初级C++STL:初阶模板 | String的使用
文章目录
- 初级模板简介
- 函数模板
-
- 模板参数的匹配原则
- 类模板
- STL标准模板库
- string
-
- string类对象的访问及遍历操作
- string类对象的容量操作
- string类对象的修改操作
- +=、insert、earse
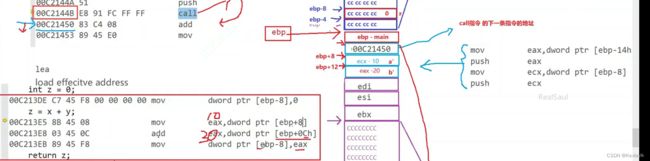
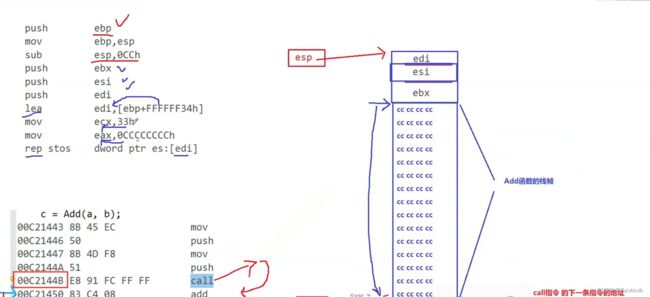
- 函数栈帧的创建和销毁
初级模板简介
如果在C++中,也能够存在这样一个模具,通过给这个模具中填充不同材料(类型),来获得不同材料的铸件(生成具体类型的代码),那将会节省许多头发。巧的是前人早已将树栽好,我们只需在此乘凉。
- 泛型编程:编写与类型无关的通用代码,是代码复用的一种手段。模板是泛型编程的基础。
- 函数模板
- 类模板
函数模板
- 函数模板代表了一个函数家族,该函数模板与类型无关,在使用时被参数化,根据实参类型产生函数的特定类型版本。
- typename是用来定义模板参数关键字,也可以使用class
- 如已经有该类型匹配的函数,会优先使用,其次是通用模板函数
函数模板是一个蓝图,它本身并不是函数,是编译器用使用方式产生特定具体类型函数的模具。所以其实模板就是将本来应该我们做的重复的事情交给了编译器。
在编译器编译阶段,对于模板函数的使用,编译器需要根据传入的实参类型来推演生成对应类型的函数以供调用。
比如:当用double类型使用函数模板时,编译器通过对实参类型的推演,将T确定为double类型,然后产生一份专门处理double类型的代码,对于字符类型也是如此。
隐式实例化、显式实例化
用不同类型的参数使用函数模板时,称为函数模板的实例化。模板参数实例化分为:隐式实例化和显式实例化。
- 隐式实例化:让编译器根据实参推演模板参数的实际类型
- 显式实例化:在函数名后的<>中指定模板参数的实际类型
template<typename T>
void Swap( T& left, T& right)
{
T temp = left;
left = right;
right = temp;
}
Add(2,3); //编译器会自动推演确定T的类型,然后执行
Add(2,(int)3.0); // 参数不同时需要强转成同一类型 称为隐式实例化
或
Add<int>(2,3.0); //显式实例化。
模板参数的匹配原则
- 一个非模板函数可以和一个同名的函数模板同时存在,而且该函数模板还可以被实例化为这个非模板函数
- 对于非模板函数和同名函数模板,如果其他条件都相同,在调动时会优先调用非模板函数而不会从该模板产生出一个实例。如果模板可以产生一个具有更好匹配的函数, 那么将选择模板。
- 模板函数不允许自动类型转换,但普通函数可以进行自动类型转换
类模板
- 有模板参数、调用参数
- 类模板的使用都是显式实例化,用
- 类模板中函数放在类外进行定义时,需要加模板参数列表,且只允许定义在同一个源文件内
- Vector类名,Vector
template<class T1,class T2....>
class basic_string
{
T& operator[] (size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _arr[pos];
}
private:
T* _arr;
int _size;
int _capacity;
};
template <class T>
Vector<T>::~Vector()
{
if(_pData)
delete[] _pData;
_size = _capacity = 0;
}
STL标准模板库
- 算法和数据结构等模板的集合体,是C++标准库的重要组成部分,有:
- 容器(Container),算法(Algorithm),迭代器(Iterator),仿函数(Function object),适配器(Adaptor),空间配置器(allocator)
- 有多个版本,底层实现略有差异,Linux用的是SGI版本
- 缺陷:没有支持线程安全,追求效率,导致内部比较复杂,还有模板本身导致的代码膨胀…
string
- 它是处理字符串的字符串类,string在底层实际是:basic_string模板类的别名
- 这个类独立于所使用的编码来处理字节:如果用来处理多字节或变长字符(如UTF-8)的序列,这个类的所有成员(如长度或大小)以及它的迭代器,将仍然按照字节(而不是实际编码的字符)来操作。
- 使用string类时,必须包含
#include以及using namespace std:string - 总结:对字符串指针数组各种操作的封装
常用的string类构造
string s1();
string s2("easy come");
string s3(s2);
string类对象的访问及遍历操作
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
| operator[] | 返回pos位置的字符,const string类对象调用,当数组名用 |
| begin+ end | begin获取一个字符的迭代器 + end获取最后一个字符下一个位置的迭代器 |
| rbegin + rend | 反过来 |
| 迭代器 | 近似于指针 |
void test1()
{
string s1();
string s2("easy come");
string s3(s2);
string::iterator it = s2.begin();
/迭代器 读取加修改
while (it !=s2.end())
{
*it += 1;
++it;
}
//it -= 1;
//while (it >= s2.begin())
//{
/ cout << *it << " ";
// it--; 迭代器无法在begin之前递减....
//}
it = s2.begin();
while (it != s2.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
//范围for 读取修改
for (auto& e : s2)
{
e -= 1;
cout << e <<" ";
}
cout << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < s2.size(); i++)
{
s2.at(i) += 1; //at 返回指定位置的字符
cout << s2.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//const对象要用const版本的迭代器--
string::const_iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
----------------------------------------------------//反向遍历
void test2()
{
string s1("it is so hard");
//正着遍历
string::iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << "have u failed in your studies? " << endl;
//反向遍历
string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin();
while (rit != s1.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
++rit;
}
cout << "No,i had not.." << endl;
}
string类对象的容量操作
resize、reserve
resize(size_t n)与resize(size_t n, char c)都是将字符串中有效字符个数改变到n个,不同的是当字符个数增多时:- resize(n)用0来填充多出的元素空间
- resize(size_t n, char c)用字符c来填充多出的元素空间。没有传,则默认用空字符填充
- 注意:resize在改变元素个数时,如果是将元素个数增多,可能会改变底层容量的大小,如果是将元素个数减少,底层空间总大小不变
reserve(size_t res_arg=0):为string对象预留空间,不改变有效元素个数,当reserve的参数小于string的底层空间总大小时,reserver不会改变容量大小。
reserve()
cout << "----reserve:一次性开好需要的空间,避免增容,提高效率--------" << endl;
string s3("A mere pawn is not to be feared");
cout << s3 << endl;
cout << "-----------如果开的空间比原来的小,没有影响-----------" << endl;
s3.reserve(10);
cout << s3 << endl;
cout << "cap:" << s3.capacity() << endl << endl;
resize()
cout << "----------resize:既要开好空间,还要初始化----------" << endl;
cout << "-----------resize:若N小于原长度,则缩减至N--------" << endl;
s3.resize(10);
cout << s3 << endl;
cout << s3.size() << endl;
cout << "cap:" << s3.capacity () << endl << endl;
size()、max_size()、capacity()
void test3()
{
string s("are u a true man?");
---//size()
//length 是老版本的 推荐是用新 的 size
cout <<" size:"<< s.size() << endl;
cout << " length:" <<s.length() << endl;
cout <<" capcity:"<< s.capacity() << endl;
cout << s << endl;
cout << "a true man 当带三尺剑,立不世之功" << endl << endl;
---//max_size()
cout << "---max_size 返回的是一个字符串能达到的最大长度----" << endl;
string s1;
cout << s1.max_size() << endl << endl;
cout << endl << "How could I die if I failed in my ambition" << endl;
}
检测增容方法
void test4()
{
string s;
//s.reserve(500);
size_t cap = s.capacity(); //没有尾插时的容量
cout << "before making s grow:\n"<<cap<<endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < 500; i++)
{
s.push_back('c');
if (cap!=s.capacity())
{
cap = s.capacity(); //每一次增容记录下来
cout << "cap changed: " << cap << "\n";
}
}
}
string类对象的修改操作
| 函数名称 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| push_back | 在字符串后尾插字符c |
| append | 在字符串后追加一个字符串 |
| operator+= | 在字符串后追加字符串str |
| find + npos | 从字符串pos位置开始往后找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置:下标 |
| rfind | 反向查找,返回该字符在字符串中的位置:下标 |
| substr | 在str中从pos位置开始,截取n个字符,然后将其返回,返回值是对象 |
| 非成员函数 | getline:输入流到对象里,遇到‘\n’就停止输入 |
+=、insert、earse
void test5()
{
string s("heheda");
string s2("hello");
s += " bukaixin";
cout << s << endl;
s2 += "w";
cout << s2 << endl;
s += s2;
cout << s << endl;
s2.insert(s2.size() - 1, " ");
s2.insert(s2.size(), "orld");
cout << s2 << endl;
/earse pos位置之后按长度删除,不写参数则全删除
s.erase(1, 6);
cout << s << endl;
s.erase();
cout << s << endl;
}
提取一个网址的协议、域名、uri
void test6()
{
string file1("test.txt.zip");
const size_t pos1 = file1.rfind("."); //倒着找的第一个字符,返回的是下标
if (pos1 != string::npos)
{
//从pos位置开始搜索,返回的是由后面的字符串构造的对象
//指定位置,要多长
string sub1 = file1.substr(pos1);
cout << sub1 << endl;
string sub2 = file1.substr(pos1,2);
cout << sub2 << endl;
}
string file2("https://www32.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/npos/");
//取出url中的域名,协议,uri
size_t pso = file2.find(":");
string agreement = file2.substr(0, pso);
cout << "agreement:" << agreement << endl;
//从指定位置向后查找 指定的字符
int pw = file2.find('/', pso + 3);
string domain = file2.substr(pso + 3, pw-(pso+3));
cout << "domain name:" << domain << endl;
string uri = file2.substr(pw);
cout << "uri:" << uri << endl;
}
getline(cin, s);
size_t pos = s.find(' ');
if (pos != string::npos)
{
// 获取从第一个空格之后有几个字符
cout << s.size() - (pos + 1) << endl;
}
else
{
cout << s.size() << endl;
}