Webflux系列之反应式编程核心基础详解
常用官网学习地址
反应编程Reatvie programmming : https://projectreactor.io/docs/core/release/reference/
webflux 官网: https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/web-reactive.html#webflux-controller
R2DBC官网: https://r2dbc.io/
spring data r2dbc -mysql: https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-data-r2dbc
r2dbc官网: https://r2dbc.io/spec/0.8.3.RELEASE/spec/html/
一. 反应式编程核心思想
demo地址:https://github.com/good-jack/webflux 里面包含了基本crud的操作
1、核心概念
反应式
反应式系统具有某些特性,使其成为低延迟、高吞吐量工作负载的理想选择。projectreactor和Spring组合一起工作,使开发人员能够构建响应性、弹性、弹性和消息驱动的企业级反应系统。
反应式处理
反应式处理是一种范例,它使开发人员能够构建非阻塞、异步的应用程序,从而能够处理背压(流控制)。
为什么使用反应式处理?
反应式系统更好地利用了现代处理器。此外,在反应式编程中加入背压可以确保解耦组件之间具有更好的弹性。
反应式宣言
英文: https://www.reactivemanifesto.org/
中文: https://www.reactivemanifesto.org/zh-CN
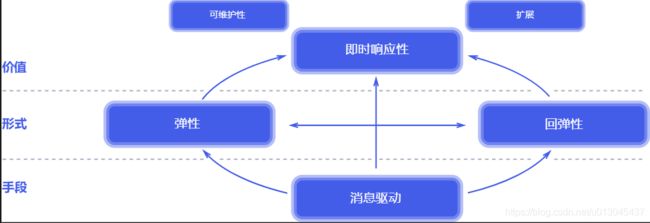
反应式系统的特质
- 即时响应性: :只要有可能, 系统就会及时地做出响应。 即时响应是可用性和实用性的基石, 而更加重要的是,即时响应意味着可以快速地检测到问题并且有效地对其进行处理。 即时响应的系统专注于提供快速而一致的响应时间, 确立可靠的反馈上限, 以提供一致的服务质量。 这种一致的行为转而将简化错误处理、 建立最终用户的信任并促使用户与系统作进一步的互动。
- 回弹性:系统在出现失败时依然保持即时响应性。 这不仅适用于高可用的、 任务关键型系统——任何不具备回弹性的系统都将会在发生失败之后丢失即时响应性。 回弹性是通过复制、 遏制、 隔离以及委托来实现的。 失败的扩散被遏制在了每个[组件](/glossary.zh-cn.md#组件)内部, 与其他组件相互隔离, 从而确保系统某部分的失败不会危及整个系统,并能独立恢复。 每个组件的恢复都被委托给了另一个(外部的)组件, 此外,在必要时可以通过复制来保证高可用性。 (因此)组件的客户端不再承担组件失败的处理。
- 弹性: 系统在不断变化的工作负载之下依然保持即时响应性。 反应式系统可以对输入(负载)的速率变化做出反应,比如通过增加或者减少被分配用于服务这些输入(负载)的资源。 这意味着设计上并没有争用点和中央瓶颈, 得以进行组件的分片或者复制, 并在它们之间分布输入(负载)。 通过提供相关的实时性能指标, 反应式系统能支持预测式以及反应式的伸缩算法。 这些系统可以在常规的硬件以及软件平台上实现成本高效的弹性。
- 消息驱动:反应式系统依赖异步的消息传递,从而确保了松耦合、隔离、位置透明的组件之间有着明确边界。 这一边界还提供了将失败作为消息委托出去的手段。 使用显式的消息传递,可以通过在系统中塑造并监视消息流队列, 并在必要时应用回压, 从而实现负载管理、 弹性以及流量控制。 使用位置透明的消息传递作为通信的手段, 使得跨集群或者在单个主机中使用相同的结构成分和语义来管理失败成为了可能。 非阻塞的通信使得接收者可以只在活动时才消耗资源, 从而减少系统开销。
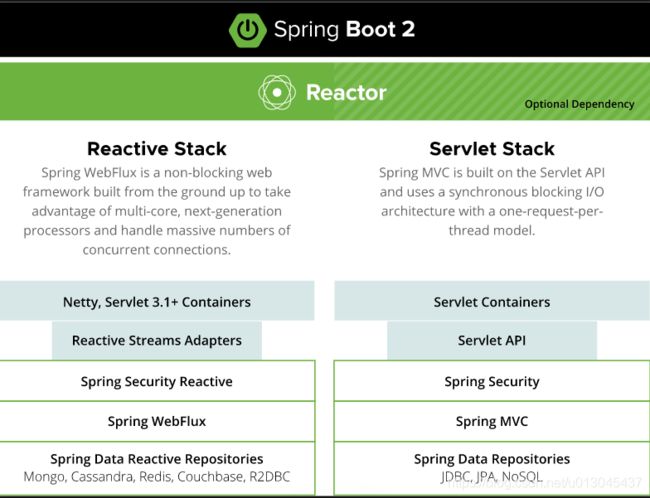
2 、Spring技术栈架构
二、函数编程基础
1、函数编程
函数编程接口
| 接口函数名 |
说明 |
| BiConsumer |
表示接收两个输入参数和不返回结果的操作。 |
| BiFunction |
表示接受两个参数,并产生一个结果的函数。 |
| BinaryOperator |
表示在相同类型的两个操作数的操作,生产相同类型的操作数的结果。 |
| BiPredicate |
代表两个参数谓词(布尔值函数)。 |
| BooleanSupplier |
代表布尔值结果的提供者。 |
| Consumer |
表示接受一个输入参数和不返回结果的操作。 |
| DoubleBinaryOperator |
代表在两个double值操作数的运算,并产生一个double值结果。 |
| DoubleConsumer |
表示接受一个double值参数,不返回结果的操作。 |
| DoubleFunction |
表示接受double值参数,并产生一个结果的函数。 |
| DoublePredicate |
代表一个double值参数谓词(布尔值函数)。 |
| DoubleSupplier |
表示表示接受double值参数,并产生一个结果的函数。值结果的提供者。 |
| DoubleToIntFunction |
表示接受一个double值参数,不返回结果的操作。 |
| DoubleFunction |
表示接受double值参数,并产生一个结果的函数。 |
| DoublePredicate |
代表一个double值参数谓词(布尔值函数)。 |
| DoubleSupplier |
DoubleToIntFunction |
| DoubleToIntFunction |
表示接受double值参数,并产生一个int值结果的函数。 |
| DoubleToLongFunction |
表示上产生一个double值结果的单个double值操作数的操作。 |
| Function |
代表接受一个double值参数,并产生一个long值结果的函数。 |
| DoubleUnaryOperator |
表示上产生一个double值结果的单个double值操作数的操作。 |
| Function |
表示接受一个参数,并产生一个结果的函数。 |
| IntConsumer |
表示接受单个int值的参数并没有返回结果的操作。 |
| IntFunction |
表示接受一个int值参数,并产生一个结果的函数。 |
| IntPredicate |
表示一个整数值参数谓词(布尔值函数)。 |
| IntSupplier |
代表整型值的结果的提供者。 |
| IntToLongFunction |
表示接受一个int值参数,并产生一个long值结果的函数。 |
| IntUnaryOperator |
表示产生一个int值结果的单个int值操作数的运算。 |
| LongBinaryOperator |
表示在两个long值操作数的操作,并产生一个ObjLongConsumer值结果。 |
| LongFunction |
表示接受long值参数,并产生一个结果的函数。 |
| LongPredicate |
代表一个long值参数谓词(布尔值函数)。 |
| LongSupplier |
表示long值结果的提供者。 |
| LongToDoubleFunction |
表示接受double参数,并产生一个double值结果的函数。 |
| LongToIntFunction |
表示接受long值参数,并产生一个int值结果的函数。 |
| LongUnaryOperator |
表示上产生一个long值结果单一的long值操作数的操作。 |
| ObjDoubleConsumer |
表示接受对象值和double值参数,并且没有返回结果的操作。 |
| ObjIntConsumer |
表示接受对象值和整型值参数,并返回没有结果的操作。 |
| ObjLongConsumer |
表示接受对象值和整型值参数,并返回没有结果的操作。 |
| ObjLongConsumer |
表示接受对象值和double值参数,并且没有返回结果的操作。 |
| ObjIntConsumer |
表示接受对象值和整型值参数,并返回没有结果的操作。 |
| ObjLongConsumer |
表示接受对象的值和long值的说法,并没有返回结果的操作。 |
| Predicate |
代表一个参数谓词(布尔值函数)。 |
| Supplier |
表示一个提供者的结果。 |
| ToDoubleBiFunction |
表示接受两个参数,并产生一个double值结果的功能。 |
| ToDoubleFunction |
代表一个产生一个double值结果的功能。 |
| ToIntBiFunction |
表示接受两个参数,并产生一个int值结果的函数。 |
| ToIntFunction |
代表产生一个int值结果的功能。 |
| ToLongBiFunction |
表示接受两个参数,并产生long值结果的功能。 |
| ToLongFunction |
代表一个产生long值结果的功能。 |
| UnaryOperator |
表示上产生相同类型的操作数的结果的单个操作数的操作。 |
2、常用函数编程示例
Consumer 一个输入 无输出
Product product=new Product();
//类名+静态方法 一个输入T 没有输出
Consumer consumer1 = Product->Product.nameOf(product);//lambda
consumer1.accept(product);
Consumer consumer = Product::nameOf;//方法引用
consumer.accept(product);
Funtion
//对象+方法 一个输入T 一个输出R
Function
System.out.println("剩余库存:" + function.apply(10));
//带参数的构造函数
Function
System.out.println("新对象:" +function1.apply(200));
Predicate 一个输入T, 一个输出 Boolean
//Predicate 一个输入T 一个输出Boolean
Predicate predicate= i -> product.isEnough(i);//lambda
System.out.println("库存是否足够:"+predicate.test(100));
Predicate predicate1= product::isEnough;//方法引用
System.out.println("库存是否足够:"+predicate1.test(100));
UnaryOperator 一元操作符 输入输出都是T
//一元操作符 输入和输出T
UnaryOperator integerUnaryOperator =product::reduceStock;
System.out.println("剩余库存:" + integerUnaryOperator.apply(20));
IntUnaryOperator intUnaryOperator = product::reduceStock;
System.out.println("剩余库存:" + intUnaryOperator.applyAsInt(30));
Supplier 没有输入 只有输出
//无参数构造函数
Supplier supplier = Product::new;
System.out.println("创建新对象:" + supplier.get());
Supplier supplier1=()->product.getStock();
System.out.println("剩余库存:" + supplier1.get());
BiFunction 二元操作符 两个输入
//类名+方法
BiFunction
System.out.println(" 剩余库存(BiFunction):" + binaryOperator.apply(product, 10));
BinaryOperator 二元操作符 ,二个输入 一个输出
//BinaryOperator binaryOperator1=(x,y)->product.reduceStock(x,y);
BinaryOperator binaryOperator1=product::reduceStock;
System.out.println(" 剩余库存(BinaryOperator):" +binaryOperator1.apply(product.getStock(),10));
三、Reactive Stream
定义:
Reactive Stream 提供异步流处理和无阻塞背压 标准规范。
https://github.com/reactive-streams/reactive-streams-jvm
http://www.reactive-streams.org/
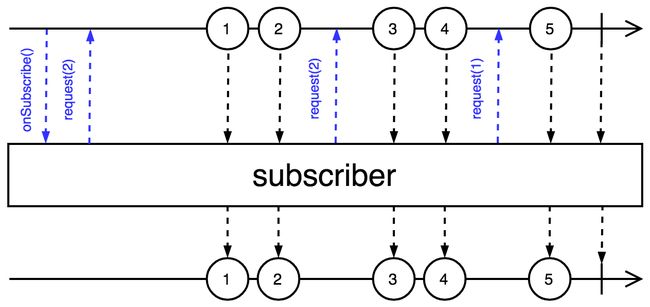
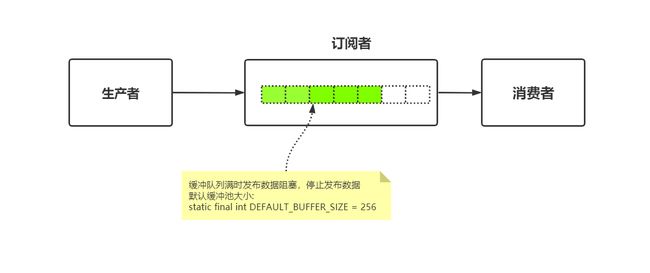
背压:
发布者与订阅者之间消息协调,订阅者需要多少数据,发布者产生多少数据,不会造成消息接收者被数据流冲垮。
SpringMVC是同步阻塞模式,数据接收是被动处理,数据会源源不断发送,如果数据处理不了,就会出现消息挤压和堵塞。
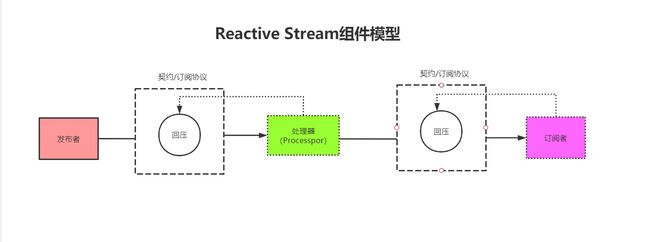
API组件
- Publisher 发布者
- Subscriber 订阅者
- Subscription 契约 /订阅关系 ,实现背压的关键
- Processor 中间处理
JDK9 Flow API
java.util.concurrent.Flow
@FunctionalInterface
public static interface Publisher {
// 发布者与订阅者建立订阅关系
public void subscribe(Subscriber subscriber);
}
public static interface Subscriber {
// 第一次建立订阅关系调用
public void onSubscribe(Subscription subscription);
//继续接收数据
public void onNext(T item);
//出现异常
public void onError(Throwable throwable);
//发送完成
public void onComplete();
}
//中间处理角色
public static interface Processor
}
返回发布服务器或订阅服务器缓存的默认值,可以在没有其他约束的情况下使用。
static final int DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 256;
/**
Returns a default value for Publisher or Subscriber buffering,that may be used in the absence of other constraints.@implNoteThe current value returned is 256.@returnthe buffer size value*/public static int defaultBufferSize() {return DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE;}
四、JDK Reactive Stream实战
第一个Reactive Stream Demo
1、创建生产者
SubmissionPublisher submissionPublisher = new SubmissionPublisher();
2、创建消费者
Flow.Subscriber subscriber = new Flow.Subscriber() {
private Flow.Subscription subscription;
@Override
public void onSubscribe(Flow.Subscription subscription) {
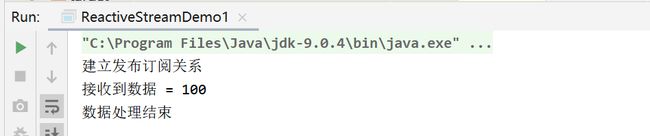
System.out.println("建立发布订阅关系");
//建立订阅关系
this.subscription = subscription;
//请求数据
this.subscription.request(1);
}
@Override
public void onNext(Integer item) {
//接收数据进行处理
System.out.println("接收到数据 = " + item);
//处理完成继续请求数据 (调节数据接收频率)
this.subscription.request(1);
//通知生产者不再接收数据
//this.subscription.cancel();
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable throwable) {
//出现异常
throwable.printStackTrace();
//通知生产者不再接收数据
this.subscription.cancel();
}
@Override
public void onComplete() {
//全部数据处理完成(发布者关闭)
System.out.println("数据处理结束");
}
};
3、发布者与消费者建立订阅关系
submissionPublisher.subscribe(subscriber);
- 发布者发布数据
submissionPublisher.submit(100);
5、发布者关闭submissionPublisher.close(); - 等待数据发送
try {
Thread.currentThread().join(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
演示代码结果
运行原理
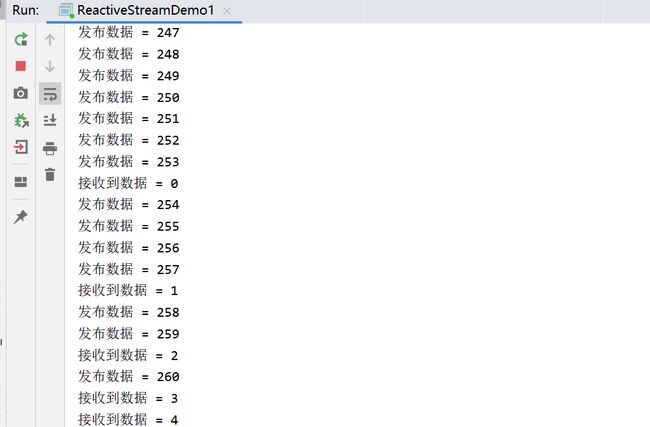
连续发布500条数据
for (int i = 0; i <500 ; i++) { System.out.println("发布数据 = " + i); submissionPublisher.submit(i); }
五、Project Reactor
官方文档: https://projectreactor.io/docs/core/release/reference/
1、 定义
Reactor
Reactor is a fourth-generation reactive library, based on the Reactive Streams
specification, for building non-blocking applications on the JVM
Reactive programming
Reactive programming is an asynchronous programming paradigm concerned with data streams and the propagation of change. This means that it becomes possible to express static (e.g. arrays) or dynamic (e.g. event emitters) data streams with ease via the employed programming language(s).
反应式编程是一种关注数据流和变更传播的异步编程范式。这意味着可以通过所使用的编程语言轻松地表达静态(例如数组)或动态(例如事件发射器)数据流
2、Reactor 核心功能
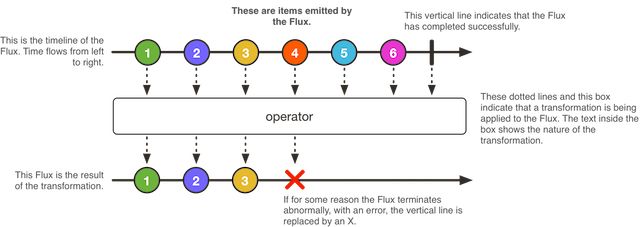
Flux: 生产者发布的0-N个异步序列元素
Flux is a standard Publisher that represents an asynchronous sequence of 0 to N emitted items, optionally terminated by either a completion signal or an error. As in the Reactive Streams spec, these three types of signal translate to calls to a downstream Subscriber’s onNext, onComplete, and onError methods.
Flux 创建Demo
Flux ints = Flux.range(1, 4);
Flux seq1 = Flux.just("bole1", "bole2", "bole3");
List iterable = Arrays.asList("bole_01", "bole_02", "bole_03");
Flux seq2 = Flux.fromIterable(iterable);
seq2.subscribe(i -> System.out.println(i));
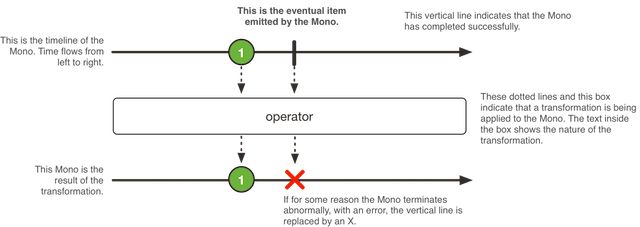
Mono:是一种特别的发布者,它最多发出一个条目。
Mono is a specialized Publisher that emits at most one item and then (optionally) terminates with an
onComplete signal or an onError signal.
Mono data = Mono.just("bole");
Mono noData = Mono.empty();
m.subscribe(i -> System.out.println(i));
3、Project Reactor工程搭建
1、新建Maven工程
2、添加Reactor依赖支持
3、创建我的第一个反应式程序
package com.bole.reactor;
import org.reactivestreams.Subscription;
import reactor.core.publisher.BaseSubscriber;
import reactor.core.publisher.Flux;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
- @Description:
- @Author: 伯乐
- @Date: 2020/12/2 13:02
*/
public class ReactorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Mono创建方式 :1个元素
Mono mono= Mono.just("mono");
mono.subscribe(i-> System.out.println("m:"+mono));
//Mono创建方式 :空序列
Mono monoEmpty= Mono.empty();
monoEmpty.subscribe(i-> System.out.println("monoEmpty:"+mono));
//Flux创建方式1
Flux flux0 = Flux.just("bole", "bole1", "bole3");
Flux flux1 = Flux.fromArray(new String[]{"bole", "bole1", "bole3"});
Flux flux2 = Flux.fromStream(Stream.of("bole", "bole1", "bole3"));
Flux flux3 = Flux.fromIterable(Arrays.asList("bole", "bole1", "bole3"));
Flux flux4 = Flux.range(1, 10);
//使用baseSubscriber
Flux.range(1, 10)
.doOnRequest(r -> System.out.println("request of " + r))
.subscribe(new BaseSubscriber() {
@Override
public void hookOnSubscribe(Subscription subscription) {
request(1);
}
@Override
public void hookOnNext(Integer integer) {
System.out.println("Cancelling after having received " + integer);
request(1);
//cancel();
}
});
//Flux创建方式 2 : 程序创建
Flux flux5 = Flux.generate(() -> 0, (i, sink) -> {
sink.next("bole" + i);
if (i > 10) {
sink.complete();
}
return i + 1;
});
flux0.doOnSubscribe(i -> {
i.request(2);
System.out.println("sub:" + i);
}).doOnNext(i -> {
System.out.println("next:" + i);
}).doOnComplete(() -> {
System.out.println("Complete");
}).subscribe();
/* Flux.generate(AtomicLong::new, (l, sink) -> {
long v = l.getAndIncrement();
sink.next("bole" + v);
if (v == 3) {
sink.complete();
}
return l;
}, l -> {
}).subscribe(i -> System.out.println("atomic :" + i));*/