(i) < s2.charAt(i)){
flag = true;
break;
// 如果没到结尾就有相等的情况,这进行下一循环:
}else if(s1.length()-1 > i || s2.length()-1 > i){
continue;
}else
{
if(s1.length() < s2.length()){
flag = true;
break;
}else {
flag = false;
break;
}
}
}
return flag;
}
public static void compar01(String[] strings){
String temp = null;
for(int i=0; i<5; i++){
for(int j = i+1; j< 5;j++){
if(!compare(strings[i],strings[j])){
temp = strings[i];
strings[i] = strings[j];
strings[j] = temp;
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i< 5; i++){
System.out.println(strings[i]);
}
}
public static void compar02(String[] strings){
List<String> stringList = Arrays.asList(strings.clone());
Collections.sort(stringList);
System.out.println(stringList);
}
}
题目:海滩上有一堆桃子,五只猴子来分。第一只猴子把这堆桃子凭据分为五份,多了一个,这只猴子把多的一个扔入海中,拿走了一份。第二只猴子把剩下的桃子又平均分成五份,又多了一个,它同样把多的一个扔入海中,拿走了一份,第三、第四、第五只猴子都是这样做的,问海滩上原来最少有多少个桃子?
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
public class HouTaoTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//假设每个猴子拿走1个,加上每个猴子仍在海里的1个,
//剩下的4个,所以从14开始,其实好多开始不重要
int num = 14;
while (true){
//执行方法IsNumber()查看桃子数是否符合要求
if(isNumber(num)){
break;
}else {
num++;
}
}
System.out.println(num);
}
public static boolean isNumber(int num){
int i=0;
while (i < 5){
//只有正确的桃子数i才会累加到5,返回true
//反之不正常时,要么直接执行else,要么先执行1到3次if再执行else返回false
if((num - 1)%5 == 0){
//(num-1)/5是每个猴子拿走的桃子,-1是每个猴子扔到海里的
num = num - (num - 1)/5 - 1;
i++;
}else{
return false;
}
}
System.out.println("i==="+i);
return true;
}
}
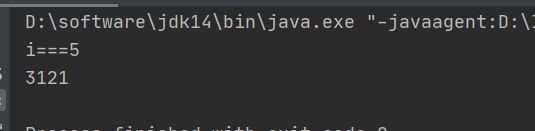
【程序41】
//题目:809*??=800*??+9*??其中??代表的两位数,8*??的结果为两位数,9*??的结果为3位数。求??代表的两位数,及809*??后的结果。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
public class FangChengShiTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 10;
int num =0;
for(;x<100;x++){
if( (10<8*x && 8*x <100)&&(100<=9*x && 9*x<1000)){
System.out.println("x====="+x);
if(809 * x == 800 * x + 9*x){
num = x;
}
}
}
System.out.println("两位数为:"+num);
System.out.println("809 * x ="+809*num);
System.out.println("800 * x + 9*x="+(800 * num + 9*num));
}
}
【程序43】
题目:求0—7所能组成的奇数个数。
解法一:用8个for循环来拼数字,此种做法需要顾忌最高位不为零的情
解法二(推荐):
该题认为数字可以重复使用,这个问题其实是一个排列组合的问题,设这个数为sun=a1a2a3a4a5a6a7a8,a1-a8表示这个数的某位的数值,
当一个数的最后一位为奇数时,那么这个数一定为奇数,不管前面几位是什么数字。如果最后一位数为偶数,
则这个数一定为偶数。
a1-a8可以取0-7这个八个数字,首位数字不为0。
即一个a为4种(个位),另一个7种(首位),
从该数为一位数到该数为8位数开始统计奇数的个数:
1.当只有一位数时也就是该数的最后一位,奇数个数为4
2.当该数为两位数时,奇数个数为47=28
3.当该数为三位数时,奇数个数为:48*7=224
。
。
。
8.当该数为八位数时,奇数个数为:4888888*7(依次为最后一位到第一位)
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
public class JiShu07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer sum = 0 , total = 0;
for(int i=1; i<9; i++){
if(i == 1){
total =4;//1357
}else if(i == 2){
total = total*7;
}else {
total *= 8;
}
System.out.println("0~7组成" + i + "位数,有:" + total + "个");
sum += total;
}
System.out.println("总计为:"+sum);
}
}
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ShuSuHeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入一个偶数:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.close();
if(n % 2 != 0){
System.out.println("你输入的不是偶数");
}
twoAdd(n);
}
// 偶数分解素数之和
public static void twoAdd(int n){
for(int i=2; i< n/2 +1;i++){
if(isPrime(i) && isPrime(n-i)){
System.out.println(n+"="+i+"+"+(n-i));
break;
}
}
}
// 判断素数
public static boolean isPrime(int m){
boolean flag = true;
for(int i=2; i< Math.sqrt(m)+1 ;i++){
if(m % i == 0){
flag = false;
break;
}
}
return flag;
}
}

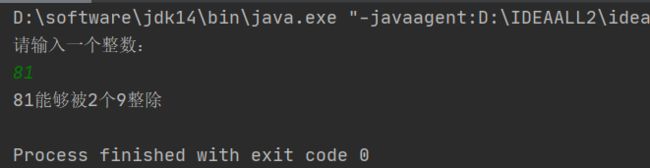
【程序45】
题目:判断一个素数能被几个9整除
//题目错了吧?能被9整除的就不是素数了!所以改成整数了。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ZhenChu9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个整数:");
int num = scanner.nextInt();
int count =0;
int tmp = num;
while (tmp % 9 == 0){
tmp = tmp / 9;
count++;
if(tmp == 0){
break;
}
}
System.out.println(num+"能够被"+count+"个9整除");
}
}
【程序46】
题目:两个字符串连接程序
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ZhiFuChuanLianJeiTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
String str1 = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
String str2 = scanner.nextLine();
String str = str1 + str2;
System.out.println("连接后的字符串是:"+str);
}
}
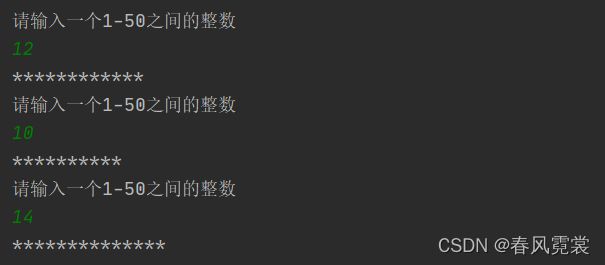
【程序47】
题目:读取7个数(1—50)的整数值,每读取一个值,程序打印出该值个数的*。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class DaYinXinTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=1,num;
while (n <= 7){
do{
System.out.println("请输入一个1-50之间的整数:");
num = scanner.nextInt();
}while (num<1 || num>50);//输入1-50的数,就会跳出循环
for(int i=1; i<=num; i++){
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
n++;
}
}
}
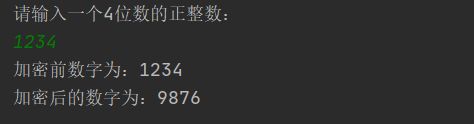
【程序48】
题目:某个公司采用公用电话传递数据,数据是四位的整数,在传递过程中是加密的,加密规则如下:每位数字都加上5,然后用和除以10的余数代替该数字,再将第一位和第四位交换,第二位和第三位交换。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class DianHJiaMiTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("请输入一个4位数的正整数:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("加密前数字为:"+num);
change(num);
}
public static void change(int num){
// 分解出位数
int x1,x2,x3,x4;
x1 = num % 10; //分解各位
x2 = num / 10 % 10; //分解十位
x3 = num / 100 % 10; //分解百位
x4 = num / 1000; //分解千位
// 代替数字
x1 = (x1 + 5) % 10;
x2 = (x2 + 5) % 10;
x3 = (x3 + 5) % 10;
x4 = (x4 + 5) % 10;
// 第一位和第四位交换
int swop;
swop = x1;
x1 = x4;
x4 = swop;
// 第二位和第三位交换
swop = x2;
x2 = x3;
x3 = swop;
System.out.println("加密后的数字为:"+x4+x3+x2+x1);
}
}
【程序49】
题目:计算字符串中子串出现的次数
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class StrJiequTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("输入字符串:");
String str1 = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入子串:");
String str2 = scanner.nextLine();
int count = 0;
if(str1.equals("")||str2.equals("")){
System.out.println("你没有输入字符串或子串,无法比较!");
}else {
for(int i=0;i<=str1.length()-str2.length();i++){
if(str1.substring(i,i+str2.length()).equals(str2)){
count++;
i = i+str2.length()-1;//减一是因为for循环有自加一
}
}
System.out.println("字串在字符串中出现:"+count+"次");
}
}
}
【程序50】
题目:有五个学生,每个学生有3门课的成绩,从键盘输入以上数据(包括学生号,姓名,三门课成绩),计算出平均成绩,把原有的数据和计算出的平均分数存放在磁盘文件 "stud "中。
package com.example.dtest.arithmetic;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ChenJiTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String[][] a = new String[5][6];
// for(int i=1; i<6; i++){
for(int i=0; i<2; i++){
System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"个学生的学号:");
a[i][0] = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"个学生的姓名");
a[i][1] = scanner.nextLine();
for(int j=2; j<5; j++){
System.out.println("请输入该学生的第"+j+"个成绩:");
a[i][j] = scanner.nextLine();
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
// 计算平均分
float avg;
int sum;
// for(int i=0; i<5; i++){
for(int i=0; i<2; i++){
sum = 0;
for(int j=2; j<5; j++){
sum = sum + Integer.parseInt(a[i][j]);
}
// 计算出每项的平均分
avg = (float)sum/3;
a[i][5] = String.valueOf(avg);
}
// 写入磁盘
String s1 = "";
try {
File file = new File("D:\\stud.txt");
if(file.exists()){
System.out.println("文件存在");
}else {
System.out.println("文件不存在,正在创建文件");
file.createNewFile();
}
BufferedWriter output = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
// for(int i=0; i<5; i++){
for(int i=0; i<2; i++){
for(int j=0; j<6; j++){
System.out.println(a[i][j]);
s1 = a[i][j] + " ";
output.write(s1);
}
// 换行:
output.write("\r\n");
}
output.close();
System.out.println("数据已经写入磁盘");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}