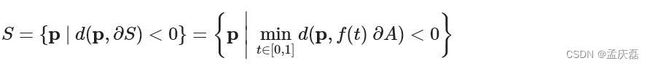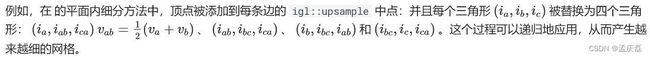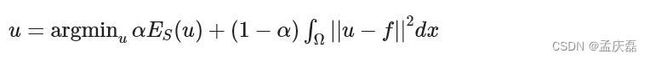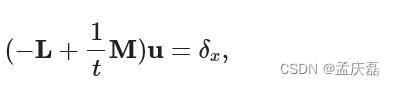Libigl学习笔记——二、第七章——其他
Libigl学习笔记——二、第七章——其他
- 第七章
- 7.1 网格统计 Mesh Statistics
- 7.2 广义绕组数 Generalized Winding Number
- 7.3 网格抽取 Mesh Decimation
- 7.4 有符号距离 Signed Distances
-
- 7.4.1 点位置 Point Location
- 7.4.2 最近点 Closest Points
- 7.4.3 符号距离 Signed Distance
- 7.5 行进立方体 Marching Cubes
- 7.6 小平面方向 Facet Orientation
- 7.7 扫描卷 Swept Volume
- 7.8 拣选 Picking
- 7.9 可扩展的局部注入映射 Scalable Locally Injective Maps
- 7.10 双射映射的单纯复数增强框架 Simplicial Complex Augmentation Framework For Bijective Maps
- 7.11 细分曲面 Subdivision Surfaces
- 7.12 数据平滑 Data Smoothing
- 7.13 形状投影 Shapeup Projections
- 7.14 行进四面体 Marching Tetrahedra
- 7.15 隐式函数网格划分 Implicit Function Meshing
- 7.16 快速测地线距离近似的热法 Heat Method For Fast Geodesic Distance Approximation
-
- 7.16.1 内在德劳奈三角测量 Intrinsic Delaunay Triangulation
- 7.17 汤和云的快速缠绕数 Fast Winding Number For Soups And Clouds
-
- 7.17.1 汤 Soups
- 7.17.2 云 Clouds
- 7.18 迭代最近点 Iterative Closest Point¶
- 7.19 分解图 Exploded View
- 7.20 蓝色噪声表面采样 Blue Noise Surface Sampling
- 7.21 矢量场平滑 Vector Field Smoothing
- 7.22 向量并行传输 Vector Parallel Transport
第七章
Libigl 包含各种各样的几何处理工具和函数,用于处理网格和与之相关的线性代数:本入门教程中讨论的内容太多了。我们在本章中列出了几个有趣的功能来重点介绍。
7.1 网格统计 Mesh Statistics
- Libigl 包含各种网格统计信息,包括面角度、面面积和奇异顶点的检测,奇异顶点是三角测量中邻域中或四边形中邻点多于或少于 4 个的顶点。
- 示例 Statistics 计算这些数量并进行基本的统计分析,以估计网格的等距和规则性:
Irregular vertices:
136/2400 (5.67%)
Areas (Min/Max)/Avg_Area Sigma:
0.01/5.33 (0.87)
Angles in degrees (Min/Max) Sigma:
17.21/171.79 (15.36)
- 第一行包含不规则顶点的数量和百分比,这对于用于定义细分曲面的四边形网格尤其重要:每个奇异点都将导致曲面上只有一个 C^1 的点。
- 第二行报告最小元素、最大元素和标准偏差的面积。这些数字按平均面积归一化,因此在上面的示例中,最大面积为 5.33 意味着最大的面比平均面大 5 倍。理想的各向同性网格的最小和最大面积都接近 1。
- 第三行测量面角,在完全规则的三角测量中,面角应接近 60 度(四边形为 90 度)。对于 FEM 而言,角度越接近 60 度,优化就越稳定。在这种情况下,很明显网格质量很差,如果用于求解偏微分方程,可能会导致伪影。
- 701案例完整展示:
#include 7.2 广义绕组数 Generalized Winding Number
- 封闭水密表面网格内部的四面体化问题是一个困难但适中的问题(参见我们的 Tetgen 包装器)。但是像TetGen这样的黑盒四边形网格器将拒绝来自多个连接组件的具有自相交、开放边界、非流形边的输入三角形网格。问题是双重的:自交存在矛盾的面约束,自交/开边界/非流形边使得在没有进一步假设的情况下确定内部和外部的问题变得不合适。
- 第一个问题可以通过“解决”所有自交叉点轻松解决。也就是说,对相交三角形进行网格划分,以便相交恰好发生在边和顶点处。这是使用 完成 igl::selfintersect 此操作的。
- TetGen通常可以将这个“已解决”网格的凸包四面体化,然后问题就变成了确定哪些t在输入网格内部,哪些在外部。也就是说,哪些应该保留,哪些应该删除。
- “广义绕组数”是一种确定麻烦网格内部和外部的可靠方法 40 。相对于某一 (V,F) 点 p∈R^3 的广义绕组数定义为标量函数:
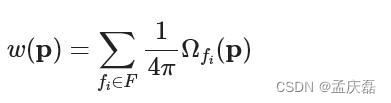
- 其中 Ωfi ,在点 p 处由(第 i 个面) F 替换的 fi 立体角。这个立体角贡献是一个简单的闭式表达式,涉及 atan2 一些点积。
- 如果确实形成一个封闭的水密表面,那么 w§=1 如果位于内部, w§=0 如果 (V,F) p 位于外部 (V,F) (V,F) 。如果关闭但自身重叠,则 (V,F) w§ 是一个整数值,计算有多少(有符号)环绕 (V,F) p 。最后,如果不是闭合的或甚至不是流形(但至少是一致的定向),则 (V,F) w§ 平滑地趋向于1 p ,因为内部 (V,F) 更多,并且趋向于0 p ,因为外部更多。
- 702案例完整展示:
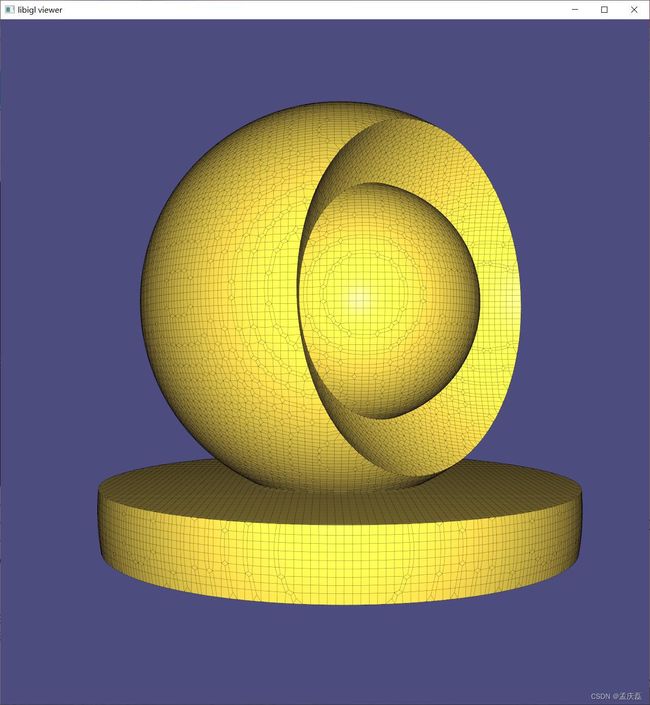
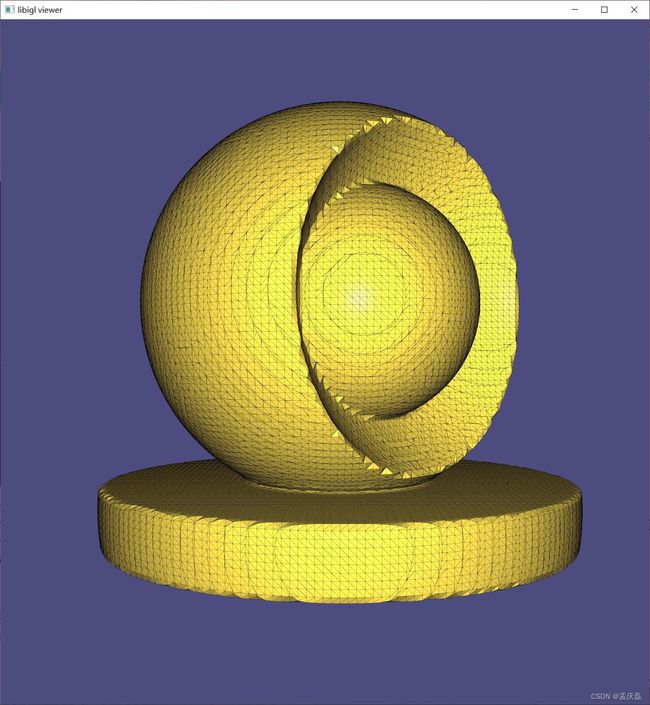
#include 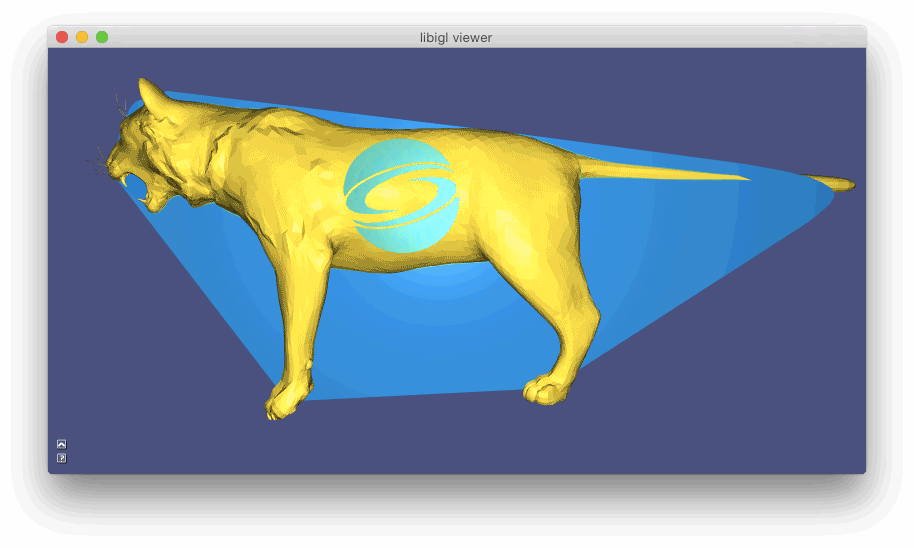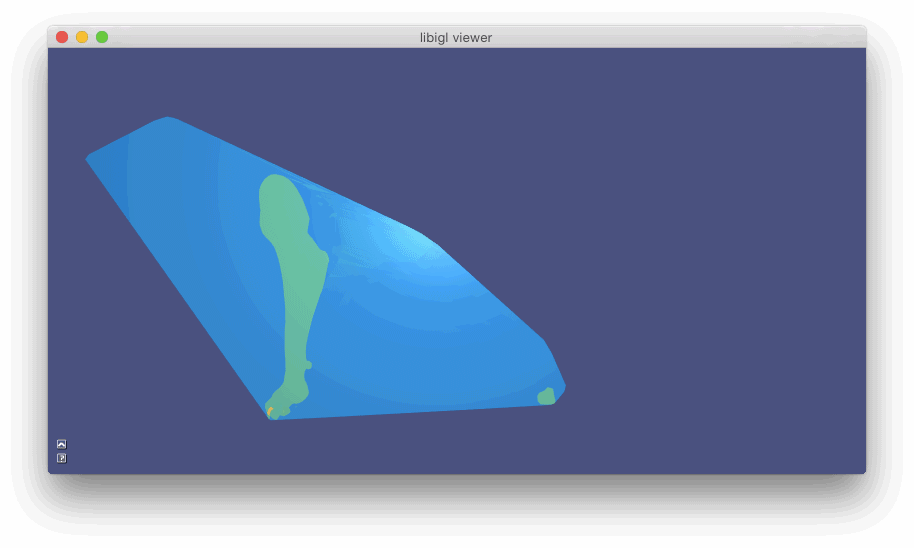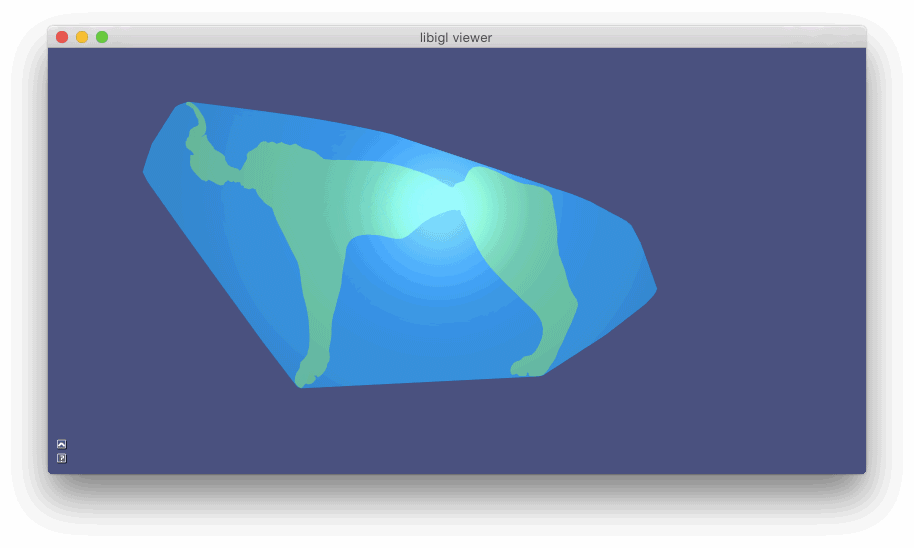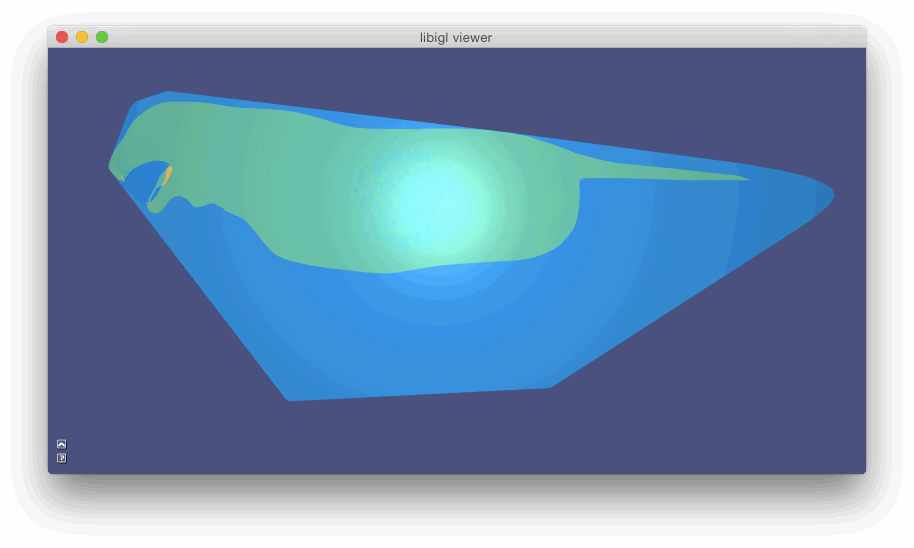 示例 702 计算具有孔和自相交点(金)的猫内部四面体网格的广义绕组数函数。银网是提取的内部Tet的表面,切片显示凸壳中所有Tet的缠绕数函数:蓝色(~ 0 ),绿色(~ 1),黄色(~2)
示例 702 计算具有孔和自相交点(金)的猫内部四面体网格的广义绕组数函数。银网是提取的内部Tet的表面,切片显示凸壳中所有Tet的缠绕数函数:蓝色(~ 0 ),绿色(~ 1),黄色(~2)
7.3 网格抽取 Mesh Decimation
- 网格简化或抽取的研究几乎与网格本身一样古老。给定一个包含太多三角形的高分辨率网格,请找到一个“近似”的低分辨率网格,其中包含更少的三角形。到目前为止,有各种不同的范式可以解决这个问题,最先进的方法相当先进。
- 一系列网格抽取方法通过从网格中连续删除元素来运行。特别是,霍普主张连续删除或塌陷边缘 39 []。该技术的通用形式是通过折叠单个边来构建从初始高分辨率网格到最低分辨率网格 M0 Mn 的 n 个网格序列:

- 霍普的原始方法和随后的后续工作提出了各种方法来选择下一个边缘在这个序列中崩溃。使用基于成本的范式,可以根据边缘的“成本”维护边缘的优先级队列(如果我删除此边缘,我的近似值会“差”多少?最便宜的边将折叠,相邻边的成本将更新。
- 为了保持拓扑(例如,如果网格组合为球体或圆环等),应该为坍缩会改变网格拓扑的边分配无限的成本。事实上,当且仅当坍缩边缘端点的共同邻居数量不正好是两个时,才会发生这种情况!
- 如果存在第三个共享顶点,则将删除另一个面,但将删除 2 条边。这可能会导致不必要的孔或非歧管“襟翼”。
 有效的边折叠和无效的边折叠
有效的边折叠和无效的边折叠
- 还有一个一次性条件,即四面体的边缘不应折叠。
- 由于 libigl(有意地)不将其实现以动态网格数据结构(例如半边数据结构)为中心,因此对拓扑更改的支持有限。尽管如此,libigl 支持隔离边崩溃、边缘崩溃序列(每个在 O(log) 时间内)和基于优先级队列的抽取。
- 最简单的是 igl::decimation .通过调用
igl::decimate(V,F,1000,U,G);
- 网格将被抽取为新的网格 (V,F) (U,G) ,以便 G 具有大多数 1000 面。这将使用默认(朴素)条件来确定边折叠的成本和合并折点的放置。最短的边首先折叠,合并的顶点放置在边中点。
- 还可以提供函数句柄( c++ lambda函数在这里很方便), cost_and_placement 并 stopping_condition 分别用于确定边缘崩溃的成本/位置和停止条件。例如,上面的默认版本实现为:
igl::decimate(V,F,shortest_edge_and_midpoint,max_m,U,G);
- 其中 shortest_edge_and_midpoint ,将边的长度指定为成本,将其中点指定为合并的顶点放置,并 max_m 计算当前面数(有效折叠将计数减少 2), true 如果计数低于 m=1000 。
- 还可以在抽取环路内更深入地刮擦并直接调用 igl::collapse_edge 。为了高效运行,此例程需要的不仅仅是通常 (V,F) 的网格表示。我们需要 E 一个边缘索引列表,其中 E.row(i) --> [s,d] ;我们需要 EMAP 将每个三角形的“半”边映射到其相应的边 F , E E.row(EMAP(f+i*F.rows)) --> [s,d] 以便如果从第 f 面的第 i 个角穿过的边是 [s,d] (直到方向);我们需要 EF 并 EI 跟踪每个边上的面入射面以及边缘出现在这些面的哪个角上,因此 EF(e,o) = f 这意味着 EI(e,o) = i 边 E.row(e) --> [s,d] 出现在其第 i 个角对面的第 fth 面中(对于 o=0 边缘方向应该匹配,因为 o=1 方向相反)。
- 发生崩溃时, F 、 E 等矩阵的大小不会改变。相反,对应于“删除”面和边缘的行设置为特殊的常量值 IGL_COLLAPSE_EDGE_NULL 。这样做可以确保我们能够在真正恒定的时间 O(1) 内去除边缘。
- 方便. IGL_COLLAPSE_EDGE_NULL==0 这意味着大多数 OPENGL 风格的渲染 F 将简单地在第一个顶点绘制一堆 0 面积三角形。
- 以下内容将折叠第一条边并将其合并的折点放置在原点:
igl::collapse_edge(0,RowVector3d(0,0,0),V,F,E,EMAP,EF,EI);
- 如果有效,则相应地调整 、 V 、 F、 E、 EF 、 EI
- 这很强大,但水平很低。要围绕这一点构建一个抽取器,您需要跟踪哪些边要塌陷,哪些边接下来要塌陷。幸运的是,libigl 还公开了基于优先级队列的边缘折叠,其中包含用于调整成本和位置的功能句柄。
- 优先级队列被实现为(有序)集 Q 或(成本,边缘索引)对和迭代器列表,以便 Qit[e] 显示与eth边缘 Q 对应的迭代器 Qit 。展示位置存储在 #E 职位 C 列表中。调用以下内容时:
igl::collapse_edge(cost_and_placement,V,F,E,EMAP,EF,EI,Q,Qit,C);
- 尝试根据 的最低 Q 成本边缘崩溃。如果有效,则相应地调整 V 、 等 F ,并且该边缘从 中 Q “弹出”。使用其相邻边也会 Qit 从 Q 其成本后弹出并重新插入 cost_and_placement ,新的放置位置会记住在 中 C 。如果无效,则边缘将从中“弹出” Q 并以无限的成本重新插入。
- 示例703演示了将这种基于优先级队列的方法与上面讨论的简单最短边中点成本/放置策略结合使用。
- 703示例完整展示:
#include 7.4 有符号距离 Signed Distances
- 在广义绕组数部分,我们研究了一种确定点是位于给定三角形汤网格内部还是外部的稳健方法。Libigl 通过加速有符号和无符号距离查询以及平面三角形网格和 3D 四面体网格的“元素内”查询来补充此算法。这些例程利用了 libigl 的通用轴对齐边界框层次结构 ( igl/AABB.h )。此类是轻量级的,并且根据设计,不存储网格的副本(而是将其作为其成员函数的输入)。
7.4.1 点位置 Point Location
- 对于四面体网格,这对于“元素内”或“点位置”查询很有用:给定一个点 q∈R3 和一个四面体网格 (V,T) 确定四面体 q 所在的位置。这是在 libigl 中完成的,用于 tet 网格 V,T 和行中的查询点列表 igl::in_element() , Q 通过 :
// Initialize AABB tree
igl::AABB<MatrixXd,3> tree;
tree.init(V,T);
VectorXi I;
igl::in_element(V,T,Q,tree,I);
- 生成的向量 I 是一个索引列表,用于 T 显示发现的第一个四面体包含 中的 Q 相应点。
- 对于重叠网格,一个点 q 可能属于多个四面体。在这些情况下,可以通过使用带有 a SparseMatrix 的 igl::in_element 重载作为输出来找到它们(而不仅仅是第一个):
SparseMatrix<int> I;
igl::in_element(V,T,Q,tree,I);
- 现在每一 I 行都显示每个 tet 是否包含相应的行 Q :表示 I(q,e)!=0 该点 q 在元素 e 中。
7.4.2 最近点 Closest Points
- 对于三角形网格,我们使用 AABB 树来加速点-网格最近点查询:给定网格 (V,F) 和查询点找到最近点 q∈R3 c∈(V,F) (其中 c 不一定是顶 (V,F) 点)。这是通过的三角形网格 V,F 和 via igl::point_mesh_squared_distance 行 P 中的点列表完成的:
VectorXd sqrD;
VectorXi I;
MatrixXd C;
igl::point_mesh_squared_distance(P,V,F,sqrD,I,C);
- 输出 sqrD 包含从每个点到 P 其最近点的(无符号)平方距离,该点 C 位于给定的元素 F 上 I (例如,可以使用从中恢复重心坐标 igl::barycentric_coordinates )。
- 如果网格 V,F 是静态的,但点集 P 正在动态变化,那么最好重用在以下期间 igl::point_mesh_squared_distance 构建的 AABB 层次结构:
igl::AABB tree;
tree.init(V,F);
tree.squared_distance(V,F,P,sqrD,I,C);
... // P changes, but (V,F) does not
tree.squared_distance(V,F,P,sqrD,I,C);
7.4.3 符号距离 Signed Distance
- 最后,从最近的点或绕组编号开始,可以对这个距离进行签名。我们 igl::signed_distance 提供了两种签名方法:所谓的“伪正态检验” 37 []和广义绕组数 40 []。
- 伪正态检验(另见) igl::pseudonormal_test 假设输入网格是水密(闭合、非自相交、流形)网格。然后给定一个查询点和它的最近点 q c∈(V,F) ,它仔细选择一个外法线 n , c 以便 sign(q−c)⋅n 揭示是在 q : -1 内部 (V,F) 还是外部: +1。一旦找到,这是一个快速 O(1) 测试,但如果不是水密的, c 可能会 V,F 失败。
- 另一种方法是使用广义绕组编号来确定符号。这对于不干净的网格非常强大 V,F ,但速度较慢:类似于 O(√n) 一次 c 定位。
- 在任何一种情况下,接口通过 igl::signed_distance 都是:
// Choose type of signing to use
igl::SignedDistanceType type = SIGNED_DISTANCE_TYPE_PSEUDONORMAL;
igl::signed_distance(P,V,F,sign_type,S,I,C,N);
- 输出如上, igl::point_mesh_squared_distance 但现在包含有符号(非平方)距离,额外输出 N (仅在 时 type == SIGNED_DISTANCE_TYPE_PSEUDON 设置) S 包含用于使用伪正态测试签名的法线。
- 704案例完整展示:
#include 7.5 行进立方体 Marching Cubes
- 通常,3D数据被捕获为在空间 f(x):R^3→R 上定义的标量场。潜伏在这个场中,标量场的等值面通常是突出的几何对象。值处的等值 v 面由 中的所有 R ^ 3 点 x 组成, f(x)=v 使得 .几何处理中的核心问题是将等值面提取为三角形网格,以便进一步进行基于网格的处理或可视化。这称为等轮廓。
- “行进立方体” 42 是在规则晶格(又名网格)上等轮廓三线性函数 f 的著名方法。此方法的核心思想是使用从查找表中选择的预定义拓扑(也称为连通性)勾勒出通过每个像元(如果有的话)的等值面轮廓,具体取决于像元每个顶点处的函数值。该方法遍历(“行进”)网格中的所有单元格(“立方体”),并将最终的水密网格拼接在一起。
- 在 libigl 中,从输入标量场构造一个三角形网格, igl::marching_cubes 该场 S 通过规则网格 (V,F) 在 nz a nx ny 的顶点位置 GV 采样:
igl::marching_cubes(S,GV,nx,ny,nz,V,F);
- 705案例完整展示:
#include 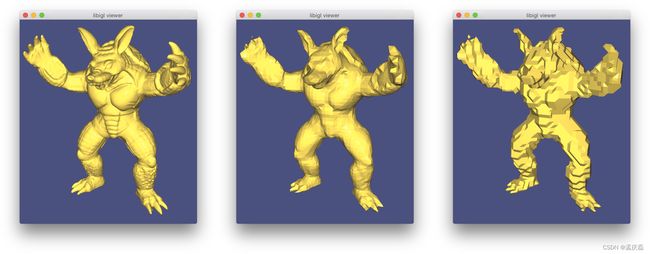 (示例705)对到输入网格(左)的符号距离进行采样,然后使用行进立方体重建表面以勾勒出0级集(中心)的轮廓。为了进行比较,将此有符号距离场固定到指示器函数并轮廓显示严重的混叠伪影。
(示例705)对到输入网格(左)的符号距离进行采样,然后使用行进立方体重建表面以勾勒出0级集(中心)的轮廓。为了进行比较,将此有符号距离场固定到指示器函数并轮廓显示严重的混叠伪影。
7.6 小平面方向 Facet Orientation
- 来自 Web 的模型偶尔到达时没有定向,因为每个三角形顶点的顺序不一致。确定网格的一致刻面方向对于双面照明(例如,一侧为红色天鹅绒,另一侧为金丝的布)和内部和外部确定(例如,使用广义绕组编号)至关重要。
- 对于表示双面板的(开放)曲面,libigl 提供了一个例程,以强制网格的每个可定向面块 ( igl::orientable_patches ) 内的方向一致:
igl::bfs_orient(F,FF,C);
- 这个简单的例程将对网格的每个面块使用广度优先搜索,以在输出面 FF 中强制实施一致的小平面方向。
- 对于表示实体对象边界的(闭合或接近闭合)曲面,libigl 提供了一个例程来重新定向面,以便顶点顺序对应于顶点的逆时针顺序,右手法线指向外。此方法 45 [] 假设宇宙的大部分是空的。也就是说,空间中的大多数点都在固体物体之外而不是内部。点在表面图块上采样。对于每个采样点,光线被射入两个半球,以计算每侧(距离加权)环境光遮蔽的平均值。贴片的方向使向外侧较少被遮挡(更轻,即面向更多的空隙空间)。
igl::embree::reorient_facets_raycast(V,F,FF,I);
- 布尔向量 I 显示哪些行 F 已被翻转。 FF
- 706案例完整展示:
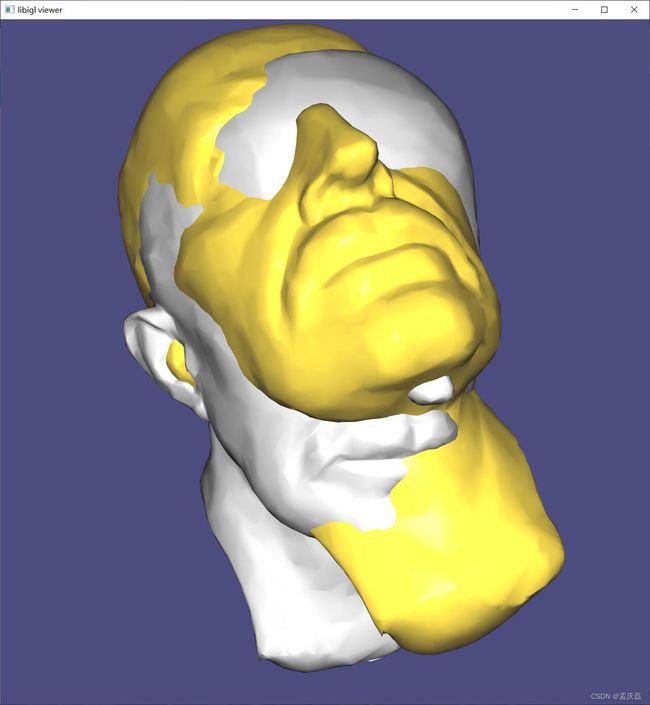
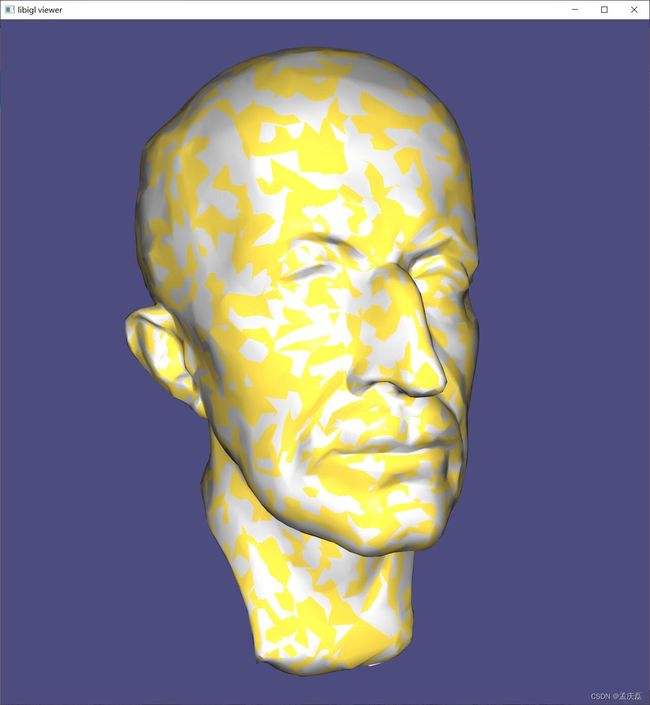
#include 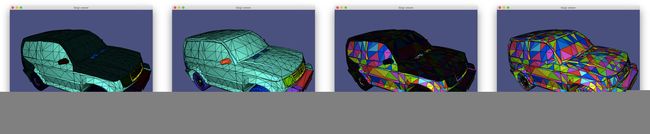 (示例 706)加载方向不一致的卡车模型(背面三角形显示较暗)。可定向的斑块具有独特的颜色,然后朝外(左中)。或者,每个单独的三角形都被视为一个“补丁”(中间右边)并独立地向外定向。
(示例 706)加载方向不一致的卡车模型(背面三角形显示较暗)。可定向的斑块具有独特的颜色,然后朝外(左中)。或者,每个单独的三角形都被视为一个“补丁”(中间右边)并独立地向外定向。
7.7 扫描卷 Swept Volume
-
移动固体物体 A 的扫描体积 S 可以定义为空间中的任何点,使得该点在某个时刻位于固体内部。换句话说,它是刚性运动 f(t) 随时间变化的固体物体的结合:
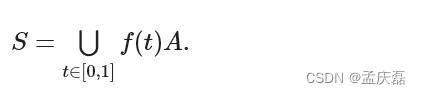
-
由三角形网格以非平凡旋转的刚性运动为界的实体的扫掠体积表面不是由三角形网格精确表示的表面:它将是一个分段规则表面。
-
要看到这一点,请考虑在执行螺钉运动时被单个边的线段扫描的曲面。
-
这意味着,如果我们想让三角形网格体的扫描体积表面经历刚性运动,并且我们希望输出是另一个三角形网格,那么我们必须对一定程度的近似误差感到满意。
-
如果是一个三角形网格,那么 ∂A 我们可以通过以下方式近似:1)在有限的步长 [0,Δt,2Δt,…,1] 上离散时间和2)使用规则网格离散空间并使用网格值的三线性插值表示距离场。最后, ∂S 输出网格通过使用行进立方体 42 进行轮廓绘制来近似。
-
这种方法类似于Schroeder等人在1994年描述的方法 44 ,以及Garg等人在2016年与布尔运算结合使用的方法 38 。
-
在 libigl 中,如果输入实体的表面由 表示 (V,F) ,则输出表面网格将在调用后: (SV,SF)
igl::copyleft::swept_volume(V,F,num_time_steps,grid_size,isolevel,SV,SF);
- 该 isolevel 参数可以设置为零以近似确切的扫描体积,大于零表示近似扫描体积的正偏移,或小于零以近似于负偏移。
- 707案例完整展示:
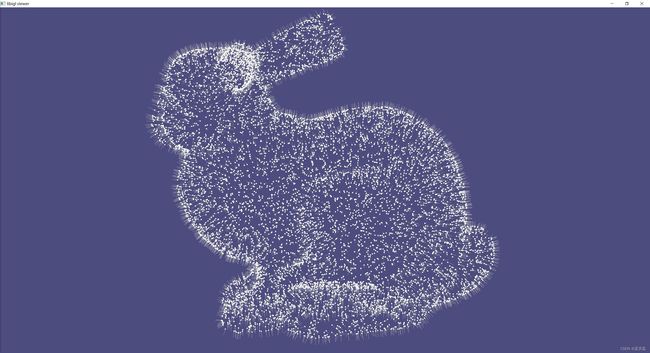
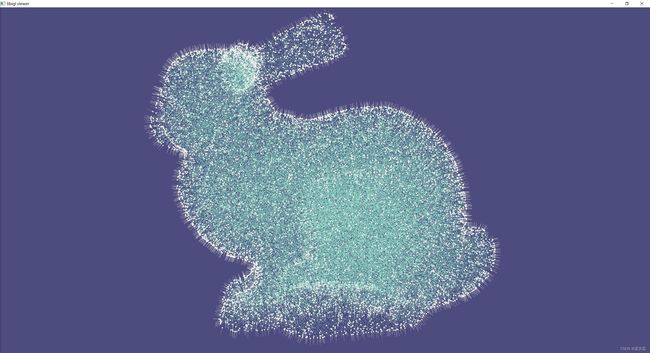
#include 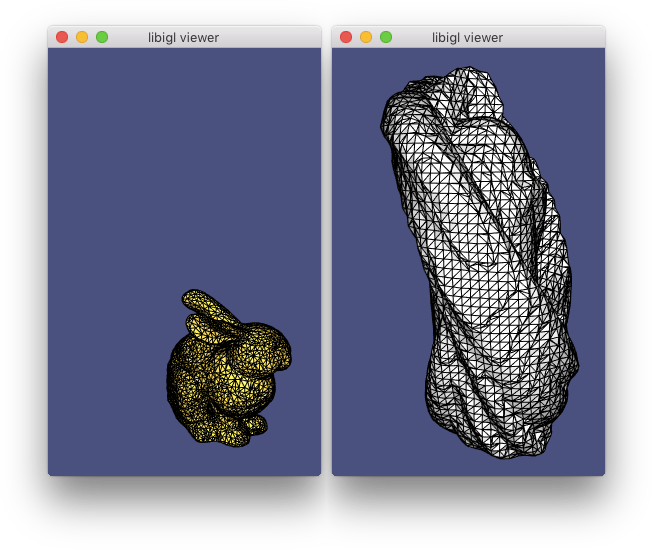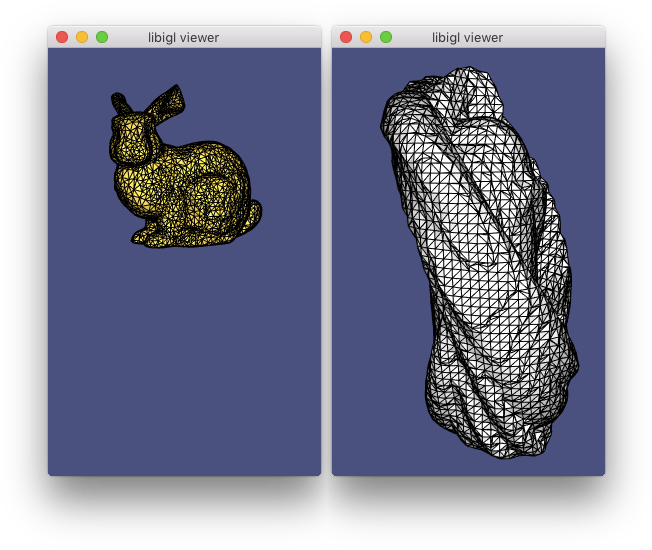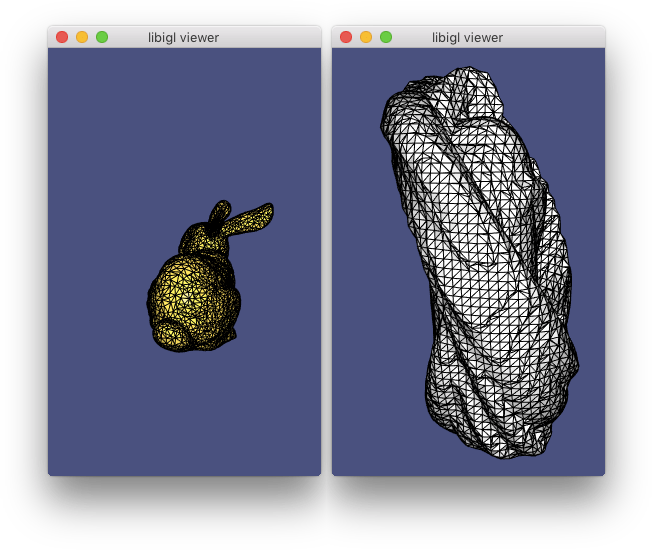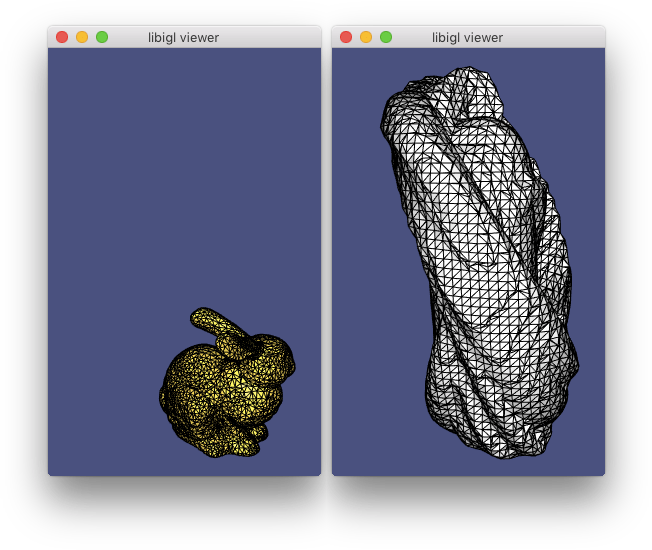 (示例707)计算兔子模型经历刚性运动(金)的扫描体积(银)的表面
(示例707)计算兔子模型经历刚性运动(金)的扫描体积(银)的表面
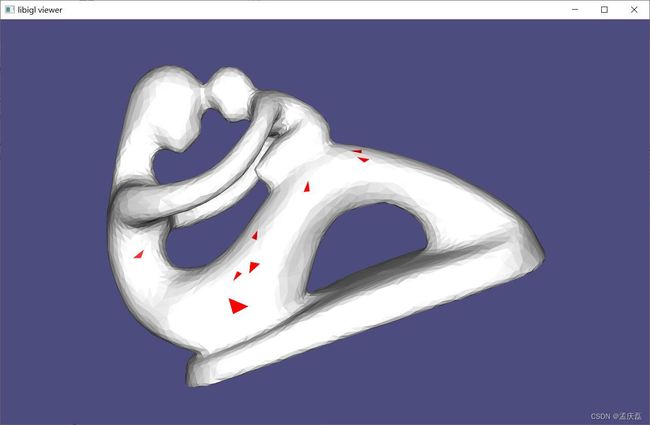
7.8 拣选 Picking
- 使用鼠标拾取顶点和面在几何处理应用程序中非常常见。虽然这看起来很简单,但其实现并不简单。Libigl 包含一个使用 Embree 光线投射器解决此问题的函数。示例 708 演示了它的用法:
bool hit = igl::unproject_onto_mesh(
Vector2f(x,y),
F,
viewer.core.view * viewer.core.model,
viewer.core.proj,
viewer.core.viewport,
*ei,
fid,
bc);
- 此函数从视图平面向视图方向投射光线。变量 x 和 y 是鼠标屏幕坐标; view 、 model 分别 proj 是视图、模型和投影矩阵; viewport 是 OpenGL 格式的视口; ei 包含由 Embree 构造的边界体积层次结构,并且 fid bc 分别是拾取位置的拾取面和重心坐标。
- 708案例完整展示:
#include 7.9 可扩展的局部注入映射 Scalable Locally Injective Maps
- 可扩展局部注入映射算法允许在大量数据集上计算本地注入映射 43 。该算法与ARAP有许多相似之处,但使用重新加权方案来最小化任意失真能量,包括那些防止引入翻转的能量。
- 示例 709 包含三个演示:(1) 大规模 2D 参数化示例,(2) 具有软约束的 2D 变形示例,以及 (3) 具有软约束的 3D 变形示例。libigl 中的实现是自包含的,并且依赖于特征来求解全局步骤中使用的线性系统。此处提供了依赖于Pardiso的优化版本。
- 709案例完整展示:
#include  使用 SLIM 算法在 10 次迭代中计算具有 50k 面的网格的局部注入参数化。
使用 SLIM 算法在 10 次迭代中计算具有 50k 面的网格的局部注入参数化。
7.10 双射映射的单纯复数增强框架 Simplicial Complex Augmentation Framework For Bijective Maps
- 单纯复数增强框架 49 算法允许高效、鲁棒地计算双射映射。该算法构建了一个脚手架结构,以利用SLIM等高效的局部注入映射算法,保证了低失真的重叠自由映射,同时具有高效和可扩展性。
- 示例 710 包含对驼峰网格进行双射参数化的演示。
- 710示例完整展示:
......
7.11 细分曲面 Subdivision Surfaces
-
给定一个带有顶点和面的粗网格(又名笼子),可以通过细分每个面来创建具有更多顶点 V 和面 F 的更高分辨率网格。也就是说,输入中的每个粗三角形都被许多较小的三角形所取代。Libigl 有三种不同的方法来细分三角形网格。
-
“平面内”细分方法不会改变网格的点集或载体表面。在现有三角形的平面上添加新顶点,并且不会移动从原始网格中幸存下来的顶点。
-
通过添加新面,细分算法会改变网格的组合。组合数学的变化和高分辨率顶点定位公式称为“细分规则”。
-
711 案例完整展示:
#include 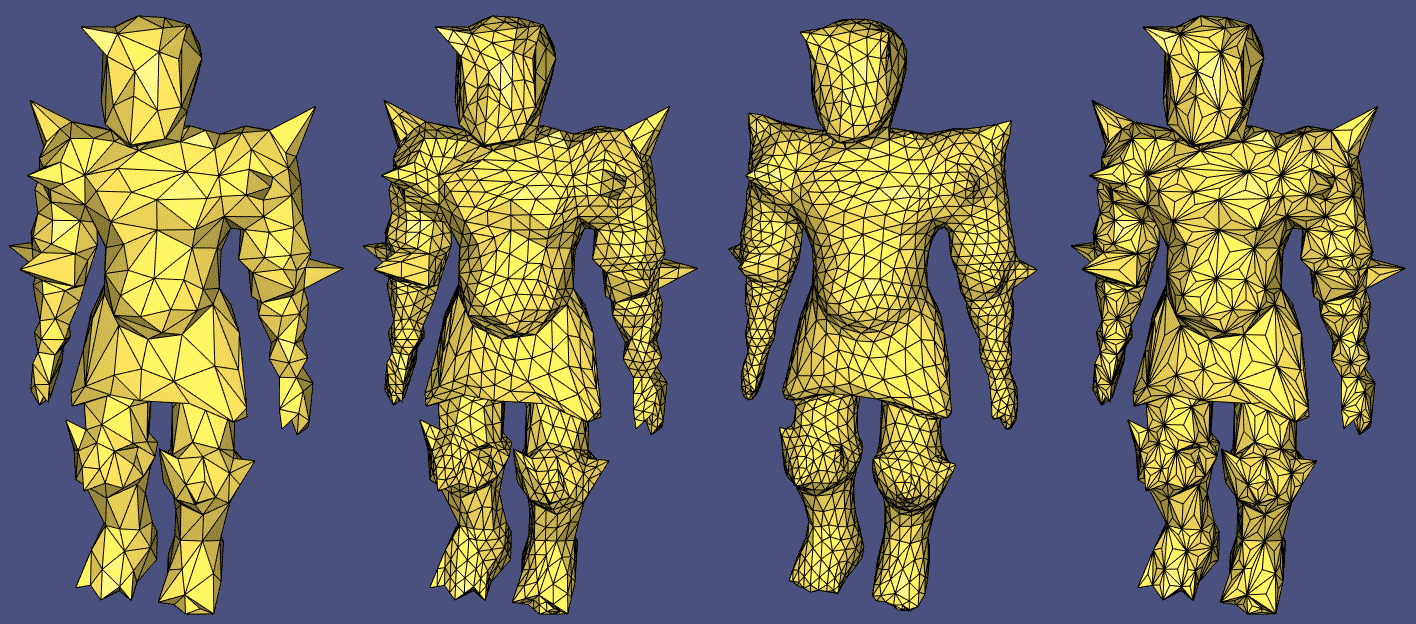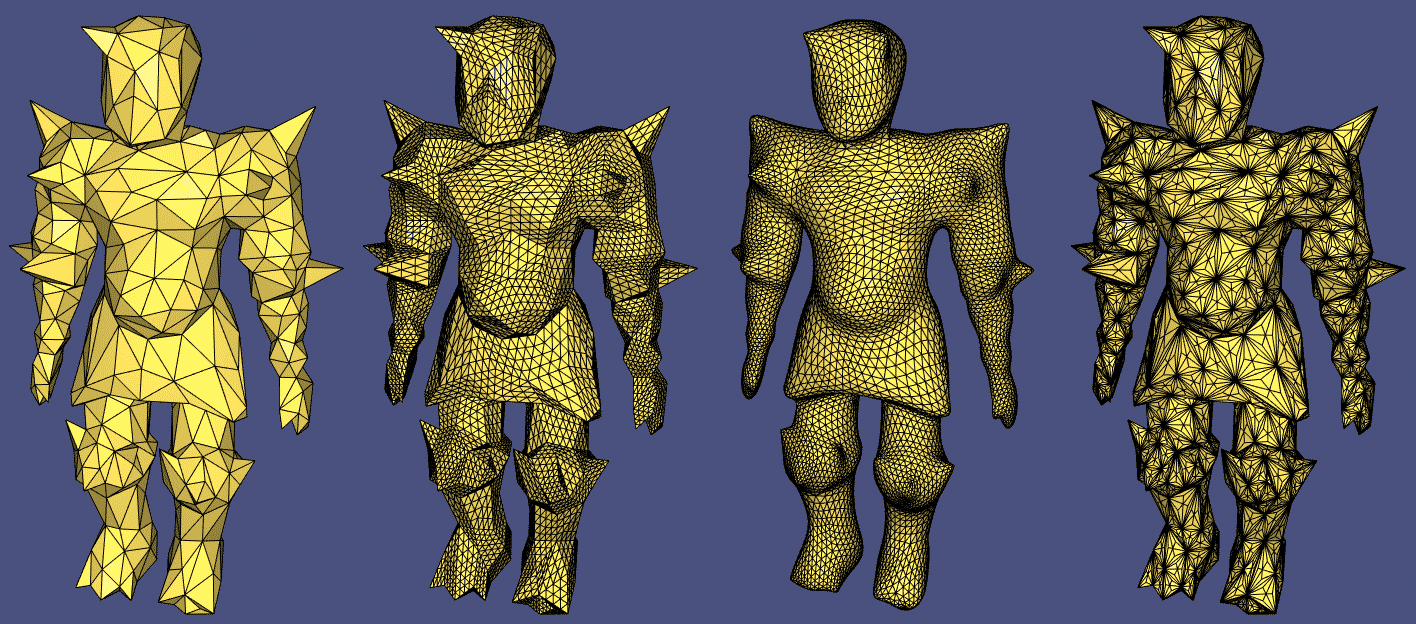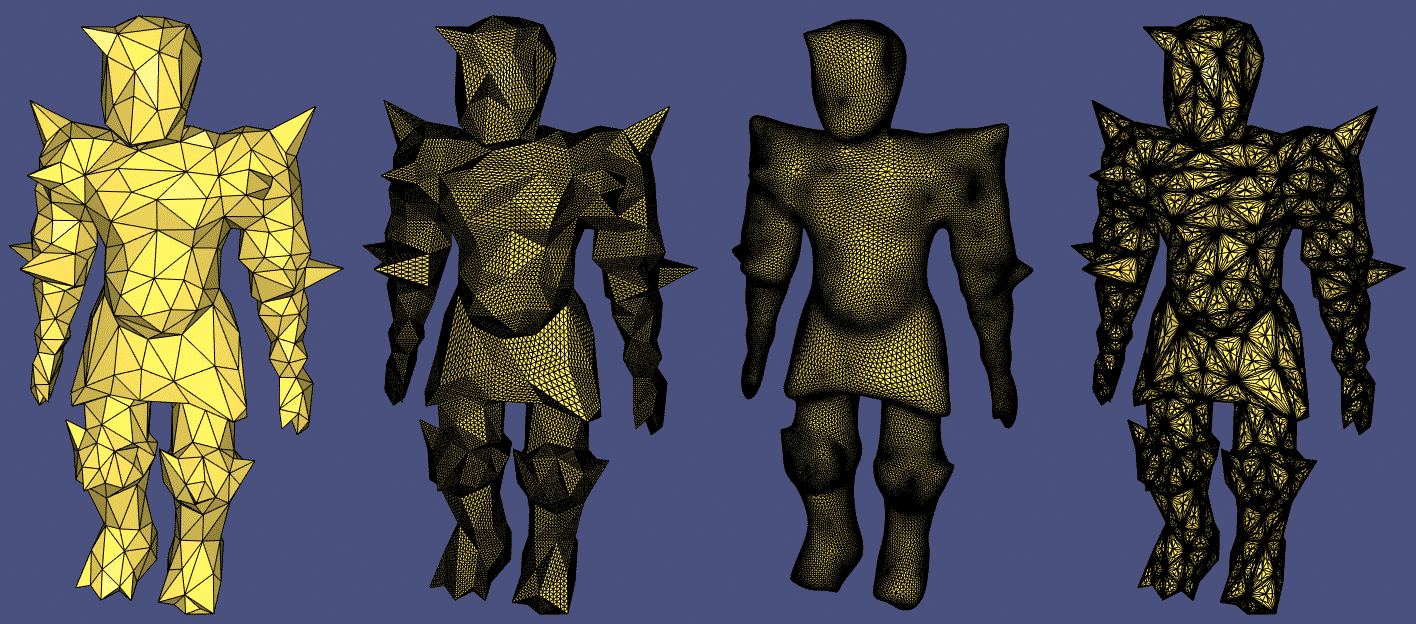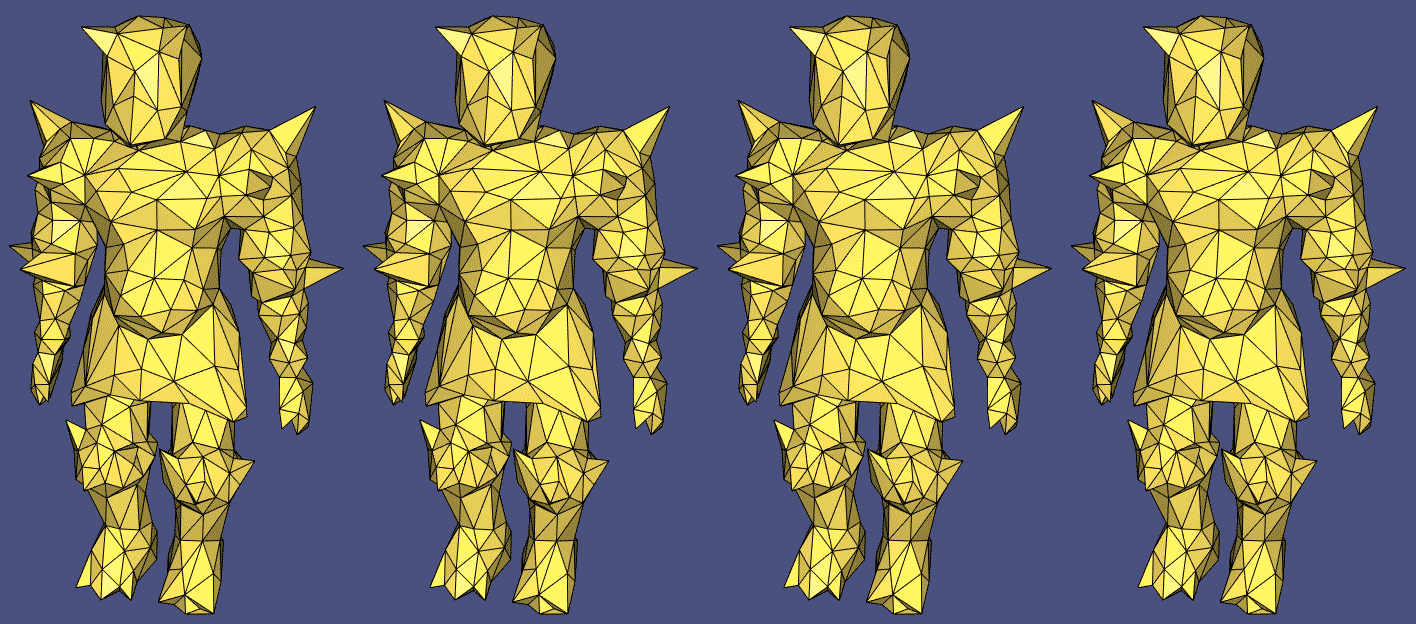 原始粗网格和三种不同的细分方法: igl::upsample 、 igl::loop 和 igl::false_barycentric_subdivision
原始粗网格和三种不同的细分方法: igl::upsample 、 igl::loop 和 igl::false_barycentric_subdivision
7.12 数据平滑 Data Smoothing
- 该参数 α 确定函数平滑的力度。
- 平滑度能量的经典选择是诺依曼边界条件为零的函数的拉普拉斯能量,它是双谐能量的一种形式。它是使用余切拉普拉斯量 L 和质量矩阵 M 构造的 QL = L’*(M\L) :然而,由于隐含的零诺依曼边界条件,如果在边界处没有零法向梯度,则 f 函数行为在边界处明显扭曲。
- 其中建议使用具有自然黑森边界条件的双调和能量,这与具有矩阵的黑森能量相对应,其中 51 H 是有限元黑森, M2 是堆叠质量矩阵 QH = H’*(M2\H) 。矩阵 H 和 QH 分别以 libigl igl::hessian igl::hessian_energy 实现。示例 712 中给出了如何使用该函数的示例。
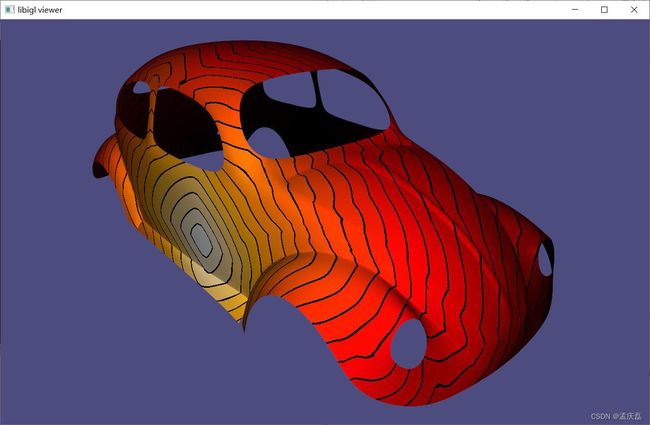
- 在下图中,可以清楚地看到具有零诺依曼边界条件的拉普拉斯能量与黑森能量之间的差异:第三幅图像中的零诺依曼边界条件使函数的等值线垂直于边界,而黑森能量给出了无偏的结果。
- 712案例完整展示:
#include 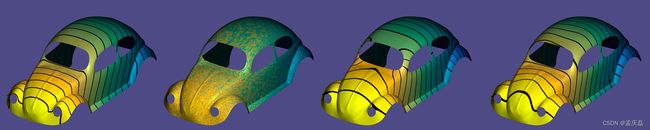 例 712)从左到右:甲虫网格上的函数,增加噪声的函数,拉普拉斯能和零诺依曼边界条件平滑的结果,以及黑森能量平滑的结果
例 712)从左到右:甲虫网格上的函数,增加噪声的函数,拉普拉斯能和零诺依曼边界条件平滑的结果,以及黑森能量平滑的结果
7.13 形状投影 Shapeup Projections
- 我们的输入是一组点 P0 (不一定是任何网格的一部分)和一组约束,其中每个约束 S={S1,S2,…Sm} 都定义在 的不同 P0 且稀疏的子集上。我们希望创建一组接近原始集合 P0 的新点(每个点 P 都有相应的索引),同时遵守约束。可以采用其他目标,例如平滑度。约束可以是非线性的,这使得问题非凸、困难且没有保证的全局最优。解决此类问题的一种非常流行的轻量级方法是局部-全局迭代算法,包括以下两个步骤:
- 对于迭代:1.局部步骤 k :计算集合 Pk−1 的投影到 S ,每个约束单独计算;这意味着将出现在多个约束中的每个点分开。这可以是一个非线性操作,但如果约束很稀疏,它是一组许多小系统。2.全局步骤:将集合 Pk 积分为尽可能接近投影的碎片集,并可能具有辅助目标函数。这就产生了一个全局但二次的目标函数。此外,得到的线性系统具有常数矩阵,因此可以进行预分解。
- 我们在 libigl 中实现的版本是 描述 27 的一般版本,位于两个文件中:
和 。实现规则性约束(创建每个面尽可能规则的网格)的演示如例 713 所示。 - 本地步骤由 类型的 igl::shapeup_projection_function 函数实例化。全局步长由两个函数完成: igl::shapeup_precomputation() ,它根据初始解 P0 和输入局部投影函数预先计算全局步长所需的矩阵,以及igl::shapeup_solve() ,它解决问题。数据结构 igl::ShapeUpData 包含运行算法所需的信息,并且可以配置;例如,不言自明的变量 Maxiterations 。
- 全局步骤可最大程度地减少以下能量:
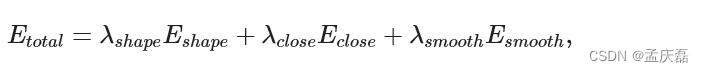
- 其中系数 λ 以 编码 igl::ShapeUpData ,并且可以在调用 igl::shapeup_precomputation() 之前更新。该 Eshape 分量是积分能量(拟合 Pk 局部投影)。该 Eclose 组件遵守位置约束,由 b 和 bc 参数给出。该 Esmooth 组件是一个可选的目标函数,为了最小化点之间的差异(在狄利克雷意义上),通过参数 E 中的“边”进行编码。两者 Eshape 也 Eclose 分别由 和 wShape 函数参数加 wClose 权。
- 713案例完整展示:
#include 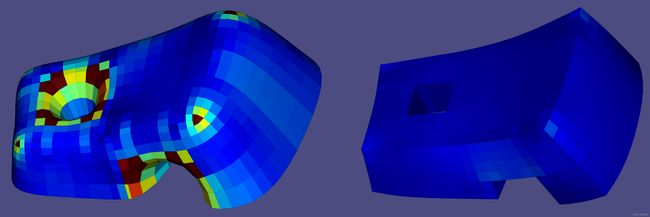 例713)半隧道网格(左)已优化为几乎完全规则(右)。色标介于 [0,0.05] 之间,测量每个面的角度与 的平均归一化偏差 90∘
例713)半隧道网格(左)已优化为几乎完全规则(右)。色标介于 [0,0.05] 之间,测量每个面的角度与 的平均归一化偏差 90∘
7.14 行进四面体 Marching Tetrahedra
- 通常,3D数据被捕获为在空间 f(x):R^3→R 上定义的标量场。潜伏在这个场中,标量场的等值面通常是突出的几何对象。值处的等值 v 面由 中的所有 R ^ 3 点 x 组成, f(x)=v 使得 .几何处理中的核心问题是将等值面提取为三角形网格,以便进一步进行基于网格的处理或可视化。这称为等轮廓。
- “行进四面体” 46 是在 3D 单纯复合体(又名 tet 网格)上等轮廓三线性函数 f 的著名方法。此方法的核心思想是使用从查找表中选择的预定义拓扑(也称为连通性)勾勒出通过每个像元(如果有的话)的等值面轮廓,具体取决于像元每个顶点处的函数值。该方法迭代(“行进”)复合体中的所有单元(“四面体”),并将最终网格拼接在一起。
- 在 libigl 中,构造一个三角形网格, igl::marching_tets 近似于在 tet 网格 (V,F) 位置 (TV, TT) 顶点采样的输入标量场 S isovalue 的值的等值水平集:
igl::marching_tets(TV,TT,S, isovalue ,V,F);
- 714案例完整展示:
#include 7.15 隐式函数网格划分 Implicit Function Meshing
- 715案例完整展示:
#include 7.16 快速测地线距离近似的热法 Heat Method For Fast Geodesic Distance Approximation
-
在上面的精确离散测地线距离示例中,将精确计算测地线距离。这是一项昂贵的操作: O(n²log(n)) 对于带有边缘的 n 网格。2013年,Crane等人 47 提出了一种方法,通过求解表面上的热方程,过滤结果,然后通过求解泊松方程重建平滑解,更快地计算近似测地线距离。该方法从瓦拉丹的观察开始,两点 x y 之间的测地线距离 d(x,y) 等于一段时间 y 后扩散 x 的热量对数的平方根 t :

-
热内核在哪里 kt,x 。我们可以将这种热扩散问题视为将热针放在上面 x ,然后在几秒钟后 t 测量点 y 的温度。
-
如果我们有足够的数值精度和精度,我们可以简单地评估 √(−4tlogu) 一个小的时间参数 t 。Crane等人观察到的问题是,我们对数值 u 的数值精度远远不够。然而,渐变的方向 ∇u 出奇地准确。因此,他们的想法是获取 的 u 梯度,归一化这些向量以获得梯度方向(单位向量)。然后求解泊松方程,将这些方向积分到实际距离值中。
-
此方法涉及反转 n×n 稀疏矩阵(运算 O(n1.⋯) ),但如果使用 Cholesky 分解,则因式分解是预计算,即使更改了测地线距离的来源,也可以重用。对于新源,只需执行反向替换。
-
在 libigl 中,您可以使用此方法通过两个步骤计算网格 ( V , F ) 从源顶点索引列表 gamma 到矢量 D 的近似测地线距离:
igl::HeatGeodesicsData<double> data;
igl::heat_geodesics_precompute(V,F,data);
...
igl::heat_geodesics_solve(data,gamma,D);
- 715案例完整展示:
#include 7.16.1 内在德劳奈三角测量 Intrinsic Delaunay Triangulation
- 测地线距离的原始热法在规则的无偏网格上效果很好:即,有限元余切矩阵和质量矩阵表现良好。但是,对于质量较差的网格,此方法可能会显示任意差的结果。增加时间参数 t 可以减少这种不稳定性,但同时可以平滑生成的近似距离。
- 相反,改进的一种途径是使用所谓的内在 Delaunay 三角测量离散拉普拉斯算子 48 。
- 由于余切拉普拉斯仅取决于三角形网格的边长,因此此新算子将通过固有地翻转边并记录边长度的变化来构造。翻转边,直到每条边都是局部 Delaunay (即,其相应的余切权重为正)。
- 您可以使用以下命令计算网格 ( V , F ) 的内在 Delaunay 三角测量:
Eigen::MatrixXd l;
igl::edge_lengths(V,F,l);
Eigen::MatrixXd l_intrinsic;
Eigen::MatrixXi F_intrinsic;
igl::intrinsic_delaunay_triangulation(l,F,l_intrinsic,F_intrinsic);
- 请注意,不使用网格顶点位置 V ,因为这是一个纯粹的内部操作。该方法输入和输出边长和三角形索引。
- 您可以使用以下方法直接构造固有的 Delaunay 余切拉普拉斯矩阵:
Eigen::SparseMatrix<double> L;
igl::intrinsic_delaunay_cotmatrix(V,F,L);
- 最后,您可以通过以下方式使用此矩阵计算热测地线:
igl::HeatGeodesicsData<double> data;
data.use_intrinsic_delaunay = true;
igl::heat_geodesics_precompute(V,F,data);
...
igl::heat_geodesics_solve(data,gamma,D);
7.17 汤和云的快速缠绕数 Fast Winding Number For Soups And Clouds
2018年,Barill等人 50 演示了如何显著加快上述广义绕组数的计算速度。三角形网格的广义缠绕数的原始定义也扩展到(定向)点云。
7.17.1 汤 Soups
- 对于三角形汤, 40 理想的精确分而治之的方法在三角形的数量上以对数缩放 O(logn) 。但是,此方法具有计算变为线性 O(n) 的故障模式。使用类似于n体系统模拟或静电问题中使用的树方法可以显着改善这一点。结果是近似的,但更紧密地遵循趋势 O(logn) ,并且常数因子要小得多。
- 计算汤的快速缠绕数有两个步骤:构建树形数据结构,然后在查询点进行评估。在 libigl 中,编程如下:
igl::FastWindingNumberBVH fwn_bvh;
igl::fast_winding_number(V.cast<float>(),F,2,fwn_bvh);
Eigen::VectorXf W;
igl::fast_winding_number(fwn_bvh,2,Q.cast<float>(),W);
- 717案例完整展示:
#include 7.17.2 云 Clouds
- 对于点云,过程类似,但可能需要更多的预计算。定义点云的缠绕数,只要每个点带有一个朝外的法线和一个面积值。可以使用libigl函数来估计面积,该函数计算每个点 igl::copyleft::cgal::point_areas 的切线空间Voronoi图。这个函数又依赖于首先计算k个 igl::knn 最近邻。该函数和最终的缠绕数计算使用 libigl igl::octree 作为边界体积层次结构。要估计使用法线 N 的点云 P 的面积使用量:
// Build octree
std::vector<std::vector<int > > O_PI;
Eigen::MatrixXi O_CH;
Eigen::MatrixXd O_CN;
Eigen::VectorXd O_W;
igl::octree(P,O_PI,O_CH,O_CN,O_W);
Eigen::VectorXd A;
{
Eigen::MatrixXi I;
igl::knn(P,20,O_PI,O_CH,O_CN,O_W,I);
// CGAL is only used to help get point areas
igl::copyleft::cgal::point_areas(P,I,N,A);
}
- 然后可以计算查询 Q 列表的快速缠绕数:
Eigen::MatrixXd O_CM;
Eigen::VectorXd O_R;
Eigen::MatrixXd O_EC;
igl::fast_winding_number(P,N,A,O_PI,O_CH,2,O_CM,O_R,O_EC);
Eigen::VectorXd W;
igl::fast_winding_number(P,N,A,O_PI,O_CH,O_CM,O_R,O_EC,Q,2,W);
7.18 迭代最近点 Iterative Closest Point¶
- 718案例完整展示:
// This file is part of libigl, a simple c++ geometry processing library.
//
// Copyright (C) 2019 Alec Jacobson 7.19 分解图 Exploded View
- 719案例完整展示:
// This file is part of libigl, a simple c++ geometry processing library.
//
// Copyright (C) 2020 Alec Jacobson 7.20 蓝色噪声表面采样 Blue Noise Surface Sampling
- 720案例完整展示:
// This file is part of libigl, a simple c++ geometry processing library.
//
// Copyright (C) 2020 Alec Jacobson 7.21 矢量场平滑 Vector Field Smoothing
- 721案例完整展示:
#include 7.22 向量并行传输 Vector Parallel Transport
- 722案例完整展示:
#include