C++ STL Map和Multimap使用方法
Map和multimap将key/value pair当作元素进行管理,可根据key的排序准则自动为元素排序.
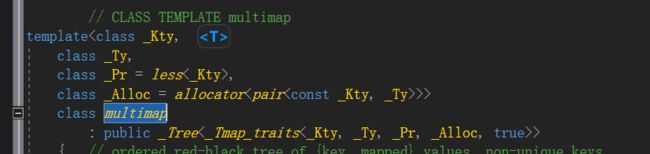
multimap允许重复元素,map不允许
头文件
注意:
第一个模板实参将成为元素的key类型,第二个模板实参将成员元素的值类型.
key和T必须满足以下两个条件:
1.key和value都是可复制的或可搬移的
2.key必须是可比较的
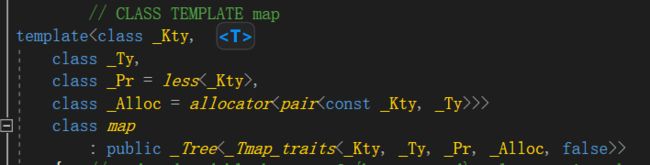
Map和Multimap的能力

和其他所有关联式容器一样,map/Multimap通常以平衡二叉树完成
Map/和Multimap根据元素的key自动对元素排序,根据已知的key查找某个元素时就能有很好的效率,而根据已知value查找元素,效率就很糟糕.
你不可以直接改变元素的key,因为这回破坏正确次序,要修改元素的key,必须先移除拥有该key的元素,然后插入拥有新key/value的元素
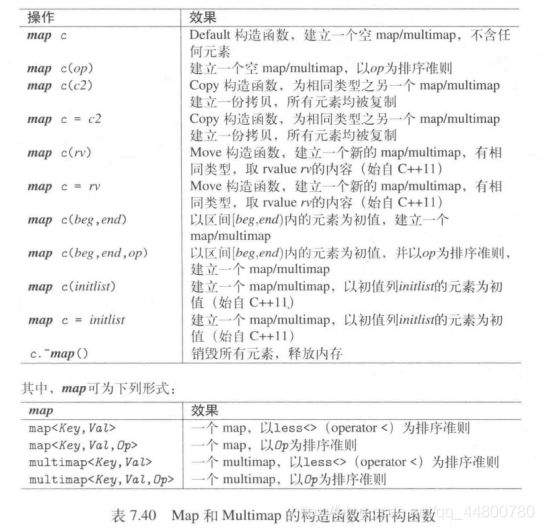
Map和Multimap的操作函数
构造函数和析构函数
类似set,有两种方式可以定义排序准则:
1.以模板参数定义:
map<float,string,greater<float>>coll;
2.以构造参数定义:可以看最下面的综合例子
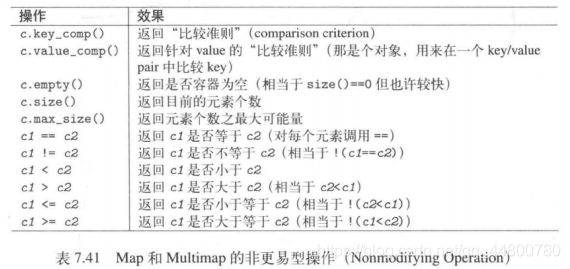
非更易型操作
特殊查找动作
赋值
迭代器函数和元素访问
Map和multimap不支持元素直接访问,但是map提供了at()以及下标操作符可以直接访问元素。
和其他所有关联式容器一样,这里的迭代器是双向迭代器.所以,无法使用随机访问迭代器的STL算法
更重要的是,所有元素的key都被视为常量,元素的实质类型是pair
所有你不能更改key,不能对map、multimap调用任何更易型算法,比如remove(),
因为remove()算法实际上是将其实参值覆盖掉被移除的元素.
下面是使用基于范围的for循环访问map元素:
map<string,float>coll;
...
for(auto elem& : coll)
{
cout << "key: " << elem.first << "\t" << "value: " << elem.second << endl;
}
以迭代器访问元素:
map<string,float>coll;
...
map<string,float>::iterator pos;
for(pos = coll.begin(); pos!= coll.end();++pos)
{
cout << "key: " << pos->first << '\t' << "value: " << pos->second << endl;
}
如果使用算法或lambda来操作map元素,可以这样做:
map<string,float>coll;
...
for_each(coll.begin(),coll.end(),[](pair<const string, float>&elem){elem.second +=10;});
for_each(coll.begin(),coll.end(),[](map<string,float>::value_type&elem){elem.second +=10;});
for_each(coll.begin(),coll.end(),[](decltype(coll)::value_type&elem){elem.second +=10;});
如果一定要改变元素的key,只有一条路:使用一个值相同的新元素替换旧元素
template<typename Cont>
inline bool replace_key(Cont & c, const typename Cont::key_type& old_key, const typename Cont::key_type& new_key)
{
typename Cont::iterator pos;
pos = c.find(old_key);
if (pos != c.end())
{
c.insert(typename Cont::value_type(new_key, pos->second));
c.erase(pos);
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
你可以这样调用:
map<string,float>coll;
replace_key(coll,"old key", "new key");
multimap,情况也一样
注意:map提供了一种非常方便的手法,让你改变元素的key:
coll["new key"] = coll["old_key"];
coll.erase("old_key");
元素的安插和移除
有三种不同的方法可以将value传入map或multimap内:
1.value_type:
map<string,float>coll;
coll.insert(map<string,float>::value_type("otto",22.3));
coll.insert(decltype(coll)::value_type("otto",22.3));
2.pair<>:
map<string,float>coll;
coll.insert(pair<string,float>("otto",22.3));
3.make_pair():
map<string,float>coll;
coll.insert(make_pair("otto",22.3));
使用emplace()安插新元素,可以这样做:
map<string,complex<float>>m;
m.emplace(std::piecewise_construct, make_tuple("hello"),make_tuple("3.4,7.8"));
想要移除某个值为value的元素,可以这样做:
map<string,float>coll;
coll.erase(key);
如果multimap内含重复元素,你无法使用erase删除重复元素中的第一个,但是可以这样做:
multimap<string,float>coll;
auto pos = coll.find(key);
if(pos!= coll.end())
{
coll.erase(pos);
}
将Map视为关联式数组

注意:如果你选择某key作为索引,而容器内却没有相应元素,那么map会自动安插一个新元素,其value被其类型的默认构造函数初始化.
优点:
你可以通过更方便的接口对map安插新元素:
map<string,float>coll;
coll["otto"] = 7.7;
coll["otto"] = 7.7处理如下:
1.如果存在key为“otto”的元素,上式会返回元素的引用。
.如果没有任何元素的key是"otto",上式便为map自动安插一个新元素,令其key为“otto”,其value则以默认构造函数完成,并返回一个引用指向新元素.
2.将7.7赋值给value
缺点:
你有可能不小心误置新元素,比如以下语句:
cout << coll["ottto"];
就会不小心安插了一个Key为“ottto”的新元素.
Map和Multimap运用实例
使用算法和Lambda:
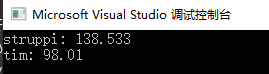
map<string, double>coll{ {"tim",9.9},{"struppi",11.77} };
for_each(coll.begin(), coll.end(), [](pair<const string, double>&elem) {elem.second *= elem.second; });
for_each(coll.begin(), coll.end(), [](const map<string, double>::value_type &elem) {cout << elem.first << ": " << elem.second << endl; });
将Map当做关联式数组:
using StringFloatMap = map<string, float>;
StringFloatMap stocks;
stocks["BASF"] = 369.50;
stocks["VW"] = 413.50;
stocks["Daimler"] = 819.00;
stocks["BMW"] = 834.00;
stocks["Siemens"] = 842.20;
StringFloatMap::iterator pos;
cout << left;
for (pos = stocks.begin(); pos != stocks.end(); ++pos)
{
cout << "stock: " << setw(12) << pos->first << "price: " << pos->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
for (pos = stocks.begin(); pos != stocks.end(); ++pos)
{
pos->second *= 2;
}
for (pos = stocks.begin(); pos != stocks.end(); ++pos)
{
cout << "stock: " << setw(12) << pos->first << "price: " << pos->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
stocks["Volkswagen"] = stocks["VW"];
stocks.erase("VW");
for (pos = stocks.begin(); pos != stocks.end(); ++pos)
{
cout << "stock: " << setw(12) << pos->first << "price: " << pos->second << endl;
}
将Map当做字典:
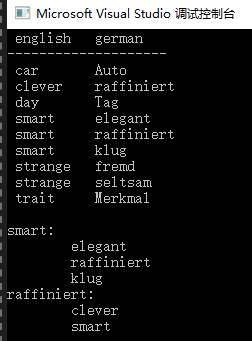
multimap<string, string>dict;
dict.insert({ {"day","Tag"},{"strange","fremd"},{"car","Auto"},{"smart","elegant"},
{"trait","Merkmal"},{"strange","seltsam"},{"smart","raffiniert"},{"smart","klug"},
{"clever","raffiniert"} });
cout.setf(ios::left, ios::adjustfield);
cout << ' ' << setw(10) << "english " << "german " << endl;
cout << setfill('-') << setw(20) << "" << setfill(' ') << endl;
for (const auto & elem : dict)
{
cout << ' ' << setw(10) << elem.first << elem.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
string word("smart");
cout << word << ": " << endl;
for (auto pos = dict.lower_bound(word); pos != dict.upper_bound(word); ++pos)
{
cout << " " << pos->second << endl;
}
word = ("raffiniert");
cout << word << ": " << endl;
for (const auto & elem : dict)
{
if (elem.second == word)
{
cout << " " << elem.first << endl;
}
}
查找具有某特定value的元素:
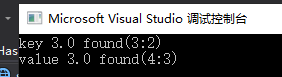
map<float, float>coll { {1,7},{2,4},{3,2},{4,3},{5,6},{6,1},{7,3} };
auto posKey = coll.find(3.0);
if (posKey != coll.end())
{
cout << "key 3.0 found(" << posKey->first << ":"
<< posKey->second << ")" << endl;
}
auto posVal = find_if(coll.begin(), coll.end(),
[](const pair<float, float>&elem) {return elem.second == 3.0; });
if (posVal != coll.end())
{
cout << "value 3.0 found(" << posVal->first << ":"
<< posVal->second << ")" << endl;
}
综合实例:运用Map、String并于运行期指定排序准则
class RuntimeStringCmp
{
public:
enum cmp_mode {normal,nocase};
private:
const cmp_mode mode;
static bool nocase_compare(char c1, char c2)
{
return toupper(c1) < toupper(c2);
}
public:
RuntimeStringCmp(cmp_mode m = normal) : mode(m) {}
bool operator() (const string & s1, const string & s2)const
{
if (mode == normal)
{
return s1 < s2;
}
else
{
return lexicographical_compare(s1.begin(), s1.end(), s2.begin(), s2.end(), nocase_compare);
}
}
};
using StringStringMap = map<string, string, RuntimeStringCmp>;
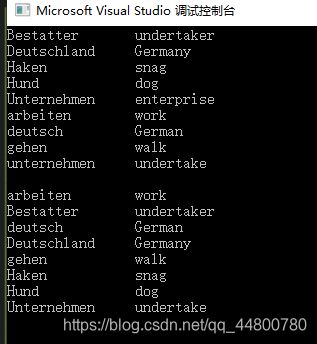
void fillAndPrint(StringStringMap&coll)
{
coll["Deutschland"] = "Germany";
coll["deutsch"] = "German";
coll["Haken"] = "snag";
coll["arbeiten"] = "work";
coll["Hund"] = "dog";
coll["gehen"] = "go";
coll["Unternehmen"] = "enterprise";
coll["unternehmen"] = "undertake";
coll["gehen"] = "walk";
coll["Bestatter"] = "undertaker";
cout.setf(ios::left, ios::adjustfield);
for (const auto & elem : coll)
{
cout << setw(15) << elem.first << " " << elem.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
StringStringMap coll1;
fillAndPrint(coll1);
RuntimeStringCmp ignorecase(RuntimeStringCmp::nocase);
StringStringMap coll2(ignorecase);
fillAndPrint(coll2);
}