超详细的顺序表(附源码)
文章目录
- 前言
- 线性表
- 顺序表
-
- 顺序表的分类
-
- 静态顺序表
- 动态顺序表
- 动态顺序表的实现
-
- 结构
- 初始化
- 销毁
- 插入
- 删除
- 查找
- 源代码
前言
顺序表是线性表的一种,代码量对于前面的学习,有明显的难度。小编也是第一次学习数据结构,如有谬误,欢迎指正。
本篇收录于《数据结构杂谈》中
线性表
线性表(linearlist)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。
线性表是⼀种在实际中⼴泛使⽤的数据结构,常⻅的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串…
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的⼀条直线。但是在物理结构上并不⼀定是连续的,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。
线性表的顺序表示指的是用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表的数据元素。
顺序表
顺序表的底层结构是数组,因此顺序表在逻辑结构上线性的,在物理结构上也是线性的。顺序表对数组进行了封装,是现在了增删改的操作。
顺序表的分类
静态顺序表
使用定长数组存储元素
typedef int SLDataType;
#define N 7
typedef struct
{
SLDataType a[N]; //定长数组
int size; //有效个数
}SL;
缺点:空间给少了不够用,给多了造成空间浪费
动态顺序表
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct
{
SLDataType* elme;
int size; //记录有效个数
int capacity; //空间容量
};
可增容
当size == capacity时,说明此顺序表已经满了,就需要去增容
动态顺序表的实现
结构
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct
{
SLDataType* elme;
int size; //记录有效个数
int capacity; //空间容量
};
顺序表是一个存储结构,因此什么数据类型都可以存储。将int类型的名字替换成SLDataTYpe,后续如果向存储别的类型,如char,short,结构体等类型时,只需要将int修改为char,short,结构体等类型,使得操作更加简化。
初始化
在之前学习过程中吗,我们定义一个int型变量时,都使用int a = 0;进行初始化,在顺序表中也是一样,需要进行初始化。
code
//初始化
void SLinit(SL* ps) {
assert(ps);
ps->arr = (SLDataType*)malloc(INT_CAPACITY * sizeof(SLDataType));
if (ps->arr == NULL) {
perror("malloc");
return;
}
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = INT_CAPACITY;
}
销毁
顺序表中使用了malloc动态开辟内存空间,因此需要在结束的时候释放内存,将内存归还予操作系统。
插入
插入有两种情况:
- 顺序表空间充足,可直接插入
- 空间不充足,需要先进行扩容,再去插入
因此在插入数据前,我们需要先判断空间大小够不够,不够我们需要去扩容
扩容时,capacity一般是以1.5倍或者是2倍去增大
//判断空间大小
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps) {
if (ps->size == ps->capacity) {
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)relloc(ps->arr, sizeof(SLDataType) * newCapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
perror("relloc");
return 1;
ps->arr = tmp;
ps->capacity == newCapacity;
}
}
头插
尾插
在pos(任意位置)插入
//插入数据
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x) {
assert(ps);
//限制pos
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
//判断是否扩容
void SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int i = 0;
for (int i = ps->size; i <pos ; i--) {
ps->arr[i] == ps->arr[i - 1]; //最后一次进来的时pos+1,arr[pos+1]==arr[pos]
}
ps->arr[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
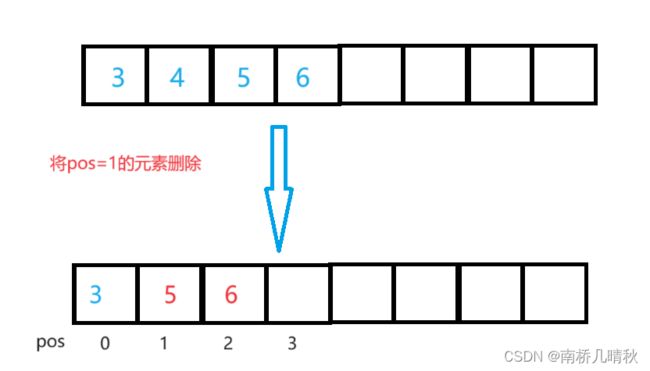
删除
删除时,不需要再去扩容,只需要将pos+1位置往前移动即可,后面元素依次往前移动。
//删除数据
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos) {
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
int i = 0;
for (i = pos; i < ps->size - 1; i++) {
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1]; //最后一次进来的是size-2,arr[size-2]=arr[size-2]
}
ps->size--;
}
查找
//查找元素
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x) {
assert(ps);
int str;
while (str < ps->size) {
if (ps->arr == x) {
return str;
}
str++;
}
return -1;
}
这里小编是拿int类型举的例子,因此在判断等于的时候直接使用了等于符号,如果是字符串的比较,那么就得需要使用字符串函数了。
源代码
小编将结构的实现和函数的声明放在了头文件中,方便阅读,将函数的具体实现放在了源文件中
.h文件
#pragma once
#include.c文件
# define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"SeqList.h"
//初始化
void SLinit(SL* ps) {
assert(ps);
ps->arr = (SLDataType*)malloc(INT_CAPACITY * sizeof(SLDataType));
if (ps->arr == NULL) {
perror("malloc");
return;
}
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = INT_CAPACITY;
}
//销毁
void SLDestory(SL* ps) {
if (ps->arr)
free(ps->arr);
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//判断空间大小
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps) {
if (ps->size == ps->capacity) {
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)relloc(ps->arr, sizeof(SLDataType) * newCapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
perror("relloc");
return 1;
ps->arr = tmp;
ps->capacity == newCapacity;
}
}
//插入数据
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x) {
assert(ps);
//限制pos
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
//判断是否扩容
void SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int i = 0;
for (int i = ps->size; i <pos ; i--) {
ps->arr[i] == ps->arr[i - 1]; //最后一次进来的时pos+1,arr[pos+1]==arr[pos]
}
ps->arr[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//删除数据
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos) {
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
int i = 0;
for (i = pos; i < ps->size - 1; i++) {
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1]; //最后一次进来的是size-2,arr[size-2]=arr[size-2]
}
ps->size--;
}
//查找元素
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x) {
assert(ps);
int str;
while (str < ps->size) {
if (ps->arr == x) {
return str;
}
str++;
}
return -1;
}