Django--Learning and understanding
-
Create a virtual environment in anaconda
-
Installing Django
pip install djangoDjango is a Python web framework that provides many features such as ORM, authentication, forms, templates, etc. It can help you develop web applications faster and easier.
-
Installing the DRF
pip install djangorestframeworkDRF is a powerful and flexible Django-based RESTful framework that provides many tools and libraries to help you quickly develop web applications based on RESTful apis.
-
Install Django-Filter
pip install django-filterDescription::Integration with DRF — django-filter 23.2 documentation
Django-filter is a Django-based library that provides a simple, flexible way to Filter sets of Django model queries. Django-Filter's API allows developers to use simple query expressions, build and apply complex filters, and select and exclude data in query sets.
Djangos Filter provides a more elegant API specification through its integration with DRF Spectacular, which supports data filtering and querying as expressed by the OpenAPI specification.
-
Installing Django Spectacular
pip install drf_spectacularDescription: DRF Spectacular is the OpenAPI specification tool for DRF. It automatically builds and generates OpenAPI specification documentation, and provides convenient API testing tools that make it easier to create, test, and maintain RESTful apis. It also supports integration with Django Filter, which allows you to filter query data by URL parameters.
Once django is installed, create a project using Django-admin, the tool that comes with Django:
django-admin startproject django_news
Go to cd django_news.
django_news
├── django_news // 项目全局文件目录
│ ├── __init__.py
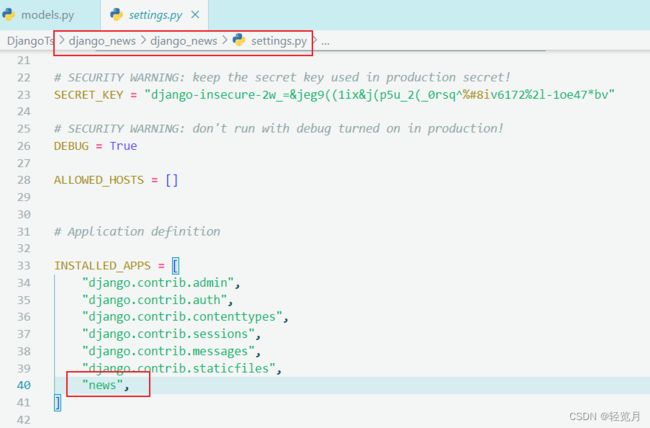
│ ├── settings.py // 全局配置
│ ├── urls.py // 全局路由
│ └── wsgi.py // WSGI服务接口
└── manage.py // 项目管理脚本To run a Development Server using manage.py:
python manage.py runserverImplement custom apps
Let's create our first custom App, named news:
python manage.py startapp newsThe resulting news application folder structure looks like this:
news // news 应用目录
├── __init__.py // 初始化模块
├── admin.py // 后台管理配置
├── apps.py // 应用配置
├── migrations // 数据库迁移文件目录
│ └── __init__.py // 数据库迁移初始化模块
├── models.py // 数据模型
├── tests.py // 单元测试
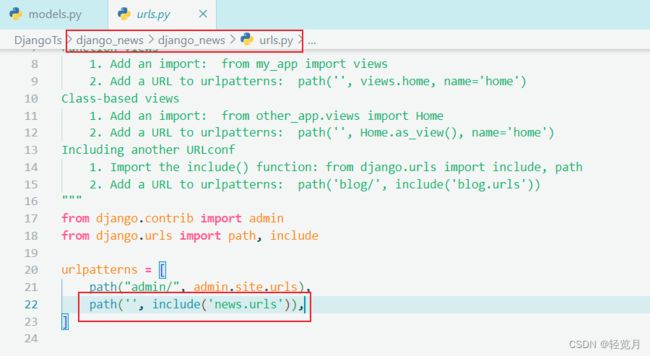
└── views.py // 视图The view function you just wrote needs to be accessible to the system. So first implement the routing table of the sub-application news and create the news/urls.py file as follows:
from django.urls import path
from . import views
urlpatterns = [
path('', views.index, name='index'),
]Implement the first Django template
Let's implement our first Django template. Create a templates directory in the news directory, then create a news directory in the templates directory, and then create the index.html file in the inner news directory:
mkdir -p news/templates/news
touch news/templates/news/index.htmlBecause Djangos template lookup mechanism collects all the templates in the application together, if two template names conflict, one of the templates will not be accessible correctly. If it is placed in the news subfolder, it can be accessed through news/index.html, and conflicts are avoided through the namespace mechanism.
The code for the template is as follows:
{% if news_list %}
{% for elem in news_list %}
-
{{ elem.title }}
{{ elem.content }}
{% endfor %}
{% else %}
暂无新闻
{% endif %}Once defined, run the following command to create the migration file:
python manage.py makemigrations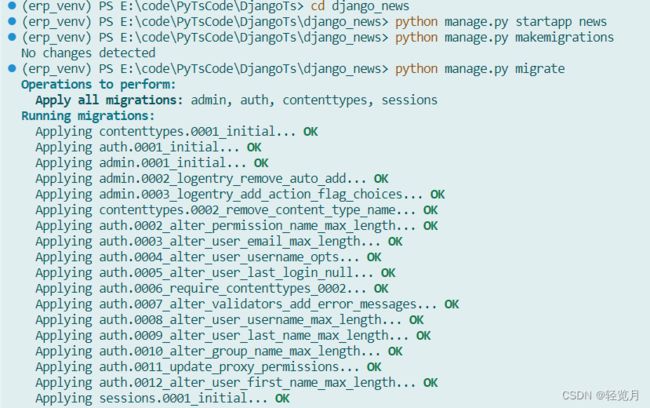
The news/migrations/0001_initial.py migration script was successfully automatically created. Then proceed to the database migration:
python manage.py migrateAfter the database migration is complete, create a super user for logging in to the background management.
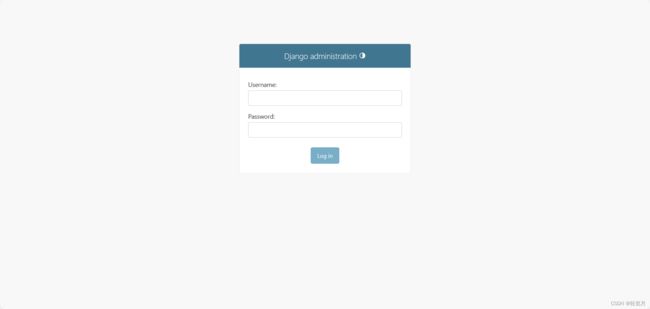
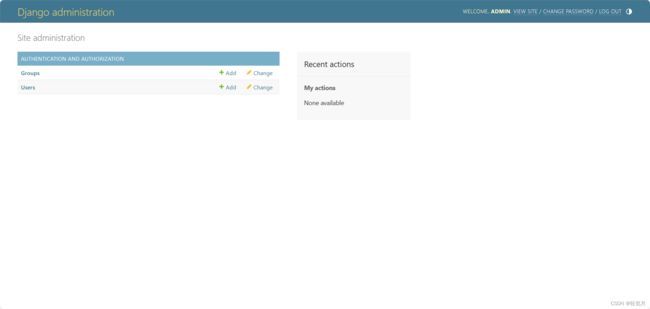
python manage.py createsuperuserEnter the user name and password as prompted. Interview localhost:8000/admin,Enter the login page of the background system:
Configure the background management interface
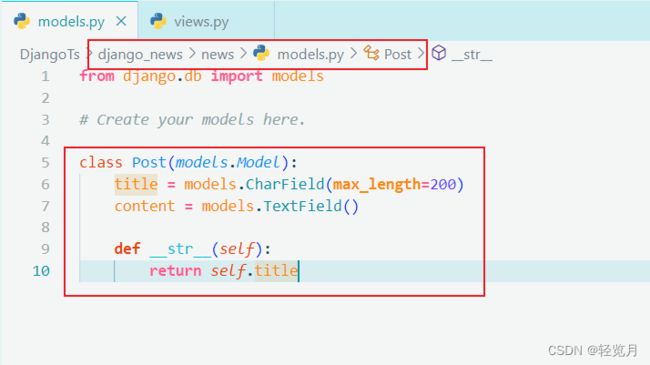
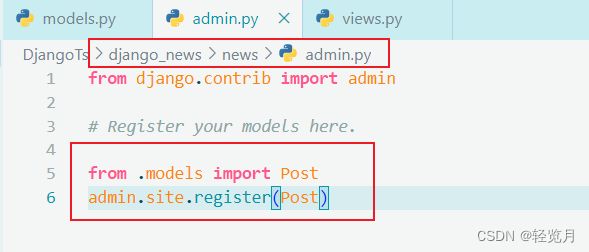
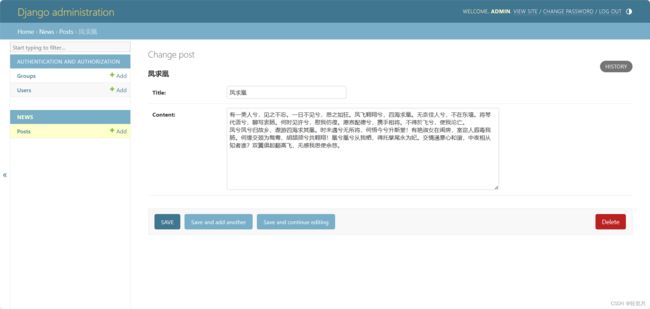
We did not implement the background management interface for the news application. Enter the following code in news/admin.py:
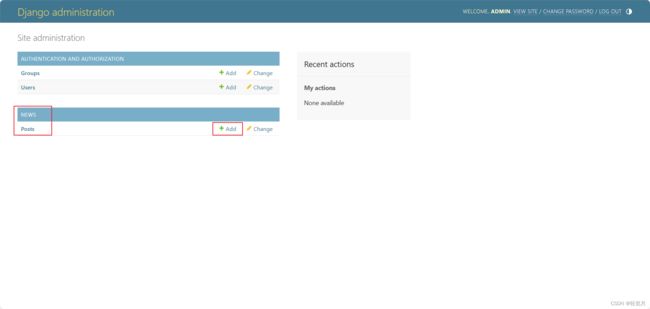
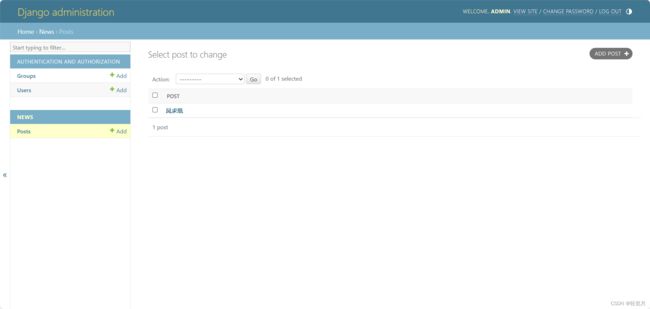
Enter the background management system again, you can see the news application and Post model created just now.
Adds a data query to the view
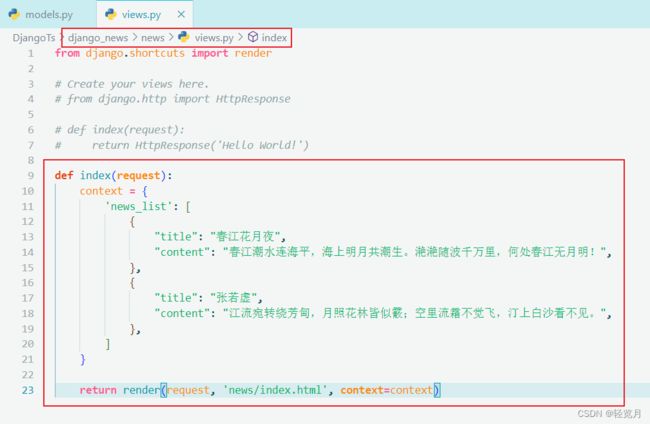
Finally, we add the code to the view to query from the database:
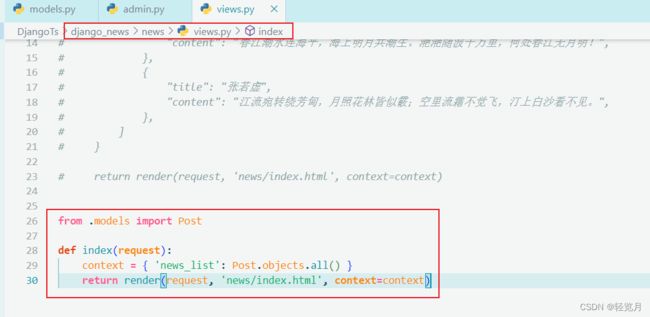
from django.shortcuts import render
from .models import Post
def index(request):
context = { 'news_list': Post.objects.all() }
return render(request, 'news/index.html', context=context)Reference article
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/98788776